Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Uploaded by
Jeffrey YuetOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Uploaded by
Jeffrey YuetCopyright:
Available Formats
OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
NEW SENIOR SECONDARY PHYSICS AT WORK
(SECOND EDITION)
Mock Examination 2020 Papers 1 and 2
Solutions
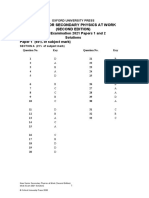
Paper 1 (60% of subject mark)
SECTION A (21% of subject mark)
Question No. Key Question No. Key
1 B 21 C
2 B 22 B
3 B 23 A
4 B 24 C
5 B 25 C
6 C 26 D
7 A 27 D
8 C 28 A
9 C 29 A
10 B 30 B
11 A 31 D
12 A 32 D
13 C 33 C
14 D
15 A
16 A
17 C
18 C
19 B
20 A
SECTION B (84 marks, 39% of subject mark)
1
(a) Steam releases a large amount of latent heat when it condenses on the
food. This heats the food quickly. 1A
(b) Pt = mc∆T+ ml 1M+1M
980t = 0.5 4200 (100 − 25) + 0.1 (2.26 106)
t = 184 s 1A
The time used is 184 s.
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 1
© Oxford University Press 2019
(c) Pt = m1c∆T1 − m2c∆T2
980t = 0.5 4200 (100 − 25) – 0.35 4200 (100 − 80) 1M
t = 131 s 1A
The time saved is 131 s.
(d) Plastic 1A
(Accept other reasonable answers)
Because it is a good insulator of heat. 1A
2
(a) Since p T for constant V,
1.2 × 10 6 273 4
= 1M
p' 273 25
p' = 1.29 × 106 Pa 1A
The gas pressure is 1.29 × 106 Pa.
1 3RT
(b) By m c 2 = , 1M
2 2N A
3RT
r.m.s. speed c 2 = mN
A
3 8.31 ( 273 25)
=
0.03
1
= 498 m s 1A
(c) When temperature decreases, the gas molecules move slower. 1A
The gas molecules collide with the container wall less vigorously and
less frequently. 1A
Therefore, the pressure decreases. 1A
3
(a) Downwards 1A
(b) Work done by Peter = KE gained by the ball + PE gained by the ball
1
= mv 2 + mgh
2
1
= 1.2 32 + 1.2 9.81 0.05 1M+1M
2
= 5.99 J
6J
(c) By W = F// s, 1M
W
average upward force =
s
6
=
0.05
= 120 N 1A
(d) Gain in KE = loss in PE
1
m (v 2 u 2 ) = mgh 1M
2
1
× (v 2 3 2 ) = 9.81 (11.5 + 0.05)
2
v = 15.3 m s–1 1A
1
The speed of the ball is 15.3 m s .
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 2
© Oxford University Press 2019
(e)
velocity / m s−1
0 time / s
t1 t2
–15.3
(An increasing trend of velocity from −15.3 m s‒1 to a less negative value
from t = 0 to t1) 1A
(Constant velocity from t = t1 to t2) 1A
4
(a) From t = 0 to 0.5 s, it moves forwards with uniform velocity. 1A
From t = 0.5 s to 8.5 s, it moves forwards with uniform deceleration. 1A
(b) Initial v of car Y = 70 km h–1
70
Distance travelled within 2 s = 2 = 38.9 m < 50 m 1M
3.6
The driver obeys the two-second rule. 1A
(c) Acceleration of car X = slope of the v–t graph
70
0
3.6 1M
=
05
= –3.89 m s–2 1A
The deceleration of car X is 3.89 m s–2.
(d) Stopping distance of car Y = Area under the v–t graph of car Y
70
(0.5 8.5) ×
3 .6 1M
=
2
= 87.5 m 1A
(e) It is the difference in displacements of the cars from t = 0 to 8.5 s. 1A
5
(a) Attach an elastic thread to the trolley and stretch the thread to pull the
trolley down the friction-compensated runway. 1A
Record the acceleration and the total mass of the trolley. 1A
Repeat by adding one and two mass bars to the trolley in turn. 1A
Precaution:
The thread should be stretched to the same length all the way down the
runway.
Or The thread should be stretched to the same length in all trials. 1A
(b) To ensure that the pulling force from the elastic thread is the net force
acting on the trolley. 1A
(c) a should be inversely proportional to m. 1A
1
or a
m
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 3
© Oxford University Press 2019
6
(a) Convex lens 1A
(b) lens X 5 cm
Q F principal axis
Q'
P'
(Correct light rays to locate the image) 1A
(Correct image P'Q') 1A
(c) (Correct light rays to locate the focus) 1A
Focal length = 6 cm 1A
1 1 1
(d) (i) 1M
u v f
1 1 1
24 v 6
v = 8 cm 1A
The image distance is 8 cm.
(ii) Linear magnification = 8/24=0.33 1A
Image height = 15 0.33 = 5 cm 1A
7
(a) The student is wrong. 1A
It is the slit separation but not the slit width that will affect the fringe
separation of the interference pattern. 1A
(b)
P O Q
(Symmetry about the central bright fringe at O) 1A
(The fringes are evenly spaced) 1A
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 4
© Oxford University Press 2019
D
(c) y
a 1M
2
2.6 10 2 .0
=
10 0.5 10 3
λ = 6.50 107 m
1A
= 650 nm
The wavelength of the laser beam is 650 nm.
(d) From d sin θ = nλ and sin ≤ 1,
d 1 103 1
n 1M
600 532 109
n ≤ 3.13
The maximum number of bright fringes can be observed is 7. 1A
8
V2
(a) P
R
220 2
1000 = 1M
R
R = 48.4 Ω 1A
The resistance of a lamp is 48.4 Ω.
As the lamps on a light post are connected in parallel,
1 1
= 9
Req R
1 9
= 1M
Req 48.4
Req = 5.38 Ω 1A
The resistance of the light post is 5.38 Ω.
l
(b) Resistance of cable =
A
(1.7 108 ) 240
= 1M
2.5 10 6
= 1.63 Ω 1A
(c) Let n be the number of light post that can be connected in a lighting
circuit.
By V = IR,
5.38
220 = 70 ( + 1.63) 1M
n
n = 3.56
At most 3 light posts can be connected in a lighting circuit. 1A
(d) The lamps are not working at their rated voltage as there is voltage
drop through the long cable. 1A
9
(a) When the magnet approaches the solenoid, the induced current flows
from P to Q through the solenoid. 1A
When the magnet moves inside the solenoid, no current is induced in
the solenoid. 1A
When the magnet leaves the solenoid, the induced current flows from
Q to P through the solenoid. 1A
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 5
© Oxford University Press 2019
(b) (i) PABRSDCQ 1A
(ii) QCBRSDAP 1A
(c) (i) Apply E = Pt.
Energy generated by shaking the flashlight for 30 s
= energy dissipated by lamp in 5 min
P × 30 = 100 ×10–3 × 5 × 60 1M
P=1W 1A
The average power of the generator is 1 W.
(ii) No. The lamp is powered by the battery and has constant
brightness. 1A
Shaking the flashlight more vigorously will only charge the
battery more quickly. 1A
(iii) Peak value of induced e.m.f. = N
t
= 330 × 0.0133 1M
= 4.39 V 1A
4.39
r.m.s. value of the induced e.m.f. = = 3.10 V 1A
2
10
(a)
conducting plates E
1A
to alarm circuit
americium-241
241
(b) 95 Am 237 4
93 Np + 2 α 2A
241
Or 95 Am 237
93 Np + 42 He 2A
(c) The negative electrons are attached to the smoke particles instead of the
positive conducting plate. 1A
This causes the current between the plates to drop and triggers the
smoke alarm. 1A
(d) Activity = A0e–kt
ln2
10
= (3.33 × 104) × e 432 1M
= 3.28 × 104 Bq 1A
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 6
© Oxford University Press 2019
Paper 2 (20% of subject mark)
SECTION A: Astronomy and Space Science (20 marks, 10% of subject mark)
Multiple-choice questions
1.1 C 1.25A
1.2 D 1.25A
1.3 A 1.25A
1.4 A 1.25A
1.5 C 1.25A
1.6 B 1.25A
1.7 B 1.25A
1.8 D 1.25A
Structured question
1
(a) Radiation at certain wavelengths is absorbed 1A
by the low-pressure gas between the star and us. 1A
(b) The light from the star is red-shifted. 1A
This indicates that the star is moving away from us. 1A
∆
(c) (i) By ≈ ,
∆
orbital speed v ≈ ×c 1M
–4 8
= (4.33 × 10 )(3 × 10 )
= 1.30 × 105 m s–1 1A
(ii) By v = ,
orbital radius r = 1M
. .
=
= 5.54 × 109 m 1A
(d) The gravitational pull between the stars provides the centripetal force.
=
M= 1M
. .
=
.
= 1.40 × 1030 kg 1A
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 7
© Oxford University Press 2019
SECTION B: Atomic World (20 marks, 10% of subject mark)
Multiple-choice questions
2.1 C 1.25A
2.2 C 1.25A
2.3 C 1.25A
2.4 A 1.25A
2.5 C 1.25A
2.6 D 1.25A
2.7 B 1.25A
2.8 B 1.25A
Structured question
2
(a) (i) The spectrum consists of discrete lines. 1A
(ii) In Bohr’s model, when an electron in a hydrogen atom drops from
a higher energy level to a lower one, a photon with energy equal to
the energy difference between the levels is emitted. 1A
Since energy levels are quantized, the energy of the photons
emitted can only take some discrete values. This results in discrete
spectral lines. 1A
(b) (i) E3→2 = E3 – E2
13.6 13.6
= 2 1M
3 22
= 1.889 eV
hc
By E = hf = , 1M
( 6.63 10 34 ) (3.00 108 )
1.889 ×1.60 × 10–19 =
7
λ = 6.58 10 m 1A
(ii) Visible light (red light) 1A
(iii) E2→3 = E3→2 = 1.889 eV
13.6 13.6
E2→4 = 2
4 22
= 2.55 eV 1A
As 1.889 eV 2 eV 2.55 eV, no energy difference between
energy levels matches the photon energy. 1A
Therefore, the photon will pass the atom without being affected. 1A
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 8
© Oxford University Press 2019
SECTION C: Energy and Use of Energy (20 marks, 10% of subject mark)
Multiple-choice questions
3.1 C 1.25A
3.2 C 1.25A
3.3 B 1.25A
3.4 D 1.25A
3.5 C 1.25A
3.6 B 1.25A
3.7 C 1.25A
3.8 C 1.25A
Structured question
3
(a) (i) U-value = = 0.043 = 2.15 W m–2 K–1 1A
d 20 103
(ii) Area of the walls and roof = (3 × 2) × 4 + 3 × 3 – 2 × 1 = 31 m2 1M
QC
= UAΔT = 2.15 × 31 × 10 = 667 W 1A
t
(iii) Average rate of heat transfer QT = 667 + 600 = 1267 W
Q 1267
OTTV = T = 1M
AT 31 2
= 38.4 W m–2 1A
(b) (i) Cooling capacity required
= 1267 + 2× 15 + 2 × 670 1M
= 2640 W 1A
(ii) Operating power of the air conditioner
2640
= = 1060 W 1M
2 .5
Energy consumed in a day
= (1.06 + 2 × 1 + 2 × 0.015) × 2 = 6.18 kWh 1M
Cost of electricity in a month
= 6.18 × 30 × 0.9
= $167 1A
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 9
© Oxford University Press 2019
SECTION D: Medical Physics (20 marks, 10% of subject mark)
Multiple-choice questions
4.1 C 1.25A
4.2 C 1.25A
4.3 B 1.25A
4.4 D 1.25A
4.5 A 1.25A
4.6 D 1.25A
4.7 B 1.25A
4.8 D 1.25A
Structured question
4
(a) Biological half-life is the time taken for half of a substance to be
removed from the body by biological processes. 1A
1 1 1
(b) = + 1M
t e t p tb
1
1 1
te =
t p tb
1
1 1
=
8 80
= 7.27 days 1A
(c) Iodine-123 is more suitable. 1A
This is because the half-life of iodine-131 is too long and it will remain
radioactive for many days after the imaging process. 1A
(d) (i) Figure 4.1 1A
(ii) In a radionuclide image, a dark region indicates that there is a high
concentration of radionuclides. 1A
In an X-ray radiographic image, a dark region indicates that the
attenuation of X-rays is small. 1A
(iii) Advantage: radionuclide images can provide functional
information about the target organ. 1A
Disadvantage: radionuclide images provide limited structural
information about the target organ. 1A
(Accept other reasonable answers)
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)
Mock Exam 2020 Solutions 10
© Oxford University Press 2019
You might also like
- Physics Mechanics ExerciseDocument9 pagesPhysics Mechanics ExerciseblahNo ratings yet
- Physics 02 - Exercise - Solutions - e PDFDocument9 pagesPhysics 02 - Exercise - Solutions - e PDFNg Ho Wang吳皓弘No ratings yet
- Redox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis (Less than 40 chars: 35 charsDocument38 pagesRedox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis (Less than 40 chars: 35 charsミーチェルNo ratings yet
- 06 Matter As ParticlesDocument10 pages06 Matter As ParticlesmahinkamNo ratings yet
- Answers To 2017-2018 F3-CHEM Final Examination: Section A: Multiple ChoicesDocument13 pagesAnswers To 2017-2018 F3-CHEM Final Examination: Section A: Multiple Choicesjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Phy BK Ans 3aDocument24 pagesPhy BK Ans 3aapi-253498969No ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power: Checkpoint 1 (p.194)Document12 pagesWork, Energy and Power: Checkpoint 1 (p.194)U KILLED MY DOGNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6.1: Basic Terminologies in 3-Dimensional ProblemsDocument35 pagesWorksheet 6.1: Basic Terminologies in 3-Dimensional ProblemsWONG ATHENANo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseDocument23 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseBernardNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Question Bank: Dse Chem MasteryDocument48 pagesThe Ultimate Question Bank: Dse Chem MasteryYip AvaNo ratings yet
- Phy BK Ans 2Document93 pagesPhy BK Ans 2wingboxzNo ratings yet
- Motion Chapter Solutions - Physics Textbook Exercises ExplainedDocument15 pagesMotion Chapter Solutions - Physics Textbook Exercises ExplainedTsz Yan LamNo ratings yet
- A4 QB-MC Ch10 Transpiration Transport and Support in PlantsDocument31 pagesA4 QB-MC Ch10 Transpiration Transport and Support in PlantsReg ChooNo ratings yet
- Structured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part VIII Chemical Reactions and EnergyDocument21 pagesStructured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part VIII Chemical Reactions and EnergyNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Reacting Masses: Calculating Amounts in Chemical ReactionsDocument36 pagesReacting Masses: Calculating Amounts in Chemical ReactionsRyan100% (1)
- New Senior Secondary MASTERING BIOLOGY OXFORD Mock - Bio - Set6 - e - AnsDocument7 pagesNew Senior Secondary MASTERING BIOLOGY OXFORD Mock - Bio - Set6 - e - AnsChun Kit LauNo ratings yet
- A4 QB-MC Ch09 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantsDocument19 pagesA4 QB-MC Ch09 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantsReg ChooNo ratings yet
- Afterschool Mole Calculation Exercise Ans.Document32 pagesAfterschool Mole Calculation Exercise Ans.J TNo ratings yet
- 3 Functions and Graphs: Review Exercise 3 (P. 3.4) ActivityDocument51 pages3 Functions and Graphs: Review Exercise 3 (P. 3.4) ActivityTsz Wai YanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 1A 1B 2 - New QuestionDocument58 pagesQuestion Bank 1A 1B 2 - New Questionteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Hkcee Past Paper Microscopic WorldDocument7 pagesChemistry Hkcee Past Paper Microscopic WorldAnn MaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1B (ENG) Question-Answer Book PDFDocument16 pagesPaper 1B (ENG) Question-Answer Book PDFsdcsNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Biology Paper 1Document32 pagesPractice Paper Biology Paper 1ddd dddNo ratings yet
- LQ - 03 Cell Activity and OrganizationDocument40 pagesLQ - 03 Cell Activity and Organizationapi-3822784100% (2)
- Chemistry Book 4A (2nd Edition)Document85 pagesChemistry Book 4A (2nd Edition)Ying Yan LamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Temperature and Thermometers: Physics Notes Heat and GasDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Temperature and Thermometers: Physics Notes Heat and GasWong Chun LamNo ratings yet
- 2002 Mathematics Paper2Document30 pages2002 Mathematics Paper2api-37009440% (1)
- F.3 Heat NoteDocument12 pagesF.3 Heat Noteskywalker_handsomeNo ratings yet
- 2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)Document22 pages2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)UniversityJCNo ratings yet
- bk2 - ch17 - Sug Ans - eDocument3 pagesbk2 - ch17 - Sug Ans - enonameNo ratings yet
- Matter as Particles Explained Through Particle TheoryDocument26 pagesMatter as Particles Explained Through Particle TheoryYuenHei Kwok0% (1)
- Integrated Science - Secondary 1Document7 pagesIntegrated Science - Secondary 1siubb0112No ratings yet
- 4BCh07 (Basic Properties of Circles 2)Document25 pages4BCh07 (Basic Properties of Circles 2)api-3826695100% (1)
- Hkdse Chemistry - A Modern View: (Second Edition) (Reprinted With Minor Amendments 2019)Document25 pagesHkdse Chemistry - A Modern View: (Second Edition) (Reprinted With Minor Amendments 2019)Tat LNo ratings yet
- South Tuen Mun Government Secondary School S4 Mathematics Chapter 2B Complex Number Multiple Choice Questions Name: - Class: S4 - Mark: - /13Document2 pagesSouth Tuen Mun Government Secondary School S4 Mathematics Chapter 2B Complex Number Multiple Choice Questions Name: - Class: S4 - Mark: - /13CHEUNG PAK YU 5D09No ratings yet
- 4ACh01 (Quadratic Equations in One Unknown)Document32 pages4ACh01 (Quadratic Equations in One Unknown)api-3826695No ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U8 3-4 SetB Final eDocument7 pagesScicent SQ U8 3-4 SetB Final eApple Lou100% (1)
- 1920 F3 Chem First Exam AnswerDocument2 pages1920 F3 Chem First Exam AnswerElsaaaNo ratings yet
- S5 Final (Compulsory) Paper II 2012-13Document9 pagesS5 Final (Compulsory) Paper II 2012-1320/21-5B-(05) HoMeiYi/何美誼No ratings yet
- Bio MC Answers (By Topics)Document6 pagesBio MC Answers (By Topics)HarmonyChuiNo ratings yet
- 1920 F3 Chem First Exam Question PaperDocument6 pages1920 F3 Chem First Exam Question PaperElsaaaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Metallic Bonding: Learning GoalDocument36 pagesChemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Metallic Bonding: Learning GoalRyanNo ratings yet
- The Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument67 pagesThe Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Multiple-Choice QuestionsZ s2021 4C Ma Ka Ki Margaret 4C16No ratings yet
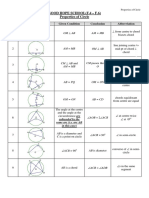
- Deductive Geometry Reasons - WebDocument24 pagesDeductive Geometry Reasons - WebJennifer Chung33% (3)
- South Tuen Mun Government Secondary School S4 Mathematics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesSouth Tuen Mun Government Secondary School S4 Mathematics Multiple Choice QuestionsCHEUNG PAK YU 5D09No ratings yet
- 2RM Cb4Aans eDocument76 pages2RM Cb4Aans eTat LNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Notes 補充筆記 (Centers of Triangle 三角形的心)Document3 pagesSupplementary Notes 補充筆記 (Centers of Triangle 三角形的心)Henry Leung0% (1)
- New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) Book 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesNew Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) Book 2 SolutionsHarry LeungNo ratings yet
- SSGS 17-18 F.6 Final Exam 1 and 2 CHEMDocument37 pagesSSGS 17-18 F.6 Final Exam 1 and 2 CHEMKelvin ChowNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseDocument27 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic Exercise[3Y25] Ng Sai YiNo ratings yet
- Math Book 5A ch.04Document40 pagesMath Book 5A ch.04Jenessa LiNo ratings yet
- Properties of Circles ExplainedDocument4 pagesProperties of Circles ExplainedJessieNo ratings yet
- Munsang College 2013-2014 Second Term Examination F. 5 Mathematics Extended Part - Module 1 (Calculus and Statistics)Document28 pagesMunsang College 2013-2014 Second Term Examination F. 5 Mathematics Extended Part - Module 1 (Calculus and Statistics)Anson Ka Kin ChanNo ratings yet
- 3 Functions and Graphs: Review Exercise 3 (P. 3.4) ActivityDocument51 pages3 Functions and Graphs: Review Exercise 3 (P. 3.4) ActivityTsz Wai YanNo ratings yet
- Phy Eng MS v4 PDFDocument11 pagesPhy Eng MS v4 PDFHuson 0710No ratings yet
- Phy Mock SolDocument16 pagesPhy Mock SolA PersonNo ratings yet
- SHCC 1718 Phy Mock Sol PDFDocument27 pagesSHCC 1718 Phy Mock Sol PDFVincent haNo ratings yet
- Phy Mock SolDocument17 pagesPhy Mock SolA PersonNo ratings yet
- 25-06-23 - JR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-B) - Jee Adv - 2017 (P-I) - Wat-9 - Key&solDocument6 pages25-06-23 - JR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-B) - Jee Adv - 2017 (P-I) - Wat-9 - Key&solAnonymous A6Jnef04No ratings yet
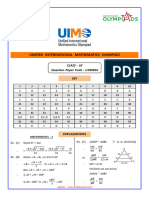
- CL - 10 - UIMO-2023-Paper-9264 KeyDocument9 pagesCL - 10 - UIMO-2023-Paper-9264 KeyShashank MauryaNo ratings yet
- Wheel MachineDocument114 pagesWheel Machinepramo_dassNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Aerodynamics Fluid MotionDocument62 pagesIntroduction to Aerodynamics Fluid Motionlucifer pandeyNo ratings yet
- Moment of InertiaDocument6 pagesMoment of Inertiarohan_nerlekar794100% (3)
- Unit 1.1 - Mechanics - Kinematics (Student)Document12 pagesUnit 1.1 - Mechanics - Kinematics (Student)Quay Wei KwangNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design1Document111 pagesGeometric Design1Ronald DarwinNo ratings yet
- Resisted Sled Sprint Training To Improve Sprint PeDocument21 pagesResisted Sled Sprint Training To Improve Sprint Pearis58No ratings yet
- Kinematics Problems With SolutionDocument17 pagesKinematics Problems With SolutionApril ClaireNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Motion DPP - 02Document6 pagesNewton's Law of Motion DPP - 02guptahimanshuu007No ratings yet
- DiscussDocument18 pagesDiscussINAMUL HASANNo ratings yet
- 1-D & 2-D Relative Motion PhysicsDocument4 pages1-D & 2-D Relative Motion PhysicsHarsh PuriNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of particlesDocument11 pagesKinematics of particlesmaitesecoNo ratings yet
- Trajectory Generation for ManipulatorsDocument39 pagesTrajectory Generation for ManipulatorsHo Lam HeungNo ratings yet
- SDO Navotas Sci8 Q1 Lumped - FVDocument50 pagesSDO Navotas Sci8 Q1 Lumped - FVMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Figure 1.1 Distributed-Mass Models Figure 1.2 Lumped-Mass ModelsDocument13 pagesFigure 1.1 Distributed-Mass Models Figure 1.2 Lumped-Mass Modelspattrapong pongpattraNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper For Class 11 Physics Mock Paper 1 With SolutionsDocument26 pagesCBSE Sample Paper For Class 11 Physics Mock Paper 1 With SolutionsAyushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Velocity & Acc - Engineering Science DMV1032 - 2132Document23 pagesVelocity & Acc - Engineering Science DMV1032 - 2132Shaik SyahmanNo ratings yet
- GenPhy1 Q1 PTDocument4 pagesGenPhy1 Q1 PTLyndrian Shalom BaclayonNo ratings yet
- Motion in 1DDocument21 pagesMotion in 1DVIGNESH KUMAR MNo ratings yet
- Physics Scheme of Work For SS 1, SS2, and SS3Document4 pagesPhysics Scheme of Work For SS 1, SS2, and SS3Isaac Ayuba100% (1)
- Kinematics Engineering PaperDocument8 pagesKinematics Engineering PaperAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- Half Car Simulink ModelDocument35 pagesHalf Car Simulink ModelFunkysajan83% (6)
- Acceleration in One DimensionDocument6 pagesAcceleration in One DimensionSimon SituNo ratings yet
- Labsheet Linear MotionDocument6 pagesLabsheet Linear MotionGnabryNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge: IMAT SyllabusDocument10 pagesGeneral Knowledge: IMAT SyllabusFernanda AntonialliNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 5 SolutionsDocument6 pagesProblem Set 5 SolutionssagarnitishpirtheeNo ratings yet
- PHY1004L. - Lab 11 - Static EquilibriumDocument5 pagesPHY1004L. - Lab 11 - Static Equilibriumdiegocely700615No ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion LabDocument5 pagesUniform Circular Motion Labapi-346003119No ratings yet
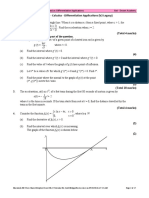
- IB Practice - Calculus - Differentiation Applications (V2 Legacy)Document52 pagesIB Practice - Calculus - Differentiation Applications (V2 Legacy)ishaanNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Tool-Path Smoothing For 6-Axis Industrial Machining RobotsDocument10 pagesKinematic Tool-Path Smoothing For 6-Axis Industrial Machining RobotsToniolo LucaNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks Motion AnalysisDocument37 pagesSolidWorks Motion AnalysisivNo ratings yet