Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
Ameer Alawadi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
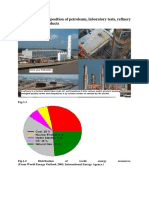
14 views18 pagesThis document summarizes 9 common chemical processes used in petrochemical industries: 1) thermal cracking, 2) catalytic cracking, 3) hydrocracking, 4) thermal reforming, 5) catalytic reforming, 6) hydrogen treatment, 7) alkylation, 8) isomerization, and 9) polymerization. For each process, the document provides a brief description of the chemical reactions involved and typical operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, and catalysts used. The overall purpose of these processes is to produce useful hydrocarbon products from crude oil through breaking carbon chains and molecular rearrangements.
Original Description:
Original Title
CHAPTER 7-converted(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes 9 common chemical processes used in petrochemical industries: 1) thermal cracking, 2) catalytic cracking, 3) hydrocracking, 4) thermal reforming, 5) catalytic reforming, 6) hydrogen treatment, 7) alkylation, 8) isomerization, and 9) polymerization. For each process, the document provides a brief description of the chemical reactions involved and typical operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, and catalysts used. The overall purpose of these processes is to produce useful hydrocarbon products from crude oil through breaking carbon chains and molecular rearrangements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views18 pagesChapter 7
Uploaded by
Ameer AlawadiThis document summarizes 9 common chemical processes used in petrochemical industries: 1) thermal cracking, 2) catalytic cracking, 3) hydrocracking, 4) thermal reforming, 5) catalytic reforming, 6) hydrogen treatment, 7) alkylation, 8) isomerization, and 9) polymerization. For each process, the document provides a brief description of the chemical reactions involved and typical operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, and catalysts used. The overall purpose of these processes is to produce useful hydrocarbon products from crude oil through breaking carbon chains and molecular rearrangements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Chemical Engineering Department
Petroleum and Gas Technology
(Second stage)
Lecturer: Eng. Firas Jamal
Lecture-10
Chapter 7
Chemical Processes in Petrochemicals Industries
Chemical processes in the petrochemical industries
The petroleum industries containing some of chemical
processes, in which occur chemical reaction or changing in
chemical structure, in petroleum products to produced a
new hydrocarbons, not found originally in crude oil. These
chemical processes now become very important in
petrochemical industries.
The common chemical processes
1- Thermal Cracking. 2- Catalytic Cracking.
3- Hydrocracking. 4- Thermal Reforming.
5- Catalytic Reforming. 6- Hydrogen Treatment.
7- Alkylation. 8- Isomerization.
9- Polymerization.
1- Thermal Cracking:
In thermal cracking process, the heavier hydrocarbon
molecules ( high boiling point oils) break into lighter
products ( paraffin and olefin ) smaller than
originally molecules as following :
The thermal cracking process are used to produced high
quantities from best automobiles fuel as above reaction is
producing pentene and hexane (gasoline) which is used for
automobiles fuel. The operating condition for thermal
cracking are ( 700 – 800 ) oC and ( 10 – 25 ) atm.
2- Catalytic Cracking:
The catalytic cracking process is a mainly process to
produced the raw materials for many petrochemical
industries and good gasoline from heavy petroleum
fractions such as gas oil.
The operating conditions are ( 450 – 550 ) oC, ( 1- 2 ) atm.
The catalysts used are :
I-Natural Clays.
II-Aluminum Silicate( Zeolite )( 87.5 % SiO2 + 12.5 % Al2O3).
III-Sodium Aluminum Silicate with molecular sieves
structure.
3-Hydrocracking
Hydrocracking is a catalytic cracking process
assisted by the presence of an elevated
partial pressure of hydrogen with
temperature (350 –450) °C and pressures of
(50–150 atm). The catalyst used could be
Sodium AluminoSilicate (Al2O3-SiO2 )-Na.
We can change sodium element by another
elements such as (Tungsten W , Cobalt Co ,
Molybdenum Mo , palladium Pd , Nickel Ni ).
This process widely used in refineries to convert
heavy oil fractions into high quality middle
distillates and light products. In this process high
molecular weight molecules are broken to form
lighter compounds.
Major products from hydrocracking are jet fuel,
diesel, relatively high-octane gasoline fractions,
and LPG.
4- Thermal Reforming:
Thermal reforming process is consider a development
for thermal cracking process. The process change the
molecular rearrangement of a low octane naphtha
to form high-octane naphtha (converts linear
hydrocarbons (paraffins) into branched alkanes
(isoparaffins) and cyclic naphthenes) by exposing the
materials to high temperatures and pressures.
The operating condition are:
( 550 ) oC and ( 85-95 ) atm.
5- Catalytic Reforming:
• The catalytic reforming is very important in
petrochemicals industries. It is a chemical process used
to convert petroleum refinery naphthas distilled from
crude oil (typically having low octane ratings) into high-
octane liquid products called reformates. The process
converts low-octane linear hydrocarbons (paraffins)
into branched alkanes (isoparaffins) and cyclic
naphthenes
• The operating conditions are ( 460-525 ) oC, ( 8.5- 12.5 )
atm.
• The catalysts used are :
I- 5 wt% Co / Al2O3 ( Cobalt / Alumina ).
II- 1 wt% Pd / Al2O3 ( Palladium / Alumina ).
III- 1 wt% Rh / Al2O3 ( Rhenium / Alumina ).
IV- 10 wt% Mo / Al2O3 ( Molybdenum / Alumina
V-10 wt% Mo /( SiO2- Al2O3 )( Molybdenum /Silica –Alumina).
VI- 0.5 wt% Pt / Al2O3 ( Platinum / Alumina ).
VII- 0.5 wt% Pt / ( SiO2-Al2O3 ) ( Platinum / Silica – Alumina ).
VIII- 5 wt% Ni / ( Al2O3 ) ( Nickel / Alumina ).
IX- 5 wt% Ni / ( SiO2 ) ( Nickel / Silica ).
X- 5 wt% Ni / ( SiO2-Al2O3 ) ( SiO3 / Silica – Alumina ).
Note: The formula ( 5 wt% Ni / ( Al2O3 ) ) meaning the Nickel
element weight is 5% from total weight of catalyst and the
nickel element support on aluminum oxide.
6- Hydrogen Treatment:
Hydrogen treatment process is used to removal
the sulphur and nitrogen compounds, cracking the
carbons chains by hydrogenation ( converted the
double bonds to single bonds ). The operating
conditions are ( 400 – 510 ) oC, ( 20 – 45 ) atm
and catalyst is ( Platinum / Silica – Alumina )
Pt / ( SiO2-Al2O3 ).
7- Alkylation :
Alkylation reactions used when reaction between
isoparaffin's and iso olefins to produce important
products.
The operating conditions are ( 25 – 45 ) oC, ( 1 ) atm.
the catalysts are Sulphuric acid H2SO4, Hydrofluoric acid
HF, phosphoric acid H3PO4 and Aluminum chloride
AlCl3. Alkylation process used to :
1- Good fuel production for automobiles and aircraftl.
2- Raw materials production for petrochemicals.
8- Isomerization :
Isomerization is the process by which one molecule is
transformed into another molecule which has exactly
the same atoms, but the atoms have a different
arrangement.
e.g. A-B-C → B-A-C
Isomerization process is important process in
petrochemicals industries which is useful to obtain of
iso composites with highly octane number.
9- Polymerization :
Polymerization process occurred usually when
reaction between two or more molecules to produced
molecule with high molecular weight. The operating
conditions are (175 – 250 ) oC , ( 1000 ) atm. the
catalysts are ( Silica - Sulphuric acid ) ( SiO2-H2SO4 ) or
( Silica – Phosphoric acid ) ( SiO2-H3PO4 ).
The polymerization mainly divided to two types are :
1- Condensation Polymerization:
It occurred between molecules which have functional
groups such as hydroxyl (R-OH) , carboxyl (R-COOH) and
ammine groups (R-NH2).
2- Addition Polymerization:
It occurred between molecules which have double
bonds such as ethylene ( CH2= CH2 ).
Thank you
You might also like
- 7 - OligomerizationDocument16 pages7 - OligomerizationAn Lê TrườngNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Crude FractionatorDocument3 pagesAtmospheric Crude Fractionatornedian_2006No ratings yet
- Thermal and Catalytic Convesion ProcessDocument54 pagesThermal and Catalytic Convesion ProcessSaiPavanNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Technology Two MarkDocument26 pagesPetroleum Technology Two Markdhanagopal saiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledapi-256504985No ratings yet
- Simple Guide To Oil RefiningDocument5 pagesSimple Guide To Oil RefiningPatel AshokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3indumathijayakaranNo ratings yet
- Purifier Maintenance 1Document54 pagesPurifier Maintenance 1Noel Nico FernandoNo ratings yet
- Catalytic CrackingDocument43 pagesCatalytic Crackingjeygar12100% (2)
- Inf Ufc 85Document13 pagesInf Ufc 85Luciano Montellano Abasto100% (2)
- Refinery Overview: Dalia Mamoun Beshir MohamedDocument8 pagesRefinery Overview: Dalia Mamoun Beshir MohamedNihad S ZainNo ratings yet
- Cracking DefinitionDocument4 pagesCracking Definitionasim zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Technology of PetroleumDocument83 pagesChemistry and Technology of PetroleumManish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refining ProcessDocument11 pagesPetroleum Refining ProcessRawsht MuradyNo ratings yet
- Group WorkDocument4 pagesGroup WorkRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Petroleum ProcessingDocument37 pagesPetroleum ProcessingKaycelyn BacayNo ratings yet
- Naptha Hydrotreating UnitDocument7 pagesNaptha Hydrotreating UnitreetiNo ratings yet
- 1 - OverviewDocument61 pages1 - Overviewalexia183No ratings yet
- Petroleum: Chemistry and Technology OFDocument83 pagesPetroleum: Chemistry and Technology OFMohamed MoüsaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Technology-Part Iii: The Process & Technology of CrackingDocument23 pagesPetroleum Technology-Part Iii: The Process & Technology of CrackingSrikrishnan KrishNo ratings yet
- CrackingDocument32 pagesCrackingMuhammad HAmAd QureshiNo ratings yet
- PERP Program - Formaldehyde and Derivatives New Report AlertDocument9 pagesPERP Program - Formaldehyde and Derivatives New Report AlertArjunLohanNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Cracking: Cat Products Become Feed To Other Units, Such As Alkylation andDocument13 pagesCatalytic Cracking: Cat Products Become Feed To Other Units, Such As Alkylation andPriscilaPrzNo ratings yet
- Petroleum RefiningDocument32 pagesPetroleum RefiningShashank Tewari100% (14)
- Introduction To PetrochemistryDocument89 pagesIntroduction To PetrochemistrySYARMIMI YUSOFNo ratings yet
- التقريرDocument15 pagesالتقريرياسر سليمانNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Petroleum IndustriesDocument55 pagesNatural Gas Petroleum IndustriesBalqis yasinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Petroleum Technology - 3Document21 pagesIntroduction To Petroleum Technology - 3Anish VazeNo ratings yet
- Franz Fischer Hans Tropsch 1923 1925Document31 pagesFranz Fischer Hans Tropsch 1923 1925Jayakaran PachiyappanNo ratings yet
- Oil-Degassing:: 1-SeparationDocument34 pagesOil-Degassing:: 1-SeparationAhmed AbdullaNo ratings yet
- PetroluemDocument37 pagesPetroluemAhmed AbdullaNo ratings yet
- 2008-04 COLOHydroAromatic MustangDocument10 pages2008-04 COLOHydroAromatic MustangGarry DavidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RefineryDocument6 pagesIntroduction To RefinerydyarNo ratings yet
- Alkylation, Isomerisation and PolymerisationDocument9 pagesAlkylation, Isomerisation and Polymerisationapi-256504985No ratings yet
- Delayed Coking Process1Document69 pagesDelayed Coking Process1amalhaj2013100% (1)
- Coking and Thermal ProcessDocument26 pagesCoking and Thermal Processkuldeep100% (3)
- Module 3: Liquid Fossil Fuel (Petroleum) Lecture 20: Secondary ProcessingDocument8 pagesModule 3: Liquid Fossil Fuel (Petroleum) Lecture 20: Secondary Processingapi-256504985No ratings yet
- OrganiconeDocument33 pagesOrganiconeAbraham AsefaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocracking TechnologyDocument11 pagesHydrocracking TechnologyAsad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Guide To Refinery ProcessDocument131 pagesGuide To Refinery Processvazzoleralex6884100% (2)
- CHE 417 - Module II Unit Processes in Petroleum Refining - 2019-2020 - ModulDocument18 pagesCHE 417 - Module II Unit Processes in Petroleum Refining - 2019-2020 - ModulOmonusi OmoladeNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24 BCHE314L TH VL2023240501233 2024-02-19 Reference-Material-IDocument75 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BCHE314L TH VL2023240501233 2024-02-19 Reference-Material-IamitheserathinasamyNo ratings yet
- Coking and Thermal ProcessesDocument8 pagesCoking and Thermal ProcessesWulandariNo ratings yet
- Merged 429 8-13Document9 pagesMerged 429 8-13shubhamNo ratings yet
- Can Be Used in SI-engines, To Increase The Resistance To Knock Not Suitable For CI-engines DueDocument21 pagesCan Be Used in SI-engines, To Increase The Resistance To Knock Not Suitable For CI-engines Duesagar shinkarNo ratings yet
- Avu and Dhdsw2003Document24 pagesAvu and Dhdsw2003Kaustav Nayak100% (1)
- Steam ReformingDocument5 pagesSteam ReformingAshok S. PathakNo ratings yet
- Thermal Cracking To Catalytic CrackingDocument21 pagesThermal Cracking To Catalytic Crackingrupapara.fch22No ratings yet
- Processing of Petroleum-1000 PDFDocument12 pagesProcessing of Petroleum-1000 PDFhgbv tttbNo ratings yet
- PetrochemicalsDocument72 pagesPetrochemicalsSaiPavanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chemistry-Crude Oil and AmmoniaDocument40 pagesUnit 2 Chemistry-Crude Oil and AmmoniacrystalNo ratings yet
- 002 Lecture OverView Refinery Lecture B W 002Document87 pages002 Lecture OverView Refinery Lecture B W 002Hassan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Production OF Formaldehyde: Oil & Gas Processing TechnologyDocument25 pagesProduction OF Formaldehyde: Oil & Gas Processing TechnologyBhinitha ChandrasagaranNo ratings yet
- Dcu IipDocument53 pagesDcu Iipmujeebmehar75% (4)
- Heavy and Extra-heavy Oil Upgrading TechnologiesFrom EverandHeavy and Extra-heavy Oil Upgrading TechnologiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Handbook of Transition Metal Polymerization CatalystsFrom EverandHandbook of Transition Metal Polymerization CatalystsRay HoffNo ratings yet
- Nanoporous Catalysts for Biomass ConversionFrom EverandNanoporous Catalysts for Biomass ConversionFeng-Shou XiaoNo ratings yet
- Liquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionFrom EverandLiquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Chapter 8Document17 pagesChapter 8Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- United States Design Patent (10) Patent No.:: US D716,698 SDocument7 pagesUnited States Design Patent (10) Patent No.:: US D716,698 SAmeer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 3Document14 pagesChapter 1 3Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Department Petroleum and Gas Technology (Second Stage) Lecturer: Eng. Firas JamalDocument31 pagesChemical Engineering Department Petroleum and Gas Technology (Second Stage) Lecturer: Eng. Firas JamalAmeer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document31 pagesChapter 4Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-2Document18 pagesChapter 2-2Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- CDEtbe Technology ProfileDocument2 pagesCDEtbe Technology ProfiledharmayogaNo ratings yet
- We Have A Problem With Our Hydrocracker VGO FeedDocument2 pagesWe Have A Problem With Our Hydrocracker VGO FeedAshwani KumarNo ratings yet
- 2001mars Society Convention Part 3Document180 pages2001mars Society Convention Part 3daver2tarletonNo ratings yet
- PetroChemical Industry Semester2Document67 pagesPetroChemical Industry Semester2احمد حمید کارسول عزیزNo ratings yet
- Feedstock Recycling and PyrolysisDocument27 pagesFeedstock Recycling and PyrolysisacornaimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction - Fundamental Petroleum Engineering, UTMDocument90 pagesChapter 1 Introduction - Fundamental Petroleum Engineering, UTMNurzanM.Jefry100% (10)
- Mercury Removal in Hydrocarbon Streams - JM Catalysts - PTQ Article PDFDocument7 pagesMercury Removal in Hydrocarbon Streams - JM Catalysts - PTQ Article PDFpsnmurthy333No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes (Organic Chem)Document6 pagesChemistry Notes (Organic Chem)Teo Jia Ming NickolasNo ratings yet
- Steam Cracking Olefins PDFDocument47 pagesSteam Cracking Olefins PDFeltipovalencia100% (1)
- Virtual Refinery ManualDocument14 pagesVirtual Refinery Manualpeng88ap100% (1)
- MSDW Mwi Maxsat WebpagepdfDocument5 pagesMSDW Mwi Maxsat Webpagepdfdonald55555No ratings yet
- Blue Smoke EmissionsDocument24 pagesBlue Smoke Emissionswilliam alachanNo ratings yet
- SSSPDocument68 pagesSSSPPrashant NirpharakeNo ratings yet
- 21st Refinery Technology Meet - The CompendiumDocument474 pages21st Refinery Technology Meet - The CompendiumAnurag Ingle100% (5)
- (CSEC Chemistry) Section B Notes and ESQsDocument45 pages(CSEC Chemistry) Section B Notes and ESQsNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- Temperature Control of Edc Thermal Cracking Furnace With A Coupled Ode and 2D-Pdes ModelDocument6 pagesTemperature Control of Edc Thermal Cracking Furnace With A Coupled Ode and 2D-Pdes ModelJUNAID RAFEYNo ratings yet
- 0620 - s05 - QP - 2. Chemistry O LevelDocument16 pages0620 - s05 - QP - 2. Chemistry O LeveltiffaNo ratings yet
- UOP H2 StudiesDocument12 pagesUOP H2 StudiesKokil JainNo ratings yet
- HDPE Production Via Slurry-Loop ProcessDocument1 pageHDPE Production Via Slurry-Loop ProcessBramJanssen76100% (1)
- PVC Green ProcessDocument21 pagesPVC Green Processburus_648558271100% (1)
- SCE3103 Exploring Materials: Topic 2: FuelDocument29 pagesSCE3103 Exploring Materials: Topic 2: FuelRosmahizaNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Waste Plastic Pyrolysis Hysys V9 Steady ConditionDocument10 pagesSimulation of Waste Plastic Pyrolysis Hysys V9 Steady ConditionhanaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Processing Refining Processing 2004Document293 pagesHydrocarbon Processing Refining Processing 2004Anonymous I29NP3c100% (1)
- AT-04304-Aspen Elearning Catalog PDFDocument83 pagesAT-04304-Aspen Elearning Catalog PDFWibisono YaminNo ratings yet
- Integration Naphtha DearomatizationDocument4 pagesIntegration Naphtha Dearomatizationfanoos10000No ratings yet
- P&id DescriptionDocument7 pagesP&id DescriptionMark Guevarra100% (2)
- 763750-UOP DTS Callidus CUBP DatasheetDocument4 pages763750-UOP DTS Callidus CUBP DatasheetMohammad HesanNo ratings yet
- 2010 - Coke Formation Reduction in The Steam Cracking of Naphtha PDFDocument22 pages2010 - Coke Formation Reduction in The Steam Cracking of Naphtha PDFAriadne ChuaNo ratings yet
- Foundations Manual (Metric) (ProMax)Document69 pagesFoundations Manual (Metric) (ProMax)Kevin Esmunaldo100% (2)
- Organic ChemistryDocument74 pagesOrganic ChemistryBoluwatife Molade100% (2)