Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lorenz NAVAL
Uploaded by
Lorenz NAVALCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lorenz NAVAL
Uploaded by
Lorenz NAVALCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 20
PROTEINS
EXERCISES:
Name: Lorenz S. Naval BS MedTech 2 - B
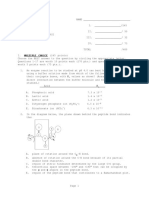
I. Characteristics of Proteins: c) COOH d) COOH
20.1 – Amino Acids H NH2 N2H H
20.2 – Nitrogen CH3 CH3 CH
20.3 – 15 percent by mass D- Alanine CH3
L-Valine
20.4 – 9,000 different kind of proteins
20.36 CH3
II. Amino Acid Standard Characteristics CH3 CH2
20.5 CH
a) YES, because amino group (H2N) and the
carboxyl group (COOH) are attached to the H2N C COOH
∝-carbon atom (C)
H
b) NO, because none of the carboxyl group are
Isoleucine
attached to the ∝-carbon atom (C), only the
amino group (H2N)
20.38
c) NO, because none of the amino acid are a) L-amino acid
attached to the ∝-carbon atom (C), only the b) Polar amino acid
carboxyl group c) Nonessential amino acid
d) Standard amino acid
d) YES, because amino group (H2N) and the
carboxyl group (COOH) are attached to the IV. Acid–Base Properties of Amino Acids
∝-carbon atom (C) (Section 20.5)
20.40 – It is due to the strong intermolecular forces
20.6 – a prefix refers to the amino acids that are between their structures.
always found in proteins
20.41
20.7 – The major structural difference among the H H
a) b)
various standard amino acids is to identify the R + - + -
group (side chain) H3N COO H3N COO
20.8 – Nonpolar Amino Acids, Polar Neutral Amino CH2 CH2 CH3
Acids, Polar Acidic Amino Acids, and Polar Basic
Amino Acids CH CH3 CH
CH3 CH3
20.9 Isoleucine
Leucine
a) Phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
b) Methionine, cysteine c) d)
H H
c) Aspartic acid, glutamic acid
d) Serine, threonine, tyrosine + - + COO
-
H3N COO H3N
III. Chirality of Amino Acids
CH2 H
20.31 – L (left) family
SH
20.32 – Glycine is the simplest structure of the Cysteine Glycine
standard amino acids that makes it achiral. Besides,
two of the groups attached to the ∝-carbon atom (C) 20.42
are identical. H
H a) H b)
I + - + -
H3N COO H3N COO
N2N – C – COOH
I
H CH2 CH2
20.34 CH2
a) b) CH
COOH COOH S
H2N H H NH2 CH2
CH2 Serine Methionine
CH2
SH SH
L-Cysteine D-Cysteine
CHAPTER 20
PROTEINS
EXERCISES:
Name: Lorenz S. Naval BS MedTech 2 - B
c) b)
H
+ -
H3N COO
CH – OH 2
CH3
Threonine Phenylalanine
20.44
a) b)
H H
+ - + -
H3N COO H2N COO
H H
pH= 5.97 pH= 13.0
c) H d) H
+ COOH + -
H3N H2N COO
H H
pH= 2.0 pH= 11.0
V. Cysteine and Disulfide Bonds (Section 20.6)
20.53 – The two cysteine molecules react with one
another forming cysteine molecule linked via
disulfide bond.
VI. Peptides (Section 20.7)
20.55 – Carboxyl group (-COOH) and Amino group
(-NH2)
20.56 O H
C N
Peptide bond
20.59
Tripeptide (Val-Phe-Cys)
20.61
a) Serine, Alanine, Cysteine (Ser-Ala-Cys)
b) Aspartic acid, Threonine, Asparagine (Asp-
Thr-Asn)
20.67
a) Alanine
b) Glycine
c) Valine
d) None
You might also like
- Adarnista - Lorenz NAVALDocument13 pagesAdarnista - Lorenz NAVALLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Accute, Communicable Infect DiseasesDocument4 pagesAccute, Communicable Infect DiseasesLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Adarnista - Lorenz NAVALDocument13 pagesAdarnista - Lorenz NAVALLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Adarnista - Lorenz NAVALDocument13 pagesAdarnista - Lorenz NAVALLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper #2 Lorenzo's OilDocument2 pagesReaction Paper #2 Lorenzo's OilLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Adarnista - Lorenz NAVALDocument13 pagesAdarnista - Lorenz NAVALLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Adarnista - Lorenz NAVALDocument13 pagesAdarnista - Lorenz NAVALLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Adarnista - Lorenz NAVALDocument13 pagesAdarnista - Lorenz NAVALLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna WorksheetDocument2 pagesDna and Rna WorksheetLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Matching Learning Styles To InstructionDocument12 pagesMatching Learning Styles To InstructionLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Exercise in Enzymes - Lorenz NAVALDocument1 pageExercise in Enzymes - Lorenz NAVALLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Adarnista - Lorenz NAVALDocument13 pagesAdarnista - Lorenz NAVALLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Fungicide - FRAC - MoA - Poster 2010 - Final - Version - PrintDocument1 pageFungicide - FRAC - MoA - Poster 2010 - Final - Version - PrintCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- Foods ReportDocument1 pageFoods ReportipinseraNo ratings yet
- Bpharm 2 Sem Biochemistry Bp203t 2020Document1 pageBpharm 2 Sem Biochemistry Bp203t 2020Arya krishnaNo ratings yet
- Major Complex: HistocompatabilityDocument42 pagesMajor Complex: HistocompatabilityAshikNo ratings yet
- BRS Biochemistry (Questions)Document21 pagesBRS Biochemistry (Questions)unknownxem100% (3)
- Group 2 B - Speech TextDocument2 pagesGroup 2 B - Speech TextAudina PriscaNo ratings yet
- Proteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino AcidsDocument45 pagesProteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino Acidsdarleen joy dimaanoNo ratings yet
- HDL-C Direct FS : Order Information ReagentsDocument3 pagesHDL-C Direct FS : Order Information ReagentsmnemonicsNo ratings yet
- 1 Blood HemostasisDocument32 pages1 Blood Hemostasisarlinda noviana100% (1)
- Brain MetabolismDocument10 pagesBrain MetabolismDr. Kaushal Kishor SharmaNo ratings yet
- 17.6 SphingolipidsDocument15 pages17.6 SphingolipidsGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- Profil LemakDocument2 pagesProfil Lemakgaluh ayuNo ratings yet
- Soal Interpretasi Kimia Klinik PATKLINDocument3 pagesSoal Interpretasi Kimia Klinik PATKLINMuhammad Aviv FirdausNo ratings yet
- CH1131 Biomolecular Engrg Lipid Metabolism To Coordination Summary 2013Document4 pagesCH1131 Biomolecular Engrg Lipid Metabolism To Coordination Summary 2013Nhân TrầnNo ratings yet
- Helmick 2021 Cold Denaturation Pea ProtDocument12 pagesHelmick 2021 Cold Denaturation Pea Protpdmallick14No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 8 Multiple Choice QuestionsDawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument31 pagesEnzymemiriam harriottNo ratings yet
- MC 2 Notes (Midterm)Document4 pagesMC 2 Notes (Midterm)Francine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Multiple choice questions (單選題) : 100%Document13 pagesMultiple choice questions (單選題) : 100%德瑞克No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - EnzymesDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - EnzymesNoor Hidayah SambliNo ratings yet
- Exam98 5Document12 pagesExam98 5Harun MohamedNo ratings yet
- MEMBRANE PLASMA - Mind MapDocument1 pageMEMBRANE PLASMA - Mind MapSimNo ratings yet
- The Golgi Apparatus: Morphology and Function With Recent FactsDocument8 pagesThe Golgi Apparatus: Morphology and Function With Recent FactsBlaxez YTNo ratings yet
- Signals and ReceptorsDocument28 pagesSignals and ReceptorsEmilio MurciaNo ratings yet
- Jus Tomat Untuk Menaikkan Kadar Hemoglobin Ibu HamilDocument8 pagesJus Tomat Untuk Menaikkan Kadar Hemoglobin Ibu HamilDiden Bima Fiya SirfefaNo ratings yet
- Homology ModelingDocument22 pagesHomology ModelingBasab GhoshNo ratings yet
- 2010 H1 & H2 Biology - Enzyme Essay Answer KeyDocument7 pages2010 H1 & H2 Biology - Enzyme Essay Answer KeyCaden LeeNo ratings yet
- The Mechanisms of Vesicle Budding and Fussion - Bonifacino 04Document14 pagesThe Mechanisms of Vesicle Budding and Fussion - Bonifacino 04Anahi FranchiNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Pathology: Lipid ProfileDocument1 pageDepartment of Chemical Pathology: Lipid ProfileIshtiaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Budiman, PROTEIN ENGINEERING, Budiman, Biomedik, 2014Document33 pagesBudiman, PROTEIN ENGINEERING, Budiman, Biomedik, 2014PMIB Matrikulasi FKUI 2018/2019No ratings yet