Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Communication Systems (ELE 3103)
Uploaded by
devangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Communication Systems (ELE 3103)
Uploaded by
devangCopyright:
Available Formats
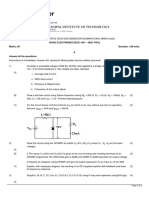
Reg. No.
V SEMESTER B.TECH (ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING)
END SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS, NOVEMBER 2018
SUBJECT: COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS [ELE 3103]
REVISED CREDIT SYSTEM
Time: 3 Hours Date: 23, November 2018 Max. Marks: 50
Instructions to Candidates:
Answer ALL the questions.
Missing data may be suitably assumed.
1A. A carrier signal of 1V amplitude and sinusoidal modulating signal of 0.5V, put in series,
are applied to a square law modulation characteristics
io =(10 + kVi + k′Vi 2 ) mA
where Vi is the input in volts. k=2mA/V & k′=0.2mA/V2. Considering only the
frequency components of the AM signal corresponding to the carrier frequency, find
the depth of the modulation in the resulting AM signal. (03)
1B. Explain DSBSC generation and detection with block diagram and mathematical
expressions. Evaluate the effect of phase error φ, in the local carrier of the detector. (05)
1C. A message signal with bandwidth 10 KHz is Lower-Side Band SSB modulated with
carrier frequency 𝑓𝑐1 = 106𝐻𝑧. The resulting signal is then passed through a narrow-
band frequency modulator with carrier frequency 𝑓𝑐2 = 109𝐻𝑧. Then find the
bandwidth of the output. (02)
2A. A single tone FM is represented by the voltage equation as
𝑉(𝑡) = 12cos(6 × 108 t + 5 sin 1250t). Determine
i. Carrier frequency
ii. Modulating frequency
iii. Modulation index
iv. Frequency deviation
v. Highest and lowest frequencies obtained by the modulated signal.
vi. Power dissipated in 10Ω resistor. (03)
2B. Explain FM super heterodyne receiver with the help of block diagram. Explain why FM
is more robust than AM. (04)
2C. Explain one application of VSB modulation with the spectrum of filter response. (03)
3A. Discuss the concept of Time division multiplexing with block diagram. (03)
ELE 3103 Page 1 of 2
𝑇
2, 𝑓𝑜𝑟 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 2
3B. Consider the signal 𝑠(𝑡) = { 𝑇
−1, 𝑓𝑜𝑟 ≤𝑡 ≤𝑇
2
a) Determine the impulse response of a filter matched to this signal and sketch it as
a function of time.
b) Plot the matched filter output of s(t) as a function of time. (04)
3C. Figure Qn.3C shows the spectrum of a message signal x(t). The signal is sampled at the
rate of fs = 1.5 fmax, where fmax = 1 Hz, is maximum signal frequency. Sketch the
spectrum of sampled version of the signal. If the sampled signal is passed through an
ideal LPF of bandwidth fmax, sketch the spectrum of the output signal from this filter. (03)
4A. For a Binary Frequency Shift Keying technique ,
a) Find the set of orthonormal basis functions to represent this set of signals.
b) Obtain the coordinates of message points and then draw the signal constellation
diagram.
c) Draw the BFSK waveform for the message signal 011010 (consider bit rate =
carrier frequency). (03)
4B. The binary sequence 1100100010 is applied to the DPSK transmitter.
a) Sketch the resulting waveform at the transmitter output with the help of the
DPSK transmitter block diagram.
b) Applying this waveform to the DPSK receiver (with block diagram) show that,
the original binary sequence is reconstructed at the receiver output. (04)
4C. Construct a [7, 4] cyclic code, where the generator polynomial coefficients are 1011.
Find the code vector for the message 0101. (03)
5A. Draw the convolution encoder structure with generator polynomial g1(D) = D+D3,
g2(D) = D+D2,g3(D)= 1+D+D2. Find the code vector corresponding to the message
1100 using state diagram for the given convolutional encoder. Justify your answer
with generator polynomial concept. (04)
5B. Decode the message signal for a received sequence 011100 using Viterbi Decoding
algorithm. State table for the convolutional encoder is as follows. (Consider the state
assignment A= 00, B=10, C=01,D=11)
Present Next State Next State Code Vector Code Vector
state (with input=0) (with input =1) (with input=0) (with input=1)
A A B 00 11
B C D 01 10
C A B 11 00
D C D 10 01 (03)
5C. With block diagram explain how CDMA technology is used in mobile communication (03)
X (f)
-fmax = -1 Hz 0 fmax = 1 Hz
Figure Qn.3C
ELE 3103 Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Communication Systems (ELE 3103) RCSDocument3 pagesCommunication Systems (ELE 3103) RCSsagarNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS 2017Document2 pagesCommunication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS 2017devangNo ratings yet
- Wavelet Analysis and Transient Signal Processing Applications for Power SystemsFrom EverandWavelet Analysis and Transient Signal Processing Applications for Power SystemsNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication (ECE - 3103) PDFDocument2 pagesAnalog Communication (ECE - 3103) PDFDevender DuaNo ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- School of Electronics Engineering: Specific Instruction To Students (If Any)Document2 pagesSchool of Electronics Engineering: Specific Instruction To Students (If Any)Dinesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Rr220401 Communication TheoryDocument8 pagesRr220401 Communication TheorySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document3 pagesHW 2Zero ChengNo ratings yet
- EE 442 Homework 4 Spectrum AnalysisDocument6 pagesEE 442 Homework 4 Spectrum AnalysisMnshNo ratings yet
- FrostDocument8 pagesFrostMnshNo ratings yet
- B1 - CAT 1 - KeyDocument6 pagesB1 - CAT 1 - KeyVamshidhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Acs UniversityqpDocument20 pagesAcs Universityqpgkk001No ratings yet
- Communication Systems (ELE 3151) RCSDocument2 pagesCommunication Systems (ELE 3151) RCSAkshat PradhanNo ratings yet
- M S RAMAIAH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Analog Communication ExamDocument2 pagesM S RAMAIAH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Analog Communication ExamRaghavendra LingrajNo ratings yet
- Question Paper: A Answer All The QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper: A Answer All The QuestionsHarshita GauravNo ratings yet
- rr221702 Analog CommunicationsDocument8 pagesrr221702 Analog CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Following Paper ID and Roll No. To Be Filled in Your Answer BookDocument4 pagesFollowing Paper ID and Roll No. To Be Filled in Your Answer BookNivedita BasuNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (ECE 1051)Document2 pagesBasic Electronics (ECE 1051)aryansorout1612No ratings yet
- EE365 MidTerm Final Solution PDFDocument11 pagesEE365 MidTerm Final Solution PDFAfnan FarooqNo ratings yet
- rr220401 Communication TheoryDocument8 pagesrr220401 Communication TheorySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- EEE302 SampQs MergedDocument78 pagesEEE302 SampQs Mergedc gNo ratings yet
- Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesSolved ProblemsRavindra KumarNo ratings yet
- Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesSolved ProblemsAhmed AnwarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet IIDocument3 pagesWorksheet IIBirhanu MelsNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS (MAKE UP) 2017Document2 pagesCommunication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS (MAKE UP) 2017devangNo ratings yet
- K.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering (Autonomous), Samayapuram, Trichy-621112 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC8491 Communication TheoryDocument2 pagesK.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering (Autonomous), Samayapuram, Trichy-621112 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC8491 Communication Theorykrithikgokul selvamNo ratings yet
- EEE321 Assignment AM and FM 2 PDFDocument2 pagesEEE321 Assignment AM and FM 2 PDFNafees HasanNo ratings yet
- Carson's Rule. Carson's Rule Defines The Approximate Modulation Bandwidth Required For A CarrierDocument4 pagesCarson's Rule. Carson's Rule Defines The Approximate Modulation Bandwidth Required For A Carriermugaao8No ratings yet
- Ece 1071 - Ece-1071 - Basic ElectronicsDocument2 pagesEce 1071 - Ece-1071 - Basic ElectronicsChalla SaiNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document2 pagesHW 5milad_7410No ratings yet
- Assignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationDocument3 pagesAssignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationRhelf Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- CUIB – SCHOOL OF IT TELECOMMUNICATIONS II TUTORIALDocument6 pagesCUIB – SCHOOL OF IT TELECOMMUNICATIONS II TUTORIALAnnNo ratings yet
- rr322205 Communication SystemsDocument7 pagesrr322205 Communication SystemsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Frequency Modulation & DemodulationDocument11 pagesFrequency Modulation & DemodulationALINo ratings yet
- 07a4ec11 Analogcommunications12Document5 pages07a4ec11 Analogcommunications12Anonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- ENGG2310A/ESTR2300 (Fall 2018) Problem Set #3Document6 pagesENGG2310A/ESTR2300 (Fall 2018) Problem Set #3Tsz Wing YipNo ratings yet
- National University Analog and Digital Communications AssignmentDocument2 pagesNational University Analog and Digital Communications AssignmentSha Dab AhMad HarniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Amplitude Modulation: 1.1 AM Signal GenerationDocument6 pagesExperiment 4: Amplitude Modulation: 1.1 AM Signal GenerationJohn NagyNo ratings yet
- Reg. No. V SEMESTER B.TECH (ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING) MAKEUP EXAM DEC 2016-JAN 2017Document2 pagesReg. No. V SEMESTER B.TECH (ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING) MAKEUP EXAM DEC 2016-JAN 2017devangNo ratings yet
- 13A04502 Digital Communication SystemsDocument2 pages13A04502 Digital Communication SystemsMallikarjuna Rao YamarthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PDFDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 PDFSourav kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- r05220405 Analog CommunicationsDocument7 pagesr05220405 Analog CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Assignment-3Document5 pagesAssignment-3Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- r05220405 Analog CommunicationsDocument8 pagesr05220405 Analog CommunicationsandhracollegesNo ratings yet
- Practice: Figure 1: An Analog MultiplierDocument2 pagesPractice: Figure 1: An Analog MultiplierHùng NghiêmNo ratings yet
- Am Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesAm Solved Problemssukhi_digra100% (2)
- Principles of CommunicationDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Communicationalapati1234567890No ratings yet
- COMMUNICATION3Document3 pagesCOMMUNICATION3october87No ratings yet
- BT - Ce - IDocument2 pagesBT - Ce - Imugaao8No ratings yet
- 13A04502 Digital Communication SystemsDocument2 pages13A04502 Digital Communication SystemsMallikarjuna Rao YamarthyNo ratings yet
- Handout 5Document7 pagesHandout 5Samama ZafarNo ratings yet
- Ra Ec 05032 Analog CommunicationsDocument1 pageRa Ec 05032 Analog CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Practice SetDocument5 pagesPractice Setrishavkumarsingh088No ratings yet
- Kuk Analog Communication Paper 2022Document3 pagesKuk Analog Communication Paper 2022ankurNo ratings yet
- NR 321001 Communication EngineeringDocument8 pagesNR 321001 Communication EngineeringSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- EE 442 Homework #4: MT T T CT TDocument6 pagesEE 442 Homework #4: MT T T CT TDatta YallapuNo ratings yet
- Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, PatialaDocument2 pagesThapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, PatialaJagat ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesTotoy AbnoyNo ratings yet
- 15 KVA DG Invoice BillDocument1 page15 KVA DG Invoice Billgouthamj0No ratings yet
- BDT 135 e-ticket booked for Adhora Ruma's journey from BBSETU_E to DHAKA on SUNDARBAN_EXPRESSDocument1 pageBDT 135 e-ticket booked for Adhora Ruma's journey from BBSETU_E to DHAKA on SUNDARBAN_EXPRESSMS.sumonNo ratings yet
- Dynamelt LC Series - MasterDocument2 pagesDynamelt LC Series - MasterITWDynatecNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning Continuity Amid and Beyond The PandemicDocument5 pagesTeaching and Learning Continuity Amid and Beyond The PandemicAmbbie Porras ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Labview Thesis ProjectsDocument5 pagesLabview Thesis Projectsdwm7sa8p100% (2)
- Qualis VHDL-QuickReferenceCard V2.1 PDFDocument2 pagesQualis VHDL-QuickReferenceCard V2.1 PDFlakithaNo ratings yet
- 150ACEBDocument1 page150ACEBBryan LeinwetterNo ratings yet
- How To Change Word Default Font in WPS Office WordDocument5 pagesHow To Change Word Default Font in WPS Office WordAkib ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Triaxial Accelerometer With Integral Magnet (A0643TX)Document2 pagesTriaxial Accelerometer With Integral Magnet (A0643TX)ORAMAYNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SAP BTPDocument15 pagesIntroduction To SAP BTPashikalin0% (1)
- CPK Guide 0211 TECH1Document11 pagesCPK Guide 0211 TECH1Mark LacroNo ratings yet
- Shakirullah Niazi: Professional SummaryDocument4 pagesShakirullah Niazi: Professional SummaryShakir UllahNo ratings yet
- 880 Series Manual - MAN-027.2021Document86 pages880 Series Manual - MAN-027.2021William RiverosNo ratings yet
- Definite Integrals and Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pagesDefinite Integrals and Trigonometric Functionskartikey papnoiNo ratings yet
- Linear IC Voltage RegulatorsDocument11 pagesLinear IC Voltage RegulatorsJavier Avalos GallosNo ratings yet
- What Is An IP AddressDocument5 pagesWhat Is An IP AddressM.h. PulokNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Ultrastar DC Ha210Document2 pagesData Sheet Ultrastar DC Ha210Marian DiaconescuNo ratings yet
- Factor Quadratic TrinomialsDocument23 pagesFactor Quadratic TrinomialsMaegan Eunice VirayNo ratings yet
- Standards Summary Sheet - ANSI A10.8-2011Document2 pagesStandards Summary Sheet - ANSI A10.8-2011DwiCahyoAgustino100% (1)
- Assessment of Customer Relationship Management On Central Hotel in The Case Hawassa CityDocument41 pagesAssessment of Customer Relationship Management On Central Hotel in The Case Hawassa Cityasu manNo ratings yet
- Computer Science (2210) Sample Paper For O Level 2Document9 pagesComputer Science (2210) Sample Paper For O Level 2Mehwish TahirNo ratings yet
- Trend Student Book Answers PDFDocument37 pagesTrend Student Book Answers PDFElena Abato SantosNo ratings yet
- Orbital and Linear Converter With Autotuning: ACT 401-xxx - ManualDocument37 pagesOrbital and Linear Converter With Autotuning: ACT 401-xxx - ManualGeraldo Candido de Azevedo NetoNo ratings yet
- Capeta 23Document55 pagesCapeta 23janof1No ratings yet
- SGT-400 Product PresentationDocument42 pagesSGT-400 Product PresentationAnita Moya100% (3)
- Public Participation in Decision-Making ProcessesDocument10 pagesPublic Participation in Decision-Making ProcessesGenniyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Vias-EgoDocument10 pages2 Vias-Egoleonardo osmelNo ratings yet
- SPG/SSG Election Report: Attachment 1Document4 pagesSPG/SSG Election Report: Attachment 1Nexus BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Assignment & LabDocument5 pagesAssignment & LabXyus PoudelNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityFrom EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- CCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationFrom EverandCCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationNo ratings yet
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireFrom EverandThe Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)From EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterFrom EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The CompTIA Network+ Computing Technology Industry Association Certification N10-008 Study Guide: Hi-Tech Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the Exam with Confidence - Practice Test with AnswersFrom EverandThe CompTIA Network+ Computing Technology Industry Association Certification N10-008 Study Guide: Hi-Tech Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the Exam with Confidence - Practice Test with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)From EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)No ratings yet
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsNo ratings yet
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationFrom EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Cyber-Warfare: A Multidisciplinary ApproachFrom EverandIntroduction to Cyber-Warfare: A Multidisciplinary ApproachRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- ITIL® 4 Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and Strategic Leader DPI certificationFrom EverandITIL® 4 Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and Strategic Leader DPI certificationNo ratings yet
- AWS Certified Advanced Networking - Specialty Exam Guide: Build your knowledge and technical expertise as an AWS-certified networking specialistFrom EverandAWS Certified Advanced Networking - Specialty Exam Guide: Build your knowledge and technical expertise as an AWS-certified networking specialistNo ratings yet
- Advanced Antenna Systems for 5G Network Deployments: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and PracticeFrom EverandAdvanced Antenna Systems for 5G Network Deployments: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)