Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hbo Ch15 Summary
Uploaded by
Jamie Rose Aragones0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views6 pagesThis document summarizes the key elements of organizational structure and common organizational designs. It identifies six elements that make up an organization's structure: work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command, span of control, centralization/decentralization, and formalization. It then describes several common organizational designs: simple structure, bureaucracy, matrix structure, virtual organization, boundaryless organization, and leaner organization. The document explains the characteristics of these different designs and discusses when each may be most appropriate based on an organization's strategies, environment, technology and size.
Original Description:
Original Title
Hbo Ch15 Summary (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the key elements of organizational structure and common organizational designs. It identifies six elements that make up an organization's structure: work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command, span of control, centralization/decentralization, and formalization. It then describes several common organizational designs: simple structure, bureaucracy, matrix structure, virtual organization, boundaryless organization, and leaner organization. The document explains the characteristics of these different designs and discusses when each may be most appropriate based on an organization's strategies, environment, technology and size.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views6 pagesHbo Ch15 Summary
Uploaded by
Jamie Rose AragonesThis document summarizes the key elements of organizational structure and common organizational designs. It identifies six elements that make up an organization's structure: work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command, span of control, centralization/decentralization, and formalization. It then describes several common organizational designs: simple structure, bureaucracy, matrix structure, virtual organization, boundaryless organization, and leaner organization. The document explains the characteristics of these different designs and discusses when each may be most appropriate based on an organization's strategies, environment, technology and size.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Chapter # 15: Foundation of Organization Structure
1. Identify the six elements of an organization’s structure
Exam Q: List six elements of organizational structure and explain three of them?(Two Times)
Organizational structure is defined as how job tasks are formally divided, grouped, and coordinated.
The key elements of organizational structure include:
I. Work specialization
Work specialization refers to Division of Work.
Work Specialization is the degree to which organizational activities are subdivided into separate
jobs (Individual specializes in doing part of an activity rather than the entire job).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Work Specialization
Work Specialization makes efficient use of employee skills.
Work Specialization increases employee skills through repetition and specialized training.
Work Specialization increases efficiency and productivity of the employee.
Work Specialization allows use of specialized equipment.
Overspecialization can result in boredom, fatigue, stress, poor quality, increased absenteeism, and
higher turnover.
II. Departmentalization
Departmentalization is defined as how the jobs are grouped together and common tasks can be
coordinated.
When jobs are grouped, departments are formed.
The jobs can be grouped and organized in the following categories:
i. Function
ii. Product
iii. Geography
iv. Process
v. Customer
III. Chain of command
Chain of command is an unbroken line of authority that extends from Top to Lowest level and
clarifies who reports to whom.
To understand the chain of command, it is necessary to understand three other following important
concepts:
a) Authority
Authority is the rights inherent (inbuilt) in a managerial position to tell people what to do
and to expect them to do it.
b) Responsibility
Responsibility is the obligation or expectation to perform.
c) Unity of Command
Unity of command is the concept that a person should have one boss and should report
only to that person.
IV. Span of control
Span of control is defined as the number of subordinates that a manager can effectively and
efficiently directs towards organizational goals.
Wider spans are more efficient in terms of cost because fewer managers needed but they can reduce
the efficiency and performance of the employee.
Narrow spans can allow manager to maintain the control over the employees but they are
expensive, make vertical communication in the organization and are more complex.
V. Centralization and Decentralization
Exam Q: Contrast Centralization and decentralization of organizational operations, which one is
better in your view. Explain.
Centralization is the degree to which decision making is concentrated at a single point in the
organization.
Decentralization is the degree to which decision making is spread throughout the organization.
The difference between centralization and decentralization is one of the hot topics these days.
Some people think that centralization is better while others are in favor of decentralization.
In early times, people used to run their organization in a centralized manner, but now the scenario
has been changed completely due to rise in extreme competition where quick decision making is
required and therefore many organizations opted for decentralization.
However, centralization still exists in some of the organizations.
Coming to the point, no organization is completely centralized or decentralized; they are
centralized or decentralized only up to the extent of the delegation of authority.
VI. Formalization.
Formalization is the degree to which jobs within the organization are standardized.
When there is high formalization, workers have very little control over their work and they have to
follow rules and procedures.
When there is low formalization, workers have more control over their work.
2. Common Organizational Designs
Exam Q: List various types of organizational structures and explain the characteristics of virtual
organization?( Three Times)
Following are the most used organizational designs
I. The Simple Structure
The first and most basic structure is the simple structure.
Simple structure has Low degree of departmentalization.
Simple Structure has wide spans of control
Simple Structure has centralized decision making
Simple Structure has low formalization in job design
Simple structure is best suited for small business
Advantages
Simple
Flexible
Inexpensive
Accountability is clear
II. The Bureaucracy
Bureaucracy is a system of organization.
Bureaucracy is an organization structure in which highly routine operating tasks achieved through
work specialization and Rules (Formalized).
Bureaucracy has narrow Span of control.
Bureaucracy has Centralized Authority and decision making is through chain of command.
In bureaucracy, Tasks are grouped into Functional departments
Advantages:
i. Standardized activities are performed effectively.
ii. Economy of Scale is achieved by putting specialist in department.
iii. Minimum duplication of equipment and personnel.
iv. Same language in each Department.
v. Less talent thus less costly Middle and Low management
vi. Rules replace Discretion
vii. Centralized Decision making due to Formalization
Disadvantages:
i. Specialization creates sub-unit conflicts and functional goals may override organization goals.
ii. Concerned with following rules. There is no room for modification when a case does not fit the
rules.
iii. It is efficient only in case of familiar problems with programmed decisions.
The Matrix Structure
The Matrix Structure is a structure that creates dual lines of authority and combines functional and
product departmentalization.
Advantages:
It gains the advantages of functional and product departmentalization while avoiding their
weaknesses
It puts specialists together thus minimizes their number and allows sharing of resources
It facilitates coordination for complex and interdepartmental activities.
Problems:
Project Delay due to difficulty in coordinating the tasks of specialists on time and within budget.
It breaks the unity of command principle
It creates confusion and conflicts among managers
III. The Virtual Organization
Exam Q: What are the characteristics of virtual Organization? Explain
Virtual organizations are developing as acceptable organizational structures.
This structure offers a small core organization that outsources many of its major functions to
competent suppliers.
Virtual organizations are highly centralized with virtually no departmentalization to provide
maximum flexibility, focusing on what the organization does best.
This type of organization reduces control over some of the key parts of the business.
It is also known as modular or network organization as shown in the following figure.
Characteristics of Virtual Organizations
The virtual organizations have the following characteristics:
i. Flat organization
ii. Dynamic
iii. Informal communication
iv. Power flexibility
v. Multi-disciplinary (virtual) teams
vi. Vague organizational boundaries
vii. Goal orientation
viii. Customer orientation
ix. Home-work
x. Absence of apparent structure
xi. Sharing of information
xii. Staffed by knowledge workers
Advantages:
Flexibility
Disadvantages:
Constant state of flux & Reorganization
Roles , Goals & responsibilities are not very clear
Cultural alignment and shared goals can be lost
Information and knowledge sharing is difficult
Leadership presence is valuable
IV. The Boundary-less Organization
It is an organization that seeks to eliminate the chain of command, has limitless span of control and
replaces departments with empowered teams.
Replace departments with cross-functional teams & organize activities around process.
It organizes more in what is called T-form concepts in order to eliminate vertical and horizontal
boundaries.
It tries to break down external barriers to customers and suppliers through their structure and style
of communication.
V. The Leaner Organization: Downsizing
The goal of this organizational form is to improve agility by creating a lean, focused, and flexible
organization.
Downsizing is a systematic effort to make an organization leaner by closing locations, reducing
staff, or selling off business units that don’t add value.
Advantages:
Cost reduction
Return to Core competencies after costly acquisitions
Disadvantages:
Employee commitment is low
Stress results in absence, Low creativity, Low concentration on job
High Turn - over
3. Two Extreme Models of Organizational Design
4. Why do Structure Differ?
The following are the major causes or determinants of an organization’s structure
I. Strategies
Following strategies are used in organizational structure:
A. Innovation Strategy
It is a strategy that emphasizes the introduction of major new products & services.
Innovative Organizations use competitive pay to attract talent.
Innovative Organizations motivate employees to take risk.
Innovative Organizations have well developed communication channels.
Innovative Organizations have clear channel of authority.
This strategy is used in Organic Model has a loose structure; low specialization, low
formalization and decentralized decision making.
B. Cost Minimization Strategy
It is a strategy that emphasizes the tight cost controls, avoidance of unnecessary
innovations & marketing expenses and price cutting.
This strategy is used in Mechanistic Model has tight control costs; extensive work
specialization, high formalization and high centralization in decision making.
C. Imitation
It is a strategy that seeks to move into new products or new markets only after their
viability (feasibility) has already been proven. This strategy:
Minimizes Risk
Maximizes opportunity for profit
Move into new product only after it is proved
This strategy is used in both organic and Mechanistic Models has Mix of loose with
tight properties; tight controls over current activities and looser controls for new
undertakings.
II. Organization Size
As organizations grow, they become more mechanistic, more specialized, with more rules and
regulations
III. Technology
How an organization transfers its inputs into outputs.
The more routine the activities, the more mechanistic the structure with greater formalization
Custom activities need an organic structure.
Cars : Assembly line
College : Lecture, case studies Exercises
IV. Environment
An organization’s environment includes institutions or forces outside the organization that
potentially affect the organization’s performance.
The more dynamic the environment, the more organic the structure will need to be to facilitate
quick decisions and fast turnaround because dynamic environment creates departmental
uncertainty.
Any organization’s environment has three dimensions:
a) Capacity
Capacity refers to the degree to which the environment can support growth.
Rich and growing environments generate excess resources.
b) Volatility
Volatility describes the degree of instability in the environment.
A dynamic environment with a high degree of unpredictable change makes it difficult
for management to make accurate predictions.
c) Complexity
Finally, complexity is the degree of heterogeneity and concentration among
environmental elements.
Simple environments—like the tobacco industry—are homogeneous and concentrated.
Environments characterized by heterogeneity and dispersion—like the broadband
industry—are complex and diverse, with numerous competitors.
You might also like
- Chap 15 Foundation of Organization StructureDocument16 pagesChap 15 Foundation of Organization StructureMuhammad Hashim MemonNo ratings yet
- BMGT200 - Final Examination - Revision Sheet - Fall 2023 2024Document14 pagesBMGT200 - Final Examination - Revision Sheet - Fall 2023 20249dnnz82fy4No ratings yet
- Rangkuman OB Chapter 15 by MSS FEUIDocument7 pagesRangkuman OB Chapter 15 by MSS FEUICahyaning SatykaNo ratings yet
- Dubrin Review 08Document11 pagesDubrin Review 08Muhammad Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structures Types ComparisonDocument5 pagesOrganizational Structures Types ComparisonMuhammad Hashim Memon100% (1)
- Organization Structure Chapter 7 SummaryDocument5 pagesOrganization Structure Chapter 7 SummaryBoyvic TyNo ratings yet
- OTB - Lecture Notes 5 - Organizational Structure - NewDocument9 pagesOTB - Lecture Notes 5 - Organizational Structure - Newadan awaleNo ratings yet
- Project Organisation StructureDocument13 pagesProject Organisation StructureHarshitaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Organizational StructureDocument7 pagesFoundations of Organizational StructureSajakul SornNo ratings yet
- 8 OrganigingDocument4 pages8 Organigingtanjimalomturjo1No ratings yet
- Organizing Technical Activities StructuresDocument5 pagesOrganizing Technical Activities StructuresJohn Philip Molina NuñezNo ratings yet
- HBO - Organizational StructureDocument35 pagesHBO - Organizational StructureDewdrop Mae RafananNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Organization Structure - Anna Beatriz OndaDocument25 pagesFoundations of Organization Structure - Anna Beatriz OndapgvsantosNo ratings yet
- OB Group AssignmentDocument32 pagesOB Group Assignmentefrata AlemNo ratings yet
- Organizing and AuthorityDocument61 pagesOrganizing and AuthorityJannatul JerinNo ratings yet
- Organizational StructuresDocument5 pagesOrganizational StructuresJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document4 pagesChapter 8meryem berradaNo ratings yet
- From Top DownDocument13 pagesFrom Top DownZainab AamirNo ratings yet
- Six Elements of Organizational StructureDocument4 pagesSix Elements of Organizational StructureMuhammad Hashim MemonNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure TypesDocument12 pagesOrganizational Structure TypesSiddhartha Singhal057No ratings yet
- BM Midterm Chapter 7Document10 pagesBM Midterm Chapter 7James MontesNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structures Types ExplainedDocument34 pagesOrganizational Structures Types ExplainedUsman NawazNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six The Organizing Function-1Document41 pagesChapter Six The Organizing Function-1SAMMYNo ratings yet
- PRNT. CH 6 Organization StructureDocument11 pagesPRNT. CH 6 Organization StructureAbdullah Al Mamun TusherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Basic Organizational DesignDocument26 pagesChapter 10 - Basic Organizational DesignSaira Khan100% (1)
- Lec 05Document9 pagesLec 05Drama LlamaNo ratings yet
- Why Is Organizational Structure ImportantDocument5 pagesWhy Is Organizational Structure ImportantSheeba ThomasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 OrganizingDocument28 pagesChapter 5 OrganizingDagm alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Organizing Technical ActivitiesDocument5 pagesOrganizing Technical ActivitiesMoises BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Organisingnotes 25052Document9 pagesOrganisingnotes 25052Aditi GNo ratings yet
- OC Organizational StructuresDocument4 pagesOC Organizational Structuresha90665No ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document6 pagesLesson 4JOHN IRVIN TAERNo ratings yet
- MBA 612 OB Ch.8Document48 pagesMBA 612 OB Ch.8Asegid H/meskelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Basic Organizational Design AnsDocument9 pagesChapter 10 Basic Organizational Design AnsSamuel AbebawNo ratings yet
- Functional Organizational DesignDocument21 pagesFunctional Organizational DesignUdara SeneviratneNo ratings yet
- Organising-functions-structuresDocument4 pagesOrganising-functions-structuresMayank DuhalniNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure Design GuideDocument40 pagesOrganizational Structure Design GuidePawan KinnalNo ratings yet
- Management 9th Edition Daft Solutions ManualDocument20 pagesManagement 9th Edition Daft Solutions Manualenstatequatrain1jahl100% (29)
- Chapter 5 OrganisingDocument6 pagesChapter 5 OrganisingTiya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Understanding Management 9th Edition Daft Solutions ManualDocument23 pagesUnderstanding Management 9th Edition Daft Solutions Manualradleydiepwxq100% (29)
- Basic Organizational DesignDocument6 pagesBasic Organizational DesignFathimath Zeen MaahirNo ratings yet
- Departmentation 2020 1Document16 pagesDepartmentation 2020 1malcomNo ratings yet
- Bab 15 Foundations of Organization StructureDocument14 pagesBab 15 Foundations of Organization StructureNiken NikenNo ratings yet
- BBA 102 - Class PresentationDocument21 pagesBBA 102 - Class PresentationAnonymous djLVrBtiDNo ratings yet
- Em-Tun AnanDocument3 pagesEm-Tun AnanjazelriarNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Drawbacks of Functional Organizational StructureDocument7 pagesBenefits and Drawbacks of Functional Organizational StructureselfiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Foundation of Organization StructureDocument22 pagesChapter 15 - Foundation of Organization StructuresamiyaNo ratings yet
- Org Man 2nd Quarter Week 1 ModuleDocument9 pagesOrg Man 2nd Quarter Week 1 ModuleMicah Shane B. SamsonNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument41 pagesOrganizingShella DumdumanNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Managerial Roles - 19 August 2021Document52 pagesClass 5 - Managerial Roles - 19 August 2021Priyanka AggarwalNo ratings yet
- HSMC 501: Organization in Industrial Management Lec 3, 4 & 5Document42 pagesHSMC 501: Organization in Industrial Management Lec 3, 4 & 5Dr. Arunava MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 12: Structural ImplementationDocument20 pagesUnit 12: Structural Implementationbhavin_civilNo ratings yet
- Management Asia Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesManagement Asia Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFirisdavid3n8lg100% (9)
- Solution Manual For Understanding Management 9th EditionDocument23 pagesSolution Manual For Understanding Management 9th EditionDanielKimqnob100% (42)
- Chapter 4Document9 pagesChapter 4Jim ThiveosNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Company StructureDocument4 pagesUnit 3 Company StructureNhư Ý Nguyễn LêNo ratings yet
- Management Asia Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions ManualDocument23 pagesManagement Asia Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manualannerobinsonebnxfojmza100% (33)
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsFrom EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsNo ratings yet
- Mobilizing Minds (Review and Analysis of Bryan and Joyce's Book)From EverandMobilizing Minds (Review and Analysis of Bryan and Joyce's Book)No ratings yet
- Hbo Ch15 SummaryDocument6 pagesHbo Ch15 SummaryJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- CH16 Hbo ReportDocument42 pagesCH16 Hbo ReportJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Power and Politics: Bsa-3A Michaela A. Revilleza John Carlo M. SequenaDocument28 pagesPower and Politics: Bsa-3A Michaela A. Revilleza John Carlo M. SequenaJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- AFAR Notes by Dr. Ferrer PDFDocument21 pagesAFAR Notes by Dr. Ferrer PDFjexNo ratings yet
- Hbo Ch15 SummaryDocument6 pagesHbo Ch15 SummaryJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Bar Review Corp Law Part IiDocument78 pagesBar Review Corp Law Part IiJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - HR Policies & Practices Selection PracticesDocument4 pagesChapter 17 - HR Policies & Practices Selection PracticesJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Leadership: Butial, Ferlyn T. Sarmiento, Sherry AnnDocument32 pagesLeadership: Butial, Ferlyn T. Sarmiento, Sherry AnnJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Bar Review Corp Law Part IDocument65 pagesBar Review Corp Law Part IAr CeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - HR Policies & Practices Selection PracticesDocument4 pagesChapter 17 - HR Policies & Practices Selection PracticesJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - 2013 EdDocument16 pagesChapter 9 - 2013 EdJean PaladaNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics MidtermDocument12 pagesBusiness Ethics MidtermJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Bar Review Corp Law Part IVDocument93 pagesBar Review Corp Law Part IVJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- CORPORATION MERGER LAWDocument80 pagesCORPORATION MERGER LAWJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Bar Review Corp Law Part IVDocument93 pagesBar Review Corp Law Part IVJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH Sarmiento&MacatangcopDocument17 pagesRESEARCH Sarmiento&MacatangcopJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH Sarmiento&MacatangcopDocument17 pagesRESEARCH Sarmiento&MacatangcopJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Business EthicsDocument8 pagesBusiness EthicsJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics MidtermDocument12 pagesBusiness Ethics MidtermJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Board Directors Removal GuideDocument34 pagesBoard Directors Removal GuideJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Attendance Sheet Gec 103 Contemporary WorldDocument1 pageAttendance Sheet Gec 103 Contemporary WorldJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- The Courts in The Administration of Justice."Document13 pagesThe Courts in The Administration of Justice."Jamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Business EthicsDocument8 pagesBusiness EthicsJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH Sarmiento&MacatangcopDocument17 pagesRESEARCH Sarmiento&MacatangcopJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Company Name "B-Mikki Grocery" MissionDocument13 pagesCompany Name "B-Mikki Grocery" MissionJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Student Number 1Document1 pageStudent Number 1Jamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- QOUTATION With Pic ContemporaryDocument1 pageQOUTATION With Pic ContemporaryJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Meeting Aug 15 ContemporaryDocument1 pageMeeting Aug 15 ContemporaryJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- GEC 103 Contemporary World: - Joseph StiglityDocument1 pageGEC 103 Contemporary World: - Joseph StiglityJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document21 pagesSet 1Soumava BasuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Risk Management Through Insurance: Certificate in Insurance ConceptsDocument23 pagesChapter-3 Risk Management Through Insurance: Certificate in Insurance ConceptsPraveen60% (5)
- Personal Entrepreneurial Competencies Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesDocument18 pagesPersonal Entrepreneurial Competencies Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesRosille VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Business Process Reengineering FinalDocument29 pagesBusiness Process Reengineering FinalMarvi Ashok100% (1)
- Basics of Management ConsultingDocument9 pagesBasics of Management ConsultingTarun AjwaniNo ratings yet
- HR-Easy automates HR tasks for improved decision makingDocument9 pagesHR-Easy automates HR tasks for improved decision makingJohn MarvelleNo ratings yet
- Hbo Chapter 1Document8 pagesHbo Chapter 1dar •No ratings yet
- Project Management & Finance Course OutlineDocument17 pagesProject Management & Finance Course OutlineHaaji Commando100% (2)
- Information Technology in Supply Chain Management: 2010 Slide 1 of 23 Role of IT in SCMDocument23 pagesInformation Technology in Supply Chain Management: 2010 Slide 1 of 23 Role of IT in SCMamitabhNo ratings yet
- Acmegrade Project Word FileDocument5 pagesAcmegrade Project Word Filenptelcare80No ratings yet
- 10 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument25 pages10 - Chapter 2 PDFJaydev JoshiNo ratings yet
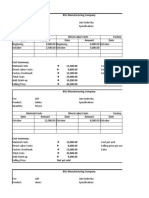
- Job Order Cost SheetDocument4 pagesJob Order Cost SheetJasmine ActaNo ratings yet
- Toyota Thailand Consulting Case StudyDocument4 pagesToyota Thailand Consulting Case StudySiwaporn WanveeratikulNo ratings yet
- S 296001-1 A3 APQP Status Report enDocument2 pagesS 296001-1 A3 APQP Status Report enfdsa01No ratings yet
- Software Engineering: LAB 11 (W13:5/Oct/) Cover Case Study On "Software Project Management Plan"Document31 pagesSoftware Engineering: LAB 11 (W13:5/Oct/) Cover Case Study On "Software Project Management Plan"Suleman MirzaNo ratings yet
- Operation Management Handout 1Document2 pagesOperation Management Handout 1Victoria ManalaysayNo ratings yet
- Importance of Quality in BusinessDocument3 pagesImportance of Quality in BusinessJennifer Andrea Pardo100% (1)
- Module 1 Mis PDFDocument48 pagesModule 1 Mis PDFTinku JoyNo ratings yet
- CSS Accounting & Auditing Topic-wise Past Papers: Marginal & Absorption CostingDocument3 pagesCSS Accounting & Auditing Topic-wise Past Papers: Marginal & Absorption CostingMasood Ahmad Aadam0% (1)
- Group Assignment 1Document5 pagesGroup Assignment 1Tari WulandariNo ratings yet
- O-Level Business Studies - 7116 Syllabus - 2013 - 2017Document10 pagesO-Level Business Studies - 7116 Syllabus - 2013 - 2017mrsundeepsNo ratings yet
- Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS) : Alicia TuovilaDocument16 pagesGenerally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS) : Alicia TuovilaDaveIversonSorianoNo ratings yet
- CFL's Financial Performance and Corporate Governance AnalysisDocument11 pagesCFL's Financial Performance and Corporate Governance AnalysisHugsNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Chapter 3 Cost ControlDocument45 pagesLevel 2 Chapter 3 Cost ControlPrakashSundaramNo ratings yet
- ELG 400 Comple SMDocument230 pagesELG 400 Comple SMVirginia Department of Emergency Management100% (2)
- SyllabusDocument94 pagesSyllabusBasit 36No ratings yet
- 06 Inbound ProcessDocument52 pages06 Inbound Processfarhanusm9712100% (1)
- Auditing, Assurance, and Internal Control: IT Auditing, Hall, 3eDocument48 pagesAuditing, Assurance, and Internal Control: IT Auditing, Hall, 3eGladysNo ratings yet
- Sombrero Case AnalysisDocument2 pagesSombrero Case AnalysisManaswini SharmaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Hoshin KanriDocument10 pagesGroup 2 Hoshin KanriShaikh Ahsan Ali Shabbir HusainNo ratings yet