Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HW Carbohydrates
Uploaded by
yanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HW Carbohydrates
Uploaded by
yanCopyright:
Available Formats
HW - CARBOHYDRATES
RICA SALOMON
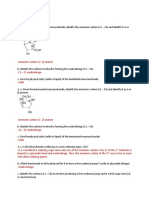
1. a) Beta anomer, C2- anomeric carbon
b) C2 - C5
c) solid
2. a) Beta anomer, C2- anomeric carbon
b) C1 - C5
c) solid
3. a) The disaccharide maltose is a reducing sugar since only one of it's two anomeric carbon is bound by
oxide linkages. Therefore when hydrolyzed with water it will yield to a free carbonyl group.
b) oxide linkage
c) C4, 2nd structure
4. a) The disaccharide sucrose is a non reducing sugar since the C1 from the 1st glucose molecule and C2
from the 2nd fructose molecule are both bound by oxide and glycosidic linkages. Hence, there is no free
carbonyl group that can reduce other compunds.
b) The answer is None. As mentioned in letter A both C1 from the 1st glucose molecule and C2 from
the 2nd fructose molecule are bounded by oxide and glycosidic linkages. Hence, it cannot yield to a free
carbonyl group when hydrolyzed.
c) The answer is none since sucrose is a non reducing sugar.
5. a) C1 - C4
b) The complete hydrolysis of a polysaccharide yield to a monosaccharide. Monosaccharides
(aldohexose and ketohexose) are all reducing sugars. When water hydrolyzes the oxide linkages, it frees
the carbonyl group. Free carbonyl group gives the sugar its reducing properties. Therefore, all
monosaccharides are reducing sugars.
c) Fehling's test is a type of oxidizing test for monosaccharides and can be used to detect glucose and
fructose. Reducing sugars give positive results in all oxidizing tests, so when there is a presence of
glucose in a solution, a brick-red precipitate will form indicating a positive result.
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry H2 Questions MCQDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry H2 Questions MCQkitonium100% (1)
- Health: Health Assessment Lecture ReviewerDocument22 pagesHealth: Health Assessment Lecture RevieweryanNo ratings yet
- Water Technology: Chemistry Question Bank For-Part ADocument34 pagesWater Technology: Chemistry Question Bank For-Part AJOSEPH HERBERT MABEL100% (2)
- Carbohydrates WorksheetDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates WorksheetNatalie Pemberton86% (7)
- 2015 JC2 H2 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Part 1 Tutorial (Teachers) UpdatedDocument18 pages2015 JC2 H2 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Part 1 Tutorial (Teachers) UpdatedJohnNo ratings yet
- Angeles, Abigail Y. 2 Mbio-5: ST NDDocument3 pagesAngeles, Abigail Y. 2 Mbio-5: ST NDAbigail AngelesNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PDFDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates PDFChristelle Marie Aquino Beroña100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry MCQ AnsDocument7 pagesAnalytical Chemistry MCQ AnsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8 (Carbonyl Compounds and Carbohydrates)Document9 pagesExercise 8 (Carbonyl Compounds and Carbohydrates)Wendell Kim Llaneta0% (1)
- COOH NotesDocument12 pagesCOOH NotesAyshath MaaishaNo ratings yet
- Solution Practice Test 2 Class 12 - Chemistry: Volume Occupied by Fow Spheres Inthe Unit Cell Total Volume of Unit CellDocument6 pagesSolution Practice Test 2 Class 12 - Chemistry: Volume Occupied by Fow Spheres Inthe Unit Cell Total Volume of Unit Cell39 Yogendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Four-Dab 2 (Mod) (2023) - Biochem-JanDocument11 pagesLesson Four-Dab 2 (Mod) (2023) - Biochem-Janhappy computersNo ratings yet
- I - Asam KarboksilatDocument45 pagesI - Asam KarboksilatAku Big Bos DayuNo ratings yet
- To Compare The Rates of Fermentation of The Following Fruit of Vegetable Juices (Apple Juice, Orange Juice, Carrot Juice)Document9 pagesTo Compare The Rates of Fermentation of The Following Fruit of Vegetable Juices (Apple Juice, Orange Juice, Carrot Juice)jayasruthilaya18No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Notes VNDocument11 pagesBiomolecules Notes VNYash WanthNo ratings yet
- Soal Babak Penyisihan Olimpiade Kimia 2016Document14 pagesSoal Babak Penyisihan Olimpiade Kimia 2016Muhaqqy50% (2)
- (A) Chem-P1Document12 pages(A) Chem-P1BeaaaaNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989580Document7 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989580abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Chemistrt r3 KeyDocument31 pagesChemistrt r3 KeyBharathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthershrshtkrkNo ratings yet
- Revision 1 200520062007Document5 pagesRevision 1 200520062007alvin2282No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones TheoryDocument28 pagesAldehydes, Ketones Theoryshilpa sakhareNo ratings yet
- Unit 14: Biomolecules: Mahendra Kalra . 9462305605Document10 pagesUnit 14: Biomolecules: Mahendra Kalra . 9462305605Pranav PillaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 14: Biomolecules: Mahendra Kalra . 9462305605Document10 pagesUnit 14: Biomolecules: Mahendra Kalra . 9462305605B乛Lac 么ICONICNo ratings yet
- Soal Babak Penyisihan Olimpiade Kimia 2016Document14 pagesSoal Babak Penyisihan Olimpiade Kimia 2016Nancy KawilarangNo ratings yet
- 2019 HCI H2 Chem MYE P1Document10 pages2019 HCI H2 Chem MYE P1qiyunNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh Region KV MS PB1Document5 pagesChandigarh Region KV MS PB1kingoo0f1No ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document11 pagesChapter 8Tandra SinhaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document7 pagesExperiment 7bernardNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Revision SlideDocument51 pagesCarboxylic Acid Revision Slidejohn nashNo ratings yet
- Al KynesDocument19 pagesAl KynesAnkit JaipuriaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument54 pagesBIOMOLECULESTanmayNo ratings yet
- QC - 2019-20 - Mock - S6 - Chem 1ADocument12 pagesQC - 2019-20 - Mock - S6 - Chem 1AOof GucciNo ratings yet
- MARKING SCHEME (2021-22) Term - Ii Chemistry Theory (043) Set ADocument5 pagesMARKING SCHEME (2021-22) Term - Ii Chemistry Theory (043) Set ASyed ShammazNo ratings yet
- Wa0005.Document10 pagesWa0005.samarkhatri300No ratings yet
- Answers To Questions (For In-Chapter Questions)Document2 pagesAnswers To Questions (For In-Chapter Questions)Nausheen ParveenNo ratings yet
- PIL HW CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesPIL HW CarbohydratesBIANCA PILNo ratings yet
- E6 Isolation of GlycogenDocument19 pagesE6 Isolation of GlycogenGlenn Vincent Tumimbang100% (1)
- Chemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondDocument2 pagesChemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondJAYLEN TRACEYNo ratings yet
- Skill Building ExercisesDocument4 pagesSkill Building ExercisesLex QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Dha Senior School For Girls Online MOCK-Examinations: There Are FORTY Questions On This Paper. Answer All QuestionsDocument12 pagesDha Senior School For Girls Online MOCK-Examinations: There Are FORTY Questions On This Paper. Answer All QuestionsaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Ncert SolutionsDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Ncert SolutionsHarsh MahalwarNo ratings yet
- Ejc H1 Chem P1Document11 pagesEjc H1 Chem P1Lim EnningNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Solomon Periodic AcidDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Solomon Periodic AcidIqbal A Mir100% (1)
- Hydrocarbons A-7Document4 pagesHydrocarbons A-7REJA MUKIB KHANNo ratings yet
- 5070 w12 QP 12Document16 pages5070 w12 QP 12mstudy123456No ratings yet
- DSE 5-8 MC - AnsDocument24 pagesDSE 5-8 MC - AnsSherry LeeNo ratings yet
- Belilios Public School Yearly: Examination, 2015-2016 ChemistryDocument58 pagesBelilios Public School Yearly: Examination, 2015-2016 ChemistryChun Kit LauNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases 1Document7 pagesAcids and Bases 1SaravananNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument8 pagesAldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsSheetal KoriNo ratings yet
- Reactions of ButylamineDocument1 pageReactions of ButylamineNikhil KottapalliNo ratings yet
- Experiment Properties of AlkenesDocument3 pagesExperiment Properties of AlkenesCalvin ChinNo ratings yet
- Units On Hydrolysis. Carbohydrates Are Also Called SaccharidesDocument5 pagesUnits On Hydrolysis. Carbohydrates Are Also Called SaccharidesSripriya RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model Paper Set - (14) MSDocument4 pagesChemistry Model Paper Set - (14) MSAditya Kumar 12ANo ratings yet
- GRP VII Tutorial AnsDocument9 pagesGRP VII Tutorial AnslayssourcreamNo ratings yet
- Silver Bells Convent School: Pre TermDocument8 pagesSilver Bells Convent School: Pre TermAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones For IitjeeDocument65 pagesAldehydes and Ketones For Iitjeevarundhall1994No ratings yet
- Aliphatic Compounds: Dihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesFrom EverandAliphatic Compounds: Dihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesNo ratings yet
- Graphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandGraphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAyrat M. DimievNo ratings yet
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsFrom EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument18 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesyanNo ratings yet
- Chap 14 Micropara ReviewerDocument25 pagesChap 14 Micropara RevieweryanNo ratings yet
- Eapp Peta - Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesEapp Peta - Reaction PaperyanNo ratings yet
- Eapp Peta - Critique PaperDocument3 pagesEapp Peta - Critique PaperyanNo ratings yet
- Don Bosco Technical Institute of Makati Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) StrandDocument5 pagesDon Bosco Technical Institute of Makati Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) StrandyanNo ratings yet
- Lec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismDocument12 pagesLec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismyanNo ratings yet
- UTS Reviewer Chapter 1 Parts 1 3Document11 pagesUTS Reviewer Chapter 1 Parts 1 3yanNo ratings yet
- HW-NUR8103 Lecture - Carbohydrate Metabolism IDocument3 pagesHW-NUR8103 Lecture - Carbohydrate Metabolism IyanNo ratings yet
- HW Lipids ARLOSDocument3 pagesHW Lipids ARLOSyan100% (1)
- Level I: Guide QuestionsDocument2 pagesLevel I: Guide QuestionsyanNo ratings yet
- Dee Diaz Rojas Mathematical LanguageDocument3 pagesDee Diaz Rojas Mathematical LanguageyanNo ratings yet
- HW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismDocument2 pagesHW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismyanNo ratings yet