Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson-4 Content Comp1
Uploaded by
AexcellRose AlmomentoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson-4 Content Comp1
Uploaded by
AexcellRose AlmomentoCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 1, Lesson 4
INSIDE A COMPUTER CABINET
INTRODUCTION
The computer as a machine consists of different components that interact with each other to provide the
desired functionality of the computer. As a user of the computer, we need to be aware of the main components
of the computer, their functions and the interconnection between the different components of the computer. This
chapter describes the different hardware components of the computer.
The computer cabinet encloses the components that are required for the running of the computer. The
components inside a computer cabinet include the power supply, motherboard, memory chips, expansion slots,
ports and interface, processor, cables and storage devices.
DISCUSSION
The computer cabinet encloses the components that are required for the running of the computer. The
components inside a computer cabinet include the power supply, motherboard, memory chips, expansion slots,
ports and interface, processor, cables and storage devices.
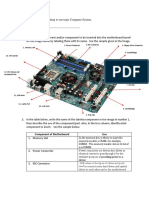
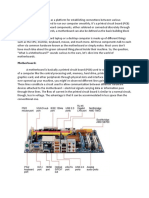
Motherboard
The computer is built up around a motherboard. The
motherboard is the most important component in the PC. It is a
large Printed Circuit Board (PCB), having many chips,
connectors and other electronics mounted on it. The
motherboard is the hub, which is used to connect all the
essential components of a computer. The RAM, hard drive,
disk drives and optical drives are all plugged into interfaces on
the motherboard. The motherboard contains the processor,
Figure 2.14
memory chips, interfaces and sockets, etc.
ROM BIOS
The motherboard may be characterized by the form
factor, chipset and type of processor socket used. Form factor refers to the motherboard’s geometry,
dimensions, arrangement and electrical requirements. Different standards have been developed to build
motherboards, which can be used in different brands of cases. Advanced Technology Extended (ATX) is the
most common design of motherboard for desktop computers. Chipset is a circuit, which controls the majority of
resources (including the bus interface with the processor, cache memory and RAM, expansion cards, etc.)
Chipset’s job is to coordinate data transfers between the various components of the computer (including the
processor and memory). As the chipset is integrated into the motherboard, it is important to choose a
motherboard, which includes a recent chipset, in order to maximize the computer’s upgradeability. The
processor socket may be a rectangular connector into which the processor is mounted vertically (slot), or a
square-shaped connector with many small connectors into which the processor is directly inserted (socket). The
Basic Input Output System (BIOS) and Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) are present on
the motherboard.
BIOS. It is the basic program used as an interface between the operating system and the motherboard.
The BIOS (Figure 2.14) is stored in the ROM and cannot be rewritten. When the computer is switched
on, it needs instructions to start. BIOS contain the instructions for the starting up of the computer. The
BIOS runs when the computer is switched on. It performs a Power On Self Test (POST) that checks that
the hardware is functioning properly and the hardware devices are present. It checks whether the
operating system is present on the hard drive. BIOS invokes the bootstrap loader to load the operating
system into memory. BIOS can be configured using an interface named BIOS setup, which can be
accessed when the computer is booting up (by pressing the DEL key).
CMOS Chip. BIOS ROMs are accompanied by a smaller CMOS (CMOS is a type of memory
technology) memory chip. When the computer is turned off, the power supply stops providing electricity
to the motherboard. When the computer is turned on again, the system still displays the correct clock
time. This is because the CMOS chip saves some system information, such as time, system date and
COMP 1 – FUNDAMENTALS OF INFO. TECH. PROF. MARIBEL B. 1
BANDOJO
essential system settings. CMOS is kept powered by a button battery located on the motherboard (Figure
2.15). The CMOS chip is working even when the computer power is switched off. Information of the
hardware installed in the computer (such as the number of tracks or sectors on each hard drive) is stored
in the CMOS chip.
Figure 2.15 Battery for CMOS chip
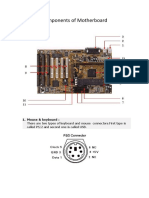
Ports and Interfaces
Motherboard has a certain number of I/O sockets that are connected to the ports and interfaces found on
the rear side of a computer (Figure 2.16). You can connect external devices to the ports and interfaces, which
get connected to the computer’s motherboard.
Serial Port— to connect old peripherals.
Parallel Port— to connect old printers.
Figure 2.16 Ports on the rear side of a PC
USB Ports—to connect newer peripherals like cameras, scanners and printers to the computer. It uses a
thin wire to connect to the devices, and many devices can share to that wire simultaneously.
Firewire is another bus, used today mostly for video cameras and external hard drives.
RJ45 connector (called LAN or Ethernet port) is used to connect the computer to a network. It
corresponds to a network card integrated into the motherboard.
VGA connector for connecting a monitor. This connector interfaces with the built-in graphics card.
Audio plugs (line-in, line-out and microphone), for connecting sound speakers and the microphone. This
connector interfaces with the built-in sound card.
PS/2 port to connect mouse and keyboard into PC.
SCSI port for connecting the hard disk drives and network connectors.
COMP 1 – FUNDAMENTALS OF INFO. TECH. PROF. MARIBEL B. 2
BANDOJO
A – Optical Drive – insertion of
CD’s and DVD’s
B – Floppy Disk Drive – insertion
of Diskettes
C – USB Port – connection of USB
type gadgets
D – Power Button – use for
Powering On
E – Card Slots – insertion of
Memory Card
F – Hard Drive Activity LED –
serves as Power Indicator
G – Front Ports Door – for
additional Optical Drive
COMP 1 – FUNDAMENTALS OF INFO. TECH. PROF. MARIBEL B. 3
BANDOJO
1. Exhaust Fan- use to minimize
heat inside the computer
2. Power Supply – Passage of
Electricity
3. PS2 Ports – Connection of Mouse
and Keyboard
(Green – Mouse)
(Lavender – Keyboard)
4. Serial Port – connection of old
types of Mouse
5. Parallel Port – connection of old
types of Printer
6. VGA Port - connection of display
cable of monitor
7. USB Ports – connection of USB
type Gadgets
8. LAN Port – use to connect RJ45
NIC
9. Audio Jacks
(Green – Primary Speaker)
(Blue – Secondary
Speaker/Headset)
(Pink – Microphone)
10. Modem – connection of internet
though telephone line.
Expansion Slots
The expansion slots (Figure 2.17) are located on the motherboard. The expansion cards are inserted in
the expansion slots. These cards give the computer new features or increased performance. There are several
types of slots:
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) slot—To connect modem and input devices.
PCI (Peripheral Component InterConnect) slot—To connect audio, video and graphics. They are much
faster than ISA cards.
AGP (Accelerated Graphic Port) slot—A fast port for a graphics card.
PCI (Peripheral Component InterConnect) Express slot—Faster bus architecture than AGP and PCI
buses.
PC Card—It is used in laptop computers. It includes Wi-Fi card, network card and external modem.
Figure 2.18 Ribbon cables inside a PC
COMP 1 – FUNDAMENTALS OF INFO. TECH. PROF. MARIBEL B. 4
BANDOJO
Memory Chips
The RAM consists of chips on a small circuit board (Figure 2.19). Two types of memory chips— Single
In-line Memory Module (SIMM) and Dual In-line Memory Module (DIMM) are used in desktop computers.
The CPU can retrieve information from DIMM chip at 64 bits compared to 32 bits or 16 bits transfer with
SIMM chips. DIMM chips are used in Pentium 4 onwards to increase the access speed.
Figure 2.19 RAM memory chip
Storage Devices
The disk drives are present inside the machine. The common disk drives in a machine are hard disk
drive, floppy drive (Figure 2.20 (i & ii)) and CD drive or DVD drive. High-storage devices like hard disk,
floppy disk and CDs (Figure 2.20 (iii) & (iv)) are inserted into the hard disk drive, floppy drive and CD drive,
respectively. These storage devices can store large amounts of data, permanently.
Processor
The processor or the CPU is the main component of the computer. Select a processor based on factors
like its speed, performance, reliability and motherboard support. Pentium Pro, Pentium 2 and Pentium 4 are
some of the processors.
Figure 2.20 Storage devices (i) Hard disk drive, (ii) DVD drive, (iii) Floppy disk, (iv) CD
SUMMARY
Inside a computer cabinet, there is a motherboard, ports and interfaces, expansion slots, ribbon cables,
RAM memory chips, high storage disk drives, and, processor.
The motherboard is characterized by the form factor, chipset and type of processor socket. Form factor
is the motherboard’s geometry, dimensions, arrangement and electrical requirements. Chipset controls
the majority of resources of the computer.
BIOS and CMOS are present on the motherboard. BIOS is stored in ROM and is used as an interface
between the operating system and the motherboard. The time, the system date, and essential system
settings are saved in CMOS memory chip present on the motherboard. When the computer power is
switched off, CMOS chip remains alive powered by a button battery.
COMP 1 – FUNDAMENTALS OF INFO. TECH. PROF. MARIBEL B. 5
BANDOJO
Ports and interfaces are located on the sides of the computer case to which the external devices can be
connected. Some of the ports and interfaces are— Serial port, Parallel port, USB port, Firewire, RJ45
connector, VGA connector, Audio plugs, PS/2 port, and SCSI port.
ASSESSMENT
1. “The motherboard is characterized by the form factor, chipset and the type of processor socket
used”. Explain.
2. Define form factor.
3. Define chipset.
4. ______________ is the most common design of the motherboard for desktop computers.
5. What is the significance of the chipset?
6. What is the function of the BIOS?
7. What is the function of the CMOS chip?
8. Explain the booting process when the computer is switched on.
9. What is POST?
10. List five ports and interfaces available on the backside of the computer to connect the devices.
11. What devices are attached to—(a) Serial Port, (b) Parallel Port, (c) USB Port, (d) Firewire,
(e) RJ45 connector, (f) VGA connector, (g) Audio plugs (Line-In, Line-Out and microphone),
(h) PS/2 Port, and (h) SCSI Port.
12. What devices are attached to—(a) ISA slots, (b) PCI slot, (c) AGP slot, (d) PCI Express slot, and (e)
PC Card.
13. What is the purpose of the Ribbon cables?
14. Two types of memory chips and are used in desktop
computers.
15. List any three storage devices that are attached to the computer.
Extra Questions
Give full form of the following abbreviations
1. IC
2. MIPS Instructions: Copy first the question
3. EISA before you write your answer. Write
4. PCI
5. USB
your answer in a yellow pad. Use as
6. AGP many as you can (no limit). After
7. BIPS writing your answer, take a picture of it
8. SIMM (every page). Also, take a selfie
9. DIMM together with your assessment (holding
10. GHz it, one picture only). Kindly reply
11. MHz
12. PCB
“RECEIVED Ma’am” in our GC once
13. BIOS you already download/open this module
14. CMOS and reply “Done Ma’am” once you
15. POST already send it. Don’t worry if I didn’t
16. ISA automatically seen/check your sent
17. ROM assessment.
18. ACC
19. IR
20. PC
21. MAR
22. MBR
23. DR
24. ATX
25. SATA
COMP 1 – FUNDAMENTALS OF INFO. TECH. PROF. MARIBEL B. 6
BANDOJO
You might also like
- Mag Bike C100Document13 pagesMag Bike C100tony445100% (1)
- Motherboard Components & Functions ExplainedDocument13 pagesMotherboard Components & Functions Explainedjussan roaring100% (3)
- Image Runner Advance c5051 Series SM Rev0 092409Document1,131 pagesImage Runner Advance c5051 Series SM Rev0 092409tytech760% (5)
- CahmDocument3 pagesCahmakkivish37No ratings yet
- ITcomDocument3 pagesITcomRodel Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- The System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterDocument10 pagesThe System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterbogusbaikawNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Assignment:: Motherboard Write-UpDocument16 pagesInformation Technology Assignment:: Motherboard Write-UpJuline AsmeryNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ComponentsDocument59 pagesComputer Hardware ComponentsJason EchevariaNo ratings yet
- INFO SHEET 4.5 MotherboARDDocument1 pageINFO SHEET 4.5 MotherboARDGeh Deng NolealNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionsCheryl Dumaguit BelaloNo ratings yet
- Homework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetDocument13 pagesHomework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetJohn Kerby CorralNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to MotherboardsDocument5 pagesThe Essential Guide to MotherboardsElleera RemorerasNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ServicingDocument44 pagesComputer Hardware ServicingSodnal M. OdeloNo ratings yet
- Motherboard parts and their functionsDocument2 pagesMotherboard parts and their functionsKurt KenNo ratings yet
- Understanding Motherboard ComponentsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Motherboard ComponentsallamNo ratings yet
- Kurt PogiDocument2 pagesKurt PogiKurt KenNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument27 pagesMotherboardமகான் சிறோன்No ratings yet
- 23 Computer Application Commerce Unit-02Document42 pages23 Computer Application Commerce Unit-02jikku thomasNo ratings yet
- Sindi Ayu Anggraeni - MotherboardDocument4 pagesSindi Ayu Anggraeni - MotherboardSindi Ayu AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Computer MotherboardDocument15 pagesComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4CABADONGA, Justin M.No ratings yet
- Basic Notes 2Document6 pagesBasic Notes 2jivan jyotNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Give All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipDocument7 pagesGive All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipjanNo ratings yet
- Ports and CablesDocument6 pagesPorts and CablesAlfredo DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Mohammad Alfaiz Khan-CSO Practical7Document3 pagesMohammad Alfaiz Khan-CSO Practical7kmohammadalfaizNo ratings yet
- 7660 Computer Maintenance and RepairDocument36 pages7660 Computer Maintenance and Repairlolmingani saipanyuNo ratings yet
- G9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardDocument10 pagesG9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardElke EstandianNo ratings yet
- Components of MotherboardDocument4 pagesComponents of MotherboardParitosh BelekarNo ratings yet
- It Workshop LAB MANUAL r16 ModifiedDocument45 pagesIt Workshop LAB MANUAL r16 ModifiedYoga VyshnaviNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: The Basic Building Block of a ComputerDocument7 pagesMotherboard: The Basic Building Block of a ComputerZeeshanNo ratings yet
- TVL CSS G11-Wlas-W1 - 2Document16 pagesTVL CSS G11-Wlas-W1 - 2Fern WehNo ratings yet
- MOTHERBOARD ELEMENTS GUIDEDocument2 pagesMOTHERBOARD ELEMENTS GUIDEMithz SuneNo ratings yet
- ITP421 WEEK 2 - MotherboardsDocument29 pagesITP421 WEEK 2 - MotherboardsJaira Mae DiazNo ratings yet
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocument39 pagesUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNo ratings yet
- Richard Anthony C. Rivera BSIT 2A (MT 7:00-8:30am)Document8 pagesRichard Anthony C. Rivera BSIT 2A (MT 7:00-8:30am)Richard Anthony RiveraNo ratings yet
- Millescent Kate DavilaDocument21 pagesMillescent Kate DavilaMillescent Kate DavilaNo ratings yet
- Tle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Document5 pagesTle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Rose FloresNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Parts and FunctionsDocument7 pagesMotherboard Parts and FunctionsZumokufu RyouchiiNo ratings yet
- Inside+a+Dell+Desktop+Computer Ovija+Document16 pagesInside+a+Dell+Desktop+Computer Ovija+Ovija SivanathanNo ratings yet
- System Unit Ports Slot FinalDocument10 pagesSystem Unit Ports Slot Finaldave vegafria100% (1)
- SSC - Ict10 - Q1 - W8 - Installing and Configuring Computer System 7Document9 pagesSSC - Ict10 - Q1 - W8 - Installing and Configuring Computer System 7Cielo Marie CastroNo ratings yet
- Hardware ServicingwdcaDocument14 pagesHardware ServicingwdcaNeil Joseph AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardDocument5 pagesComputer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardErickson JavonitallaNo ratings yet
- UC1 - Computer Parts (Part of Oral QuestioningDocument14 pagesUC1 - Computer Parts (Part of Oral QuestioningDlanor AvadecNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1Document9 pagesAssignment No.1asma abbasNo ratings yet
- CHTDocument45 pagesCHTRajesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Contoh Makalah Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesContoh Makalah Dalam Bahasa InggrisMerry ErawatiNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing NC II: PC Assembly and Hardware TroubleshootingDocument27 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing NC II: PC Assembly and Hardware TroubleshootingShie FanilagNo ratings yet
- Computer System ComponentsDocument11 pagesComputer System ComponentsNoone F. moonNo ratings yet
- CMN Lab Expt-1Document3 pagesCMN Lab Expt-1Aaryan SinghNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument20 pagesMotherboardJeyc RapperNo ratings yet
- System Board, Baseboard, Planar Board or Logic Board, or Colloquially, A Mobo) Is TheDocument5 pagesSystem Board, Baseboard, Planar Board or Logic Board, or Colloquially, A Mobo) Is TheluqmanNo ratings yet
- ItwslabDocument77 pagesItwslabKalyan Reddy AnuguNo ratings yet
- CHT Practical 1 KUKDocument3 pagesCHT Practical 1 KUKDhruv SharmaNo ratings yet
- And The Last One IsDocument4 pagesAnd The Last One IsSơn Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- CSS Quarterly Exam 1Document18 pagesCSS Quarterly Exam 1seph bronNo ratings yet
- Homework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetDocument14 pagesHomework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetJohn Kerby CorralNo ratings yet
- Parts of ComputerDocument2 pagesParts of ComputerCIANO, Dellaney Joy A.No ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris (1) KhafliDocument7 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris (1) KhafliHolisNo ratings yet
- Input Output ProcessDocument9 pagesInput Output ProcessElixa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Mining Machine ApplicationsDocument54 pagesReference Guide To Mining Machine ApplicationsYohanes WibowoNo ratings yet
- MTD Model 146S845H788 (Tmo 3399006) (1996) Parts ListDocument24 pagesMTD Model 146S845H788 (Tmo 3399006) (1996) Parts ListdgroffwaNo ratings yet
- DS-ZF 5355 PDFDocument5 pagesDS-ZF 5355 PDFGabriel Esteban González FrancoNo ratings yet
- ProductSpecialLights EngDocument32 pagesProductSpecialLights EngPT. Andara Prima UtamaNo ratings yet
- Contoh TroubleShooting RecordDocument3 pagesContoh TroubleShooting RecordJelski Hizkia IlatNo ratings yet
- M Series Spares Catalogue - Issue 7Document6 pagesM Series Spares Catalogue - Issue 7luongnamNo ratings yet
- MI 2892 Power Master AngDocument2 pagesMI 2892 Power Master Angvivek jayswalNo ratings yet
- Tranquility 27 (TT) Series Tranquility 20 (TS) Series Tranquility 16 (TC) Series Tranquility (TR) SeriesDocument84 pagesTranquility 27 (TT) Series Tranquility 20 (TS) Series Tranquility 16 (TC) Series Tranquility (TR) SeriesMichael MartinNo ratings yet
- Making A PCB: Report and PPT - PresentationDocument6 pagesMaking A PCB: Report and PPT - PresentationKaranSinghNo ratings yet
- Igo36 Product GuideDocument16 pagesIgo36 Product GuideHernando Acosta100% (1)
- Bentley Int Arnage 2007Document20 pagesBentley Int Arnage 2007Ian HarrisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 Av-334 MW TubesDocument13 pagesLecture 15 Av-334 MW TubesAli EmadNo ratings yet
- Awqaf Aae SD Hvac Mec 003 2Document1 pageAwqaf Aae SD Hvac Mec 003 2Ahmad Saleem AlawwadNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 3WL1350-4FG76-4GA4: ModelDocument5 pagesData Sheet 3WL1350-4FG76-4GA4: ModelSyed AhmedNo ratings yet
- MAIN DIFFERENCES Between TS44 and TFS Rev.3 May2018Document3 pagesMAIN DIFFERENCES Between TS44 and TFS Rev.3 May2018younesNo ratings yet
- Viessmann Data Logger DL2 BrochureDocument2 pagesViessmann Data Logger DL2 Brochuree-ComfortUSANo ratings yet
- Sanyo Denki 1Document351 pagesSanyo Denki 1kaosdelosandesNo ratings yet
- Weldcraft Full CatalogDocument28 pagesWeldcraft Full CatalogRoyal Friady HalimNo ratings yet
- Heavy-Duty Trailers and Cargotrailers: Common Sales and Service NetworkDocument4 pagesHeavy-Duty Trailers and Cargotrailers: Common Sales and Service NetworkWilman OngNo ratings yet
- LT9211 Datasheet R2.1Document18 pagesLT9211 Datasheet R2.1周勇No ratings yet
- Drawings All - 2017-06-23Document118 pagesDrawings All - 2017-06-23Syed IrtazaNo ratings yet
- Aq-H Relays: FeaturesDocument3 pagesAq-H Relays: Featuresmarcio carvalhoNo ratings yet
- 10,000 Psi Air/Hydraulic Foot Pump: ModelDocument14 pages10,000 Psi Air/Hydraulic Foot Pump: ModelBracken FlaglerwestNo ratings yet
- ABB-Adjustable Frequency Drives - SubmittalDocument25 pagesABB-Adjustable Frequency Drives - SubmittaljoseNo ratings yet
- FG Available Aug 12 2022Document78 pagesFG Available Aug 12 2022Mayra Olalde GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 2 Link Belt MG434 Service Manual EnglishDocument80 pages2 Link Belt MG434 Service Manual EnglishraulNo ratings yet
- 7055-3F - 7070-1F Catalog PDFDocument12 pages7055-3F - 7070-1F Catalog PDFPHÁT NGUYỄN THẾ100% (1)
- Varilight Catalogue PDFDocument58 pagesVarilight Catalogue PDFRavi AlagumalaiNo ratings yet