0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views39 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Week 2 Overview
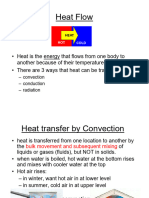
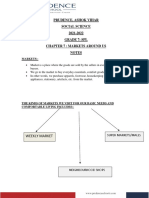
The document provides an overview of General Chemistry 1 for week 2 day 1. It includes reminders about assignments, tests, and activities. It reviews objectives from week 1 on isotopes, chemical formulas, and naming compounds. It then previews upcoming lessons on atomic structure, particles that compose matter like atoms, molecules, and ions. Examples are provided to identify elements from isotope information and calculate average atomic mass. Applications of stable and radioactive isotopes are discussed. The document concludes with an overview of compound formulas, structural representations, and examples of common chemical substances.
Uploaded by
tokyo tokyoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views39 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Week 2 Overview
The document provides an overview of General Chemistry 1 for week 2 day 1. It includes reminders about assignments, tests, and activities. It reviews objectives from week 1 on isotopes, chemical formulas, and naming compounds. It then previews upcoming lessons on atomic structure, particles that compose matter like atoms, molecules, and ions. Examples are provided to identify elements from isotope information and calculate average atomic mass. Applications of stable and radioactive isotopes are discussed. The document concludes with an overview of compound formulas, structural representations, and examples of common chemical substances.
Uploaded by
tokyo tokyoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd