Professional Documents
Culture Documents
U2A1 Equations of Lines in 3
Uploaded by
uyenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
U2A1 Equations of Lines in 3
Uploaded by
uyenCopyright:
Available Formats
U2A1:
Equations of Lines in 2-Space
Saturday, October 23, 2021 10:05 PM
Review - The Scalar Equation of a Line in 2-Space
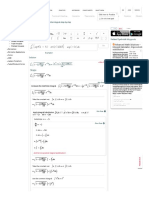
Example: Determine an equation of the line through the point A(-1,3) with
slope 2.
!
Example: Determine an equation of the line with slope and passing
"
through the point (-1, 2).
The Vector Equation of a Line in 2 Space
In order to determine a straight line it is enough to specify a point on the line and a vector
parallel to the line. The vector is called a direction vector for the line.
Every point in the Cartesian plane is associated with an ordered pair of numbers called the
coordinates. A vector drawn from the origin to the point at the head of the vector is called a
position vector.
Example:
Determine a vector equation for the line through 𝐴(−1,2) with direction
vector 𝑚
))⃗ = (3, 1).
Example:
Why is it possible to have many different vector equations for this line?
Example:
Determine a vector equation for the line through 𝑃# = (2, −1) with
direction vector 𝑚
))⃗ = (4, 3).
Example:
Determine three points on the line 𝑟⃗ = (2, −1) + 𝑡(4, 3).
The Parametric Equations of a Line in 2-Space
Example:
Determine parametric equaJons for the line 𝑟⃗ = (−1, 3) + 𝑡(1, 2).
Example:
Determine the vector and parametric equations for the line through the
points A(1, -3) and B(4,1).
Example:
What are the parametric equations for the line with vector equation 𝑟⃗ =
(2, −1) + 𝑡(4, 3)?
Making Connections between the Scalar and Vector Equations of a Line
You can use the vector or parametric equations to find two points on the
line.
Example:
Find a scalar equation for the line with vector equation 𝑟⃗ = (2, −1) +
𝑡(4, 3).
The scalar equation can also be determined from the parametric equations
by solving each equation for t.
Example:
Find a scalar equation for the line with parametric equations x = 1 – 2t, y =
2 + 3t.
The scalar equation can also be determined by using a vector that is
perpendicular to the line.
Example:
Find a scalar equation for the line with vector equation 𝑟⃗ = (2, −1) +
𝑡(4, 3).
Example:
Determine a scalar equation for the line through 𝑃# = (−1, 2) and parallel
to the line with equations x = 1 + 2t, y = 2 – 3t.
Example:
Determine a scalar equation for the line with vector equation 𝑟⃗ = (2, 5) +
𝑡(3, −1).
Example:
Find a vector equation for the line with scalar equation 3x – 2y + 6 = 0.
Example:
A scalar equation of a line is 2x – 3y + 12 = 0. Determine a vector equation
for this line.
You might also like
- Electromagnetic Fields and WavesDocument96 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and WavesTrevor100% (1)
- Engineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves 2nd Edition PDFDocument638 pagesEngineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves 2nd Edition PDFxieapi88% (42)
- Vector and Tensor Analysis with ApplicationsFrom EverandVector and Tensor Analysis with ApplicationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Introduction To Calculus of Vector FieldsDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Calculus of Vector Fieldssalem aljohiNo ratings yet
- Principal Roots of Rational and Irrational Week 6Document13 pagesPrincipal Roots of Rational and Irrational Week 6Khenchy FalogmeNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument60 pagesAnalytic GeometryLouise Umali100% (1)
- Math Grade 9 Q1 Module 2.solving Quadratic Equations 2Document12 pagesMath Grade 9 Q1 Module 2.solving Quadratic Equations 2Princess Jovelyn Gutierrez100% (1)
- Louis H. Kauffman - Remarks On Formal Knot TheoryDocument37 pagesLouis H. Kauffman - Remarks On Formal Knot TheoryOkommNo ratings yet
- Tensor Analysis-Chapter 1Document81 pagesTensor Analysis-Chapter 1qftgaugeNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis: 1.1 Scalars and VectorsDocument9 pagesVector Analysis: 1.1 Scalars and VectorsJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Full Math 102 NotesDocument104 pagesFull Math 102 NotesBrutus LutusNo ratings yet
- Index: Electromagnetic Field Theory Lab File SESSION 2020-21Document31 pagesIndex: Electromagnetic Field Theory Lab File SESSION 2020-21archanaNo ratings yet
- Cartesian Vector FormatDocument11 pagesCartesian Vector FormatSherzod DosmetovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document47 pagesChapter 01Ye NoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Guide in Vector AnalysisDocument13 pagesLecture Guide in Vector AnalysiskennethNo ratings yet
- L2 Vector AlgebraDocument28 pagesL2 Vector AlgebraRyan Jhay YangNo ratings yet
- Geometry 03Document10 pagesGeometry 03GabiandoNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics I (Lecture - Notes)Document318 pagesApplied Mathematics I (Lecture - Notes)Hadera GebremariamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-SpaceDocument68 pagesChapter 3 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-SpacesugandirezifNo ratings yet
- Physics 11th Unit 2 KinematicsDocument31 pagesPhysics 11th Unit 2 Kinematicsvisiblemotivation7No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 MaaDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 1 Maasisinamimi62No ratings yet
- Planar Transformations and DisplacementsDocument33 pagesPlanar Transformations and DisplacementsRizi AdhityaNo ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument113 pagesVector CalculusHergene FanerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Vector GeometryDocument86 pagesChapter 4 - Vector Geometrycondoleeza smithNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Vector AlgebraDocument166 pagesIntroduction and Vector Algebra357911No ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument3 pagesThree Dimensional Co-Ordinate GeometrybabaigoswamiNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Three Dimensional GeometryDocument41 pagesCh-11 Three Dimensional Geometryjaved alamNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional GeometryDocument41 pagesThree Dimensional GeometryJhulphiya JafarullahNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - 5 NotesDocument76 pagesWeek 3 - 5 NotesPatrick LauNo ratings yet
- 3 - Dimensional Geometry - Day - 4: Equation of A Line in Three DimensionsDocument6 pages3 - Dimensional Geometry - Day - 4: Equation of A Line in Three Dimensionsmanisha choudharyNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis: 1.1 Scalars and VectorsDocument9 pagesVector Analysis: 1.1 Scalars and VectorsJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis: 1.1 Scalars and VectorsDocument9 pagesVector Analysis: 1.1 Scalars and VectorsJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2.-DikonversiDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 2.-DikonversiHardianti EkaputriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Vectors: 1 Learning OutcomesDocument20 pagesChapter 6 Vectors: 1 Learning OutcomesElizabeth SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Vector AlgebraDocument3 pagesVector AlgebraanhhuyalexNo ratings yet
- Module1 ACEE4EmagsDocument21 pagesModule1 ACEE4Emagsjosephryanbeloria45No ratings yet
- Chapter No. 2 (F)Document27 pagesChapter No. 2 (F)riffatrasheedseseNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 2 First Year NotesDocument39 pagesChapter No. 2 First Year Notesmuhammad ilyasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics (EM) - The Study of Electric and Magnetic PhenomenaDocument12 pagesElectromagnetics (EM) - The Study of Electric and Magnetic Phenomenadesmond_fren4ever9522No ratings yet
- 1 Vector Analysis Algebra and Basics of Vector SY 2020 2021 SampleDocument49 pages1 Vector Analysis Algebra and Basics of Vector SY 2020 2021 SampleMarc RiveraNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Dirac Delta FunctionDocument39 pagesVectors and Dirac Delta FunctionSubrata RakshitNo ratings yet
- Elliot Benjamin and C. Snyder - On The Construction of The Regular Hendecagon by Marked Ruler and CompassDocument17 pagesElliot Benjamin and C. Snyder - On The Construction of The Regular Hendecagon by Marked Ruler and CompassEduardo MullerNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Vectors in The Plane (2-D)Document24 pages1.1 Vectors in The Plane (2-D)M Venter KheeNo ratings yet
- Math 101a - Topic 2Document6 pagesMath 101a - Topic 2Takashi TiteNo ratings yet
- Math 101a - Topic 2Document6 pagesMath 101a - Topic 2Takashi TiteNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics (EM) - The Study of Electric and Magnetic PhenomenaDocument34 pagesElectromagnetics (EM) - The Study of Electric and Magnetic PhenomenablindwidowNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 PackDocument25 pagesUnit 8 Pack11zeshan11No ratings yet
- AETN3111-L3-Vector AnalysisDocument42 pagesAETN3111-L3-Vector Analysissonahassan70007No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Vectors inDocument62 pagesChapter 3 Vectors inAdo ElnandoNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ApparatusDocument31 pagesMathematical Apparatus140557No ratings yet
- 3D-PPt MODULE 1Document12 pages3D-PPt MODULE 1AYASHA DASNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CoordinatesDocument13 pagesChapter 8 CoordinatesWei ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CoordinatesDocument15 pagesChapter 8 CoordinatesMadihah RamlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document48 pagesChapter 2KelleyNo ratings yet
- Barron's SAT Subject Test Physics-Pages-64-77Document14 pagesBarron's SAT Subject Test Physics-Pages-64-77JohanNo ratings yet
- Applied1-Unit1 - vectors-2011ECDocument33 pagesApplied1-Unit1 - vectors-2011ECTadesseNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Vector Analysis and Coordinate Geometry 9350843145 9789350843147 CompressDocument204 pagesTextbook of Vector Analysis and Coordinate Geometry 9350843145 9789350843147 Compressmirzazobaer42No ratings yet
- Applying Marxist Literary Theory To HamletDocument3 pagesApplying Marxist Literary Theory To HamletuyenNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue Growth Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesPlant Tissue Growth Worksheet AnswersuyenNo ratings yet
- Personal Reflection On Democracy in Canada: Greece. in A Democratic Society, Minority Rights Are Protected by The LawsDocument1 pagePersonal Reflection On Democracy in Canada: Greece. in A Democratic Society, Minority Rights Are Protected by The LawsuyenNo ratings yet
- Receipt - Novel Essay - Ella Minnow PeaDocument2 pagesReceipt - Novel Essay - Ella Minnow Peauyen0% (2)
- Cell Division MitosisDocument41 pagesCell Division MitosisuyenNo ratings yet
- SNC 1D0 Name: - Atoms & Elements Date: - Unit TestDocument5 pagesSNC 1D0 Name: - Atoms & Elements Date: - Unit TestuyenNo ratings yet
- Investigating Whether Mass Is Conserved in A Reaction by Zoe TruongDocument7 pagesInvestigating Whether Mass Is Conserved in A Reaction by Zoe TruonguyenNo ratings yet
- Learn Korean Ep. 83: "Decide To Do": Past TenseDocument4 pagesLearn Korean Ep. 83: "Decide To Do": Past TenseuyenNo ratings yet
- Learn Korean Ep. 28: Verb Endings (Part 2)Document3 pagesLearn Korean Ep. 28: Verb Endings (Part 2)uyenNo ratings yet
- Markus Persson: "I Think The Only Way I Could Make Something Fun and Big Is If I Don't Expect It To Be." Markus PerssonDocument9 pagesMarkus Persson: "I Think The Only Way I Could Make Something Fun and Big Is If I Don't Expect It To Be." Markus PerssonuyenNo ratings yet
- Your Time: NameDocument2 pagesYour Time: NameuyenNo ratings yet
- Directorate of Learning Systems: Distance Education ProgrammeDocument21 pagesDirectorate of Learning Systems: Distance Education ProgrammeuyenNo ratings yet
- X: An Uncertain: Key People That Made A DifferenceDocument4 pagesX: An Uncertain: Key People That Made A DifferenceuyenNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems: DiagramsDocument1 pageBiology Unit Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems: DiagramsuyenNo ratings yet
- Political Cartoon AnalysisDocument6 pagesPolitical Cartoon AnalysisuyenNo ratings yet
- Mitosis ReviewDocument2 pagesMitosis ReviewuyenNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Special Occasions: 1. Occasion (N.)Document2 pagesUnit 4: Special Occasions: 1. Occasion (N.)uyenNo ratings yet
- Biology 30 Student Notes Cells Genetics PopulationDocument47 pagesBiology 30 Student Notes Cells Genetics PopulationuyenNo ratings yet
- OrbitCube 05052010Document57 pagesOrbitCube 05052010JackophiliNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis For VAR SystemsDocument11 pagesStability Analysis For VAR SystemsCristian CernegaNo ratings yet
- College Mathematics For Business Economics Life Sciences and Social Sciences 13th Edition Barnett Solutions Manual 1Document78 pagesCollege Mathematics For Business Economics Life Sciences and Social Sciences 13th Edition Barnett Solutions Manual 1steve100% (34)
- Sparse MatrixDocument13 pagesSparse Matrixstudy.ruby1568No ratings yet
- HTTP Tutorial Math Lamar Edu Classes Alg GraphRationalFcns AspxDocument8 pagesHTTP Tutorial Math Lamar Edu Classes Alg GraphRationalFcns AspxAkash TutiNo ratings yet
- MITx - 18.03Fx - DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS - FOURIER SERIES AND PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONSDocument5 pagesMITx - 18.03Fx - DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS - FOURIER SERIES AND PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONSAyur TadimallaNo ratings yet
- Definite Integral Calculator - SymbolabDocument2 pagesDefinite Integral Calculator - SymbolabRichie ChanNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 23 Oct 2022Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 23 Oct 2022Aditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Index Laws RevisionDocument4 pagesIndex Laws RevisionMaria Rajendran M100% (1)
- 4026Q1 Specimen Additional MathsDocument16 pages4026Q1 Specimen Additional MathsBlessed Endibye KanyembaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Day 5 - 6Document12 pagesWorksheet Day 5 - 6jagannivasNo ratings yet
- Abra Kadabra Algebra!: Content UnderstandingDocument22 pagesAbra Kadabra Algebra!: Content UnderstandingRAE ANN INESNo ratings yet
- Notes: 1.1 Backwards and Forward Kolmogorov EquationsDocument3 pagesNotes: 1.1 Backwards and Forward Kolmogorov Equationsxi shengNo ratings yet
- Ishan Paper 2 2 ChaptersDocument2 pagesIshan Paper 2 2 ChaptersSANKET MEHTANo ratings yet
- 2.image GeometryDocument31 pages2.image GeometrySrikanth Goud NagelliNo ratings yet
- Instructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaDocument8 pagesInstructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaAndrea Rabago AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Ms. Katrina Boticario (Teacher Kath)Document29 pagesMs. Katrina Boticario (Teacher Kath)Keahlyn BoticarioNo ratings yet
- Multiple Regression Model - Matrix FormDocument22 pagesMultiple Regression Model - Matrix FormGeorgiana DumitricaNo ratings yet
- Complex NoDocument37 pagesComplex NoSripati Jha100% (1)
- Addmath Part 1 - AmendedDocument23 pagesAddmath Part 1 - Amendednorazily81No ratings yet
- Module 5Document57 pagesModule 5Nasrul ZairiNo ratings yet
- Book by Jaromir KubenDocument523 pagesBook by Jaromir Kubenkothapalli21No ratings yet
- Soalan Set 9Document11 pagesSoalan Set 9Muhammad Zaid SabriNo ratings yet
- Math 225 Linear Algebra II Lecture Notes: John C. Bowman University of Alberta Edmonton, CanadaDocument61 pagesMath 225 Linear Algebra II Lecture Notes: John C. Bowman University of Alberta Edmonton, CanadaNir PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDocument6 pages8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardNo ratings yet
- Lap 2-3 SummaryDocument1 pageLap 2-3 Summaryshan darylNo ratings yet
- Exercise 03Document5 pagesExercise 03gfjggNo ratings yet
- 08 Matrix Transformations - IIDocument26 pages08 Matrix Transformations - IISadiqNo ratings yet