Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 (History Timeline of CELL)
Uploaded by
Gmail愛してますOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 (History Timeline of CELL)
Uploaded by
Gmail愛してますCopyright:
Available Formats
GENERAL BIOLOGY (RESEARCHED REVIEWER)
History Timeline-of Nervanz De Guzman
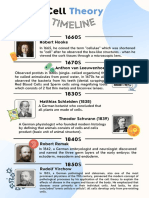
1595 – Zacharias Janssen(Brother; Hans Janssen), a Dutch
Spectacle maker that was credited with the 1st compound microscope.
1665 - Robert Hooke, a British Scientist who used one of the first light
microscope to look at thin slices of plant tissues of Cork.
- He published Micrographia, a book containing detailed
drawings of many biological specimens, including the first
drawing of cells on what he observed on thin slices of cork
under microscope.
- He saw that it was composed by neat holes with walls. Later he
called this empty chambers/holes as “cells”
-2nd cell theory
1674 – Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch businessman and scientist
in the Golden Age of Dutch science and technology.
- He discovered Protozoa and Bacteria (9 years after
Protozoa) that helped lay the foundations for the sciences
of bacteriology and protozoology.
- Leeuwenhoek studied the structure of the optic lens, striations
in muscles, the mouthparts of insects, and the fine structure
of plants and discovered parthenogenesis in aphids.
- In 1680 he noticed that yeasts consist of minute globular
particles.
- He extended Marcello Malpighi’s demonstration in 1660 of
the blood capillaries by giving the first accurate description
of red blood cells.
- The father of Microbio
CALLED CELLS ANIMAL CUOLES
-DISCOVERED SPERM
1833 – Robert Brown, a Scottish Botanist was responsible for
discovering the nucleus of a cell, he is perhaps best known for his
discovery of the random movement of microscopic particles in a
surrounding solution, later referred to as "Brownian motion."
- He was studying orchids under microscope when he observed
an opaque area, which he called the "areola" or "nucleus", in
the cells of the flower's outer layer.
GENERAL BIOLOGY (RESEARCHED REVIEWER)
1838 – Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, proposed
the cell theory.
- Mathhias Schleiden(1938), a German botanist that studied
different varieties of plants and concluded that all plants are
“aggregates of fully individualize, independent, separate beings,
namely the cells themselves”
- Theodor Schwann(1839), a German zoologist, stated that all
animals are also made up of cells and proposed a cellular basis
of life.
1840 – Albrecht von Roelliker, a Swiss anatomist who discovered that
egg and sperm cells are cells.
- He realized that human beings were form of cells from the
beginning to the end.
1855 – Rudolf Virchow, a German physicist, pathologist, and
anthropologist that expounds his famous conclusion(epigram): “Omnis
cellula e cellula”, that is develop only from existing cells[cells come
from pre-existing cells]. (The epigram was actually coined by François-
Vincent Raspail, but popularized by Virchow.)
- Before Virchow came out with this theory, it was believed that
new cells were created from a fluid called blastema.
(defies life comes from death)
1856 – Nathanael Pringsheim, observed on how a cell of sperm
penetrated an egg cell.
- He was among the first to observe sexual reproduction in
algae. He showed that these tiny organisms release sperm and
egg cells into the water, where they combine. He also
described the alternation of generations, or reproduction by
spores, in mosses.
- One of the founders of the Algology on his study of algal
reproduction.
- He first issue of the botanical journal Jahrbücher für
wissenschaftliche Botanik (“Annals of Scientific Botany”).
GENERAL BIOLOGY (RESEARCHED REVIEWER)
1857- Albert von Kölliker described Mitochondria.
- Mitochondria, often reffered to as “powerhouses of the cell”,
were first discovered in 1857 by Albert von Kolliker, and later
coined “bioblasts” (life germs) by Richard Altman in 1886.
The organelles were then renamed “mitochondria” by Carl
Benda twelve years later.
1879 – Walther Flemming was a German biologist and the pioneer of
Cytogenetics. He described how chromosomes behave during mitosis.
- Flemming used aniline dyes, a by-product of coal tar, to stain
cells of salamander embryos. He was able to visualize the
threadlike material as the cells divide.
1883 - August Friedrich Leopold Weismann a German evolutionary
biologist. He discovered that germ cells are haploid chromosomes.
- He formulated the germ-plasm theory of inheritance. In order
to prove that the disuse or loss of somatic structures would
not affect the subsequent offspring. (Directly discrediting J-
B Lamarck)
- Germ plasm, which is independent from all other cells of the
body (somatoplasm), is the essential element of germ cells
(eggs and sperm) and is the hereditary material that is passed
from generation to generation
1898 – Camillo Golgi an Italian Biologist who communicated to the
Medical–Surgical Society of Pavia, the discovery of the “internal
reticular apparatus”, a novel intracellular organelle which he
observed in nerve cells with the silver impregnation he had introduced
for the staining of the nervous system.
1938 – Behrens used differential centrifugation on separating nuclei
from cytoplasm.
1939 - Siemens Elmiskop IA produced the first commercial
transmission electron microscope.
- Although current transmission electron microscopes are
capable of two million-power magnification, as scientific
instruments, they remain based upon Ruska's prototype
(family prototype).
GENERAL BIOLOGY (RESEARCHED REVIEWER)
1952 – George Otto Gey & co-workers originated HeLa cell line (a
continuos Human cell line)
- This cell line was from a cervical adenocarcinoma from a
31-year-old Afro-American female. It has proved to be a very
vigorously growing cell line and is one of the most extensively
used cell lines in the world.
A cell line is a permanently established cell culture that will proliferate
indefinitely given appropriate fresh medium and space. Lines differ
from cell strains in that they have escaped the Hayflick limit and become
immortalized.
1953- James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins proposed the
double-helix structure of DNA because of the x-ray photo of DNA
created by their friend Rosalind Franklin using a technique called
X-ray crystallography.
- The photo revealed the helical shape of the DNA molecule.
Watson and Crick realized that DNA was made up of two
chains of nucleotide pairs.
- There were three models suggested for DNA replication:
conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive (Dispersive
and conservative proposed by Watson and Crick)
1955 – Harry Eagle an American Physician and Pathologist
systematically defined the nutritional needs of animal cells in culture.
- Animal cells are more difficult to culture than
microorganisms because they require many more nutrients
and typically grow only when attached to specially coated
surfaces.
- Nine amino acids, referred to as the essential amino
acids, cannot be synthesized by adult vertebrate animals and
thus must be obtained from their diet.
- Animal cells grown in culture also must be supplied with these
nine amino acids, namely, histidine, isoleucine, leucine,
lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan,
and valine.
GENERAL BIOLOGY (RESEARCHED REVIEWER)
1957 – Matthew Meselson, Franklin Stahl, & Jerome Vinograd
developed density gradient centrifugation in cesium chloride solutions
for separating nucleic acids.
- The exact split between heavy and light nitrogen characterized
semi-conservative DNA replication. Meselson and Stahl
made three conclusions based on their results.
1998 – Mice are used for cloning somatic cells
1999 – A.J. Hamilton & David Baulcombe discovered siRNA as part
of post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) in plants.
- Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short
interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-
stranded RNA non-coding RNA molecules, typically 20-27
base pairs in length, similar to miRNA, and operating within
the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway.
You might also like
- Zacharias Janssen: Van LeeuwenhoekDocument4 pagesZacharias Janssen: Van LeeuwenhoekCharl BaranganNo ratings yet
- History of Cell BiologyDocument5 pagesHistory of Cell BiologyGusMar OyNo ratings yet
- History of Cell Biology DiscoveryDocument3 pagesHistory of Cell Biology DiscoveryMegurine LukaNo ratings yet
- Enrichment Bio ActivityDocument8 pagesEnrichment Bio ActivityPrincess Bea PengsonNo ratings yet
- Timeline MineDocument1 pageTimeline MineJane Angela FerrerNo ratings yet
- Development of Cell TheoryDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Cell TheoryCATHERINE MAE ARIENDANo ratings yet
- Unknownfiles 0Document3 pagesUnknownfiles 0RJ TannieNo ratings yet
- The Smallest Unit of Life: Submitted By: Submitted To: Biology TeacherDocument30 pagesThe Smallest Unit of Life: Submitted By: Submitted To: Biology TeacherJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Tarea 2 Teoríacelular López Marmolejo Clere MishellDocument3 pagesTarea 2 Teoríacelular López Marmolejo Clere Mishellclere02marmolejoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 BioDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 BioMarie Guia Stella GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Wacky History of Cell TheoryDocument21 pagesThe Wacky History of Cell TheoryIrish SolomonNo ratings yet
- Brief History of Cell DiscoveryDocument3 pagesBrief History of Cell DiscoveryRobert Ford100% (1)
- History of Cell Biology in 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesHistory of Cell Biology in 40 CharactersTalhaNo ratings yet
- History of Cell: Robert HookeDocument4 pagesHistory of Cell: Robert HookeJenny HermosadoNo ratings yet
- Cells: Discovery of The CellDocument3 pagesCells: Discovery of The CellRenee RoSeNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of Life: A History of Cell DiscoveryDocument3 pagesBuilding Blocks of Life: A History of Cell DiscoveryRenee RoSeNo ratings yet
- The Cell Theory TimelineDocument16 pagesThe Cell Theory TimelinesilvajunjosephNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellwahyu kurniawanNo ratings yet
- GenBio1 Lecure Notes - Plant CellDocument8 pagesGenBio1 Lecure Notes - Plant CellCatherine DitanNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellBeatrice de CastroNo ratings yet
- Genereal BiologyDocument6 pagesGenereal BiologyEd JayNo ratings yet
- CSIR-NET Cell Biology NotesDocument32 pagesCSIR-NET Cell Biology NotesSrinivas Nakka100% (1)
- q1 Genbio Notes (To Highlight)Document16 pagesq1 Genbio Notes (To Highlight)saturosjuliaclarisseNo ratings yet
- Postulate of Cell TheoryDocument31 pagesPostulate of Cell TheoryChrystal Tala CustodioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 the Cell and Development of Cell TheoryDocument155 pagesLecture 2 the Cell and Development of Cell TheoryCharlotte PinedaNo ratings yet
- Cell TimelineDocument4 pagesCell TimelineLady MeowNo ratings yet
- The Cell TheoryDocument20 pagesThe Cell TheoryyvetteNo ratings yet
- History of Cell BiologyDocument3 pagesHistory of Cell BiologyJay R Chiva100% (1)
- General Biology 1 Module 2Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 2Ennyliejor YusayNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 - The History of Cell and Cell TheoryDocument11 pagesLesson1 - The History of Cell and Cell TheoryMobileLegends SbNo ratings yet
- Notes - General Biology 1Document25 pagesNotes - General Biology 1GARCIA, Denmar Djasthine P.No ratings yet
- Bio Lesson 6Document31 pagesBio Lesson 6it'smeliza E.No ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1Document1 pageGen Bio 1Mary Joy IntiaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Biology ScientistsDocument13 pagesNcert Biology ScientistsSrujana ShettiNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Grade8Document31 pagesCell Theory Grade8Emmie Grace S. AbrahamNo ratings yet
- The Cell TheoryDocument12 pagesThe Cell Theorylordy i dont knowNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Refers To The Idea That: MicrographiaDocument5 pagesCell Theory Refers To The Idea That: MicrographiadeltasixNo ratings yet
- Bio CellsDocument4 pagesBio CellsONIPOP OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- The Basic Unit of Life - Cell TheoryDocument21 pagesThe Basic Unit of Life - Cell TheoryMARY ANN PANGANNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory TimelineDocument1 pageCell Theory TimelineTrisha PadlanNo ratings yet
- General Biology Cell Theory ReviewDocument1 pageGeneral Biology Cell Theory ReviewPrincess Alyssa Bianca BardonNo ratings yet
- Genbio 1Document16 pagesGenbio 1Sherain Kaye GalanayNo ratings yet
- What Is A CellDocument12 pagesWhat Is A CellMaries San PedroNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document1 pageCell (Biology)piping stressNo ratings yet
- Discovery of Cells and The Development of Cell TheoryDocument3 pagesDiscovery of Cells and The Development of Cell TheoryLast FazeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Cell TheoryDocument15 pagesLesson 1 - Cell TheoryKenny JohnstonNo ratings yet
- Class 1 - History of Cell BiologyDocument12 pagesClass 1 - History of Cell BiologyUrbiAnahitaNo ratings yet
- Formulation of The Cell TheoryDocument4 pagesFormulation of The Cell Theoryapi-345209915No ratings yet
- Cell 2Document15 pagesCell 2teaNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell TheoryDocument44 pages1 Cell TheoryJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument31 pagesCell TheoryJohn Erniest Tabungar AustriaNo ratings yet
- Cells HistoryDocument15 pagesCells HistoryNicole CatahanNo ratings yet
- Bio Day 1Document27 pagesBio Day 1John Paul NarvasNo ratings yet
- GEN - Bio 1Document2 pagesGEN - Bio 1Nash MartinezNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument3 pagesCell TheoryJulius HernandezNo ratings yet
- The Song of the Cell: An Exploration of Medicine and the New HumanFrom EverandThe Song of the Cell: An Exploration of Medicine and the New HumanRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (78)
- Lecture 1 & 5 Introduction To Plant Breeding and Reproduction in PlantsDocument18 pagesLecture 1 & 5 Introduction To Plant Breeding and Reproduction in PlantssasidharnaikNo ratings yet
- Controlling Factors in Craniofacial GrowthDocument82 pagesControlling Factors in Craniofacial GrowthPrachodh0% (1)
- Thyroid Gland 2021Document28 pagesThyroid Gland 2021Dr. Ali100% (1)
- MLL4 Supplemental Figure 136155-JCI-RG-RV-3 - SD - 424851Document15 pagesMLL4 Supplemental Figure 136155-JCI-RG-RV-3 - SD - 424851李博No ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument10 pagesFUNGIAnonymous pICw4fQNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology Lecture 2 Metabolic Clearance RatesDocument64 pagesEndocrine Physiology Lecture 2 Metabolic Clearance RatesHello SunshineNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenDocument14 pagesRespiration in Plants: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenJK JHA100% (1)
- TF1820533 PDFDocument2 pagesTF1820533 PDFPrenoojNo ratings yet
- LSM - 4223 Introduction VC 2014 PDFDocument34 pagesLSM - 4223 Introduction VC 2014 PDFTimmy RichardoNo ratings yet
- Ex. BISC 421 SyllabusDocument4 pagesEx. BISC 421 SyllabuscaleatherNo ratings yet
- 3 - IB Biology (2016) - 1.3 - Membrane Structure PPT Part BDocument10 pages3 - IB Biology (2016) - 1.3 - Membrane Structure PPT Part BUlises DeyesNo ratings yet
- 23andme and The FDADocument4 pages23andme and The FDAChristodoulos DolapsakisNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Monera lecture notes uncover prokaryotesDocument5 pagesKingdom Monera lecture notes uncover prokaryotesWARRIORS100% (1)
- Brochure a-PRF and I-PRFDocument4 pagesBrochure a-PRF and I-PRFDumitruChele0% (1)
- Walter B. Cannon and " Voodoo' Death": A Perspective From 60 Years OnDocument3 pagesWalter B. Cannon and " Voodoo' Death": A Perspective From 60 Years OnPatricksia Utopian STsetia Ciel'erNo ratings yet
- Biology 1234Document4 pagesBiology 1234Anup Singh TanwarNo ratings yet
- NBME 3 BLOCK 1-4 (With Answers)Document204 pagesNBME 3 BLOCK 1-4 (With Answers)sarah50% (2)
- KCSE PREMOCKS Set 2Document262 pagesKCSE PREMOCKS Set 2Micah IsabokeNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1!!!Document29 pagesGenetics 1!!!klxNo ratings yet
- (1032) Development and Design of BioassaysDocument15 pages(1032) Development and Design of BioassaysKraken UrNo ratings yet
- LSBM - Fellows 27th Dec 2022 2 PDFDocument2 pagesLSBM - Fellows 27th Dec 2022 2 PDFMullai Kodi KNo ratings yet
- Nurs 102-3 Ap 2014 Course OutlineDocument3 pagesNurs 102-3 Ap 2014 Course Outlineapi-349389012No ratings yet
- Sex Selection: Prepared By: Ms. Mary Shein Love D. CubicoDocument5 pagesSex Selection: Prepared By: Ms. Mary Shein Love D. CubicoClint FloresNo ratings yet
- 9700 m17 Ms 22Document9 pages9700 m17 Ms 22SofiNo ratings yet
- (Mebooksfree Com) Con&Pat&Exa&Pre&Bha&3rdDocument645 pages(Mebooksfree Com) Con&Pat&Exa&Pre&Bha&3rdCamelia-Elena Plesa100% (1)
- Execise 15Document2 pagesExecise 15Ananya PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Biology Approaches To DesigningDocument13 pagesChemical Biology Approaches To Designingcrowned-lionNo ratings yet
- GATE Life SciencesDocument6 pagesGATE Life SciencesstudyurselfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cells and TissuesDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Cells and TissuesNathaliaNo ratings yet
- Protein Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesProtein Lesson Planapi-270183943No ratings yet