Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6
Uploaded by
Ameer Alawadi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views13 pagesThis document discusses the production of hydrogen gas (H2) and carbon monoxide (CO) from petroleum products and their uses industrially. It describes two methods for producing H2 and CO: (1) the methane-water vapor reaction and (2) the methane-oxygen reaction. These gases are used to produce important materials like ammonia, hydrocarbons, and alcohols. Ammonia production from H2 and nitrogen involves an exothermic reaction. Hydrocarbons can be produced from H2 and CO in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis using cobalt or iron catalysts. Methanol is also produced from H2 and CO in an exothermic reaction using catalysts like zinc oxide
Original Description:
Original Title
CHAPTER 6 -converted
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the production of hydrogen gas (H2) and carbon monoxide (CO) from petroleum products and their uses industrially. It describes two methods for producing H2 and CO: (1) the methane-water vapor reaction and (2) the methane-oxygen reaction. These gases are used to produce important materials like ammonia, hydrocarbons, and alcohols. Ammonia production from H2 and nitrogen involves an exothermic reaction. Hydrocarbons can be produced from H2 and CO in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis using cobalt or iron catalysts. Methanol is also produced from H2 and CO in an exothermic reaction using catalysts like zinc oxide
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views13 pagesChapter 6
Uploaded by
Ameer AlawadiThis document discusses the production of hydrogen gas (H2) and carbon monoxide (CO) from petroleum products and their uses industrially. It describes two methods for producing H2 and CO: (1) the methane-water vapor reaction and (2) the methane-oxygen reaction. These gases are used to produce important materials like ammonia, hydrocarbons, and alcohols. Ammonia production from H2 and nitrogen involves an exothermic reaction. Hydrocarbons can be produced from H2 and CO in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis using cobalt or iron catalysts. Methanol is also produced from H2 and CO in an exothermic reaction using catalysts like zinc oxide
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Chemical Engineering Department
Petroleum and Gas Technology
(Second stage)
Lecturer: Eng. Firas Jamal
Lecture-9
Chapter 6
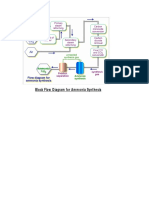
Gases Production from Petroleum Products
Gases Production from Petroleum Products
1- Production of H2 & CO :
Some gases are produced from petroleum products such as
Hydrogen and mono carbon oxide gases, which are
produced by two methods :
I- Methane – water vapor Reaction:
The reaction is occurring according to the following
reaction :
CH4 + H2O ↔ CO + 3H2 ∆H = + 49 kcal / mol
The operation conditions of the reaction are ( 1 )
atmospheric pressure, ( 700 - 870 ) oC temperature.
The catalysts used are ( Nickel Ni , Magnesium oxide MgO
, Aluminum oxide, also known Alumina Al2O3 , Silicon
oxide , also known Silica SiO2 ).
The production of gases, such as Hydrogen H2 and mono
Carbon oxide CO, can be increasing by increasing the
reaction temperature, i.e by heating because the reaction
is endothermic.
II- Methane – Oxygen Reaction:
The reaction is occurring according to the following
reaction :
CH4 + 1/2 O2 → CO + 2H2 ∆H = - 8.4 kcal / mol
The operation conditions of the reaction are ( 41 ) atm.
pressure, ( 1100 - 1500 ) oC temperature.
No catalysts used.
The production of gases, such as Hydrogen H2 and
mono carbon oxide CO, can be increasing by decreasing
the reaction temperature, i.e by cooling, because the
reaction is exothermic.
The gases produced from the first method was
under atmospheric pressure therefore must
compressing it at high pressure to liquefied.
But the gases produced from second method are
compressing and liquefied under reaction pressure
and it is needed pure oxygen which is produced from
air by expensive process.
So the first method is the best because it is low cost.
2-Uses of H2 & CO in Industrial :
H2 & CO gases are used in industrial to produced some
important materials such as ammonia, hydrocarbons,
alcohols and another materials.
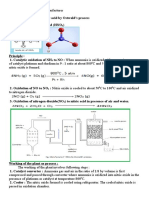
I- Ammonia Production :
Ammonia is producing according to the following reaction :
1/2 N2 + 3/2 H2 ↔ NH3 ∆H = - 9.5 kcal / mol
ammonia is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent
smell
The operation conditions of the reaction are ( 300 )
atmospheric pressure, ( 500 ) oC temperature.
The catalysts used are (Iron III oxide (or ferric oxide) Fe2O3 ,
potassium oxide K2O , Aluminum oxide (also known Alumina)
Al2O3 and Silicon oxide SiO2 ).
The production of ammonia gas can be increasing by
decreasing the reaction temperature, i.e by cooling, because
the reaction is exothermic.
Ammonia uses :
❖Fertilizers production.
❖Explosives materials production.
❖The ammonia nitrate (NH4NO3) production.
❖Nitric acid production (HNO₃).
• II- Hydrocarbon Production ( Fischer Tropsch
Synthesis ) :
In this method the hydrocarbons are preparation from
reaction the H2 and Co, the catalysts used ( cobalt Co )
or ( iron Fe ) as following reactions:
The iron as catalyst is producing the olefin
hydrocarbons, but the cobalt is producing
paraffin hydrocarbon.
In Fischer Tropsch reaction can be obtain the
strength chain from paraffin and olefin and the
double bond in the olefins in the end of the
chain always.
III- Alcohol Production :
The methanol is preparation according to the following
reaction :
CO + 2 H2 ↔ CH3OH ∆H = - 26 kcal / mol
The operation conditions of the reaction are ( 360 )
atmospheric pressure, ( 300 – 400 ) oC temperature.
The catalysts used are (zinc oxide ZnO , Chromium
oxide CrO , Copper oxide CuO ).
The production of methanol can be increasing by
decreasing the reaction temperature, i.e by cooling,
because the reaction is exothermic.
Thank you
You might also like
- Vane Mist Eliminator DesignDocument2 pagesVane Mist Eliminator DesignEng Alf100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger GuideDocument16 pagesHeat Exchanger GuideYoNo ratings yet
- Recovery Catalytic Converters RefiningDocument20 pagesRecovery Catalytic Converters RefiningAFLAC ............80% (5)
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument23 pagesShell and Tube Heat ExchangerBernard BaluyotNo ratings yet
- LSU Protandim StudyDocument8 pagesLSU Protandim StudyLifeVantage™ Protandim®No ratings yet
- HNO3 Production PDFDocument25 pagesHNO3 Production PDFWaseem RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Wa 2-2022Document19 pagesWa 2-2022Hayate100% (1)
- Ammonia Production From Natural GasDocument3 pagesAmmonia Production From Natural GasnakeyahxoNo ratings yet
- Production of AmmoniaDocument29 pagesProduction of AmmoniaBhavna Bajpai83% (6)
- Ammonia ProductionDocument7 pagesAmmonia ProductionIkhtiander IkhtianderNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Process DescriptionDocument7 pagesAmmonia Process DescriptionAnanda BalaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Industries: Industrial GasesDocument5 pagesChemical Process Industries: Industrial GasesjantskieNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Plant ReportDocument15 pagesAmmonia Plant ReportAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Urea ProductionDocument10 pagesAmmonia Urea ProductionSameer PanditaNo ratings yet
- UreaDocument18 pagesUreaDian Anggraini PurbaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia PlantDocument10 pagesAmmonia PlantHemal Patel Sam75% (4)
- Sulfuric Acid Manufacture: Analysis, Control and OptimizationFrom EverandSulfuric Acid Manufacture: Analysis, Control and OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Ammonia ConversionDocument24 pagesAmmonia ConversionKashan AslamNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Plant Brief DescriptionDocument4 pagesAmmonia Plant Brief DescriptionMohd Adnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Fuel AnalysisDocument34 pagesFuel AnalysisYedla Santosh kumar100% (2)
- Episode 3: Production of Synthesis Gas by Steam Methane ReformingDocument31 pagesEpisode 3: Production of Synthesis Gas by Steam Methane ReformingSAJJAD KHUDHUR ABBASNo ratings yet
- Fischer-Tropsch ProcessDocument5 pagesFischer-Tropsch ProcessBilal Arif100% (1)
- Kimre - Innovative Clean Air TechnologiesDocument16 pagesKimre - Innovative Clean Air TechnologiesKimre Inc100% (1)
- NitrogenDocument21 pagesNitrogendjalokfree11No ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering: INTRODUCTION TO COMPANY (Pak American Fertilizers LTD.)Document24 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering: INTRODUCTION TO COMPANY (Pak American Fertilizers LTD.)Badar RasheedNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Chemical Process Technology II Lesson 1 Nitrogen Industries (M)Document22 pagesUnit 3 Chemical Process Technology II Lesson 1 Nitrogen Industries (M)Green JeskNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and Urea ProductionDocument10 pagesAmmonia and Urea Productionwaheed_bhattiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AmmoniaDocument15 pagesIntroduction To AmmoniaHameed Akhtar100% (1)
- 1صناعاتDocument15 pages1صناعاتroaanaseem267No ratings yet
- Annex 3.2 Industrial Processes Sector-Ammonia Production-Kellog Process Detailed Description PDFDocument5 pagesAnnex 3.2 Industrial Processes Sector-Ammonia Production-Kellog Process Detailed Description PDFErol DAĞNo ratings yet
- Haber Process For The Production of Ammonia 1Document4 pagesHaber Process For The Production of Ammonia 1Nisha SundarNo ratings yet
- Manufacture Nitric AcidDocument9 pagesManufacture Nitric AcidDjayustinus Heri HermawanNo ratings yet
- Químicos Basados en El MetanoDocument22 pagesQuímicos Basados en El MetanoArianna PadillaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Industries: Ammonia Ammonium NitrateDocument5 pagesNitrogen Industries: Ammonia Ammonium NitrateabdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Industrial 4&5 PDFDocument63 pagesIndustrial 4&5 PDFDejene KidaneNo ratings yet
- Gaseous FuelsDocument8 pagesGaseous FuelsvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Production of Ammonia: Sunny ChawlaDocument6 pagesProduction of Ammonia: Sunny ChawlapsshnkrNo ratings yet
- Block Flow Diagram For Ammonia SynthesisDocument2 pagesBlock Flow Diagram For Ammonia SynthesisK.R Technosafe EngineersNo ratings yet
- Fertiliser Manufacturing Processes and Its Environmental ProblemsDocument69 pagesFertiliser Manufacturing Processes and Its Environmental ProblemsAulizar MarioNo ratings yet
- Uses of Sulphuric AcidDocument14 pagesUses of Sulphuric AcidFaizul FaiiziNo ratings yet
- Flowsheet Development and Simulation of Ethane Production From Synthesis Gas by Using HysysDocument9 pagesFlowsheet Development and Simulation of Ethane Production From Synthesis Gas by Using HysysazimNo ratings yet
- Modern Manufacture 2079Document25 pagesModern Manufacture 2079Aaditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Absorber), A Solution of An Ethanolamine, Often 2,2' - (Methylimino) Bis-Ethanol (N-MethylDocument2 pagesAbsorber), A Solution of An Ethanolamine, Often 2,2' - (Methylimino) Bis-Ethanol (N-MethylNurfarhana JelenNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Nitric AcidDocument2 pagesPreparation of Nitric AcidSANA SAFDARNo ratings yet
- Haber AmmoniaDocument22 pagesHaber AmmoniaKabilanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document21 pagesUnit 1Fitrya ChiequzaNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Final-1Document40 pagesUnit II - Final-1S kabileshNo ratings yet
- Production of AmmoniaDocument4 pagesProduction of AmmoniaadeelrehmanNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Products: Ariziel Ruth D. MarquezDocument9 pagesNitrogen Products: Ariziel Ruth D. MarquezPaolo GochingcoNo ratings yet
- 2 Manufacture of Ammonia, Nitric Acid and Calcium Ammonium NitrateDocument14 pages2 Manufacture of Ammonia, Nitric Acid and Calcium Ammonium NitrateKarez MartoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Chemistry ReportDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Chemistry ReportHymcduckNo ratings yet
- Production of Ammonia Via Steam Reforming of Natural GasDocument1 pageProduction of Ammonia Via Steam Reforming of Natural Gasvaratharajan g rNo ratings yet
- NH From Synthesis Gas (CO + H) : Chemicals and Fertilizers From Ammonia (Moulijn Et Al.)Document12 pagesNH From Synthesis Gas (CO + H) : Chemicals and Fertilizers From Ammonia (Moulijn Et Al.)Chaitanya PottiNo ratings yet
- KkimiaDocument27 pagesKkimiaNoralyz LyzcatNo ratings yet
- Petrochemical Products From Methane (Compatibility Mode)Document62 pagesPetrochemical Products From Methane (Compatibility Mode)Jack Chee83% (6)
- Nitrogen IndustriesDocument53 pagesNitrogen Industriesmulugeta damisuNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSangam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Modern Chemical ManufacturerDocument8 pagesModern Chemical ManufacturerUltra Gamer (sishant)No ratings yet
- 8-Clean Combustion TechnologiesDocument58 pages8-Clean Combustion TechnologiesNomaan AsimNo ratings yet
- Go 5 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid, Nitric AcidDocument21 pagesGo 5 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid, Nitric AcidcikaifaNo ratings yet
- Bosch-Meiser Urea Process, 1922Document7 pagesBosch-Meiser Urea Process, 1922Wow WowNo ratings yet
- Ammonia: How Is Ammonia Manufactured?Document3 pagesAmmonia: How Is Ammonia Manufactured?Khondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- HW1Document4 pagesHW1blvckops890No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2pragati agrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document17 pagesChapter 8Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- United States Design Patent (10) Patent No.:: US D716,698 SDocument7 pagesUnited States Design Patent (10) Patent No.:: US D716,698 SAmeer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document18 pagesChapter 7Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 3Document14 pagesChapter 1 3Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Department Petroleum and Gas Technology (Second Stage) Lecturer: Eng. Firas JamalDocument31 pagesChemical Engineering Department Petroleum and Gas Technology (Second Stage) Lecturer: Eng. Firas JamalAmeer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document31 pagesChapter 4Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-2Document18 pagesChapter 2-2Ameer AlawadiNo ratings yet
- The Cast Oil Casting Case StudyDocument2 pagesThe Cast Oil Casting Case StudyAtta E Mustafa Mughal100% (1)
- Composting and BriquettingDocument69 pagesComposting and BriquettingJhanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.V4 Kombi Final Manual Balancing Valve F.endDocument13 pages1.V4 Kombi Final Manual Balancing Valve F.endKurkuma PlusNo ratings yet
- Find Out The Best Alignment Among The Two Alignments With Your Own Basic Assumed Scores?Document2 pagesFind Out The Best Alignment Among The Two Alignments With Your Own Basic Assumed Scores?Geetha AnjaliNo ratings yet
- 2003 UtahDocument2 pages2003 UtahAEHSFOUNDATIONNo ratings yet
- Chlor Alkali Brochure Thyssenkrupp NuceraDocument13 pagesChlor Alkali Brochure Thyssenkrupp NuceraSrinivasan KNo ratings yet
- The Multiple-Stress Creep-Recovery (MSCR) Test and SpecificationDocument42 pagesThe Multiple-Stress Creep-Recovery (MSCR) Test and SpecificationVinayaka RamNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid Extraction From Aqueous Solutions Using Fatty AcidsDocument8 pagesAcetic Acid Extraction From Aqueous Solutions Using Fatty AcidsNur Zuliana Mat ZinNo ratings yet
- CH 20 ExercisesDocument1 pageCH 20 ExercisesPaul BryanNo ratings yet
- Urals 304Document3 pagesUrals 304Himanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Evaluation of Dispersible Tablets of A Model Antibiotic DrugDocument9 pagesPreparation and Evaluation of Dispersible Tablets of A Model Antibiotic DrugSangram KendreNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Recent Advances in HPLC InstrumentationDocument16 pagesAn Overview of Recent Advances in HPLC Instrumentationlovina candra kiranaNo ratings yet
- Meth Orange Post LabDocument4 pagesMeth Orange Post LabConnor LaBellaNo ratings yet
- Selected Questions of Chapter Aldehyde K Solved Sample Papers For Class 12 ChemistryDocument33 pagesSelected Questions of Chapter Aldehyde K Solved Sample Papers For Class 12 ChemistrySsNo ratings yet
- Omniseal HandbookDocument60 pagesOmniseal HandbookMuhamed RafficNo ratings yet
- Entry Exam - M.Sc. / 2015-2016 Chemical Engineering Department University of Baghdad Date 2/9/2015 (2 Attempt) Time: 3 HrsDocument5 pagesEntry Exam - M.Sc. / 2015-2016 Chemical Engineering Department University of Baghdad Date 2/9/2015 (2 Attempt) Time: 3 Hrshiba thamirNo ratings yet
- Conplast SP360 : High Performance Water Reducing Admixture Uses Technical SupportDocument4 pagesConplast SP360 : High Performance Water Reducing Admixture Uses Technical Supportpravi3434No ratings yet
- (40-9-2) NPTEL - Instrumentation in CryogenicsDocument44 pages(40-9-2) NPTEL - Instrumentation in CryogenicsThermal_EngineerNo ratings yet
- As 1856-2004 Electroplated Coatings - SilverDocument9 pagesAs 1856-2004 Electroplated Coatings - SilverSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment 1Document3 pagesThermodynamics Assignment 1Twinkle Anne RosalesNo ratings yet
- 0620 s04 QP 1Document16 pages0620 s04 QP 1Varun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Afff 1% - 15 - , 3% 5 C - MSDSDocument4 pagesAfff 1% - 15 - , 3% 5 C - MSDSWilliam ChandraNo ratings yet
- CIE As and A-Level Chemistry Coursebook 2nd-Edition (1) 82-98Document17 pagesCIE As and A-Level Chemistry Coursebook 2nd-Edition (1) 82-98Trương Nguyễn Hoàng AnNo ratings yet