Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UM1724 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-64 Boards (MB1136)
UM1724 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-64 Boards (MB1136)
Uploaded by
MihaiNeacsuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UM1724 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-64 Boards (MB1136)
UM1724 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-64 Boards (MB1136)
Uploaded by
MihaiNeacsuCopyright:
Available Formats
UM1724
User manual
STM32 Nucleo-64 boards (MB1136)
Introduction
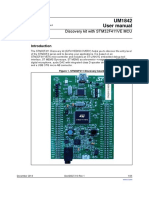
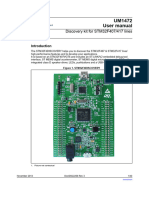
The STM32 Nucleo-64 boards based on the MB1136 reference board (NUCLEO-F030R8,
NUCLEO-F070RB, NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F091RC, NUCLEO-F103RB,
NUCLEO-F302R8, NUCLEO-F303RE, NUCLEO-F334R8, NUCLEO-F401RE,
NUCLEO-F410RB, NUCLEO-F411RE, NUCLEO-F446RE, NUCLEO-L010RB,
NUCLEO-L053R8, NUCLEO-L073RZ, NUCLEO-L152RE, NUCLEO-L452RE,
NUCLEO-L476RG) provide an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts
and build prototypes with the STM32 microcontrollers in the LQFP64 package, choosing
from the various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The
ARDUINO® Uno V3 connectivity support and the ST morpho headers provide an easy
means of expanding the functionality of the Nucleo open development platform with a wide
choice of specialized shields. The STM32 Nucleo boards do not require any separate probe
as they integrate the ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger and programmer. The STM32 Nucleo boards
come with the comprehensive free software libraries and examples available with the
STM32Cube MCU Packages, as well as direct access to the Arm® Mbed™ online resources
at http://mbed.org/.
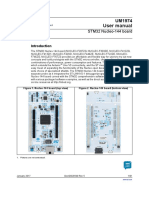
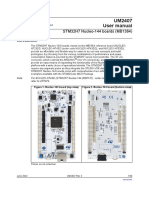
Figure 1. STM32 Nucleo-64 board
Picture is not contractual.
August 2020 UM1724 Rev 14 1/68
www.st.com 1
Content UM1724
Content
1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Codification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Development environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1 System requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.2 Development toolchains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.3 Demonstration software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4 Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
5 Quick start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.1 Getting started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.2 NUCLEO-L476RG bootloader limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.3 Hardware configuration variants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
6 Hardware layout and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
6.1 Pre-cut PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
6.2 Embedded ST-LINK/V2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
6.2.1 Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6.2.2 ST-LINK/V2-1 firmware upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6.2.3 Using the ST-LINK/V2-1 to program and debug the STM32 on board . 18
6.2.4 Using ST-LINK/V2-1 to program and debug an external
STM32 application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.3 Power supply and power selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.3.1 Power supply input from the USB connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.3.2 External power supply inputs: VIN and E5V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
6.3.3 External power supply input: +3.3V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
6.3.4 External power supply output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
6.4 LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
6.5 Push-buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
6.6 JP6 (IDD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Content
6.7 OSC clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.7.1 OSC clock supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.7.2 OSC 32 kHz clock supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.8 USART communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.9 Solder bridges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
6.10 Extension connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.11 ARDUINO® connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.12 ST morpho connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
7 Nucleo-64 boards information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
7.1 Product marking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
7.2 Board revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
7.3 Board known limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
UM1724 Rev 14 3/68
3
List of Tables UM1724
List of Tables
Table 1. Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 2. Codification explanation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 3. ON/OFF conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 4. Jumper states . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 5. Debug connector CN4 (SWD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 6. JP1 configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 7. External power sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 8. Power-related jumper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 9. +3.3 V external power source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 10. Solder bridges. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 11. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F030R8, NUCLEO-F070RB,
NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F091RC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 12. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F103RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 13. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F302R8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 14. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F303RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 15. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F334R8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 16. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F401RE and NUCLEO-F411RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 17. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L053R8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 18. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L010RB and NUCLEO-L073RZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table 19. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F446RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 20. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F410RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 21. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L152RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 22. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L452RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 23. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L476RG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 24. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F030R8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Table 25. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F070RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Table 26. ST morpho connector on
NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F091RC, NUCLEO-F303RE, NUCLEO-F334R8. . . . . . . . . 55
Table 27. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F103RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Table 28. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F302R8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 29. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F401RE,
NUCLEO-F411RE, NUCLEO-F446RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Table 30. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-L010RB,
NUCLEO-L053R8, NUCLEO-L073RZ, NUCLEO-L152RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 31. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-L452RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table 32. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-L476RG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Table 33. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F410RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 34. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
4/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 List of Figures
List of Figures
Figure 1. STM32 Nucleo-64 board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Figure 2. Hardware block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 3. Top layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 4. Bottom layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 5. STM32 Nucleo board mechanical dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 6. Typical configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 7. Updating the list of drivers in Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 8. Connecting the STM32 Nucleo board to program the on-board STM32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 9. Using ST-LINK/V2-1 to program the STM32 on an external application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 10. NUCLEO-F030R8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 11. NUCLEO-F070RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 12. NUCLEO-F072RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 13. NUCLEO-F091RC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 14. NUCLEO-F103RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 15. NUCLEO-F302R8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 16. NUCLEO-F303RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 17. NUCLEO-F334R8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 18. NUCLEO-F401RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 19. NUCLEO-F411RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 20. NUCLEO-L053R8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 21. NUCLEO-L073RZ and NUCLEO-L010RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 22. NUCLEO-L152RE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 23. NUCLEO-L452RE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 24. NUCLEO-L476RG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 25. NUCLEO-F446RE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 26. NUCLEO-F410RB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
UM1724 Rev 14 5/68
5
Features UM1724
1 Features
The STM32 Nucleo board offers the following features:
• STM32 microcontroller in LQFP64 package
• Three LEDs:
– USB communication (LD1), user LED (LD2), power LED (LD3)
• Two push-buttons: USER and RESET
• Two types of extension resources
– ARDUINO® Uno V3 connectivity
– ST morpho extension pin headers for full access to all STM32 I/Os
• Flexible board power supply:
– USB VBUS or external source (3.3 V, 5 V, 7-12 V)
– Power management access point
• On-board ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger and programmer with SWD connector
– Selection-mode switch using the kit as a standalone ST-LINK/V2-1
• USB re-enumeration capability. Three different interfaces supported on USB:
– Virtual COM port
– Mass storage
– Debug port
• Comprehensive free software libraries and examples available with the STM32Cube
MCU Package
• Arm® Mbed™(a) (see http://mbed.org)
a. Arm and Mbed are registered trademarks or trademarks of Arm Limited (or its subsidiaries) in the US
and/or elsewhere.
6/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Ordering information
2 Ordering information
To order an STM32 Nucleo-64 board, refer to Table 1. Additional information is available
from the datasheet and reference manual of the target STM32.
Table 1. Ordering information
Board
Order code Targeted STM32 Differentiating feature
reference
NUCLEO-F030R8 STM32F030R8T6
NUCLEO-F070RB STM32F070RBT6
NUCLEO-F072RB STM32F072RBT6
NUCLEO-F091RC STM32F091RCT6U
NUCLEO-F103RB STM32F103RBT6
NUCLEO-F302R8 STM32F302R8T6
Arm® Mbed Enabled™
NUCLEO-F303RE STM32F303RET6
NUCLEO-F334R8 STM32F334R8T6
NUCLEO-F401RE STM32F401RET6U
MB1136
NUCLEO-F410RB STM32F410RBT6U
NUCLEO-F411RE STM32F411RET6U
NUCLEO-F446RE STM32F446RET6U
NUCLEO-L010RB STM32L010RBT6 -
NUCLEO-L053R8 STM32L053R8T6
NUCLEO-L073RZ STM32L073RZT6U Arm® Mbed Enabled™
NUCLEO-L152RE STM32L152RET6
NUCLEO-L452RE STM32L452RET6U -
®
NUCLEO-L476RG STM32L476RGT6U Arm Mbed Enabled™
UM1724 Rev 14 7/68
67
Ordering information UM1724
2.1 Codification
The meaning of the codification is explained in Table 2.
Table 2. Codification explanation
NUCLEO-XXYYRT Description Example: NUCLEO-L452RE
MCU series in STM32 Arm
XX STM32L4 Series
Cortex MCUs
STM32 product line in the
YY STM32L452
series
R STM32 package pin count 64 pins
STM32 Flash memory size:
– 8 for 64 Kbytes
– B for 128 Kbytes
T – C for 256 Kbytes 512 Kbytes
– E for 512 Kbytes
– G for 1 Mbyte
– Z for 192 Kbytes
The order code is printed on a sticker placed at the top or bottom side of the board.
8/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Development environment
3 Development environment
3.1 System requirements
• Windows® OS (7, 8 and 10), Linux® 64-bit, or macOS®
• USB Type-A to Mini-B cable
3.2 Development toolchains
• IAR Systems - IAR Embedded Workbench®(a)
• Keil®: MDK-ARM(a)
• GCC-based IDEs
• Arm® Mbed™ online(b) (see http://mbed.org)
3.3 Demonstration software
The demonstration software, included in the STM32Cube MCU Package corresponding to
the on-board microcontroller, is preloaded in the STM32 Flash memory for easy
demonstration of the device peripherals in standalone mode. The latest versions of the
demonstration source code and associated documentation can be downloaded from
www.st.com.
4 Conventions
Table 3 provides the conventions used for the ON and OFF settings in the present
document.
Table 3. ON/OFF conventions
Convention Definition
Jumper JP1 ON Jumper fitted
Jumper JP1 OFF Jumper not fitted
Solder bridge SBx ON SBx connections closed by solder or 0-ohm resistor
Solder bridge SBx OFF SBx connections left open
In this document, the references are “STM32 Nucleo board” and “STM32 Nucleo boards” for
all information that is common to all sale types.
®
a. On Windows only.
b. Refer to the http://mbed.com website and to Table 1: Ordering information, to determine which order codes
are
supported.
UM1724 Rev 14 9/68
67
Quick start UM1724
5 Quick start
The STM32 Nucleo board is a low-cost and easy-to-use development platform used to
quickly evaluate and start development with an STM32 microcontroller in LQFP64 package.
Before installing and using the product, accept the Evaluation Product License Agreement
from the www.st.com/epla web page.
For more information on the STM32 Nucleo board and to access the demonstration
software, visit www.st.com/stm32nucleo website.
5.1 Getting started
Follow the sequence below to configure the STM32 Nucleo board and launch the demo
software:
1. Check the jumper position on the board, JP1 off, JP5 (PWR) on U5V, JP6 on (IDD),
CN2 on (NUCLEO) selected.
2. For correct identification of all device interfaces from the host PC, install the Nucleo
USB driver available from the www.st.com/stm32nucleo web page, prior to connecting
the board.
3. Connect the STM32 Nucleo board to a PC with a USB cable ‘Type-A to Mini-B’ through
USB connector CN1 to power the board. The red LED LD3 (PWR) and LD1 (COM)
must light up. LD1 (COM) and green LED LD2 must blink.
4. Press button B1 (left button).
5. Observe the blinking frequency of LED LD2 at different frequencies, by clicking on the
button B1.
6. The demonstration software and several software examples on how to use the STM32
Nucleo board features are available at the www.st.com/stm32nucleo web page.
7. Develop the application using the available examples.
5.2 NUCLEO-L476RG bootloader limitations
Boot from system Flash memory results in executing bootloader code stored in the system
Flash memory, protected against write and erase. This allows in-system programming (ISP),
that is, flashing the STM32 user Flash memory. It also allows writing data into RAM. The
data come in via one of the communication interfaces such as USART, SPI, I2C bus, USB,
or CAN.
The bootloader version can be identified by reading the bootloader ID at the address
0x1FFF6FFE.
The STM32L476RGT6 part soldered on the NUCLEO-L476RG main board is marked with a
date code, corresponding to its date of manufacturing. STM32L476RGT6 parts with the date
code prior or equal to week 22 of 2015 are fitted with bootloader V 9.0, affected by the
limitations to be worked around, as described hereunder. Parts with the date code starting
from week 23 of 2015 contain bootloader V 9.2 in which the limitations no longer exist.
To locate the visual date code information on the STM32L476RGT6 package, refer to the
section “Package information” of the datasheet (DS10198) available at www.st.com. Date
code related portion of the package marking takes Y WW format, where Y is the last digit of
10/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Quick start
the year and WW is the week. For example, a part manufactured in week 23 of 2015 bares
the date code 5 23.
The bootloader ID of the bootloader V 9.0 is 0x90.
The following limitations exist in the bootloader V 9.0:
1. RAM data get corrupted when written via USART/SPI/I2C/USB interface
Description:
Data write operation into RAM space via USART, SPI, I2C bus, or USB results in wrong or
no data written.
Workaround:
To correct the issue of the wrong write into RAM, download STSW-STM32158 bootloader
V 9.0 patch package from the www.st.com website and load ‘Bootloader V9.0 SRAM patch’
to the STM32, following the information in readme.txt file available in the package.
2. User Flash memory data get corrupted when written via CAN interface
Description:
Data write operation into user Flash memory space via CAN interface results in wrong or no
data written.
Workaround:
To correct the issue of the wrong write into Flash memory, download the STSW-STM32158
bootloader V 0.9 patch package from the www.st.com website and load ‘Bootloader V9.0
CAN patch’ to the STM32, following the information in readme.txt file available in the
package.
5.3 Hardware configuration variants
The board can be delivered with different configurations of the oscillator of the target
STM32. For all the details concerning high-speed configurations of the oscillator refer to
Section 6.7.1. For all the details concerning low-speed configurations of the oscillator refer
to Section 6.7.2.
UM1724 Rev 14 11/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
6 Hardware layout and configuration
The STM32 Nucleo board is designed around the STM32 microcontrollers in a 64-pin LQFP
package.
Figure 2 shows the connections between the STM32 and its peripherals (ST-LINK/V2-1,
push-button, LED, ARDUINO® connectors, and ST morpho connector).
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the location of these features on the STM32 Nucleo board.
Figure 5 shows the mechanical dimension of the STM32 Nucleo board.
Figure 2. Hardware block diagram
ST-LINK part
Mini
USB
Embedded
ST-LINK/V2-1
SWD
B1
USER STM32
ST morpho extension header
ST morpho extension header
Microcontroller
IO IO
ARDUINO® connector
ARDUINO® connector
IO RESET IO
B2 LED
RESET LD4
MCU part
MS34374V2
12/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Figure 3. Top layout
CN1
CN2 ST-LINK USB
ST-LINK/Nucleo mini B connector
selector
LD1
CN4 (Red/Green LED)
SWD connector COM
B1 USER B2
button RESET button
JP6 IDD SB2
measurement 3.3 V regulator output
LD3
(Red LED) LD2
power (Green LED)
CN6
ARDUINO® CN5
connector ARDUINO® connector
CN7
ST morpho CN10
connector ST morpho connector
CN9
CN8 ARDUINO® connector
ARDUINO®
connector
32 KHz
crystal(1)
U5
STM32
microcontroller
MS34376V3
1. Crystal may be present or not depending on board version, refer to Section 6.7.2.
UM1724 Rev 14 13/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Figure 4. Bottom layout
SB13, SB14 SB4, SB6, SB8, SB10 SB3, SB5, SB7, SB9
ST-LINK USART (RESERVED) (DEFAULT)
SB15
ST-LINK SWO
SB11
ST-LINK
SB16 RESET
ST-LINK MCO
SB17
USER button
SB21
USER LED
SB50
ST-LINK MCO
MS34375V1
14/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Figure 5. STM32 Nucleo board mechanical dimensions
UM1724 Rev 14 15/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
6.1 Pre-cut PCB
The STM32 Nucleo board is divided into two parts: ST-LINK part and target STM32 part.
The ST-LINK part of the PCB can be cut out to reduce the board size. In this case, the
remaining target STM32 part can only be powered by VIN, E5V, and +3.3V on the ST
morpho connector CN7, or VIN and +3.3V on ARDUINO® connector CN6. It is still possible
to use the ST-LINK part to program the main STM32 using wires between CN4 and SWD
signals available on the ST morpho connector (SWCLK CN7 pin 15 and SWDIO CN7 pin
13).
6.2 Embedded ST-LINK/V2-1
The ST-LINK/V2-1 programming and debugging tool is integrated into the STM32 Nucleo
board.
The ST-LINK/V2-1 makes the STM32 Nucleo boards Mbed Enabled™.
The embedded ST-LINK/V2-1 supports only SWD for STM32 devices. For information about
debugging and programming features, refer to the user manual ST-LINK/V2 in-circuit
debugger/programmer for STM8 and STM32 (UM1075), which describes in details all the
ST-LINK/V2 features.
The changes versus the ST-LINK/V2 version are listed below.
• New features supported on ST-LINK/V2-1:
– USB software re-enumeration
– Virtual COM port interface on USB
– Mass storage interface on USB
– USB power management request for more than 100 mA power on USB
• Features not supported on ST-LINK/V2-1:
– SWIM interface
– Minimum supported application voltage limited to 3 V
• Known limitation:
– Activating the readout protection on ST-LINK/V2-1 target prevents the target
application from running afterward. The target readout protection must be kept
disabled on ST-LINK/V2-1 boards.
There are two different ways to use the embedded ST-LINK/V2-1 depending on the jumper
states (see Table 4 and Figure 6):
• Program/debug the on-board STM32 (Section 6.2.2)
• Program/debug an MCU in an external application board using a cable connected to
SWD connector CN4 (Section 6.2.4).
Table 4. Jumper states
Jumper state Description
ST-LINK/V2-1 functions enabled for on-board programming
Both CN2 jumpers ON
(default)
ST-LINK/V2-1 functions enabled for external CN4 connector
Both CN2 jumpers OFF
(SWD supported)
16/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Figure 6. Typical configuration
Hardware requirements:
- Computer with Windows® 7, 8 or 10
- USB cable Type-A to Mini-B
Development toolchain:
- IAR™ EWARM
- Keil® MDK-ARM
- GCC-based IDE
MS19052V5
6.2.1 Driver
Before connecting the Nucleo-64 board to a Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows 10 PC via
USB, a driver for ST-LINK/V2-1 must be installed. It can be downloaded from the
www.st.com website.
In case the STM32 Nucleo-64 board is connected to the PC before installing the driver, the
PC device manager may report some Nucleo interfaces as “Unknown”.
To recover from this situation, after installing the dedicated driver, the association of
“Unknown” USB devices found on the STM32 Nucleo-64 board to this dedicated driver,
must be updated in the device manager manually.
Note: It is recommended to proceed using a USB Composite Device, as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7. Updating the list of drivers in Device Manager
6.2.2 ST-LINK/V2-1 firmware upgrade
The ST-LINK/V2-1 embeds a firmware upgrade mechanism for the in-situ upgrade through
the USB port. As the firmware may evolve during the lifetime of the ST-LINK/V2-1 product
(for example new functionality, bug fixes, support for new microcontroller families), it is
recommended to visit www.st.com website before starting to use the STM32 Nucleo board
and periodically, in order to stay up-to-date with the latest firmware version.
UM1724 Rev 14 17/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
6.2.3 Using the ST-LINK/V2-1 to program and debug the STM32 on board
To program the STM32 on the board, plug in the two jumpers on CN2, as shown in red in
Figure 8. Do not use the CN4 connector as this could disturb the communication with the
STM32 microcontroller of the STM32 Nucleo board.
Figure 8. Connecting the STM32 Nucleo board to program the on-board STM32
CN2 jumpers ON
CN4 SWD
connector
MS34378V2
6.2.4 Using ST-LINK/V2-1 to program and debug an external
STM32 application
It is very easy to use the ST-LINK/V2-1 to program the STM32 on an external application.
Simply remove the two jumpers from CN2 as illustrated in Figure 9: Using ST-LINK/V2-1 to
program the STM32 on an external application, and connect the application to the CN4
debug connector according to Table 5.
Note: SB12 NRST (target STM32 RESET) must be OFF if CN4 pin 5 is used in the external
application.
18/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 5. Debug connector CN4 (SWD)
Pin CN4 Designation
1 VDD_TARGET VDD from application
2 SWCLK SWD clock
3 GND ground
4 SWDIO SWD data input/output
5 NRST RESET of target STM32
6 SWO Reserved
Figure 9. Using ST-LINK/V2-1 to program the STM32 on an external application
CN2 jumpers OFF
CN4
SWD connector
MS34379V2
UM1724 Rev 14 19/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
6.3 Power supply and power selection
The power supply is provided either by the host PC through the USB cable, or by an
external source: VIN (From 7 V to 12 V), E5V (5 V) or +3.3V power supply pins on CN6 or
CN7. In case VIN, E5V or +3.3V is used to power the STM32 Nucleo board, using an
external power supply unit or auxiliary equipment, this power source must comply with the
standard EN-60950-1: 2006+A11/2009, and must be Safety Extra Low Voltage (SELV) with
limited power capability.
6.3.1 Power supply input from the USB connector
The ST-LINK/V2-1 supports USB power management allowing to request more than
100 mA current to the host PC.
All parts of the STM32 Nucleo board and shield can be powered from the ST-LINK USB
connector CN1 (U5V or VBUS). Note that only the ST-LINK part is power supplied before
the USB enumeration as the host PC only provides 100 mA to the board at that time. During
the USB enumeration, the STM32 Nucleo board requires 300 mA of current to the host PC.
If the host is able to provide the required power, the targeted STM32 microcontroller is
powered and the red LED LD3 is turned ON, thus the STM32 Nucleo board and its shield
can consume a maximum of 300 mA current, not more. If the host is not able to provide the
required current, the targeted STM32 microcontroller and the MCU part including the
extension board are not power supplied. As a consequence, the red LED LD3 remains
turned OFF. In such a case it is mandatory to use an external power supply as explained in
the next Section 6.3.2: External power supply inputs: VIN and E5V.
When the board is power supplied by USB (U5V) a jumper must be connected between pin
1 and pin 2 of JP5 as shown in Table 8.
JP1 is configured according to the maximum current consumption of the board when
powered by USB (U5V). JP1 jumper can be set in case the board is powered by USB and
maximum current consumption on U5V does not exceed 100 mA (including an eventual
extension board or ARDUINO® shield). In such a condition, USB enumeration always
succeeds since no more than 100 mA is requested to the PC. Possible configurations of
JP1 are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6. JP1 configuration table
Jumper state Power supply Allowed current
JP1 jumper OFF 300 mA max
USB power through CN1
JP1 jumper ON 100 mA max
Warning: If the maximum current consumption of the NUCLEO and its
extension boards exceeds 300 mA, it is mandatory to power
the NUCLEO using an external power supply connected to
E5V or VIN.
Note: In case the board is powered by a USB charger, there is no USB enumeration, so the led
LD3 remains set to OFF permanently and the target STM32 is not powered. In this specific
case, the jumper JP1 needs to be set to ON, to allow target STM32 to be powered anyway.
20/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
6.3.2 External power supply inputs: VIN and E5V
The external power sources VIN and E5V are summarized in Table 7. When the board is
power supplied by VIN or E5V, the jumpers configuration must be the following:
• Jumper on JP5 pin 2 and pin 3
• Jumper removed on JP1
Table 7. External power sources
Input Connectors Voltage Max
Limitation
power name pins range current
From 7 V to 12 V only and input current
capability is linked to input voltage:
800 mA input current
CN6 pin 8 when Vin = 7 V
VIN 7 V to 12 V 800 mA
CN7 pin 24 450 mA input current
when 7 V < Vin <= 9 V
250 mA input current
when 9 V < Vin <= 12 V
4.75 V to
E5V CN7 pin 6 500 mA -
5.25 V
Table 8. Power-related jumper
Jumper Description
U5V (ST-LINK VBUS) is used as a power source when JP5 is set as shown below
(Default setting)
U5V
E5V
3 2 1
JP5
VIN or E5V is used as a power source when JP5 is set as shown below.
U5V
E5V
3 2 1
Using VIN or E5V as external power supply
VIN or E5V can be used as an external power supply in case the current consumption of the
STM32 Nucleo and extensions boards exceeds the allowed current on USB. In this
condition, it is still possible to use the USB for communication, for programming or
debugging only, but it is mandatory to power supply the board first using VIN or E5V then
connect the USB cable to the PC. Proceeding this way ensures that the enumeration occurs
thanks to the external power source.
The following power sequence procedure must be respected:
UM1724 Rev 14 21/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
1. Connect the jumper between pin 2 and pin 3 of JP5
2. Check that JP1 is removed
3. Connect the external power source to VIN or E5V
4. Power on the external power supply 7 V< VIN < 12 V to VIN, or 5 V for E5V
5. Check that LD3 is turned ON
6. Connect the PC to USB connector CN1
If this order is not respected, the board may be supplied by VBUS first then by VIN or E5V,
and the following risks may be encountered:
1. If more than 300 mA current is needed by the board, the PC may be damaged or the
current supply can be limited by the PC. As a consequence, the board is not powered
correctly.
2. 300 mA is requested at enumeration (since JP1 must be OFF) so there is a risk that the
request is rejected and the enumeration does not succeed if the PC cannot provide
such current. Consequently, the board is not power supplied (LED LD3 remains OFF).
6.3.3 External power supply input: +3.3V
It can be of interest to use the +3.3V (CN6 pin 4 or CN7 pin 12 and pin 16) directly as power
input for instance in case the 3.3V is provided by an extension board. When the STM32
Nucleo board is power supplied by +3.3V, the ST-LINK is not powered, thus the
programming and debug features are unavailable. The +3.3V external power source is
summarized in Table 9.
Table 9. +3.3 V external power source
Input power
Connectors pins Voltage range Limitation
name
CN6 pin 4 Used when ST-LINK part of PCB is cut
+3.3V 3 V to 3.6 V
CN7 pin 12 and pin 16 or SB2 and SB12 OFF
Two different configurations are possible when using +3.3V to power the board:
• ST-LINK is removed (PCB cut) or
• SB2 (3.3V regulator) and SB12 (NRST) are OFF.
6.3.4 External power supply output
When powered by USB, VIN, or E5V, the +5V (CN6 pin 5 or CN7 pin 18) can be used as an
output power supply for an ARDUINO® shield or an extension board. In this case, the
maximum current of the power source specified in Table 7 must be respected.
The +3.3V (CN6 pin 4 or CN7 pin 12 and 16) can be used also as power supply output. The
current is limited by the maximum current capability of the regulator U4 (500 mA max).
22/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
6.4 LEDs
The tricolor LED (green, orange, red) LD1 (COM) provides information about ST-LINK
communication status. LD1 default color is red. LD1 turns to green to indicate that
communication is in progress between the PC and the ST-LINK/V2-1, with the following
setup:
• Slow blinking Red/Off: at power-on before USB initialization
• Fast blinking Red/Off: after the first correct communication between the PC and
ST-LINK/V2-1 (enumeration)
• Red LED On: when the initialization between the PC and ST-LINK/V2-1 is complete
• Green LED On: after a successful target communication initialization
• Blinking Red/Green: during communication with the target
• Green On: communication finished and successful
• Orange On: Communication failure
User LD2: the green LED is a user LED connected to ARDUINO® signal D13 corresponding
to STM32 I/O PA5 (pin 21) or PB13 (pin 34) depending on the STM32 target. Refer to
Table 11 to Table 23 when:
• the I/O is HIGH value, the LED is on
• the I/O is LOW, the LED is off
LD3 PWR: the red LED indicates that the STM32 part is powered and +5V power is
available.
6.5 Push-buttons
B1 USER: the user button is connected to the I/O PC13 (pin 2) of the STM32
microcontroller.
B2 RESET: this push-button is connected to NRST, and is used to RESET the STM32
microcontroller.
Note: The blue and black plastic hats that are placed on the push-buttons can be removed if
necessary, for example when a shield or when an application board is plugged on top of the
Nucleo board. This will avoid pressure on the buttons and consequently a possible
permanent target STM32 RESET.
6.6 JP6 (IDD)
Jumper JP6, labeled IDD, is used to measure the STM32 microcontroller consumption by
removing the jumper and by connecting an ammeter:
• Jumper ON: STM32 microcontroller is powered (default).
• Jumper OFF: an ammeter must be connected to measure the STM32 microcontroller
current. If there is no ammeter, the STM32 microcontroller is not powered.
UM1724 Rev 14 23/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
6.7 OSC clock
6.7.1 OSC clock supply
There are four ways to configure the pins corresponding to the external high-speed clock
(HSE):
• MCO from ST-LINK: MCO output of ST-LINK MCU is used as an input clock. This
frequency cannot be changed, it is fixed at 8 MHz and connected to
PF0/PD0/PH0-OSC_IN of the STM32 microcontroller.
The following configuration is needed:
– SB55 OFF and SB54 ON
– SB16 and SB50 ON
– R35 and R37 removed
• HSE oscillator on-board from X3 crystal (not provided): for typical frequencies and
its capacitors and resistors, refer to the STM32 microcontroller datasheet. Refer to the
AN2867 Application note for oscillator design guide for STM32 microcontrollers.The X3
crystal has the following characteristics: 8 MHz, 16 pF, 20 ppm, and DIP footprint. It is
recommended to use 9SL8000016AFXHF0 manufactured by Hong Kong X'tals
Limited.
The following configuration is needed:
– SB54 and SB55 OFF
– R35 and R37 soldered
– C33 and C34 soldered with 20 pF capacitors
– SB16 and SB50 OFF
• Oscillator from external PF0/PD0/PH0: from an external oscillator through pin 29 of
the CN7 connector.
The following configuration is needed:
– SB55 ON
– SB50 OFF
– R35 and R37 removed
• HSE not used: PF0/PD0/PH0 and PF1/PD1/PH1 are used as GPIOs instead of clocks
The following configuration is needed:
– SB54 and SB55 ON
– SB16 and SB50 (MCO) OFF
– R35 and R37 removed
There are two possible default configurations of the HSE pins, depending on the version of
the STM32 Nucleo board hardware.
The board version MB1136 C-01 or MB1136 C-02 is mentioned on the sticker, placed on the
bottom side of the PCB.
The board marking MB1136 C-01 corresponds to a board, configured as HSE not used.
The board marking MB1136 C-02 (or higher) corresponds to a board, configured to use
ST-LINK MCO as the clock input.
24/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Note: For NUCLEO-L476RG and NUCLEO-L452RE the ST-LINK MCO output is not connected to
OSCIN to reduce power consumption in low power mode. Consequently, NUCLEO-L476RG
and NUCLEO-L452RE configurations correspond to HSE not used.
6.7.2 OSC 32 kHz clock supply
There are three ways to configure the pins corresponding to the low-speed clock (LSE):
• On-board oscillator: X2 crystal. Refer to the Oscillator design guide for STM8S,
STM8A and STM32 microcontrollers application note (AN2867) for oscillator design
guide for STM32 microcontrollers.It is recommended to use ABS25-32.768KHZ-6-T,
manufactured by Abracon Corporation.
• Oscillator from external PC14: from external oscillator through the pin 25 of CN7
connector.
The following configuration is needed:
– SB48 and SB49 ON
– R34 and R36 removed
• LSE not used: PC14 and PC15 are used as GPIOs instead of low-speed clocks.
The following configuration is needed:
– SB48 and SB49 ON
– R34 and R36 removed
There are three possible default configurations of the LSE depending on the version of the
STM32 Nucleo board hardware.
The board version MB1136 C-01 or MB1136 C-02 is mentioned on the sticker placed on the
bottom side of the PCB.
The board marking MB1136 C-01 corresponds to a board configured as LSE not used.
The board marking MB1136 C-02 (or higher) corresponds to a board configured with
on-board 32 kHz oscillator.
The board marking MB1136 C-03 (or higher) corresponds to a board using new LSE crystal
(ABS25) and C26, C31, and C32 value update.
6.8 USART communication
The USART2 interface available on PA2 and PA3 of the STM32 microcontroller can be
connected to ST-LINK MCU, ST morpho connector, or to ARDUINO® connector. The choice
can be changed by setting the related solder bridges. By default, the USART2
communication between the target STM32 and ST-LINK MCU is enabled, in order to
support virtual COM port for Mbed™ (SB13 and SB14 ON, SB62 and SB63 OFF). If the
communication between the target STM32 PA2 (D1) or PA3 (D0) and shield or extension
board is required, SB62 and SB63 must be ON, while SB13 and SB14 must be OFF. In such
a case, it is possible to connect another USART to ST-LINK MCU using flying wires between
the ST morpho connector and CN3. For instance, on NUCLEO-F103RB it is possible to use
USART3 available on PC10 (TX) and PC11 (RX). Two flying wires need to be connected as
follow:
• PC10 (USART3_TX) available on CN7 pin 1 to CN3 pin RX
• PC11 (USART3_RX) available on CN7 pin 2 to CN3 pin TX
UM1724 Rev 14 25/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
6.9 Solder bridges
Table 10. Solder bridges
Bridge State(1) Description
X3, C33, C34, R35, and R37 provide a clock as shown in electrical
OFF
schematics PF0/PD0/PH0, PF1/PD1/PH1 are disconnected from CN7.
SB54, SB55 (X3 crystal)(2)
PF0/PD0/PH0 and PF1/PD1/PH1 are connected to CN7. (R35, R37, and
ON
SB50 must not be fitted).
SB3, SB5, SB7,SB9
ON Reserved, do not modify.
(DEFAULT)
SB4,SB6, SB8,SB10
OFF Reserved, do not modify.
(RESERVED)
X2, C31, C32, R34, and R36 deliver a 32 kHz clock. PC14, PC15 are not
SB48, SB49 OFF
connected to CN7.
(X2 crystal)(3)
ON PC14 and PC15 are only connected to CN7. Remove only R34, R36.
SB17 ON B1 push button is connected to PC13.
(B1-USER) OFF B1 push button is not connected to PC13.
The NRST signal of the CN4 connector is connected to the NRST pin of the
ON
STM32.
SB12 (NRST)
The NRST signal of the CN4 connector is not connected to the NRST pin of
OFF
the STM32.
ON The SWO signal of the CN4 connector is connected to PB3.
SB15 (SWO)
OFF The SWO signal is not connected.
OFF No incidence on STM32F103CBT6 (ST-LINK MCU) NRST signal.
SB11 (STM_RST)
ON STM32F103CBT6 (ST-LINK MCU) NRST signal is connected to GND.
OFF USB power management is functional.
SB1 (USB-5V)
ON USB power management is disabled.
ON Output of voltage regulator LD39050PU33R is connected to 3.3V.
SB2 (3.3 V)
OFF Output of voltage regulator LD39050PU33R is not connected.
ON Green user LED LD2 is connected to D13 of ARDUINO® signal.
SB21 (LD2-LED)
OFF Green user LED LD2 is not connected.
PC1 and PC0 (ADC in) are connected to A4 and A5 (pin 5 and pin 6) on
ON ARDUINO® connector CN8 and ST morpho connector CN7. Thus SB46 and
SB56,SB51 (A4 and A5) SB52 must be OFF.
PC1 and PC0 (ADC in) are disconnected to A4 and A5 (pin 5 and pin 6) on
OFF
ARDUINO® connector CN8 and ST morpho connector CN7.
PB9 and PB8 (I2C) are disconnected to A4 and A5 (pin 5 and pin 6) on
OFF
ARDUINO® connector CN8 and ST morpho connector CN7.
SB46,SB52
(I2C on A4 and A5) PB9 and PB8 (I2C) are connected to A4 and A5 (pin 5 and pin 6) on
ON ARDUINO® connector CN8 and ST morpho connector CN7 as I2C signals.
Thus SB56 and SB51 must be OFF.
26/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 10. Solder bridges (continued)
Bridge State(1) Description
ON VBAT or VLCD on STM32 is connected to VDD.
SB45 (VBAT/VLCD)
OFF VBAT or VLCD on STM32 is not connected to VDD.
ON VDDA/VREF+ on STM32 is connected to VDD.
SB57 (VDDA/VREF+) VDDA/VREF+ on STM32 is not connected to VDD and can be provided from
OFF
pin 8 of CN5 (Used for external VREF+ provided by ARDUINO® shield)
PA2 and PA3 on STM32 are disconnected to D1 and D0 (pin 2 and pin 1) on
OFF
ARDUINO® connector CN9 and ST morpho connector CN10.
SB62, SB63 (USART) PA2 and PA3 on STM32 are connected to D1 and D0 (pin 2 and pin 1) on
ON ARDUINO® connector CN9 and ST morpho connector CN10 as USART
signals. Thus SB13 and SB14 must be OFF.
PA2 and PA3 on STM32F103CBT6 (ST-LINK MCU) are connected to PA3
ON and PA2 on STM32 to have USART communication between them. Thus
SB13, SB14 SB61, SB62, and SB63 must be OFF.
(ST-LINK-USART)
PA2 and PA3 on STM32F103CBT6 (ST-LINK MCU) are disconnected to PA3
OFF
and PA2 on STM32.
MCO on STM32F103CBT6 (ST-LINK MCU) are disconnected to
OFF
PF0/PD0/PH0 on STM32.
SB16,SB50(MCO)(2)
MCO on STM32F103CBT6 (ST-LINK MCU) are connected to PF0/PD0/PH0
ON
on STM32.
1. The default SBx state is shown in bold.
2. The default configuration depends on the board version. Refer to Section 6.7.1: OSC clock supply for details.
3. The default configuration depends on the board version. Refer to Section 6.7.2: OSC 32 kHz clock supply for details.
All the other solder bridges present on the STM32 Nucleo board are used to configure
several I/Os and power supply pins for compatibility of features and pinout with STM32
supported.
All STM32 Nucleo boards are delivered with the solder-bridges configured according to the
target supported STM32.
6.10 Extension connectors
Figure 10 to Figure 26 show the signals connected by default to ARDUINO® Uno V3
connectors (CN5, CN6, CN8, CN9) and to ST morpho connector (CN7 and CN10), for each
STM32 Nucleo board.
UM1724 Rev 14 27/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Figure 10. NUCLEO-F030R8
NUCLEO-F030R8
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
PF6 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
PF7 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PF0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PF1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 PF5
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 PF4
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv34385V3
Figure 11. NUCLEO-F070RB
NUCLEO-F070RB
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PF0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PF1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VDD 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv36554V1
28/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Figure 12. NUCLEO-F072RB
NUCLEO-F072RB
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PF0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PF1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv34386V3
Figure 13. NUCLEO-F091RC
NUCLEO-F091RC
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
PF11-BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PF0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PF1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv35752V1
UM1724 Rev 14 29/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Figure 14. NUCLEO-F103RB
NUCLEO-F103RB
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PD0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PD1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv34382V3
Figure 15. NUCLEO-F302R8
NUCLEO-F302R8
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PB13 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PB14 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PB15 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PA7
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PA6
PF0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PA5
PF1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv34931V3
30/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Figure 16. NUCLEO-F303RE
NUCLEO-F303RE
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PF0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PF1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv35753V1
Figure 17. NUCLEO-F334R8
NUCLEO-F334R8
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PF0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PF1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv34932V3
UM1724 Rev 14 31/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Figure 18. NUCLEO-F401RE
NUCLEO-F401RE
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 NC
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PH0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PH1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv34384V3
Figure 19. NUCLEO-F411RE
NUCLEO-F411RE
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 NC
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PH0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PH1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv34933V3
32/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Figure 20. NUCLEO-L053R8
NUCLEO-L053R8
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PH0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PH1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VLCD 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv34934V3
Figure 21. NUCLEO-L073RZ and NUCLEO-L010RB
NUCLEO-L073RZ
NUCLEO-L010RB
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PH0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PH1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VLCD 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv49223V1
UM1724 Rev 14 33/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Figure 22. NUCLEO-L152RE
NUCLEO-L152RE
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PH0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PH1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VLCD 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv34383V3
Figure 23. NUCLEO-L452RE
NUCLEO-L452RE
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PH0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PH1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv44302V1
34/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Figure 24. NUCLEO-L476RG
NUCLEO-L476RG
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 PB11
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PH0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PH1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv36556V1
Figure 25. NUCLEO-F446RE
NUCLEO-F446RE
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PD2 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 NC
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PH0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PH1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv38556V1
UM1724 Rev 14 35/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Figure 26. NUCLEO-F410RB
NUCLEO-F410RB
CN7 CN6 CN5 CN10
PC9
PC10 1 2 PC11 1 2 PC8
D15 PB8 10
PC12 3 4 PB11 3 4 PC6
D14 PB9 9
VDD 5 6 E5V 5 6 PC5
AVDD AVDD 8
BOOT0 7 8 GND 7 8 U5V
GND GND 7
NC 9 10 1 NC NC 9 10 NC
D13 PA5 6
NC 11 12 2 IOREF IOREF 11 12 PA12
D12 PA6 5
PA13 13 14 3 RESET RESET 13 14 PA11
D11 PA7 4
PA14 15 16 4 +3V3 +3V3 15 16 PB12
D10 PB6 3
PA15 17 18 5 +5V +5V 17 18 NC
D9 PC7 2
GND 19 20 6 GND GND 19 20 GND
D8 PA9 1
PB7 21 22 7 GND GND 21 22 PB2
PC13 23 24 8 VIN VIN D7 PA8 8 23 24 PB1
PC14 25 26 NC D6 PB10 7 25 26 PB15
PC15 27 28 1 PA0 A0 D5 PB4 6 27 28 PB14
PH0 29 30 2 PA1 A1 D4 PB5 5 29 30 PB13
PH1 31 32 3 PA4 A2 D3 PB3 4 31 32 AGND
VBAT 33 34 4 PB0 A3 D2 PA10 3 33 34 PC4
PC2 35 36 5 PC1 A4 D1 PA2 2 35 36 NC
PC3 37 38 6 PC0 A5 D0 PA3 1 37 38 NC
CN8 CN9
Arduino Morpho
MSv38557V1
36/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
6.11 ARDUINO® connectors
CN5, CN6, CN8, and CN9 are female connectors compatible with ARDUINO® standard.
Most shields designed for ARDUINO® can fit the STM32 Nucleo boards.
The ARDUINO® connectors on the STM32 Nucleo board support the ARDUINO® Uno V3.
For compatibility with ARDUINO® Uno V1, apply the following modifications:
• SB46 and SB52 must be ON,
• SB51 and SB56 must be OFF to connect I2C on A4 (pin 5) and A5 (pin 6 of CN8).
Caution 1: The I/Os of STM32 microcontroller are 3.3 V compatible instead of 5 V for ARDUINO® Uno
V3.
Caution 2: SB57 must be removed before implementing ARDUINO® shield with VREF+ power being
provided on CN5 pin 8. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details on SB57.
Table 11 to Table 23 show the pin assignment of each main STM32 microcontroller on
ARDUINO® connectors.
Table 11. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F030R8, NUCLEO-F070RB,
NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F091RC
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC_IN0
2 A1 PA1 ADC_IN1
3 A2 PA4 ADC_IN4
CN8 analog
4 A3 PB0 ADC_IN8
(1)
5 A4 PC1 or PB9 ADC_IN11 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC_IN10 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
CN5 digital
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
UM1724 Rev 14 37/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 11. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F030R8, NUCLEO-F070RB,
NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F091RC (continued)
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM17_CH1 or SPI1_MOSI
CN5 digital
3 D10 PB6 TIM16_CH1N or SPI1_CS
2 D9 PC7 TIM3_CH2
1 D8 PA9 -
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3(2)
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2(3)
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
2. PWM is not supported by D6 on STM32F030 and STM32F070 since the timer is not available on PB10.
3. PWM is not supported by D3 on STM32F030 and STM32F070 since the timer is not available on PB3.
38/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 12. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F103RB
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC -
-
2 IOREF 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND ground
8 VIN Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC_0
2 A1 PA1 ADC_1
3 A2 PA4 ADC_4
CN8 analog
4 A3 PB0 ADC_8
5 A4 PC1 or PB9(1) ADC_11 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC_10 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
8 AREF AVDD
-
7 GND ground
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
CN5 digital
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM3_CH2 or SPI1_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 TIM4_CH1 or SPI1_CS
2 D9 PC7 TIM3_CH2
1 D8 PA9
-
8 D7 PA8
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
UM1724 Rev 14 39/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 13. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F302R8
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC_IN1
2 A1 PA1 ADC_IN2
3 A2 PA4 ADC_IN5
CN8 analog
4 A3 PB0 ADC_IN11
(1)
5 A4 PC1 or PB9 ADC_IN7 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC_IN6 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
6 D13 PB13 SPI2_SCK
CN5 digital
5 D12 PB14 SPI2_MISO
4 D11 PB15 TIM15_CH2 or SPI2_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 TIM16_CH1N or SPI2_CS
2 D9 PC7 -
1 D8 PA9 -
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM16_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
40/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Warning: PWM is not supported by D9 on STM32F302 since the timer is not
available on PC7.
Table 14. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F303RE
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC1_IN1
2 A1 PA1 ADC1_IN2
3 A2 PA4 ADC2_IN1
CN8 analog 4 A3 PB0 ADC3_IN12
5 A4 PC1 or PB9(1) ADC12_IN7 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC12_IN6 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
CN5 digital
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM17_CH1 or SPI1_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 TIM4_CH1 or SPI1_CS
2 D9 PC7 TIM3_CH2
1 D8 PA9 -
UM1724 Rev 14 41/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 14. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F303RE (continued)
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
CN9 digital 5 D4 PB5 -
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
Table 15. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F334R8
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC1_IN1
2 A1 PA1 ADC1_IN2
3 A2 PA4 ADC2_IN1
CN8 analog
4 A3 PB0 ADC1_IN11
(1)
5 A4 PC1 or PB9 ADC_IN7 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC_IN6 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
CN5 digital
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM17_CH1 or SPI1_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 TIM16_CH1N or SPI1_CS
42/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 15. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F334R8 (continued)
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
2 D9 PC7 TIM3_CH2
CN5 digital
1 D8 PA9 -
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
Table 16. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F401RE and NUCLEO-F411RE
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC1_0
2 A1 PA1 ADC1_1
3 A2 PA4 ADC1_4
CN8 analog
4 A3 PB0 ADC1_8
(1)
5 A4 PC1 or PB9 ADC1_11 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC1_10 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
CN5 digital
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
UM1724 Rev 14 43/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 16. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F401RE and NUCLEO-F411RE (continued)
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM1_CH1N or SPI1_MOSI
CN5 digital
3 D10 PB6 TIM4_CH1 or SPI1_CS
2 D9 PC7 TIM3_CH2
1 D8 PA9 -
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
44/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 17. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L053R8
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC_IN0
2 A1 PA1 ADC_IN1
3 A2 PA4 ADC_IN4
CN8 analog
4 A3 PB0 ADC_IN8
(1)
5 A4 PC1 or PB9 ADC_IN11 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC_IN10 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
CN5 digital
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM12_CH2 or SPI1_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 SPI1_CS
2 D9 PC7 TIM12_CH2
1 D8 PA9 -
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM12_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
UM1724 Rev 14 45/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Warning: PWM is not supported by D10 on STM32L053 since the timer is not
available on PB6.
Table 18. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L010RB and NUCLEO-L073RZ
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC_IN0
2 A1 PA1 ADC_IN1
CN8 3 A2 PA4 ADC_IN4
analog 4 A3 PB0 ADC_IN8
5 A4 PC1 or PB9(1) ADC_IN11 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC_IN10 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
CN5 digital
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM22_CH2 or SPI1_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 SPI1_CS
2 D9 PC7 TIM3_CH2
1 D8 PA9 -
46/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 18. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L010RB and NUCLEO-L073RZ (continued)
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
Warning: PWM is not supported by D10 on STM32L010 and STM32L073 since the
timer is not available on PB6.
Table 19. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F446RE
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC123_IN0
2 A1 PA1 ADC123_IN1
CN8 3 A2 PA4 ADC12_IN4
analog 4 A3 PB0 ADC12_IN8
(1)
5 A4 PC1 or PB9 ADC123_IN11 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC123_IN10 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
CN5 digital
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
UM1724 Rev 14 47/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 19. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F446RE (continued)
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
CN5 digital
4 D11 PA7 TIM14_CH1 || SPI1_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 TIM4_CH1 || SPI1_CS
2 D9 PC7 TIM8_CH2
1 D8 PA9 -
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
48/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 20. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F410RB
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC1_0
2 A1 PA1 ADC1_1
CN8 3 A2 PA4 ADC1_4
analog 4 A3 PB0 ADC1_8
(1)
5 A4 PC1 or PB9 ADC1_11 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC1_10 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 PB8 D15 I2C1_SCL
9 PB9 D14 I2C1_SDA
8 - AREF AVDD
7 - GND ground
6 PA5 D13 SPI1_SCK
CN5 digital
5 PA6 D12 SPI1_MISO
4 PA7 D11 TIM1_CH1N || SPI1_MOSI
3 PB6 D10 SPI1_CS
2 PC7 D9 -
1 PA9 D8 -
8 PA8 D7 -
7 PB10 D6 -
6 PB4 D5 -
5 PB5 D4 -
CN9 digital
4 PB3 D3 -
3 PA10 D2 -
2 PA2 D1 USART2_TX
1 PA3 D0 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
UM1724 Rev 14 49/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Warning: PWM is not supported by D3, D5, D6, D9 and D10 on STM32F410RB
since timer is not available on PB6, PC7, PB10, PB4, PB3.
Table 21. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L152RE
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC_IN0
2 A1 PA1 ADC_IN1
3 A2 PA4 ADC_IN4
CN8 analog
4 A3 PB0 ADC_IN8
5 A4 PC1 or PB9(1) ADC_IN11 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8(1) ADC_IN10 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
CN5 digital
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM11_CH1 or SPI1_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 TIM4_CH1 or SPI1_CS
2 D9 PC7 TIM3_CH2
1 D8 PA9 -
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
CN9 digital
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
50/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 21. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L152RE (continued)
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
CN9 digital
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
Table 22. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L452RE
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC1_IN5
2 A1 PA1 ADC1_IN6
CN8 3 A2 PA4 ADC1_IN9
analog 4 A3 PB0 ADC1_IN15
5 A4 PC1 or PB9(1) ADC1_IN2 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
(1)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8 ADC1_IN1 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
CN5 digital
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM1_CH1N or SPI1_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 TIM16_CH1N or SPI1_CS
2 D9 PC7 TIM3_CH2
1 D8 PA9 -
CN9 digital 8 D7 PA8 -
UM1724 Rev 14 51/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 22. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L452RE (continued)
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital 4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
Table 23. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L476RG
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
Left connectors
1 NC - -
2 IOREF - 3.3V Ref
3 RESET NRST RESET
4 +3.3V - 3.3V input/output
CN6 power
5 +5V - 5V output
6 GND - ground
7 GND - ground
8 VIN - Power input
1 A0 PA0 ADC12_IN5
2 A1 PA1 ADC12_IN6
CN8 3 A2 PA4 ADC12_IN9
analog 4 A3 PB0 ADC12_IN15
5 A4 PC1 or PB9(1) ADC123_IN2 (PC1) or I2C1_SDA (PB9)
(1)
6 A5 PC0 or PB8 ADC123_IN1 (PC0) or I2C1_SCL (PB8)
Right connectors
10 D15 PB8 I2C1_SCL
9 D14 PB9 I2C1_SDA
8 AREF - AVDD
7 GND - ground
CN5 digital
6 D13 PA5 SPI1_SCK
5 D12 PA6 SPI1_MISO
4 D11 PA7 TIM17_CH1 or SPI1_MOSI
3 D10 PB6 TIM4_CH1 or SPI1_CS
52/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 23. ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-L476RG (continued)
Connector Pin Pin name STM32 pin Function
2 D9 PC7 TIM3_CH2
CN5 digital
1 D8 PA9 -
8 D7 PA8 -
7 D6 PB10 TIM2_CH3
6 D5 PB4 TIM3_CH1
5 D4 PB5 -
CN9 digital
4 D3 PB3 TIM2_CH2
3 D2 PA10 -
2 D1 PA2 USART2_TX
1 D0 PA3 USART2_RX
1. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
6.12 ST morpho connector
The ST morpho connector consists in male pin headers (CN7 and CN10) accessible on both
sides of the board. They can be used to connect the STM32 Nucleo board to an extension
board or a prototype/wrapping board placed on top or on bottom side of the STM32 Nucleo
board. All signals and power pins of the STM32 are available on ST morpho connector. This
connector can also be probed by an oscilloscope, logical analyzer or voltmeter.
Table 24 to Table 33 show the pin assignments of each STM32 on ST morpho connector.
Table 24. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F030R8
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PD2 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
7 BOOT0(1) GND 8 7 AVDD U5V(2) 8
9 PF6 - 10 9 GND - 10
11 PF7 IOREF 12 11 PA5 PA12 12
13 PA13 RESET 14 13 PA6 PA11 14
15 PA14 +3.3V 16 15 PA7 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 PB11 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13(3) VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14(3) - 26 25 PB10 PB15 26
UM1724 Rev 14 53/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 24. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F030R8 (continued)
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PB14 28
29 PF0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PB13 30
31 PF1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VBAT PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
PC1 or
35 PC2 36 35 PA2 PF5 36
PB9(4)
PC0 or
37 PC3 38 37 PA3 PF4 38
PB8(4)
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pin5-7 of CN7. Two unused
jumpers are available on CN11 and CN12 (bottom side of the board).
2. U5V is 5 V power from ST-LINK/V2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5V.
3. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to use them
as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
4. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
Table 25. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F070RB
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PD2 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
7 BOOT0(1) GND 8 7 AVDD U5V(2) 8
9 - - 10 9 GND - 10
11 - IOREF 12 11 PA5 PA12 12
13 PA13(3) RESET 14 13 PA6 PA11 14
15 PA14(3) +3.3V 16 15 PA7 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 PB11 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13 VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14 - 26 25 PB10 PB15 26
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PB14 28
29 PF0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PB13 30
31 PF1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VDD PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
35 PC2 PC1 or PB9(4) 36 35 PA2 - 36
37 PC3 PC0 or PB8(4) 38 37 PA3 - 38
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pin5-7 of CN7.
2. U5V is 5 V power from ST-LINK/V2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5V.
3. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to use them
as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
4. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
54/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 26. ST morpho connector on
NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F091RC, NUCLEO-F303RE, NUCLEO-F334R8
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PD2 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
7 BOOT0(1)(2) GND 8 7 AVDD U5V (3)
8
9 - - 10 9 GND - 10
11 - IOREF 12 11 PA5 PA12 12
13 PA13(4) RESET 14 13 PA6 PA11 14
(4)
15 PA14 +3.3V 16 15 PA7 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 PB11 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13 VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14 - 26 25 PB10 PB15 26
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PB14 28
29 PF0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PB13 30
31 PF1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VBAT PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
PC1 or
35 PC2 36 35 PA2 - 36
PB9(5)
PC0 or
37 PC3 38 37 PA3 - 38
PB8(5)
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pin5-7 of CN7. Two unused
jumpers are available on CN11 and CN12 (bottom side of the board).
2. CN7 pin 7 (BOOT0) can be configured by engineering byte as PF11 on NUCLEO-F091RC.
3. U5V is 5 V power from ST-LINK/V2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5V.
4. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to use them
as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
5. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
Table 27. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F103RB
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PD2 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
UM1724 Rev 14 55/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 27. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F103RB (continued)
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
7 BOOT0(1) GND 8 7 AVDD U5V(2) 8
9 - - 10 9 GND - 10
11 - IOREF 12 11 PA5 PA12 12
(3)
13 PA13 RESET 14 13 PA6 PA11 14
15 PA14(3) +3.3V 16 15 PA7 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 PB11 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13 VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14 - 26 25 PB10 PB15 26
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PB14 28
29 PD0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PB13 30
31 PD1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VBAT PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
PC1 or
35 PC2 36 35 PA2 - 36
PB9(4)
PC0 or
37 PC3 38 37 PA3 - 38
PB8(4)
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pin5-7 of CN7. Two unused
jumpers are available on CN11 and CN12 (bottom side of the board).
2. U5V is 5 V power from ST-LINK/V2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5 V.
3. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to use them
as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
4. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
56/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 28. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F302R8
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PD2 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
7 BOOT0(1) GND 8 7 AVDD U5V (2)
8
9 - - 10 9 GND - 10
11 - IOREF 12 11 PB13 PA12 12
13 PA13(3) RESET 14 13 PB14 PA11 14
(3)
15 PA14 +3.3V 16 15 PB15 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 PB11 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13 VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14 - 26 25 PB10 PA7 26
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PA6 28
29 PF0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PA5 30
31 PF1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VBAT PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
PC1 or
35 PC2 36 35 PA2 - 36
PB9(4)
PC0 or
37 PC3 38 37 PA3 - 38
PB8(4)
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pin5-7 of CN7. Two unused
jumpers are available on CN11 and CN12 (bottom side of the board).
2. U5V is 5 V power from ST-LINK/V2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5V.
3. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to use them
as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
4. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
UM1724 Rev 14 57/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 29. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F401RE,
NUCLEO-F411RE, NUCLEO-F446RE
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PD2 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
7 BOOT0(1) GND 8 7 AVDD U5V (2)
8
9 - - 10 9 GND - 10
11 - IOREF 12 11 PA5 PA12 12
13 PA13(3) RESET 14 13 PA6 PA11 14
(3)
15 PA14 +3.3V 16 15 PA7 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 - 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13 VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14 - 26 25 PB10 PB15 26
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PB14 28
29 PH0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PB13 30
31 PH1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VBAT PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
PC1 or
35 PC2 36 35 PA2 - 36
PB9(4)
PC0 or
37 PC3 38 37 PA3 - 38
PB8(4)
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pin5-7 of CN7. Two unused
jumpers are available on CN11 and CN12 (bottom side of the board).
2. U5V is 5 V power from ST-LINK/V2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5V.
3. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to use them
as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
4. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
58/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 30. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-L010RB,
NUCLEO-L053R8, NUCLEO-L073RZ, NUCLEO-L152RE
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PD2 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
7 BOOT0(1) GND 8 7 AVDD U5V (2)
8
9 - - 10 9 GND - 10
11 - IOREF 12 11 PA5 PA12 12
13 PA13(3) RESET 14 13 PA6 PA11 14
(3)
15 PA14 +3.3V 16 15 PA7 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 PB11 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13 VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14 - 26 25 PB10 PB15 26
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PB14 28
29 PH0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PB13 30
31 PH1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VLCD PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
PC1 or
35 PC2 36 35 PA2 - 36
PB9(4)
PC0 or
37 PC3 38 37 PA3 - 38
PB8(4)
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pin5-7 of CN7. Two unused
jumpers are available on CN11 and CN12 (bottom side of the board).
2. U5V is 5 V power from ST-LINK/V2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5V.
3. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to use them
as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
4. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
UM1724 Rev 14 59/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 31. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-L452RE
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PD2 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
PH3 /
7 GND 8 7 AVDD U5V(2) 8
BOOT0(1)
9 - - 10 9 GND - 10
11 - IOREF 12 11 PA5 PA12 12
(3)
13 PA13 RESET 14 13 PA6 PA11 14
15 PA14(3) +3.3V 16 15 PA7 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 PB11 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13 VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14 - 26 25 PB10 PB15 26
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PB14 28
29 PH0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PB13 30
31 PH1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VBAT PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
PC1
35 PC2 or 36 35 PA2 - 36
PB9(4)
PC0
37 PC3 or 38 37 PA3 - 38
PB8(4)
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pins 5-7 of CN7.
2. U5V is 5 V power from ST-LINK/V2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5V.
3. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to
use them as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
4. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
60/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Hardware layout and configuration
Table 32. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-L476RG
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PD2 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
7 BOOT0(1) GND 8 7 AVDD U5V (2)
8
9 - - 10 9 GND - 10
11 - IOREF 12 11 PA5 PA12 12
13 PA13(3) RESET 14 13 PA6 PA11 14
(3)
15 PA14 +3.3V 16 15 PA7 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 PB11 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13 VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14 - 26 25 PB10 PB15 26
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PB14 28
29 PH0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PB13 30
31 PH1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VBAT PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
PC1 or
35 PC2 36 35 PA2 - 36
PB9(4)
PC0 or
37 PC3 38 37 PA3 - 38
PB8(4)
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pin5-7 of CN7.
2. U5V is 5 V power from ST-LINK/V2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5V.
3. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to use them
as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
4. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
UM1724 Rev 14 61/68
67
Hardware layout and configuration UM1724
Table 33. ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F410RB
CN7 odd pins CN7 even pins CN10 odd pins CN10 even pins
Pin Name Name Pin Pin Name Name Pin
1 PC10 PC11 2 1 PC9 PC8 2
3 PC12 PB11 4 3 PB8 PC6 4
5 VDD E5V 6 5 PB9 PC5 6
7 BOOT0(1) GND 8 7 AVDD U5V (2)
8
9 - - 10 9 GND - 10
11 - IOREF 12 11 PA5 PA12 12
13 PA13(3) RESET 14 13 PA6 PA11 14
(3)
15 PA14 +3.3V 16 15 PA7 PB12 16
17 PA15 +5V 18 17 PB6 - 18
19 GND GND 20 19 PC7 GND 20
21 PB7 GND 22 21 PA9 PB2 22
23 PC13 VIN 24 23 PA8 PB1 24
25 PC14 - 26 25 PB10 PB15 26
27 PC15 PA0 28 27 PB4 PB14 28
29 PH0 PA1 30 29 PB5 PB13 30
31 PH1 PA4 32 31 PB3 AGND 32
33 VBAT PB0 34 33 PA10 PC4 34
(4)
35 PC2 PC1 or PB9 36 35 PA2 - 36
37 PC3 PC0 or PB8(4) 38 37 PA3 - 38
1. The default state of BOOT0 is LOW. It can be set to HIGH when a jumper is on pin5-7 of CN7.
2. U5V is 5 V power from the ST-LINKV2-1 USB connector and it rises before +5V.
3. PA13 and PA14 share with SWD signals connected to ST-LINK/V2-1, it is not recommended to use them
as IO pins if the ST-LINK part is not cut.
4. Refer to Table 10: Solder bridges for details.
62/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Nucleo-64 boards information
7 Nucleo-64 boards information
7.1 Product marking
The sticker located on the top or bottom side of the PCB board shows the information about
product identification such as board reference, revision, and serial number.
The first identification line has the following format: ‘MBxxxx-Variant-yzz’, where ‘MBxxxx’ is
the board reference, ‘Variant’ (optional) identifies the mounting variant when several exist,
‘y’ is the PCB revision and ‘zz’ is the assembly revision: for example B01.
The second identification line is the board serial number used for traceability.
Evaluation tools marked as “ES” or “E” are not yet qualified and therefore not ready to be
used as reference design or in production. Any consequences deriving from such usage will
not be at ST charge. In no event, ST will be liable for any customer usage of these
engineering sample tools as reference design or in production.
‘E’ or ‘ES’ marking examples of location:
• On the target STM32 that is soldered on the board (for illustration of STM32 marking,
refer to the STM32 datasheet “Package information” paragraph at the www.st.com
website).
• Next to the evaluation tool ordering part number that is stuck or silk-screen printed on
the board.
Some boards feature a specific STM32 device version that allows the operation of any stack
or library. This STM32 device shows a ‘U’ marking option at the end of the standard part
number and is not available for sales.
In order to use the same commercial stack in his application, a developer may need to
purchase a part number specific to this stack/library. The price of those part numbers
includes the stack/library royalties.
The board reference for the STM32 Nucleo-144 boards is MB1136.
UM1724 Rev 14 63/68
67
Nucleo-64 boards information UM1724
7.2 Board revision history
Revision C-01
The revision C-01 is the initially released version.
Revision C-02
Add LSE:
• X2(32 KHz)
• R34 and R36 changed from OFF to 0 Ω
• C31 and C32 changed from OFF to 10 pF
• SB48 and SB49 changed from ON to OFF
Remove HSE:
• SB16 and SB50 changed from OFF to ON
• SB55 changed from ON to OFF
Note that for the NUCLEO-L4xxRx Nucleo-64 boards:
• SB16 and SB50 must be OFF.
• SB55 changed must be ON.
Revision C-03
• X2 changed to ABS25-32.768KHZ-6-TB
• C31 and C32 changed from 10 pF to 4.3 pF
• C26 changed from 2.2 µF to 4.7 µF
Revision C-04
• T2 changed from STS7PF30L to STS9P3LLH6
7.3 Board known limitations
Revisions C-01 to C-04
None
64/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Revision history
Revision history
Table 34. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
10-Feb-2014 1 Initial release.
13-Feb-2014 2 Updated Figure 1, Chapter 5.5 and Table 10.
Extended the applicability to NUCLEO-F302R8. Updated Table 1:
Ordering information, Section 6.11: Arduino connectors and
11-Apr-2014 3 Section 6.12: ST morpho connector.
Updated Figure 1
Updated the board figure: Figure 1.
Updated HSE and LSE configuration description: Section 6.7.1,
10-June-2014 4
Section 5.5, and Section 6.7.2. Extended the applicability to
NUCLEO-F334R8, NUCLEO-F411RE, and NUCLEO-L053R8.
Updated the electrical schematics figures: Figure 27, Figure 28,
Figure 29, and Figure 30.
20-June-2014 5 Refer to the AN2867 for oscillator design guide for STM32
microcontrollers in Section 6.7.1: OSC clock supply and
Section 6.7.2: OSC 32 KHz clock supply.
Extended the applicability to NUCLEO-F091RC and NUCLEO-
F303RE;
Updated Table 1: Ordering information;
Updated Table 11: Arduino connectors on NUCLEO-F030R8,
NUCLEO-F070RB, NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F091RC;
Updated Table 26: ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F072RB,
30-Sept-2014 6 NUCLEO-F091RC, NUCLEO-F303RE, NUCLEO-F334R8;
Updated Figure 6: Typical configuration;
Added Figure 13: NUCLEO-F091RC;
Added Figure 16: NUCLEO-F303RE;
Updated Section 6.7.2: OSC 32 KHz clock supply;
Updated Figure 27: Top and Power(1/4) ,Figure 28: STM32 MCU;
UM1724 Rev 14 65/68
67
Revision history UM1724
Table 34. Document revision history (continued)
Date Revision Changes
Extended the applicability to NUCLEO-F070RB, NUCLEO-
L073RZ, and NUCLEO-L476RG;
Updated Table 1: Ordering information;
Updated Section 6.2: Embedded ST-LINK/V2-1;
Updated Section 6.7.1: OSC clock supply;
Added Figure 11: NUCLEO-F070RB;
Added Figure 21: NUCLEO-L073RZ;
Added Figure 24: NUCLEO-L476RG
19-Jan-2015 7 Updated Table 11: Arduino connectors on NUCLEO-F030R8,
NUCLEO-F070RB, NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F091RC
Added Table 18: Arduino connectors on NUCLEO-L073RZ
Added Table 23: Arduino connectors on NUCLEO-L476RG
Added Table 25: ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-F070RB
Updated Table 30: ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-L053R8,
NUCLEO-L073RZ, NUCLEO-L152RE
Added Table 32: ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-L476RG
Updated schematics from Figure 27: Top and Power(1/4) to
Figure 30: Extension connectors
Extended the applicability to Updated Table 1: Ordering
information;
Added Figure 25: NUCLEO-F446RE and Figure 26: NUCLEO-
08-Jul-2015 8
F410RB
Updated Section 6.11: Arduino connectors on page 37 and
Section 6.12: ST morpho connector on page 53
04-Aug-2015 9 Added Section 5.4: NUCLEO-L476RG bootloader limitations.
Updated Section 6.9: Solder bridges and Section 6.7.1: OSC clock
17-Nov-2015 10
supply.
Updated Introduction, Section 3: Ordering information,
Section 6.10: Extension connectors, Section 6.11: Arduino
29-Nov-2015 11
connectors, Section 6.12: ST morpho connector to add NUCLEO-
L452RE.
Updated document title and cover page.
Updated Chapter 2: Product marking and Section 5.3:
Development toolchains.
Expanded document scope to NUCLEO-L010RB:
– Updated Table 1: Ordering information
15-Dec-2017 12
– Updated Table 18: Arduino connectors on NUCLEO-L010RB
and NUCLEO-L073RZ
– Updated Table 21: NUCLEO-L073RZ and NUCLEO-L010RB
– Updated Table 30: ST morpho connector on NUCLEO-L010RB,
NUCLEO-L053R8, NUCLEO-L073RZ, NUCLEO-L152RE
66/68 UM1724 Rev 14
UM1724 Revision history
Table 34. Document revision history (continued)
Date Revision Changes
Updated document title, Introduction, Chapter 2: Ordering
information, Section 2.1: Product marking, Section 2.2:
3-Apr-2019 13 Codification, and Section 5.1: Getting started.
Added Chapter 3: Development environment and Section 3.3:
Demonstration software.
Updated the connector reference in the description of SB54 and
SB55 in Table 10: Solder bridges.
Removed pin 10 duplicated rows in Table 11: ARDUINO®
connectors on NUCLEO-F030R8, NUCLEO-F070RB, NUCLEO-
F072RB, NUCLEO-F091RC, Table 12: ARDUINO® connectors on
19-Aug-2020 14 NUCLEO-F103RB, Table 16: ARDUINO® connectors on
NUCLEO-F401RE and NUCLEO-F411RE, and Table 19:
ARDUINO® connectors on NUCLEO-F446RE.
Removed electrical schematics.
Added Section 7 including Product marking, Board revision
history, and Board known limitations.
UM1724 Rev 14 67/68
67
UM1724
IMPORTANT NOTICE – PLEASE READ CAREFULLY
STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, enhancements, modifications, and
improvements to ST products and/or to this document at any time without notice. Purchasers should obtain the latest relevant information on
ST products before placing orders. ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale in place at the time of order
acknowledgement.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection, and use of ST products and ST assumes no liability for application assistance or
the design of Purchasers’ products.
No license, express or implied, to any intellectual property right is granted by ST herein.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the information set forth herein shall void any warranty granted by ST for such product.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks of ST. For additional information about ST trademarks, please refer to www.st.com/trademarks. All other
product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces information previously supplied in any prior versions of this document.
© 2020 STMicroelectronics – All rights reserved
68/68 UM1724 Rev 14
You might also like
- A Practical Approach To Compiler Construction PDFDocument263 pagesA Practical Approach To Compiler Construction PDFPrakash Chandra75% (4)
- PIC Microcontroller Projects in C: Basic to AdvancedFrom EverandPIC Microcontroller Projects in C: Basic to AdvancedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (10)
- Frankenstein Critical Analysis Evaluation EssayDocument4 pagesFrankenstein Critical Analysis Evaluation Essayselina_kolls100% (3)
- T&T PresentationDocument17 pagesT&T PresentationMohammed HussainNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis - The Home DepotDocument7 pagesFinancial Analysis - The Home DepotbroetalzarmyNo ratings yet
- UM1724 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-64 Boards (MB1136)Document69 pagesUM1724 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-64 Boards (MB1136)Basti NichtechtdernameNo ratings yet
- UM1724 User ManualDocument69 pagesUM1724 User ManualdavidNo ratings yet
- User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-144 Boards (MB1137)Document85 pagesUser Manual: STM32 Nucleo-144 Boards (MB1137)Omri AssafNo ratings yet
- STM32 Nucleo-64 BoardsDocument66 pagesSTM32 Nucleo-64 BoardsFaggotNo ratings yet
- Data NUCLEO-G0B1REDocument44 pagesData NUCLEO-G0B1REEnrique Mtz SanchezNo ratings yet
- User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-144 BoardsDocument82 pagesUser Manual: STM32 Nucleo-144 BoardsJose RobertoNo ratings yet
- Manual Tarjeta - Programador PDFDocument81 pagesManual Tarjeta - Programador PDFWILMER CRUZ DIAZNo ratings yet
- UM2407 User Manual: STM32H7 Nucleo-144 Boards (MB1364)Document50 pagesUM2407 User Manual: STM32H7 Nucleo-144 Boards (MB1364)Jonathan GonzagaNo ratings yet
- UM2408 User Manual: STM32H7 Nucleo-144 Boards (MB1363)Document56 pagesUM2408 User Manual: STM32H7 Nucleo-144 Boards (MB1363)ravikiranzz12345No ratings yet
- En DM00093903Document36 pagesEn DM00093903anjanNo ratings yet
- Um2407 stm32h7 Nucleo144 Boards mb1364 StmicroelectronicsDocument49 pagesUm2407 stm32h7 Nucleo144 Boards mb1364 StmicroelectronicsFelipeAlmeidaNo ratings yet
- En DM00039084 PDFDocument34 pagesEn DM00039084 PDFHưng NgôNo ratings yet
- STM32F3DISCOVERY - User ManualDocument36 pagesSTM32F3DISCOVERY - User ManualBayo PuddicombeNo ratings yet
- Nucleo-32 User ManualDocument34 pagesNucleo-32 User ManualAdrian_666No ratings yet
- UM1670 User Manual: Discovery Kit With STM32F429ZI MCUDocument36 pagesUM1670 User Manual: Discovery Kit With STM32F429ZI MCUDjordje LazarevićNo ratings yet
- UM1570 User Manual: Discovery Kit With STM32F303VC MCUDocument37 pagesUM1570 User Manual: Discovery Kit With STM32F303VC MCUNguyễn Đức ThuậnNo ratings yet
- f411 User ManuelDocument36 pagesf411 User ManuelDeniz Melek TürkNo ratings yet
- Stm32f4 Hardware DevelopmentDocument43 pagesStm32f4 Hardware DevelopmentrevaNo ratings yet
- An5093 Getting Started With stm32g4 Series Hardware Development Boards StmicroelectronicsDocument35 pagesAn5093 Getting Started With stm32g4 Series Hardware Development Boards StmicroelectronicsnounkhayNo ratings yet
- UM2179 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-144 Boards (MB1312)Document48 pagesUM2179 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-144 Boards (MB1312)Cristiano BacelarNo ratings yet
- AN4938 Application Note: Getting Started With STM32H74xI/G and STM32H75xI/G Hardware DevelopmentDocument46 pagesAN4938 Application Note: Getting Started With STM32H74xI/G and STM32H75xI/G Hardware DevelopmentHoàng Nam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- AN4206 Application Note: Getting Started With STM32F3 Series Hardware DevelopmentDocument34 pagesAN4206 Application Note: Getting Started With STM32F3 Series Hardware DevelopmentOmarBinNaeemNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With stm32f030xx and stm32f070xx Series Hardware Development StmicroelectronicsDocument26 pagesGetting Started With stm32f030xx and stm32f070xx Series Hardware Development StmicroelectronicsDinesh DhimanNo ratings yet
- STM32F4 User ManualDocument42 pagesSTM32F4 User ManualAndrei SerghieNo ratings yet
- An2586 Getting Started With Stm32f10xxx Hardware Development StmicroelectronicsDocument29 pagesAn2586 Getting Started With Stm32f10xxx Hardware Development StmicroelectronicsGERMANNo ratings yet
- UM1658 User Manual: Discovery Kit For STM32F030 Value Line MicrocontrollersDocument39 pagesUM1658 User Manual: Discovery Kit For STM32F030 Value Line MicrocontrollerschvsuryaraoNo ratings yet
- Nucleo L152REDocument46 pagesNucleo L152REdiralarkNo ratings yet
- UM2435 User Manual: Bluetooth Low Energy and 802.15.4 Nucleo Pack Based On STM32WB Series MicrocontrollersDocument48 pagesUM2435 User Manual: Bluetooth Low Energy and 802.15.4 Nucleo Pack Based On STM32WB Series MicrocontrollersCoedozNo ratings yet
- STM32F7xxx - Hardware Development PDFDocument54 pagesSTM32F7xxx - Hardware Development PDFYen DaoNo ratings yet
- An4938 Getting Started With Stm32h74xig and Stm32h75xig Hardware Development Stmicroelectronics PDFDocument47 pagesAn4938 Getting Started With Stm32h74xig and Stm32h75xig Hardware Development Stmicroelectronics PDFMax INo ratings yet
- STM32F0 User ManualDocument41 pagesSTM32F0 User Manualandrestv93No ratings yet
- STM32 Nucleo Boards User Manual - ST PDFDocument54 pagesSTM32 Nucleo Boards User Manual - ST PDFSebastian PeñaNo ratings yet
- STM32F429 User ManualDocument38 pagesSTM32F429 User ManualrsudjianNo ratings yet
- UM1956 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-32 Boards (MB1180)Document37 pagesUM1956 User Manual: STM32 Nucleo-32 Boards (MB1180)Oleg ZovNo ratings yet
- ELEKTOR19740Document8 pagesELEKTOR19740abdul shaggyNo ratings yet
- UM1658 User Manual: Discovery Kit For STM32F030 Value Line MicrocontrollersDocument39 pagesUM1658 User Manual: Discovery Kit For STM32F030 Value Line Microcontrollersprashant wagreNo ratings yet
- Application Note AN2586Document28 pagesApplication Note AN2586francisval20No ratings yet
- STM8S Geeting StartedDocument42 pagesSTM8S Geeting Started黃智淵No ratings yet
- Um1079 User ManualDocument39 pagesUm1079 User ManualBharat G Hegde100% (1)
- stm32 PDFDocument38 pagesstm32 PDFpriyaNo ratings yet
- CMB Io-7Document74 pagesCMB Io-7zinab90No ratings yet
- STM32 Nucleo Boards ManualDocument63 pagesSTM32 Nucleo Boards ManualMauro H. S. WencelewskiNo ratings yet
- OpenocdDocument127 pagesOpenocdEne AlexandruNo ratings yet
- ArduinoDocument60 pagesArduinoMonark HunyNo ratings yet
- UM1932 User Manual: Discovery Kit With STM32F469NI MCUDocument40 pagesUM1932 User Manual: Discovery Kit With STM32F469NI MCUWilliBilliNo ratings yet
- UM2411 User Manual: Discovery Kit With STM32H747XI MCUDocument61 pagesUM2411 User Manual: Discovery Kit With STM32H747XI MCUFarouk ElNo ratings yet
- Blue PillDocument1,381 pagesBlue Pillfifa9mbarduinoNo ratings yet
- Mars Zx3 Soc Module: Reference Design For Mars Pm3 Base Board User ManualDocument42 pagesMars Zx3 Soc Module: Reference Design For Mars Pm3 Base Board User ManualgunrjsNo ratings yet
- AN4660Document39 pagesAN4660Toldo94No ratings yet
- Stm32f411 Manual UserDocument35 pagesStm32f411 Manual UserMinh Hoàng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 3 Stm32f4discovery User Manual 2Document40 pages3 Stm32f4discovery User Manual 2haystackmuddyNo ratings yet
- MC68HC705J1ADocument162 pagesMC68HC705J1Ailm86No ratings yet
- UM1564 User Manual: STM32373C-EVAL Evaluation BoardDocument66 pagesUM1564 User Manual: STM32373C-EVAL Evaluation Boardsandeep tanavadekarNo ratings yet
- 68hc705j1 Microcontrolador MotorolaDocument163 pages68hc705j1 Microcontrolador MotorolaNefi Martinez TorresNo ratings yet
- UM1472 User Manual: Stm32F4Discovery STM32F4 High-Performance Discovery BoardDocument38 pagesUM1472 User Manual: Stm32F4Discovery STM32F4 High-Performance Discovery BoardAdnan SahanićNo ratings yet
- UM1237Document166 pagesUM1237KifNo ratings yet
- Tutorialv0 3Document92 pagesTutorialv0 3Malu MohanNo ratings yet
- FinFET Modeling for IC Simulation and Design: Using the BSIM-CMG StandardFrom EverandFinFET Modeling for IC Simulation and Design: Using the BSIM-CMG StandardRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Poly MetamorphicDocument40 pagesPoly MetamorphicPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Acpi 6 2Document1,192 pagesAcpi 6 2Prakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- AMD64 TechnologyDocument3,269 pagesAMD64 TechnologyPrakash Chandra100% (1)
- Bypassing Anti-Analysis of Commercial Protector Methods Using DBI ToolsDocument19 pagesBypassing Anti-Analysis of Commercial Protector Methods Using DBI ToolsPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Bh-Us-08-Bulygin Chip Based Approach To Detect RootkitsDocument38 pagesBh-Us-08-Bulygin Chip Based Approach To Detect RootkitsPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- On The Spectre and Meltdown Processor Security VulnerabilitiesDocument15 pagesOn The Spectre and Meltdown Processor Security VulnerabilitiesPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Zeun 20Document22 pagesZeun 20Prakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Uninformed V3a3Document46 pagesUninformed V3a3Prakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Unveiling Your KeystrokesDocument51 pagesUnveiling Your KeystrokesPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- 32F411Ediscovery: Discovery Kit With STM32F411VE MCUDocument5 pages32F411Ediscovery: Discovery Kit With STM32F411VE MCUPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Obfuscated Malware Detection Using Deep Generative ModelsDocument13 pagesObfuscated Malware Detection Using Deep Generative ModelsPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Malware Detection With LSTM Using Opcode LanguageDocument7 pagesMalware Detection With LSTM Using Opcode LanguagePrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- A Cross-Architecture Instruction Embedding Modelfor Natural Language Processing-Inspired BinaryCode AnalysisDocument8 pagesA Cross-Architecture Instruction Embedding Modelfor Natural Language Processing-Inspired BinaryCode AnalysisPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Detecting Unseen Malicious VBA Macros With NLPTechniquesDocument9 pagesDetecting Unseen Malicious VBA Macros With NLPTechniquesPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Mitigating Cache Based Side Channels Attacks Using RandomizationDocument6 pagesMitigating Cache Based Side Channels Attacks Using RandomizationPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- 0013 Linux Kernel Slides PDFDocument476 pages0013 Linux Kernel Slides PDFPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- BranchScope A New Side-Channel AttackDocument15 pagesBranchScope A New Side-Channel AttackPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Amazon - in - Online Return Center: Tell Us About Your Return ExperienceDocument2 pagesAmazon - in - Online Return Center: Tell Us About Your Return ExperiencePrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- You Are Already A Member: Click The Login Button Below To Access This SiteDocument1 pageYou Are Already A Member: Click The Login Button Below To Access This SitePrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- AipythonDocument221 pagesAipythonPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- English Language: Directions (1 - 15) : Rend Each ParagraphDocument5 pagesEnglish Language: Directions (1 - 15) : Rend Each ParagraphanjanNo ratings yet
- g+5 Building Pr1Document13 pagesg+5 Building Pr1aftabNo ratings yet
- Prolonged and Multipatient Use of Prefilled Disposable OxigenDocument3 pagesProlonged and Multipatient Use of Prefilled Disposable OxigenJorge CunhaNo ratings yet
- Johnson vs. McintoshDocument25 pagesJohnson vs. McintoshGuiller C. MagsumbolNo ratings yet
- Digital SAT Maths Module 2 - EasierDocument11 pagesDigital SAT Maths Module 2 - EasierRico YupitaNo ratings yet
- The English Long BowDocument6 pagesThe English Long BowBruno BarbosaNo ratings yet
- CHN 1 REq. 1 - INITIAL DATA BASE FORM (Revised)Document14 pagesCHN 1 REq. 1 - INITIAL DATA BASE FORM (Revised)Chiz EscubuaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Csec School Based AssessmentDocument9 pagesMathematics Csec School Based AssessmentJ HhhNo ratings yet
- JCB Light Equipment GuideDocument28 pagesJCB Light Equipment GuideMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Tofu CookbookDocument23 pagesTofu Cookbookgpberard3426100% (3)
- UCSP Week 2 DLLDocument8 pagesUCSP Week 2 DLLZeporah OrdonNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook The U S Banking System Laws Regulations and Risk Management 1St Ed 2020 Edition Felix I Lessambo All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook The U S Banking System Laws Regulations and Risk Management 1St Ed 2020 Edition Felix I Lessambo All Chapter PDFjames.sheehan941100% (6)
- Test - Module 4Document37 pagesTest - Module 4Namaste100% (1)
- Chapter 4. Gear Train: Engr. Jonathan S. RodolfoDocument15 pagesChapter 4. Gear Train: Engr. Jonathan S. Rodolfojoshua alhambraNo ratings yet
- Number Systems: By: Miss. Chrisna L. FucioDocument49 pagesNumber Systems: By: Miss. Chrisna L. FucioChrisna FucioNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 - Ver 5Document2 pagesExercise 4 - Ver 5THƯ LÊNo ratings yet
- CrimPro Case Digests 07.14.18Document16 pagesCrimPro Case Digests 07.14.18yannie isananNo ratings yet
- Intel AMTDocument18 pagesIntel AMTprabhashankerNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Study Guide KeyDocument2 pagesUnit 4 Study Guide Keyapi-333357291No ratings yet
- CNN E: Learning Convolutional Neural Networks With Interactive VisualizationDocument11 pagesCNN E: Learning Convolutional Neural Networks With Interactive VisualizationSanjeebNo ratings yet
- ChocolateDocument6 pagesChocolateKunal NairNo ratings yet
- Aops Community Russian TST 2015: Days 1-6 Day 7 P1Document4 pagesAops Community Russian TST 2015: Days 1-6 Day 7 P1魏志恒No ratings yet
- Ige TD 13Document131 pagesIge TD 13Dr.BassamNo ratings yet
- Shiv Resume 2Document2 pagesShiv Resume 2SHIVNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Paper: Submitted By: Jeric Cataag Boctuanon Submitted To: Wendell A. AlferezDocument4 pagesSynthesis Paper: Submitted By: Jeric Cataag Boctuanon Submitted To: Wendell A. AlferezMarie Fe EgarNo ratings yet
- Cc-rd310w-Spd01 HP Eng v5Document11 pagesCc-rd310w-Spd01 HP Eng v5Daryl SubidoNo ratings yet
- Software Trimble RealWorks Vs TBC Comparativa 0520Document21 pagesSoftware Trimble RealWorks Vs TBC Comparativa 0520Szikzai Alexandru RobertNo ratings yet