Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evelopment of EAM Quations: Chapter Objectives
Uploaded by
AHMED SHAKEROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evelopment of EAM Quations: Chapter Objectives
Uploaded by
AHMED SHAKERCopyright:
Available Formats
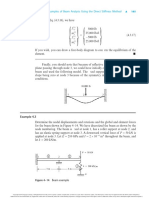
CHAPTER
4
DEVELOPMENT OF
BEAM EQUATIONS d
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES
. To review basic concepts of beam bending.
. To derive the stiffness matrix for a beam element.
. To demonstrate beam analysis using the direct stiffness method.
. To illustrate the effects of shear deformation in shorter beams.
. To introduce the work-equivalence method for replacing distributed loading by a
set of discrete loads.
. To introduce the general formulation for solving beam problems with distributed
loading acting on them.
. To analyze beams with distributed loading acting on them.
. To compare the finite element solution to an exact solution for a beam.
. To derive the stiffness matrix for the beam element with nodal hinge.
. To show how the potential energy method can be used to derive the beam ele-
ment equations.
. To apply Galerkin’s residual method for deriving the beam element equations.
Introduction
We begin this chapter by developing the stiffness matrix for the bending of a beam
element, the most common of all structural elements as evidenced by its prominence
in buildings, bridges, towers, and many other structures. The beam element is con-
sidered to be straight and to have constant cross-sectional area. We will first derive
the beam element stiffness matrix by using the principles developed for simple
beam theory.
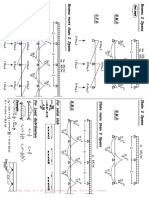
We will then present simple examples to illustrate the assemblage of beam
element stiffness matrices and the solution of beam problems by the direct stiffness
method presented in Chapter 2. The solution of a beam problem illustrates that the
degrees of freedom associated with a node are a transverse displacement and a rota-
tion. We will include the nodal shear forces and bending moments and the resulting
shear force and bending moment diagrams as part of the total solution.
166
Copyright 2010 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.
You might also like
- Work-Equivalence Method: 4.4 Distributed Loading DDocument1 pageWork-Equivalence Method: 4.4 Distributed Loading DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- General Formulation: 4.4 Distributed Loading DDocument1 pageGeneral Formulation: 4.4 Distributed Loading DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-13 Beam Example: 4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DDocument1 pageFigure 4-13 Beam Example: 4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- D 4 Development of Beam Equations: Figure 4-16 Fixed-Fixed Beam Subjected To Applied Force and MomentDocument1 pageD 4 Development of Beam Equations: Figure 4-16 Fixed-Fixed Beam Subjected To Applied Force and MomentAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DDocument1 page4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Distributed Loading: D 4 Development of Beam EquationsDocument1 page4.4 Distributed Loading: D 4 Development of Beam EquationsAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DDocument1 page4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DDocument1 page4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- D 4 Development of Beam EquationsDocument1 pageD 4 Development of Beam EquationsAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-10 Nodal Forces and Moment On The Beam: D 4 Development of Beam EquationsDocument1 pageFigure 4-10 Nodal Forces and Moment On The Beam: D 4 Development of Beam EquationsAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- D 4 Development of Beam EquationsDocument1 pageD 4 Development of Beam EquationsAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- D 4 Development of Beam EquationsDocument1 pageD 4 Development of Beam EquationsAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DDocument1 page4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness MethodDocument1 page4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness MethodAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DDocument1 page4.3 Examples of Beam Analysis Using The Direct Stiffness Method DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- D 4 Development of Beam EquationsDocument1 pageD 4 Development of Beam EquationsAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- D 4 Development of Beam EquationsDocument1 pageD 4 Development of Beam EquationsAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Beam Stiffness DDocument1 page4.1 Beam Stiffness DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- D 4 Development of Beam Equations: M X V XDocument1 pageD 4 Development of Beam Equations: M X V XAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Example of Assemblage of Beam Stiffness Matrices DDocument1 page4.2 Example of Assemblage of Beam Stiffness Matrices DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Beam Stiffness DDocument1 page4.1 Beam Stiffness DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Beam Stiffness DDocument1 page4.1 Beam Stiffness DAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 46 - (3rd Civil) Summary of Systems-1Document1 page46 - (3rd Civil) Summary of Systems-1AHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization: Submitted By, Dinesh.RDocument23 pagesSoil Stabilization: Submitted By, Dinesh.RAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- 46 - (3rd Civil) Summary of Systems-1Document1 page46 - (3rd Civil) Summary of Systems-1AHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Finite Difference MethodDocument16 pagesFinite Difference MethodMartua Mario100% (1)
- Exercise 5 - Network Diagram and Critical PathDocument4 pagesExercise 5 - Network Diagram and Critical PathRouda AldosariNo ratings yet
- Trapezoidal RuleDocument19 pagesTrapezoidal RuleShawn GonzalesNo ratings yet
- G7 Error Analysis Multi-Step EquationsDocument10 pagesG7 Error Analysis Multi-Step EquationsJulie BurkeNo ratings yet
- Plant Health Monitoring Using Digital Image Processing: By: Sivapriya.GDocument12 pagesPlant Health Monitoring Using Digital Image Processing: By: Sivapriya.Gsivapriya gNo ratings yet
- CONSYSDocument3 pagesCONSYSADITYA MATHURNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument3 pagesRegressionaraceliNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Control of Production Systems: Soci Igebiete: ....Document6 pagesAnalysis and Control of Production Systems: Soci Igebiete: ....Huricane TriangleNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Classifier SelectionDocument22 pagesDynamic Classifier SelectionYusuf YeşilyurtNo ratings yet
- ECM2105 Control: Prathyush P Menon, Christopher Edwards Date: 16-Jan-2014, Room H101Document9 pagesECM2105 Control: Prathyush P Menon, Christopher Edwards Date: 16-Jan-2014, Room H101Eduardo FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 392 T 1 W 12 SolnDocument2 pages392 T 1 W 12 SolnHongyi Frank LiangNo ratings yet
- Program 1Document25 pagesProgram 1Asif BadegharNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Books On Artificial IntelligenceDocument8 pagesTop 10 Books On Artificial IntelligenceZinny WorldNo ratings yet
- Introduction-Brownian-motion 230410 214901Document2 pagesIntroduction-Brownian-motion 230410 214901Gamma FactsNo ratings yet
- Differential Equation - DPP 01 - Saakaar Batch For IIT JAM MathematicsDocument3 pagesDifferential Equation - DPP 01 - Saakaar Batch For IIT JAM MathematicsSadhana YadavNo ratings yet
- SL AA Prob Distributions IBQsDocument6 pagesSL AA Prob Distributions IBQsjleodennisNo ratings yet
- Lupis Chemical Thermodynamics of Materials 1983Document598 pagesLupis Chemical Thermodynamics of Materials 1983Anonymous 9rJe2lOskx100% (5)
- Sequential Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pagesSequential Circuit AnalysismankindaNo ratings yet
- COMS 6998 Lec 1Document8 pagesCOMS 6998 Lec 1vejifon253No ratings yet
- A FEC Decoding in LTE and WiMAX SystemsDocument4 pagesA FEC Decoding in LTE and WiMAX SystemsseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Witches' Brew: Industrial Scale Data Poisoning Via Gradient MatchingDocument21 pagesWitches' Brew: Industrial Scale Data Poisoning Via Gradient MatchingsdasdNo ratings yet
- Department of The Navy: Chief Information Officer 1000 Navy Pentagon WASHINGTON DC 20350-1000Document3 pagesDepartment of The Navy: Chief Information Officer 1000 Navy Pentagon WASHINGTON DC 20350-1000FedScoopNo ratings yet
- Turbo Codes Decoding AppsDocument13 pagesTurbo Codes Decoding AppslakshmigajendranNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication S. HaykinDocument79 pagesDigital Communication S. HaykinasddNo ratings yet
- Journal of Statistical Software: Presiduals: An R Package For Residual AnalysisDocument27 pagesJournal of Statistical Software: Presiduals: An R Package For Residual AnalysisRomualdoNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics (CSE 4103)Document34 pagesComputer Graphics (CSE 4103)Atik Israk LemonNo ratings yet
- Antenna Azimuth Position Control System Using PIDDocument12 pagesAntenna Azimuth Position Control System Using PIDAyumuNo ratings yet
- IME672 - Lecture 48Document21 pagesIME672 - Lecture 48Himanshu BeniwalNo ratings yet
- NLP PG Syllabus 2023Document3 pagesNLP PG Syllabus 2023rjoshittaNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin Dataiku 190330145244Document36 pagesBitcoin Dataiku 190330145244Sushant RanadeNo ratings yet