Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VIRUSES
Uploaded by
Theresa Lambayon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageviruses
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentviruses
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageVIRUSES
Uploaded by
Theresa Lambayonviruses
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
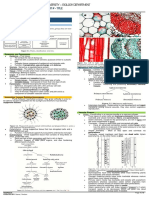
VIRUSES It is in this process that results in
acquisition of the viral phospholipid envelope.
Attachment (endocytosis) -viral
proteins and the cap seed or Temperate bacteriophage have both
phospholipids envelop and interact with lytic and lysogenic cycle
specific receptors on the host cellular Lytic cycle – lytic phages, bacterial cells
surface, and this specificity determines are broken open lyst and destroyed
the host range or tropism of the virus. after immediate replication of the
Penetration the process of attachment virion. As soon as the cell destroyed,
to a specific receptor can induce the page progeny can find new host to
conformational changes in cap seed infect
viral proteins or the lipid envelop that o Ex. Microphage T4
results in the fusion of viral and cellular o Lytic phage is more suitable for
membrane. Some DNA viruses can lytic therapy
enter the host cell through receptor Lysogenic cycle - does not result in
mediated endocytosis. immediate lysing of the cell
Uncoating – the viral cap seed is o Those phages that are able to
removed and degraded by several undergo lysogeny are known as
enzymes or host enzymes releasing the temperate phages. Their viral
viral genomic nucleic acid. genome will integrate with host
Replication – after the viral genome has DNA and replicate along with it
been uncoated, transcription or fairly harmlessly.
translation of the viral genome is o The virus remains dormant
initiated. It is at this stage of viral until host conditions
replication that differs greatly between deteriorate due to depletion of
DNA and RNA viruses, and viruses with nutrients. At this point, they
opposite nucleic acid polarity. This initiate the reproductive cycle
process culminates in the de novo resulting In the lysis of the host
synthesis of viral proteins and genomes. cell
Assembly – after de novo synthesis of o PHAGE LAMBDA OF THE E.COLI
viral proteins and genomes, viral
proteins are packaged with a newly
replicated viral genomes to new virion
that are ready to released host cell. This
process can also be referred to as
Maturation.
Virion release – there are two methods
of viral release: Lysis or budding. Lysis
result from a dead of the host cell. This
type of process is called cytolytic.
Ex.Variola major (aka smallpox)
Envelope viruses (e.g
influenza virus) typically release
from the host cell by budding.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Minimally Invasive ProceduresDocument35 pagesMinimally Invasive ProceduresAlex Pieces100% (2)
- Psychiatric Evaluation of AdultsDocument62 pagesPsychiatric Evaluation of Adultsl1o2stNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope PartsDocument3 pagesCompound Microscope PartsTheresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument53 pagesDermatologyaditiNo ratings yet
- Practice Bulletin Multifetal GestationDocument16 pagesPractice Bulletin Multifetal GestationSusana Torres0% (1)
- Bio 49 Activity 1Document6 pagesBio 49 Activity 1Theresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0968000415001644 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0968000415001644 MainTheresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Plant TissueDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Plant TissueTheresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Plant CellDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Plant CellTheresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S030090841400337X MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S030090841400337X MainTheresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Functional Advantages of Conserved Intrinsic Disorder in RNA-Binding ProteinsDocument16 pagesFunctional Advantages of Conserved Intrinsic Disorder in RNA-Binding ProteinsTheresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Scope & Branches of Microbiology - Has An Impact On Medicine, Agriculture, Food Science, Immunology, Ecology, Genetics, BiochemistryDocument3 pagesScope & Branches of Microbiology - Has An Impact On Medicine, Agriculture, Food Science, Immunology, Ecology, Genetics, BiochemistryTheresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- REFLECTION PAPER (Gen. Ecology)Document3 pagesREFLECTION PAPER (Gen. Ecology)Theresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- 013 Ipp en - 36Document50 pages013 Ipp en - 36Theresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Theoretical BackgroundDocument26 pagesTheoretical BackgroundTheresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument7 pagesReview of Related LiteratureTheresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Chy 46.1 - Lambayon - Activity 2 (Cleaning and Marking of Laboratory Ware)Document3 pagesChy 46.1 - Lambayon - Activity 2 (Cleaning and Marking of Laboratory Ware)Theresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 Scientific Paper (A Microbiological Survey of The Different Representative Organisms of Bacteria)Document4 pagesExercise 2 Scientific Paper (A Microbiological Survey of The Different Representative Organisms of Bacteria)Theresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDocument19 pagesCardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDurgesh PushkarNo ratings yet
- Genomic Characterization of Co-Existing Neoplasia and Carcinoma Lesions Reveals Distinct Evolutionary Paths of Gallbladder CancerDocument11 pagesGenomic Characterization of Co-Existing Neoplasia and Carcinoma Lesions Reveals Distinct Evolutionary Paths of Gallbladder CancerleartaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Group Study Case 1Document8 pagesClinical Group Study Case 1Olivia JagroopNo ratings yet
- Dampak Perkembangan Teknologi Terhadap AnakDocument23 pagesDampak Perkembangan Teknologi Terhadap Anakyeyen fitriaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System MedicationsDocument2 pagesRespiratory System Medicationsmlbrown8No ratings yet
- 3 Mic125Document8 pages3 Mic125nadiazkiNo ratings yet
- Pola Kehilangan Gigi Dan Kebutuhan Perawatan GigiDocument5 pagesPola Kehilangan Gigi Dan Kebutuhan Perawatan GigiPraprimadani MursyidNo ratings yet
- CR 110520Document14 pagesCR 110520genellemaarteNo ratings yet
- 002 POS Format 1Document9 pages002 POS Format 1Roland Philip GoNo ratings yet
- 3 Lebanese Code of EthicsDocument72 pages3 Lebanese Code of Ethicsali abdel hadiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Etiology of PCP: HIV InfectionDocument20 pagesPathophysiology and Etiology of PCP: HIV InfectionJehan Sendix100% (1)
- A Case Presentation: Ectopic PregnancyDocument10 pagesA Case Presentation: Ectopic PregnancyJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Gingival Diseases in Childhood - A Review: Abst TDocument4 pagesGingival Diseases in Childhood - A Review: Abst TMagfhiro Rangga AndalasNo ratings yet
- BMUS Safety Guidelines 2009 Revision FINAL Nov 2009Document18 pagesBMUS Safety Guidelines 2009 Revision FINAL Nov 2009Damien Matthias LeeNo ratings yet
- Adult Assessment ToolDocument4 pagesAdult Assessment ToolRiss CalmaNo ratings yet
- Karimzadeh 2021Document7 pagesKarimzadeh 2021Istika Nasya AgustinNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Behavioral and Emotional Disorders ADocument7 pagesPrevalence of Behavioral and Emotional Disorders AEricka GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- 1998 Does Knuckle Cracking Lead To Arthritis of The Fingers PDFDocument2 pages1998 Does Knuckle Cracking Lead To Arthritis of The Fingers PDFMatías RamírezNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Peri Operative Nursing: Are Prepared For Surgery, Undergo Surgical Procedures and RecoverDocument15 pagesOperating Room Peri Operative Nursing: Are Prepared For Surgery, Undergo Surgical Procedures and RecoverRackz Glova AmaroNo ratings yet
- Early and Late Preeclamsia Are Characterized by High Cardiac Output, But in The Presence of Fetal Growth Restriction, Cardiac Output Is Low Insights From A Prospective Study PDFDocument12 pagesEarly and Late Preeclamsia Are Characterized by High Cardiac Output, But in The Presence of Fetal Growth Restriction, Cardiac Output Is Low Insights From A Prospective Study PDFJustiawan NazwanNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Outline Notes - Docx NewDocument4 pagesExam 1 Outline Notes - Docx NewHeather MoralesNo ratings yet
- Perawatan Paliatif Pada Hiv/Aids: SolikinDocument45 pagesPerawatan Paliatif Pada Hiv/Aids: SolikinirpanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Fetal MRIDocument80 pagesBasics of Fetal MRIjturos2003No ratings yet
- Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnant Women Admitted On Maternity Ward in Jinja Regional Referral HospitalDocument10 pagesPrevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnant Women Admitted On Maternity Ward in Jinja Regional Referral HospitalKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Healthy AgingDocument13 pagesHealthy AgingCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Pregnant Women Visit in Puskesmas As An Effect of Using Ultrasound in Pregnancy ExaminationDocument12 pagesImprovement of Pregnant Women Visit in Puskesmas As An Effect of Using Ultrasound in Pregnancy ExaminationKharinaNo ratings yet