Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dna Protein: Following The Instructions in The Genetic Code
Uploaded by
Nurisma Devi Wahyuningsih0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views9 pagesThe document summarizes how DNA is used as a set of instructions to create proteins through transcription and translation. DNA contains the genetic code and is copied into mRNA via transcription. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and interacts with ribosomes and tRNAs to translate the mRNA code into proteins according to the DNA instructions.
Original Description:
DNA protein
Original Title
Handout Dna Protein
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes how DNA is used as a set of instructions to create proteins through transcription and translation. DNA contains the genetic code and is copied into mRNA via transcription. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and interacts with ribosomes and tRNAs to translate the mRNA code into proteins according to the DNA instructions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views9 pagesDna Protein: Following The Instructions in The Genetic Code
Uploaded by
Nurisma Devi WahyuningsihThe document summarizes how DNA is used as a set of instructions to create proteins through transcription and translation. DNA contains the genetic code and is copied into mRNA via transcription. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and interacts with ribosomes and tRNAs to translate the mRNA code into proteins according to the DNA instructions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
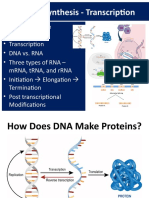
DNA → PROTEIN:
Following the Instructions in the
Genetic Code
DNA → PROTEIN
• Whenever your cells divide to make new cells,
they must copy your DNA through DNA
replication
• The working cells of your body are constantly
reading the DNA code and using the instructions
to build molecules, such as proteins, that they
need to do their jobs for the body.
• Proteins are constructed by the combined efforts
of two processes: transcription and translation
• DNA contains your genetic code
• DNA contains the nitrogenous base thymine,
while RNA contains uracil. (Both contain
adenine, guanine, and cytosine.)
• DNA molecules are double-stranded, while
RNA molecules are singlestranded.
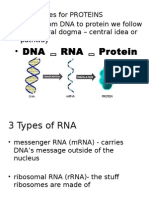
RNA
• Several types of RNA molecules are built from
the information in DNA. Each type of RNA has
a different function in cells:
• mRNA carries the code for protein structure
from the DNA to ribosomes where it can be
used to produce proteins.
• tRNA decodes the message in mRNA by
matching amino acids to the mRNA code.
• rRNA is part of the structure of the ribosome.
DNA
• DNA contains the genetic code of the cell, a
code that controls the cell’s structure and
function.
• A gene is a single blueprint for a worker
molecule. If you think of your entire genome
as a big file cabinet, each drawer would be a
chromosome, and the files within the drawers
would be the genes.
Transkripsi: DNA → RNA
• RNA polimerase berikatan dgn promoter,
membuka rantai double helix DNA, 1 rantai
digunakan sebagai pola u/membentuk RNA
• mRNA meng-copy informasi
• RNA memanjang
• RNA polimerase mencapai sekuens ujung
Translasi: RNA → protein
• mRNA is then shipped out of the nucleus and
into the cytoplasm
• ribosomes and tRNAs use the code in the
mRNA to build the protein.
You might also like
- Protein Synthesis: Class Notes NotesDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis: Class Notes NotesDale HardingNo ratings yet
- DNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisDocument69 pagesDNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisRomelyn Grace BorbeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 7Document33 pagesLecture Notes 7depictingmeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 DNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien Synthesis 2017Document32 pagesChapter 11 DNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien Synthesis 2017dianeNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisDocument32 pagesDNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisA. Nurul Virninda YusufNo ratings yet
- Expression of DNA Through RNADocument13 pagesExpression of DNA Through RNAjmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: - The Formation of New Proteins Using The Code Carried On DNADocument20 pagesProtein Synthesis: - The Formation of New Proteins Using The Code Carried On DNABien Emilio B NavarroNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Genetic Materials DNA ReplicationDocument44 pagesUnderstanding The Genetic Materials DNA Replicationnoeme babiaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument43 pagesTranscription and TranslationSaqlain Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument56 pagesDna and Rna StructureZeah RealNo ratings yet
- DNA STRUCTURE-Replication, Transcription, and TranslationDocument24 pagesDNA STRUCTURE-Replication, Transcription, and TranslationAj FloresNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument23 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyEros James Jamero100% (1)
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument41 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biologyanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument53 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDeborah Chloe EnriquezNo ratings yet
- DNADocument64 pagesDNAsapphireriego01No ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument10 pagesDNA ReplicationKurt CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)Document18 pagesRibonucleic Acid (RNA)Serap BayramNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio ReviewerFaye Lianne MaderoNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesProtein SynthesisAnthony MoloneyNo ratings yet
- H.-Nucleic AcidsDocument69 pagesH.-Nucleic AcidsBrianna Pauline BantugNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologyYasin Putra Esbeye100% (2)
- TransciptionDocument23 pagesTransciptionJaidenNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument50 pagesCentral DogmaIvilyn ManguladNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BiologyDocument40 pagesChapter 3 BiologyAnam FNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologySubash SubaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologySubash SubaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologySowmya PNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologypathinfoNo ratings yet
- 3 5 1 Heredity and Inheritance (DNA RNA)Document17 pages3 5 1 Heredity and Inheritance (DNA RNA)6ix9ine SoulNo ratings yet
- Rna Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesRna Protein Synthesisapi-545652980No ratings yet
- Protien SynthesisDocument20 pagesProtien Synthesisapi-277471896No ratings yet
- Unit 7 DNA RNA Protein SynthesisDocument24 pagesUnit 7 DNA RNA Protein SynthesisSyed Majid KhanNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument42 pagesDna StructureCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument33 pagesRNA and Protein SynthesisRaphael Ongodia100% (2)
- Dna Rna Protsin 2020Document48 pagesDna Rna Protsin 2020RaragloriaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Chromosomes, Genes and DNADocument47 pagesChapter 16 Chromosomes, Genes and DNAZin Min KhantNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Document69 pagesBasics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Nando NanginNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes - HONORS-Website PDFDocument30 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis Notes - HONORS-Website PDFSphumelele AndiswaNo ratings yet
- DNA - The Moldecule of HeredityDocument36 pagesDNA - The Moldecule of HeredityRemiel MarticioNo ratings yet
- DNA To CellsDocument4 pagesDNA To CellsClaraNo ratings yet
- Dna Protein Synthesis 2015Document25 pagesDna Protein Synthesis 2015James ReiterNo ratings yet
- Dna & RnaDocument70 pagesDna & RnaEvette dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Dna, Rna & Proteins: The Molecules of LifeDocument32 pagesDna, Rna & Proteins: The Molecules of LifeMeri hardinaNo ratings yet
- Transes Biochem ProteinsynthesisDocument6 pagesTranses Biochem ProteinsynthesisPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- RNA - Cell Physiology...Document13 pagesRNA - Cell Physiology...siddhi meenaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. Proteins SynthesisDocument57 pagesUnit 6. Proteins Synthesismunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 21 Sylvia Mader ModifiedDocument29 pagesBiology Chapter 21 Sylvia Mader ModifiedabdallahNo ratings yet
- Transcription Kezia Joice BautistaDocument43 pagesTranscription Kezia Joice BautistaKeziajoicee Bautista0% (1)
- Guided Notes Lesson 4Document4 pagesGuided Notes Lesson 4Raine RagadioNo ratings yet
- Genbio Lesson 1 4Document26 pagesGenbio Lesson 1 4Greenard Imperial GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Rotein Ynthesis: Big PictureDocument3 pagesRotein Ynthesis: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsDocument12 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsAnne RussellNo ratings yet
- 2022 Investigating The Structure & Function of DNADocument23 pages2022 Investigating The Structure & Function of DNAayaanaghariaNo ratings yet
- The Central DogmaDocument7 pagesThe Central DogmaTobias Domenite P.No ratings yet
- Microbial GeneticsDocument72 pagesMicrobial GeneticsKhánh Trà QuốcNo ratings yet
- Topic 15-18 Content ADocument28 pagesTopic 15-18 Content ALeanne Krystel CastroNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument14 pagesDNA and RNAMelody Miras MacabontocNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit 3Document27 pagesBiology Notes Unit 3Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA, and Protein SynthesisDocument19 pagesDNA, RNA, and Protein SynthesisAnonymous qMToncNo ratings yet