Professional Documents
Culture Documents
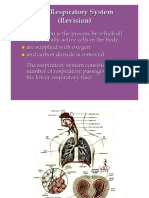
Notes For 21 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Uploaded by
Lexie Duke0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesThe respiratory system functions to obtain oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide. It consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract. Air flows through the nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and into the alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. The processes of respiration include ventilation, gas transport, cellular respiration and perfusion. Oxygen is transported in the blood bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells while carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate ions and bound to hemoglobin. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema are conditions where airflow is obstructed or the alveoli are destroyed, impairing gas exchange.
Original Description:
notes
Original Title
Notes for 21--RESPIRATORY SYSTEM (2) (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe respiratory system functions to obtain oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide. It consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract. Air flows through the nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and into the alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. The processes of respiration include ventilation, gas transport, cellular respiration and perfusion. Oxygen is transported in the blood bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells while carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate ions and bound to hemoglobin. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema are conditions where airflow is obstructed or the alveoli are destroyed, impairing gas exchange.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesNotes For 21 - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Uploaded by
Lexie DukeThe respiratory system functions to obtain oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide. It consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract. Air flows through the nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and into the alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. The processes of respiration include ventilation, gas transport, cellular respiration and perfusion. Oxygen is transported in the blood bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells while carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate ions and bound to hemoglobin. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema are conditions where airflow is obstructed or the alveoli are destroyed, impairing gas exchange.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
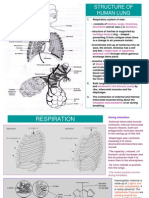
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
(Notes are color-coded to match my notebook so you can see order and stay with the order for organization)
EQ: What is the function of the Respiratory System?
To obtain O2 and eliminate CO2
EQ: What are the 2 conducting passages for breathing?
1. Upper Respiratory Tract
Nasal Cavity, Pharynx (Throat), Larynx (Voice Box)
2. Lower Respiratory Tract
Trachea (Windpipe), Bronchi, Lungs
These organs are lined with mucous membranes. In some
areas, the membranes have hairs that help filter the air while
other regions move mucus.
EQ: What is the pathway of air?
NostrilsLarynxTracheaBronchiBronchiolesAlveoli in the Lungs
**This is where you will make the chest vest from the “Breathe In, Breathe
Out” worksheet; look in the module as it is labeled to match this
EQ: What are the processes that involve respiration?
1. Ventilation (inhalation & exhalation)
2. Transport of gases (O2 & CO2) through diffusion (passive
transport) at higher to lower without using energy to
complete; exchanges gases between the alveoli and the
capillaries surrounding them inside the lungs (PICTURE
you need to draw goes here; it is in the module in my
notebook pics and it will also be in class on the board)
3. Cellular respiration
4. Perfusion (cardiovascular system pumps blood
throughout the lungs)
EQ: How is O2 transported in the blood?
**O2 is not very soluble in liquid so---
1. A small amount (1.5%) is carried in the plasma (liquid)
portion of blood
2. The other 98.5% is bound to the protein hemoglobin in
red blood cells
**Hemoglobin saturation at 100% means that every part of
the heme structure in the red blood cells is bound to O2;
normal healthy individuals should have a Hb (hemoglobin)
saturation rate of 95-99%
**When hemoglobin is NOT transporting O2, it tends to have
a bluish-purple tint to it creating the maroon color of
deoxygenated blood
EQ: How is CO2 transported in blood?
1. A small amount (5%) is carried in plasma as dissolved gas
2. Some CO2 (10%) binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells
forming carbaminohemoglobin (See pic from my
notebook in module that you will need to draw-we will
also do this in class on the board)
3. Most CO2 (85%) is transported as dissolved bicarbonate
ions (HCO3-) in the plasma
EQ: What is COPD & emphysema?
COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Inflammatory lung disease that blocks or obstructs the
airflow from the lungs; symptoms include difficulty breathing,
cough, mucus production, wheezing usually from smoking.
Can further lead to heart disease & lung cancer.
Emphysema: condition where the alveoli at the ends of the
bronchioles are destroyed by smoking; this means that CO2 &
O2 cannot be exchanged properly between capillaries &
alveoli for ventilation. Emphysema can also lead to COPD.
You might also like
- Case Study CopdDocument7 pagesCase Study CopdIrveen Joy RamirezNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Respiratory SysteDocument5 pagesFunctions of The Respiratory SysteMohd FirdausNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs Lesson PlanDocument13 pagesIrregular Verbs Lesson Planapi-311868026No ratings yet
- Augusta Issue 1145 - The Jail ReportDocument24 pagesAugusta Issue 1145 - The Jail ReportGreg RickabaughNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Blood: PlasmaDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Blood: Plasmaعبدالحكيم النهديNo ratings yet
- SPM Notes On Chapter RespirationDocument18 pagesSPM Notes On Chapter RespirationSyamila YusofNo ratings yet
- 05 RespiratoryDocument38 pages05 Respiratoryglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gaseslpc4944No ratings yet
- Topic 10 - Respiratory System Chapter 18Document6 pagesTopic 10 - Respiratory System Chapter 18api-388956899No ratings yet
- Respiratory System For PowelDocument41 pagesRespiratory System For PowelNikko Bondoc ManaloNo ratings yet
- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTADocument32 pagesOxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTArithikaNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Human Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiration: Human Respiratory SystemSheehan MathurNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Organization of The Respiratory System. Stages of Respiration. Regulation of RespirationDocument39 pagesStructural and Functional Organization of The Respiratory System. Stages of Respiration. Regulation of RespirationMohammed Faizuddin siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument4 pagesRespiration NotesJana AldourNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch17 Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument4 pages11 Biology Notes Ch17 Breathing and Exchange of GasesParimala deviNo ratings yet
- Breathing & Exchange of Gases NotesDocument7 pagesBreathing & Exchange of Gases NotesKankana Biswas100% (1)
- General Physiology II - Transport of Oxygen & Carbon - SIUST, College of DentistryDocument7 pagesGeneral Physiology II - Transport of Oxygen & Carbon - SIUST, College of DentistryNoor Al-Deen MaherNo ratings yet
- FON oxygenationPPTDocument58 pagesFON oxygenationPPTSaeed khanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Part 2Document23 pagesUnit 6 Part 2Ina NordsethNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 7Document18 pagesBiology Chapter 7edain84No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange and Alveoli 2Document18 pagesGas Exchange and Alveoli 213obasuyioNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument10 pagesNcert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesAyush DuttaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch17-pdf1Document9 pages11 Biology Notes ch17-pdf1LishaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 RespirationDocument26 pagesChapter 1 RespirationaqilajandinNo ratings yet
- Notes of Human Physiology Class 11Document9 pagesNotes of Human Physiology Class 11ADWAITH LALU100% (1)
- Mechanism of Respiration, Fermentation and ChemoheterothropDocument59 pagesMechanism of Respiration, Fermentation and Chemoheterothropd25No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRaluca MoldovanNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation 1 PDFDocument4 pagesOxygenation 1 PDFAbdullah Al NomanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument7 pagesChapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESprernatiwary508No ratings yet
- Reflection Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesReflection Respiratory SystemAin Sufiza0% (1)
- List Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseDocument5 pagesList Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseEmMa DHieyahNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPDocument8 pagesMaterial Downloaded From SUPERCOPfast-track for n2021No ratings yet
- Review of Respiratory PhysiologyDocument53 pagesReview of Respiratory PhysiologyMiftahul IfahNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument12 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessneh882016No ratings yet
- Basic Respiratory Mechanics (DR Arif)Document36 pagesBasic Respiratory Mechanics (DR Arif)Rizqi Luqmanul HakimNo ratings yet
- Mad 41869 CH 08 PG 141158Document18 pagesMad 41869 CH 08 PG 141158Carolina Lagos LiebigNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Document9 pagesLecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Resp System - PADocument27 pagesOverview of The Resp System - PAwajdjnbNo ratings yet
- Oxygen InsufficiencyDocument24 pagesOxygen InsufficiencyRatna VimalNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Gas Exchange (Science)Document7 pagesBreathing and Gas Exchange (Science)lanalorineperez89No ratings yet
- Hand Note - Session-1 2Document12 pagesHand Note - Session-1 2Abod AbodNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 2 RespirationJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Respiration: 1.1 Human Breathing MechanismDocument3 pagesRespiration: 1.1 Human Breathing MechanismHalizah RamthanNo ratings yet
- Airway CopdDocument16 pagesAirway Copdfaisal alharbiNo ratings yet
- Sistem PernafasanDocument87 pagesSistem Pernafasantaufik HidayatNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument51 pagesGaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsJesimie OriasNo ratings yet
- Respiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsDocument8 pagesRespiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- 000respiration in HumansDocument21 pages000respiration in HumanskunalNo ratings yet
- Respiration: The Exchange of GasesDocument20 pagesRespiration: The Exchange of GasesElyza Marie OcampoNo ratings yet
- First Step To ModDocument41 pagesFirst Step To Modcarlos ali issaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Physiology PDFDocument121 pagesRespiratory System Physiology PDFVizhiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Notes - KEYDocument3 pagesRespiratory System Notes - KEYjoy100% (1)
- Respiratory System 8Document32 pagesRespiratory System 8Naanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Critical Care Nurse Training Program R.A.I.S.E. Nepal ProjectDocument240 pagesRespiratory System: Critical Care Nurse Training Program R.A.I.S.E. Nepal ProjectTika RawatNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemCraigNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases: Respiratory OrgansDocument4 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gases: Respiratory OrgansSreeyansu RajNo ratings yet
- 9 RespirationDocument3 pages9 RespirationKavin ManimaranNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument4 pagesRespirationSiti NorhayatiNo ratings yet
- COPD Case ICUDocument19 pagesCOPD Case ICUKim Vizcarra100% (1)
- Biology Semester 2Document49 pagesBiology Semester 2MoonNo ratings yet
- Network Tools and Protocols Lab 2: Introduction To Iperf3Document17 pagesNetwork Tools and Protocols Lab 2: Introduction To Iperf3Fabio MenesesNo ratings yet
- Radiology PearlsDocument2 pagesRadiology PearlsSalman Rashid100% (2)
- English Paper 1 Mark Scheme: Cambridge Lower Secondary Sample Test For Use With Curriculum Published in September 2020Document11 pagesEnglish Paper 1 Mark Scheme: Cambridge Lower Secondary Sample Test For Use With Curriculum Published in September 2020ABEER RATHINo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7Th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7Th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFbrainykabassoullw100% (10)
- 4th - STD - MM - Kerala Reader Malayalam Vol 1Document79 pages4th - STD - MM - Kerala Reader Malayalam Vol 1Rajsekhar GNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Repertorization Tiwari Link PageDocument11 pagesEssentials of Repertorization Tiwari Link PageBibin TSNo ratings yet
- Would You Like Eddy Current, Video & Strip Chart in One Portable Case?Document2 pagesWould You Like Eddy Current, Video & Strip Chart in One Portable Case?Daniel Jimenez MerayoNo ratings yet
- ToobaKhawar 6733 VPL Lab Sat 12 3 All TasksDocument38 pagesToobaKhawar 6733 VPL Lab Sat 12 3 All TasksTooba KhawarNo ratings yet
- Steel Sections PDFDocument36 pagesSteel Sections PDFTonderai RusereNo ratings yet
- BronchiolitisDocument5 pagesBronchiolitisreshianeNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors - Strategic ManagementDocument16 pagesTata Motors - Strategic ManagementVaishakh MenonNo ratings yet
- TA35 & TA40 Articulated Dumptruck Maintenance Manual: Click Here For Table ofDocument488 pagesTA35 & TA40 Articulated Dumptruck Maintenance Manual: Click Here For Table ofKot878100% (2)
- 007: The Stealth Affair ManualDocument11 pages007: The Stealth Affair Manualcodigay769No ratings yet
- Internal Audit, Compliance& Ethics and Risk Management: Section 1) 1.1)Document6 pagesInternal Audit, Compliance& Ethics and Risk Management: Section 1) 1.1)Noora Al ShehhiNo ratings yet
- Thermo Scientific 49iq: Ozone Analyzer-UV PhotometricDocument2 pagesThermo Scientific 49iq: Ozone Analyzer-UV PhotometricAnish KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Character AnalysisDocument3 pagesCharacter AnalysisjefncomoraNo ratings yet
- Learning Spoken English in Half The TimeDocument86 pagesLearning Spoken English in Half The TimeΔέσποινα ΤζουτNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Flight of Projectile, Air Resistance Neglected: OverviewDocument7 pagesLesson 5 Flight of Projectile, Air Resistance Neglected: OverviewNadjer C. AdamNo ratings yet
- Zielinski AnArcheology For AnArchivesDocument10 pagesZielinski AnArcheology For AnArchivesPEDRO JOSENo ratings yet
- Tcs IntroDocument12 pagesTcs IntroRomi.Roy1820 MBANo ratings yet
- TODO Data Sheet PDFDocument70 pagesTODO Data Sheet PDFJake ZyrusNo ratings yet
- A. in What Way Is Khatri A Surplus Unit?Document5 pagesA. in What Way Is Khatri A Surplus Unit?Aakriti SanjelNo ratings yet
- Lorenzo JDocument2 pagesLorenzo Japi-528402595No ratings yet
- Reducing Motor Vehicle Crashes in B.C.Document260 pagesReducing Motor Vehicle Crashes in B.C.Jeff NagelNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 1st Quarter Poetry Writing WorkshopDocument3 pagesPerformance Task 1st Quarter Poetry Writing WorkshopNicole john ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 10th English Pta Model Question Papers 217163Document36 pagesNamma Kalvi 10th English Pta Model Question Papers 217163609001No ratings yet
- Logical Database Design ModelingDocument2 pagesLogical Database Design ModelingGio Agudo100% (1)
- 2022+ACCF+111+Class+test+2 Moderated+versionDocument8 pages2022+ACCF+111+Class+test+2 Moderated+versionLucas LuluNo ratings yet