Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Buku Tugas 22
Uploaded by
roy tambunanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Buku Tugas 22
Uploaded by
roy tambunanCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of Contents iii
Contents
Foreword The Plastics Pipe Institute Handbook of Polyethylene Pipe
Chapter 1 Introduction 5
Features and Benefits of PE Pipe 6
References 13
Chapter 2 Inspections, Tests and Safety Considerations
Introduction 15
PE Piping in the Field 16
Packaging for Commercial Transport 16
Receiving Inspection 18
Checking and Inspecting the Order 19
Receiving Report & Reporting Damage 19
Field Handling 20
Handling Equipment 21
Unloading Site 22
Unloading Bulk Packaged Pipe, Fittings and Fabrications 22
Unloading Large Fabrications, Manholes and Tanks 22
Pre-Installation Storage 22
Pipe Stacking Heights 23
Exposure to UV and Weather 24
Cold Weather Handling 25
General Considerations Before and During Installation 25
Pre-Construction 25
Joining and Connections 25
Cleaning Before Joining 27
Field Fusion Joining 27
During Construction and Installation 28
Damage Inspections 28
Butt Fusion Joint Quality 28
Soil Tests 29
Deflection Tests for ID controlled Pipes 30
Post Installation 32
Leak Testing – Considerations for All Procedures 32
Pressure System Leak Testing – Hydrostatic 34
Pressure System Leak Testing – Pneumatic 35
Pressure System Leak Testing – Initial Service 36
Non-Pressure System Leak Testing 37
Non-Testable Systems 37
Considerations for Post Start-Up and Operation 37
Disinfecting Water Mains 37
0ii-xviii.indd 3 1/16/09 9:38:34 AM
iv Table of Contents
Cleaning 38
Squeeze-Off 38
References 41
Chapter 3 Material Properties
Introduction 43
PE Plastics 45
History of PE 46
Manufacture of PE 46
Polymer Characteristics 47
Density 47
Crystallinity 48
Molecular Weight 50
Effect of Molecular Weight Distribution on Properties 53
PE Piping Materials 55
Structural Properties 56
PE Pipe Material Designation Code Identifies the
Standard Classification of Essential Properties 56
Stress/Strain Response and its Representation by
Means of an Apparent Modulus 57
Apparent Modulus Under Compressive Stress 63
Stress/Fracture Behavior and the Determination of Working Strength 64
Establishing a PE’s Long-Term Hydrostatic Strength (LTHS)
and its Derivative, The Hydrostatic Design Basis (HDB) 66
Compensating for the Effect of Temperature on Working Strength 72
Compressive Strength 73
Evaluating the Resistance to Slow Crack Growth (SCG)
of a Sharply Notched PE Specimen 73
Resistance to Pressure Surges 74
Reaction to Occasional Pressure Surges 75
Reaction to Frequently Occurring Pressure Surges 75
Other Engineering Properties 76
Mechanical Properties 76
Resistance to Rapid Crack Propagation 79
Abrasion Resistance 79
Thermal Properties 80
Coefficient of Expansion/Contraction 80
Thermal Conductivity 81
Specific Heat 81
Material Classification Properties 81
Density 82
0ii-xviii.indd 4 1/16/09 9:38:34 AM
You might also like
- PPI - Handbook of Polyethylene Pipe (2nd ED)Document626 pagesPPI - Handbook of Polyethylene Pipe (2nd ED)card89100% (5)
- Handbook of PE PipeDocument623 pagesHandbook of PE PipeRodrigo De Gaspari100% (2)
- Golf Course Irrigation: Environmental Design and Management PracticesFrom EverandGolf Course Irrigation: Environmental Design and Management PracticesNo ratings yet
- DC Drilling Motor Maintenance Manual PDFDocument56 pagesDC Drilling Motor Maintenance Manual PDFMarta VladNo ratings yet
- Guide Specifications For NUTRUSS Cold-Formed Steel FramingDocument6 pagesGuide Specifications For NUTRUSS Cold-Formed Steel FramingKeysha ApriliaNo ratings yet
- ROC203 Operator Instructions PDFDocument55 pagesROC203 Operator Instructions PDFMohan Charanchath100% (3)
- Handbook of Poly Ethelene Pipe PDFDocument557 pagesHandbook of Poly Ethelene Pipe PDFMuhammadUsmanNo ratings yet
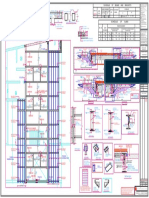
- (R4) Details of Mother Slab PDFDocument1 page(R4) Details of Mother Slab PDFsurya prakashNo ratings yet
- Plant Integrity BookletDocument79 pagesPlant Integrity Bookletkihal zohirNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Estimating StandardsDocument15 pagesProcess Plant Estimating StandardsCarl Williams75% (4)
- Decommissioning ProgrammesDocument57 pagesDecommissioning ProgrammesBehrang BaghernejadNo ratings yet
- Awwa M55 - 2006Document178 pagesAwwa M55 - 2006박인식100% (2)
- ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE - Distillation - Column - Rev05Document30 pagesENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINE - Distillation - Column - Rev05syazwanjohnmazlan100% (2)
- Planning Irrigation Scheme RehabilitationDocument123 pagesPlanning Irrigation Scheme RehabilitationsileshibekeleNo ratings yet
- Basic Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering - (Malestrom)Document153 pagesBasic Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering - (Malestrom)Nguyen Dang Hanh100% (15)
- Bridge Loading Requirements and Design LoadsDocument7 pagesBridge Loading Requirements and Design Loadswey5316No ratings yet
- 3.3 Over Head Sign BoardDocument4 pages3.3 Over Head Sign BoardBilal A Barbhuiya100% (3)
- Residential Development Cost EstimationDocument11 pagesResidential Development Cost EstimationMasambu Hillary100% (2)
- KLM - Fluid Flow Measurement Selection and SizingDocument16 pagesKLM - Fluid Flow Measurement Selection and SizingShakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Contamination Control in Healthcare Product Manufacturing Volume 1 - ContenidoDocument12 pagesContamination Control in Healthcare Product Manufacturing Volume 1 - ContenidocargscribNo ratings yet
- NYSDOT Approved Materials ListDocument13 pagesNYSDOT Approved Materials ListalbertmunozNo ratings yet
- Llo See DD Gts v3 W en 02Document428 pagesLlo See DD Gts v3 W en 02LLNo ratings yet
- Pipe and Tubing Extrusion: Technical GuideDocument46 pagesPipe and Tubing Extrusion: Technical GuideGIRMAY BERHENo ratings yet
- Pipe and Tubing Extrusion: Technical GuideDocument48 pagesPipe and Tubing Extrusion: Technical GuideSunil Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- TG7 PipeDocument48 pagesTG7 PipeMahesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Facilities HSE Audit QuestionnaireDocument142 pagesFacilities HSE Audit QuestionnaireFajar IslamNo ratings yet
- FacilitiesDocument129 pagesFacilitiesHedi Ben MohamedNo ratings yet
- 02TBLT1123EPCAgtKotePitlineCompletion1 PDF 2023 Dec 14-11-38 14Document198 pages02TBLT1123EPCAgtKotePitlineCompletion1 PDF 2023 Dec 14-11-38 14gouri sankaramangalamNo ratings yet
- PPI Handbook Guide to Polyethylene Pipe ConduitDocument42 pagesPPI Handbook Guide to Polyethylene Pipe ConduitMuhammed SiddikNo ratings yet
- Sewer Servicing Guide YVWDocument50 pagesSewer Servicing Guide YVWkjdara100% (1)
- Table of Contents OverviewDocument50 pagesTable of Contents OverviewAnthony WaaliaNo ratings yet
- 2018-01 Guide To PE - PP Polyolefin Film ExtrusionDocument42 pages2018-01 Guide To PE - PP Polyolefin Film ExtrusionRikiNo ratings yet
- Xstream Service ManualDocument52 pagesXstream Service ManualBagus Sri WibowoNo ratings yet
- WS4609 Underground-Services-Guidebook D3Document48 pagesWS4609 Underground-Services-Guidebook D3joeNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurancebuilding Demolition OccupationalDocument8 pagesQuality Assurancebuilding Demolition OccupationalSenathirajah SatgunarajahNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Miura BoilersDocument61 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Miura BoilersPreeth jayasingheNo ratings yet
- Termoformierka Manual-FMDH660 - UK - V3.0 - 140616 - LowresDocument57 pagesTermoformierka Manual-FMDH660 - UK - V3.0 - 140616 - LowresAndrzej RogalaNo ratings yet
- Vulcathene Technical BrochureDocument78 pagesVulcathene Technical BrochurekprasannanNo ratings yet
- contentUM20170820170814142114238DV4000 Manual EN AR DC68-03408P-08 PDFDocument80 pagescontentUM20170820170814142114238DV4000 Manual EN AR DC68-03408P-08 PDFRaed SulaihNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Plan - Kitime ProjectDocument26 pagesQuality Control Plan - Kitime ProjectBiniyam TseguNo ratings yet
- MOTI Fibre Reference GuideDocument70 pagesMOTI Fibre Reference Guidesed8edNo ratings yet
- Automatic Isoperibol Calorimeter: Operating Instruction ManualDocument110 pagesAutomatic Isoperibol Calorimeter: Operating Instruction ManualsergeyNo ratings yet
- Defriess Report On MLPPDocument55 pagesDefriess Report On MLPPFerryNo ratings yet
- Vulcathenetechnical PDFDocument78 pagesVulcathenetechnical PDFovidiuNo ratings yet
- Vulcathene Technical Brochure (Feb 10)Document78 pagesVulcathene Technical Brochure (Feb 10)Stuart ScroggieNo ratings yet
- WT 5680 HvaDocument80 pagesWT 5680 HvaDan PinvidicNo ratings yet
- Nisr 20120192 enDocument62 pagesNisr 20120192 engeraldmiaNo ratings yet
- Transsynergic 4000Document212 pagesTranssynergic 4000裴兆奇No ratings yet
- FSP 3000r7Document1,134 pagesFSP 3000r7motooNo ratings yet
- Geg A: Pressure Testing Process Piping and Equipment 670.219Document36 pagesGeg A: Pressure Testing Process Piping and Equipment 670.219puwarin najaNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINES Instrumentation Sizing and Selection Rev Web PDFDocument23 pagesENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINES Instrumentation Sizing and Selection Rev Web PDFEslam ShiblNo ratings yet
- Work ProgrammeScheduleDocument3 pagesWork ProgrammeScheduleRoshanNo ratings yet
- 2022-07-07 - Fefco Lca 2021Document50 pages2022-07-07 - Fefco Lca 2021herramentalesNo ratings yet
- 42,0426,0360, EaDocument300 pages42,0426,0360, EaCelia AfonsoNo ratings yet
- Annual Report EN 2019Document37 pagesAnnual Report EN 2019Mohamed AbdinNo ratings yet
- Management and Remediation of Sites in The Petroleum IndustryDocument68 pagesManagement and Remediation of Sites in The Petroleum IndustryWow KerenNo ratings yet
- QAP Energy MetersDocument1 pageQAP Energy MetersQAD LotusNo ratings yet
- Lrdcifbpuducherryfactoriesrules 1964Document499 pagesLrdcifbpuducherryfactoriesrules 1964Satheesh DhandapaniNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument122 pagesManualdarwin ramirezNo ratings yet
- Installation Operating and Maintenance M PDFDocument44 pagesInstallation Operating and Maintenance M PDFFranciscoNo ratings yet
- acxDocument88 pagesacxMuhsin Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Transpuls Synergic 4000Document212 pagesTranspuls Synergic 4000gabiNo ratings yet
- Siemens Vacuum Recloser 3ADDocument56 pagesSiemens Vacuum Recloser 3ADValentina ArthurNo ratings yet
- 42,0426,0135, enDocument76 pages42,0426,0135, enerniewatersNo ratings yet
- Off Shore Piping Design, Layout and Stress Analysis (Project Standards and Specifications)Document5 pagesOff Shore Piping Design, Layout and Stress Analysis (Project Standards and Specifications)sachin nagavkarNo ratings yet
- Jis K 6739-1-2Document2 pagesJis K 6739-1-2roy tambunan100% (1)
- Iso 4437-2007-2-3 (1) - 2Document1 pageIso 4437-2007-2-3 (1) - 2roy tambunanNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1693-13 Standard Test Method For Enviromental Stress-Cracking Ofethylene Plastics-7-8Document2 pagesASTM D1693-13 Standard Test Method For Enviromental Stress-Cracking Ofethylene Plastics-7-8roy tambunanNo ratings yet
- Iso 4437-2007-2-3 (1) - 2Document1 pageIso 4437-2007-2-3 (1) - 2roy tambunanNo ratings yet
- Iso 4437-2007-2-3 (1) - 2Document1 pageIso 4437-2007-2-3 (1) - 2roy tambunanNo ratings yet
- Restoratu 678 OBoomDocument2 pagesRestoratu 678 OBoomroy tambunanNo ratings yet
- HVAC Applications For PE Pipe: Table of Contents XiiiDocument2 pagesHVAC Applications For PE Pipe: Table of Contents Xiiiroy tambunanNo ratings yet
- Produk Hoslk AssementDocument4 pagesProduk Hoslk Assementroy tambunanNo ratings yet
- ASTM D2564-12 Solvent Cements For Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems-4-5Document2 pagesASTM D2564-12 Solvent Cements For Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems-4-5roy tambunanNo ratings yet
- PE Pipe and Fittings ManufacturingDocument3 pagesPE Pipe and Fittings Manufacturingroy tambunanNo ratings yet
- Buku Tugas 22Document2 pagesBuku Tugas 22roy tambunanNo ratings yet
- HVAC Applications For PE Pipe: Table of Contents XiiiDocument2 pagesHVAC Applications For PE Pipe: Table of Contents Xiiiroy tambunanNo ratings yet
- HVAC Applications For PE Pipe: Table of Contents XiiiDocument2 pagesHVAC Applications For PE Pipe: Table of Contents Xiiiroy tambunanNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Polyethylene (PE) Pipe: ForewordDocument3 pagesHandbook of Polyethylene (PE) Pipe: ForewordrafaelNo ratings yet
- Asemmbleng Book 2Document2 pagesAsemmbleng Book 2roy tambunanNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Polyethylene (PE) Pipe: ForewordDocument3 pagesHandbook of Polyethylene (PE) Pipe: ForewordrafaelNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel Project Proposal by SlidesgoDocument47 pagesSolar Panel Project Proposal by SlidesgoDAVID ANTONIO BARROS VALLENo ratings yet
- Handbook of Polyethylene (PE) Pipe: ForewordDocument3 pagesHandbook of Polyethylene (PE) Pipe: ForewordrafaelNo ratings yet
- Book 2 TugasDocument2 pagesBook 2 Tugasroy tambunanNo ratings yet
- Web Project Proposal by SlidesgoDocument38 pagesWeb Project Proposal by Slidesgotatiana diazNo ratings yet
- HVAC Applications For PE Pipe: Table of Contents XiiiDocument2 pagesHVAC Applications For PE Pipe: Table of Contents Xiiiroy tambunanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering by SlidesgoDocument51 pagesElectrical Engineering by Slidesgoxiomara molinaNo ratings yet
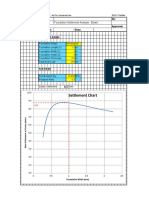
- Settlement Chart: Foundation Settlement Analysis - ElasticDocument2 pagesSettlement Chart: Foundation Settlement Analysis - ElasticCSEC Uganda Ltd.No ratings yet
- Hydraulics 1 Lec 2 20 21 PDFDocument28 pagesHydraulics 1 Lec 2 20 21 PDFAngelo Luis RosNo ratings yet
- Esp Calculation Sheet - m1Document7 pagesEsp Calculation Sheet - m1Buraq Aircondition Cont & Gen Maint LLC BuraqNo ratings yet
- Introduction Kirsch y LameDocument2 pagesIntroduction Kirsch y LameAlvaro FabianNo ratings yet
- Activity Report 2 (Soil Sampling) Fajardo Bsce3aDocument6 pagesActivity Report 2 (Soil Sampling) Fajardo Bsce3aGuilbert FajardoNo ratings yet
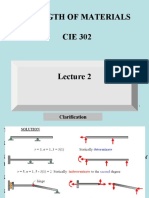
- Strength of Materials CIE 302Document29 pagesStrength of Materials CIE 302kingNo ratings yet
- BRIDGE DESIGN MANUALDocument49 pagesBRIDGE DESIGN MANUALdulancivil100% (11)
- 10 - Lateral Earth Pressure - Active and PassiveDocument8 pages10 - Lateral Earth Pressure - Active and PassiveNoaman RehanNo ratings yet
- Aging Characteristics of Warm-Mix Asphalt BindersDocument7 pagesAging Characteristics of Warm-Mix Asphalt BindersPedro FariettaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design Guide 2002 02Document119 pagesSeismic Design Guide 2002 02treyNo ratings yet
- Project Report of Etabs SampleDocument31 pagesProject Report of Etabs SampleBißék Śílwàl0% (1)
- Prefabricated Vertical DrainsDocument25 pagesPrefabricated Vertical Drainsdory.azarhotmail.comNo ratings yet
- PP11280 SpecificationDocument2 pagesPP11280 Specificationudummy552No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document59 pagesUnit 2Pavan G ReddyNo ratings yet
- Effects of Increasing Allowable Compressive Stressat Prestress TransferDocument11 pagesEffects of Increasing Allowable Compressive Stressat Prestress TransferProfessor Dr. Nabeel Al-Bayati-Consultant EngineerNo ratings yet
- BURGOS ULO3aDocument3 pagesBURGOS ULO3aPeter Carl BurgosNo ratings yet
- Report-L & T-ALH-163-R3-okDocument32 pagesReport-L & T-ALH-163-R3-okShubham MauryaNo ratings yet
- 7-8 Sentrina Alaminos Cost ControlDocument60 pages7-8 Sentrina Alaminos Cost ControlQueenie PerezNo ratings yet
- W8,9,10 Chapter 5-Statically Determinate TrussesDocument38 pagesW8,9,10 Chapter 5-Statically Determinate TrussesNor HakimNo ratings yet
- EAC NotesDocument105 pagesEAC NotesAyush JainNo ratings yet
- E Spec Guide BCI and VL PDFDocument36 pagesE Spec Guide BCI and VL PDFcphammond83No ratings yet
- DN-016-Rev 0-Design Procedure of RC BeamsDocument82 pagesDN-016-Rev 0-Design Procedure of RC BeamsAbdullah Abdel-MaksoudNo ratings yet