Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Task #2 SIA-210 Perancangan Fondasi 1: Deep Foundation
Uploaded by
Rafi Yahdian AmnaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Task #2 SIA-210 Perancangan Fondasi 1: Deep Foundation
Uploaded by
Rafi Yahdian AmnaCopyright:
Available Formats
222018019
TASK #2
SIA-210 Perancangan Fondasi 1
Deep Foundation
Problem No 1
a) In which conditions that require pile foundation, please explain!
b) Piles can be divided into four categories: (a) steel piles, (b) concrete piles, (c)
wooden (timber) piles, and (d) composite piles. Please explain about these piles!
c) Piles also can be divided into three major categories depending on their lengths
and the mechanisms of load transfer to the soil. These categories are (a) point
bearing piles, (b) friction piles, and (c) compaction piles. Please explain about
these piles!
Problem No 2
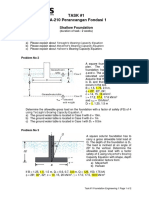
A Driven Closed-Ended Steel Pipe Pile
circular in cross section, is shown in figure,
Loose sand, , Calculate the following.
H1 c=0 a) The ultimate point load using Meyerhof’s
procedure.
b) The ultimate point load using Vesic’s
procedure. Take Irr = 50
H2 Loose sand, sat,
c=0 c) The ultimate frictional resistance, Qs
[take K= 1,4 and ‘ = 0,6 ’]
d) The Allowable load of the pile (use FS =
4)
Dense sand, sat, H1 = 2.95, 3.0, 3.05 m
c=0 H2 = 2.95, 3.0, 3.05 m
H3 = 14.5, 15, 15.5 m
H3
Loose Sand Parameters
sand = 15.5, 15.75, 16 kN/m3
sat sand = 18.5, 18.7, 19 kN/m3
= 30o, 31o, 32o
Dense Sand Parameters
sat sand = 19.0, 19.5, 19.7 kN/m3
= 35o, 36o, 37o
Task #2 Foundation Engineering 1 Page 1 of 4
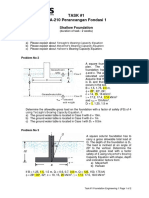
Problem No 3
A concrete pile 405 x 405 mm in cross
section is shown in figure.
H1 = 8.0, 8.5, 9.0 m
H2 = 13, 14, 15 m
Df Silty Clay Parameters
Silty Clay 1
H1 Silty Clay 1
silty clay = 17.6, 17.7, 17.8 kN/m3
cu = 27, 28, 29 kN/m2
Silty Clay 2
sat silty clay = 19.5, 19.6, 19.7 kN/m3
cu = 80, 85, 90 kN/m2
a) Calculate the point bearing
Silty Clay 2
capacity, Qp.
H2 b) Calculate the ultimate skin
resistance by using the method.
c) Calculate the ultimate skin
resistance by using the method.
d) Calculate the ultimate skin
resistance by using the method.
e) Calculate the allowable load of the
pile with all methods above – use
FS = 4.
Problem No 4
The plan of a group pile (friction pile) in sand is shown in figure. The piles are circular in
cross section and have an outside diameter of 460 mm. The center-to-center spacing pf
the piles (d) are 920 mm. Find the efficiency of the pile group using:
a) Simplified Equation.
b) Converse-Labarre Equation.
c) Fled Equation.
(1) (2) (3)
Task #2 Foundation Engineering 1 Page 2 of 4
Problem No 5
Find the ultimate bearing capacity of pile based on SPT data using Meyerhoff method if:
a) The pile is circular in cross section and have an outside diameter of”
300mm, 400mm, 500mm, 600mm
b) The pile is square in cross section:
350x350mm, 400x400mm, 450x450mm
Task #2 Foundation Engineering 1 Page 3 of 4
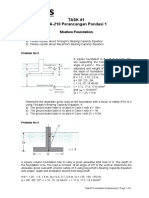
Problem No 6 Q
Figure shows a group pile in clay.
H1 = 2.75, 3.0, 3.25 m H1 Sand,
H2 = 2.75, 3.0, 3.25 m
H3 = 17, 18, 19 m
H4 = 4.5, 5.0, 5.5 m H2 Sand, sat
H5 = 2.75, 3.0, 3.25 m
d = 14, 15, 16 m
Q = 1300, 1350, 1400 kN
Sand Parameters
sand = 15.5, 15.75, 16 kN/m3
sat sand = 18.5, 18.7, 19 kN/m3 d Normally consolidated
H3 clay 1
Clay Parameters sat, eo, Cc
Normally Consolidated Clay 1
sat clay = 19.0, 19.1, 19.2 kN/m3
eo = 0.75, 0.8, 0.85
Cc = 0.75, 0.8, 0.85
Normally Consolidated Clay 2 Normally consolidated
sat clay = 18.0, 18.1, 18.2 kN/m3 clay 2
H4 sat, eo, Cc
eo = 0.8, 0.9, 1.0
Cc = 0.3, 0.32, 0.35
Normally Consolidated Clay 3 Normally consolidated
sat clay = 19.1, 19.3, 19.5 kN/m3 H5 clay 2
eo = 0.65, 0.7, 0.75 sat, eo, Cc
Cc = 0.25, 0.27, 0.29
a) Estimate the immediate settlement.
b) Estimate the consolidation settlement.
c) Estimate the total settlement of the foundation.
Task #2 Foundation Engineering 1 Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- Pile Design & Analysis of Single Piles. ExamplesDocument61 pagesPile Design & Analysis of Single Piles. ExamplesMohammed HussainNo ratings yet
- Lateral Pile Capacity Caculation Using Broms's Method (Free Head Type)Document4 pagesLateral Pile Capacity Caculation Using Broms's Method (Free Head Type)Sanjeewani Disna JayamaliNo ratings yet
- Standard CHB Sizes Are From Thicknesses of 100mm (4"), 150mm (6") and 200mm (8") X Height of 200mm (8") X Length of 400mm (16")Document7 pagesStandard CHB Sizes Are From Thicknesses of 100mm (4"), 150mm (6") and 200mm (8") X Height of 200mm (8") X Length of 400mm (16")kennysaweg100% (1)
- BITS-PILANI HYDERABAD SOIL MECHANICS EXAMDocument8 pagesBITS-PILANI HYDERABAD SOIL MECHANICS EXAMVinayaka RamNo ratings yet
- Mth603 Solved Mcqs Final Term by JunaidDocument41 pagesMth603 Solved Mcqs Final Term by Junaidnafeesa BIBiNo ratings yet
- A Short History of Nearly Everything by Bill Bryson BlinksDocument17 pagesA Short History of Nearly Everything by Bill Bryson BlinksKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes of Engineering MaterialsDocument7 pagesLecture Notes of Engineering Materialsahsan888100% (1)
- Task #1 SIA-210 Perancangan Fondasi 1: Shallow FoundationDocument2 pagesTask #1 SIA-210 Perancangan Fondasi 1: Shallow Foundationdaffa rizkyNo ratings yet
- Task #1 SIA-210 Perancangan Fondasi 1: Shallow FoundationDocument2 pagesTask #1 SIA-210 Perancangan Fondasi 1: Shallow Foundationdaffa rizkyNo ratings yet
- Task #1 SIA-210 Perancangan Fondasi 1: Shallow FoundationDocument2 pagesTask #1 SIA-210 Perancangan Fondasi 1: Shallow Foundationdaffa rizkyNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundation Design ProblemsDocument2 pagesShallow Foundation Design Problemsdaffa rizkyNo ratings yet
- Soal Tugas #1 SIA-210 Perancangan Pondasi 1Document2 pagesSoal Tugas #1 SIA-210 Perancangan Pondasi 1Indra Noer HamdhanNo ratings yet
- Machine Foundation Machine Design 2 Project MotorDocument6 pagesMachine Foundation Machine Design 2 Project Motorkentavila06No ratings yet
- Assignment #1-Soil Exploration and Stress DistributionDocument2 pagesAssignment #1-Soil Exploration and Stress Distributionanurag shakyaNo ratings yet
- -4618918اسئلة مدني فحص التخطيط مع الأجوبة من د. طارق الشامي & م. أحمد هنداويDocument35 pages-4618918اسئلة مدني فحص التخطيط مع الأجوبة من د. طارق الشامي & م. أحمد هنداويAboalmaail Alamin100% (1)
- Irjet V8i7747Document6 pagesIrjet V8i7747KhanNo ratings yet
- Refresher MODULE – Construction Estimate and Planning (Part 1Document1 pageRefresher MODULE – Construction Estimate and Planning (Part 1Mohammad Hussein Masiu BacaramanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Akhir Teknik Pondasi IiDocument3 pagesTugas Akhir Teknik Pondasi IiOkha JuliansyahNo ratings yet
- CWall Ex1Document5 pagesCWall Ex1Virginia gabyella saraunNo ratings yet
- Civil TipsDocument5 pagesCivil Tipssanojev83% (6)
- Outline of Foundation Cast-In-Place RC Pile - Pile Diameter:d 1.5m - Pile Length: L 40.0m - Unit Weight of RC Concrete: 24.5 KN/MDocument121 pagesOutline of Foundation Cast-In-Place RC Pile - Pile Diameter:d 1.5m - Pile Length: L 40.0m - Unit Weight of RC Concrete: 24.5 KN/MDevendrasinh PadhiyarNo ratings yet
- Take Off & BoqDocument86 pagesTake Off & BoqAfomiya ZelalemNo ratings yet
- Discussion Ch81Document7 pagesDiscussion Ch81Grace Enesio PerezNo ratings yet
- Bsc-Civil-Level 02 - Semester 02-2008-2009 - CE 2070 Engineering Cost EstimationDocument6 pagesBsc-Civil-Level 02 - Semester 02-2008-2009 - CE 2070 Engineering Cost EstimationHimalFernandoNo ratings yet
- Project: Footing Number: Engineer: Date:: Design 3-Pile Cap FootingDocument3 pagesProject: Footing Number: Engineer: Date:: Design 3-Pile Cap FootingMars TinNo ratings yet
- Ch.8-Examples 2Document8 pagesCh.8-Examples 2Mohammed AlmansorNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan RL - Ash, CJ Konya, Rencana, AktualDocument15 pagesPerhitungan RL - Ash, CJ Konya, Rencana, AktualTengku Deli100% (1)
- Design of Substructure 4 PileDocument328 pagesDesign of Substructure 4 PileisurupushNo ratings yet
- Transport - CSE30312 - CSE29357 - CBR Test (2022)Document6 pagesTransport - CSE30312 - CSE29357 - CBR Test (2022)Bitch CarrieNo ratings yet
- Soal - Soal Latihan Pondasi TiangDocument6 pagesSoal - Soal Latihan Pondasi TiangNashwa QausarNo ratings yet
- Pile Capacity Jhanjharpur-RobDocument1 pagePile Capacity Jhanjharpur-RobVenkat RaoNo ratings yet
- CE477 Tutorials-Piles - 2023Document2 pagesCE477 Tutorials-Piles - 2023daanaahishmaelsNo ratings yet
- End Semester Examination Advanced Foundation EngineeringDocument2 pagesEnd Semester Examination Advanced Foundation EngineeringSuman SahaNo ratings yet
- Report ND Struktur Ipl LNKDocument1,331 pagesReport ND Struktur Ipl LNKArif MatondangNo ratings yet
- Design of Rectangular Is0Lated Footings 1: F2: Footing MarkDocument2 pagesDesign of Rectangular Is0Lated Footings 1: F2: Footing MarkFarly VergelNo ratings yet
- Lateral Pile Capacity Caculation Using Broms's Method (Free Head Type)Document4 pagesLateral Pile Capacity Caculation Using Broms's Method (Free Head Type)Sanjeewani Disna JayamaliNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Bridge (8mx18m) Deck Slab DesignDocument16 pagesMathcad - Bridge (8mx18m) Deck Slab DesignSreyleap NhetNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Column Footing DesignDocument37 pagesReinforced Concrete Column Footing DesignTarunNo ratings yet
- Flexural Analysis of BeamsDocument48 pagesFlexural Analysis of BeamsHussain Al AmerNo ratings yet
- Gate Test - 11 (Civil) : R Ey FDocument6 pagesGate Test - 11 (Civil) : R Ey FnikhilNo ratings yet
- Assignment Submission Date: Exam Questions on Soil MechanicsDocument6 pagesAssignment Submission Date: Exam Questions on Soil MechanicsMuhammad YounisNo ratings yet
- CIE-352 Tutorial Sheet 1Document3 pagesCIE-352 Tutorial Sheet 1Perpetual hubbyNo ratings yet
- Community Well EstimateDocument3 pagesCommunity Well EstimateNimiteshNo ratings yet
- CE366 Homework 1 Solutions and Submission DetailsDocument4 pagesCE366 Homework 1 Solutions and Submission DetailsBahri AkhanNo ratings yet
- CE 3141 Fall 2020Document3 pagesCE 3141 Fall 2020Alamin NobinNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity Based On Plate Load Test NDJDocument12 pagesBearing Capacity Based On Plate Load Test NDJNazmi Dhiyauddin100% (1)
- Quantity Estimate for Slab Culvert ProjectDocument116 pagesQuantity Estimate for Slab Culvert ProjectRajendra K KarkiNo ratings yet
- 파일수평지지력 (Broms)Document4 pages파일수평지지력 (Broms)Sigit BintanNo ratings yet
- Heat of Hydration StressesDocument7 pagesHeat of Hydration StressesAnkur BarsainyaNo ratings yet
- Fair Face Concrete ARDocument12 pagesFair Face Concrete ARcecdesign09No ratings yet
- Model Question Paper (CBCS Scheme) Fifth Semester B.E. Degree Examination (CIVIL) Applied Geotechnical Engineering (15CV53Document2 pagesModel Question Paper (CBCS Scheme) Fifth Semester B.E. Degree Examination (CIVIL) Applied Geotechnical Engineering (15CV53Vijay KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Finalproject MergedDocument85 pagesFinalproject MergedMICHAELDANE SALANGUITNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper (CBCS Scheme)Document2 pagesModel Question Paper (CBCS Scheme)Veeresh PattarNo ratings yet
- A Study On PDC Drill Bits QualityDocument18 pagesA Study On PDC Drill Bits QualityAzri HamimNo ratings yet
- Drain Sump CalculationDocument3 pagesDrain Sump CalculationAgarry EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- qs-reviewer (2)Document11 pagesqs-reviewer (2)Gerald Vincent BorjaNo ratings yet
- CE 3207 - Geotech IIDocument2 pagesCE 3207 - Geotech IIPranto KhanNo ratings yet
- CE - 303 - GE - End Sem-1Document3 pagesCE - 303 - GE - End Sem-1Anudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Pile Capacity Calculation of Abutment M2 (AASHTO LRFD, 10.8)Document4 pagesPile Capacity Calculation of Abutment M2 (AASHTO LRFD, 10.8)Franklin MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering ECADocument24 pagesSoil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering ECADebasis MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Design Principles of Metal-Cutting Machine ToolsFrom EverandDesign Principles of Metal-Cutting Machine ToolsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Co2 - Co Laser: Physics 111B: Advanced Experimentation Laboratory University of California, BerkeleyDocument16 pagesCo2 - Co Laser: Physics 111B: Advanced Experimentation Laboratory University of California, Berkeleysara3elena3manolacheNo ratings yet
- Roald K. Wangsness - Electromagnetic Fields-Wiley (1986)Document598 pagesRoald K. Wangsness - Electromagnetic Fields-Wiley (1986)jujujaga86No ratings yet
- Destructive Testing and Non Destructive TestingDocument71 pagesDestructive Testing and Non Destructive TestingJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Getto multiplo predisposto per moduli induttiviDocument2 pagesGetto multiplo predisposto per moduli induttiviAbdulaziz AlrawiNo ratings yet
- Bostrig SC UnarmoredDocument3 pagesBostrig SC UnarmoredEnrique MartínezNo ratings yet
- IT Viktor SchaubergerDocument22 pagesIT Viktor SchaubergerairmikserNo ratings yet
- Disintegration TesterDocument3 pagesDisintegration TesterFarhatNo ratings yet
- Hydrogel RheologyDocument24 pagesHydrogel RheologyAna Clara SoaresNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument97 pagesMachine DesignGourav Kapoor100% (4)
- Full Download Futures Options and Swaps 5th Edition Kolb Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Futures Options and Swaps 5th Edition Kolb Solutions Manualfract.hiation.7wtul100% (35)
- EXERCISE 6 + SolutionsDocument6 pagesEXERCISE 6 + SolutionsEmmanuel WadiraNo ratings yet
- Med - 00000619 - 1193753698 - Quartz Crystal Theory 2007Document6 pagesMed - 00000619 - 1193753698 - Quartz Crystal Theory 2007haha2012No ratings yet
- Module 2Document76 pagesModule 2Raj KamalNo ratings yet
- Common Wire Splices and JointsDocument15 pagesCommon Wire Splices and JointsNorman PolilinNo ratings yet
- Ijser: The Lebesgue Integral and Measure TheoryDocument2 pagesIjser: The Lebesgue Integral and Measure TheoryMRNo ratings yet
- Check for Punching Shear Capacity of Interior Column SlabDocument2 pagesCheck for Punching Shear Capacity of Interior Column SlabFeroz Khan PatthanNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1415 Standard Test Method For Rubber Property - International Hardness PDFDocument5 pagesASTM D1415 Standard Test Method For Rubber Property - International Hardness PDFManikanda Saravanan100% (1)
- Week 10 - Differential EntropyDocument22 pagesWeek 10 - Differential EntropyLOmesh SaHuNo ratings yet
- M.E CAD - CAM SyllabusDocument10 pagesM.E CAD - CAM SyllabusHariharan HDNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nuclear, Particle, and Astrophysics - Module PH0016Document4 pagesIntroduction To Nuclear, Particle, and Astrophysics - Module PH0016johnsonchelsea123No ratings yet
- Met Glossary 1963 PDFDocument327 pagesMet Glossary 1963 PDFjavier albaNo ratings yet
- Gas Liquid Separator DesignDocument3 pagesGas Liquid Separator DesignSoheil MoradiNo ratings yet
- Expt.6 BEEE101P TheveninsTinkerCADDocument6 pagesExpt.6 BEEE101P TheveninsTinkerCADBaba YagaNo ratings yet
- Free 300 Ebook CombinatoricsDocument48 pagesFree 300 Ebook CombinatoricsAhmad ArifNo ratings yet
- Dupont Oasis 120TWT561 Datasheet 1Document2 pagesDupont Oasis 120TWT561 Datasheet 1kamlesh vaishnavNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle-Car Side Impact Simulation:, IncludingDocument10 pagesMotorcycle-Car Side Impact Simulation:, IncludingPromit ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledTomas CanalesNo ratings yet