Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 10 Science Cells Test
Uploaded by
Shimaa SamirOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 10 Science Cells Test
Uploaded by
Shimaa SamirCopyright:
Available Formats
Back Print
Name Class Date
Assessment
Chapter Test B
Cell Structure and Function
In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the
term or phrase.
______ 1. mitochondrion a. stores DNA and synthesizes RNA
______ 2. endoplasmic reticulum b. digests molecules, old organelles,
and foreign substances
______ 3. plasma membrane c. site of protein synthesis
______ 4. ribosome d. processes and packages sub-
stances produced by the cell
______ 5. cell e. prepares proteins for export and
______ 6. Golgi apparatus synthesizes steroids
f. regulates movement of substances
______ 7. nucleus into and out of cell
______ 8. lysosome g. transfers energy to ATP
h. the basic unit of life
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes
each statement or best answers each question.
______ 9. The maximum size to which a cell may grow is limited mainly by the
cell’s
a. shape. c. function.
b. surface area. d. internal organization.
______10. The discovery of cells is linked most directly with
a. early investigations of causes of diseases.
b. observations of large, unicellular organisms.
c. the development of the microscope.
d. efforts to reproduce organisms in the laboratory.
______11. Which of the following are components of the plasma membrane that
have a significant role in its functioning?
a. lipids c. carbohydrates
b. proteins d. All of the above
______12. In which of the following types of cells would you expect to find a
large number of mitochondria?
a. bone c. muscle
b. skin d. blood
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Modern Biology 29 Chapter Test
Back Print
Name Class Date
Cell Structure and Function, Chapter Test B continued
______13. Microfilaments and microtubules
a. contain digestive enzymes.
b. function in cell structure and movement.
c. are sites of protein synthesis.
d. are sites of photosynthesis.
______14. Which of the following is the correct order of structures in living
things, from the simplest to the most complex?
a. cells, tissues, organs, organ systems
b. cells, organs, tissues, organ systems
c. cells, organs, organ systems, tissues
d. organ systems, organs, tissues, cells
______15. Short, hairlike organelles that can move and may cover a unicellular
organism or line the respiratory tract are called
a. chromatin strands. c. cilia.
b. flagella d. spindle fibers.
______16. Name two functions of the proteins embedded in the plasma
membrane.
a. They transport substances across the membrane and aid in
protein synthesis.
b. They store wastes and form the outer layer of the membrane.
c. They serve as attachment sites for molecules in the extracellular
fluid and transport substances across the membrane.
d. They aid in cell movement and serve as attachment sites for mole-
cules in the extracellular fluid.
______ 17. Which of the following membrane proteins are integral proteins?
a. cell-surface markers c. transport proteins
b. receptor proteins d. All of the above
______18. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Colonial organisms are multicellular.
b. Colonial organisms are unicellular.
c. Colonial organisms have specialized tissues.
d. The cells of colonial organisms are genetically different from each
other.
______19. Which scientist determined that cells come only from other cells?
a. van Leeuwenhoek c. Schwann
b. Schleiden d. Virchow
______20. Which of the following helps plant cells remain rigid?
a. plasma membrane c. chloroplast
b. nucleus d. central vacuole
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Modern Biology 30 Chapter Test
Back Print
Name Class Date
Cell Structure and Function, Chapter Test B continued
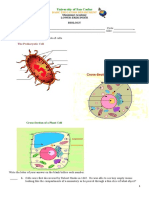
Refer to the figure below, which shows the packaging and
distribution of proteins inside the cell, to answer questions 21–23.
A B
Cell membrane C
______21. The structures labeled A are
a. vesicles. c. ribosomes.
b. lysosomes. d. chloroplasts.
______22. The structure labeled B is
a. the endoplasmic reticulum. c. a mitochondrion.
b. a Golgi apparatus. d. the nucleus.
______23. The structure labeled C is a(n)
a. mitochondrion. c. ribosome.
b. endoplasmic reticulum. d. vesicle.
Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided.
24. What are the three parts of the cell theory?
25. Name two different kinds of animal cells, and describe how their shape is
related to their function.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Modern Biology 31 Chapter Test
Back Print
Name Class Date
Cell Structure and Function, Chapter Test B continued
26. Describe two differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
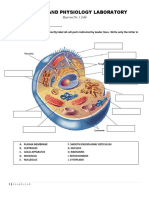
Refer to the diagram below to answer question 27.
27. The diagram depicts a plant cell. Write the names of structures a–e in the blanks.
c
b d
e
a
f. Which of these structures are found in plants but not in animals?
28. What are the major roles of the nucleus, and what parts of the nucleus carry
out these roles?
29. What is a colonial organism, and what does it have in common with a multi-
cellular organism?
30. Where in the cell do the following steps of energy conversion occur?
a. Glucose taken into the cell
b. Glucose boken down to yield ATP
c. ATP used for cellular activities
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Modern Biology 32 Chapter Test
Back Print PAGE
TEACHER RESOURCE
Cell Structure and Function Homeostasis and
Chapter Test B (Advanced) Cell Transport
1. g 13. b Chapter Test A (General)
2. e 14. a 1. e 11. b
3. f 15. c 2. i 12. c
4. c 16. c 3. h 13. d
5. h 17. d 4. f 14. c
6. d 18. b 5. a 15. d
7. a 19. d 6. b 16. d
8. b 20. d 7. c 17. b
9. b 21. c 8. g 18. b
10. c 22. a 9. d 19. c
11. d 23. d 10. d 20. a
12. c 21. energy
24. (1) All living things are composed of 22. passive transport
one or more cells. (2) Cells are the 23. equilibrium
basic units of structure and function in 24. active transport
an organism. (3) Cells come only from 25. carrier proteins
the reproduction of existing cells.
25. Answers will vary. Skin cells are flat Homeostasis and
and platelike for covering and protect-
ing the body’s surface. Nerve cells are Cell Transport
specialized for transmitting nerve Chapter Test B (Advanced)
impulses. 1. d 12. a
26. Answers include the following: eukary- 2. b 13. b
otes contain a membrane-bound nucleus 3. h 14. c
and other organelles; prokaryotes do 4. g 15. d
not. 5. f 16. b
27. a. secondary cell wall; b. central 6. a 17. c
vacuole; c. nucleus; d. chloroplast; 7. c 18. b
e. primary cell wall. f. The central 8. e 19. a
vacuole, chloroplast, and cell wall 9. c 20. d
are found in plants but not in animals. 10. b 21. b
28. Answers include the following: The 11. d 22. b
nucleus contains DNA and RNA. 23. The rigid cell walls of plants prevent
Ribosomes are synthesized and them from expanding too much as the
partially assembled in the nucleolus. cells take in water through osmosis.
The contents of the nucleus are Some unicellular eukaryotes have
enclosed by the nuclear envelope. contractile vacuoles that collect
RNA is synthesized in the nucleus excess water and pump it out of the
and then passes into the cytoplasm cell. Many animal cells increase the
through pores in the nuclear envelope. water concentration inside the cell by
29. A colonial organism is a collection of removing dissolved particles from the
genetically identical cells that live cytoplasm to maintain homeostasis. If
together in a closely connected group. cells are not able to prevent excess
It is thought that multicellular organisms water from entering the cell, they may
arose from a colonial ancestor. expand and eventually burst.
30. a. plasma membrane; b. mitochondria; 24. passive: diffusion, osmosis, and
c. cytoplasm and other organelles facilitated diffusion; active: sodium-
potassium pump, endocytosis, and
exocytosis
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Modern Biology 408 Answer Key
You might also like
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle WorksheetLaarni Faye Sarmiento100% (1)
- Cell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement MembraneDocument2 pagesCell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement Membranerahul mauryaNo ratings yet
- Questions-Biological Science DavaoDocument10 pagesQuestions-Biological Science DavaoMARY ANN TIONGSONNo ratings yet
- Cell QuizDocument9 pagesCell QuizAhdzorizm PlcnNo ratings yet
- Evol RelationshipsDocument15 pagesEvol RelationshipsCarla BanzuelaNo ratings yet
- Cell Processes Blank ReviewDocument4 pagesCell Processes Blank ReviewDr-Qussai ZuriegatNo ratings yet
- Bio Ch. 7 practice test answers keyDocument6 pagesBio Ch. 7 practice test answers keyShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in BloodDocument12 pagesWorksheet in BloodBryan Mae H. DegorioNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Cells TestDocument12 pagesAP Biology Cells Testchrwelch3No ratings yet
- Pfizer Analysis PDFDocument3 pagesPfizer Analysis PDFBhumika ChaubeNo ratings yet
- Biology McqsDocument58 pagesBiology Mcqskamilbisma100% (2)
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetDaichi ライアン100% (1)
- Unit 6 & 7 Cell EnergyDocument17 pagesUnit 6 & 7 Cell EnergyRut ChristineNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Review: Passive and Active ProcessesDocument4 pagesCellular Transport Review: Passive and Active ProcessesSri Widowati100% (1)
- AP BIOLOGY MID TERM PRETEST REVIEWDocument30 pagesAP BIOLOGY MID TERM PRETEST REVIEWKrisnavimala Krishnan0% (1)
- hssb0400s StudygdbDocument12 pageshssb0400s StudygdbMohamed HassaneinNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active Transport Internet AssignmentDocument4 pagesPassive and Active Transport Internet AssignmentShalu PundirNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test BiologyDocument3 pagesAchievement Test BiologyCiv NortubNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Ch. 3 Cell Structure & FunctionDocument19 pagesPractice Test Ch. 3 Cell Structure & Functionrofi modiNo ratings yet
- Cell Test PracticeDocument7 pagesCell Test Practiceapi-240396878No ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocument236 pagesPharmacology - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVNo ratings yet
- Evolution PDFDocument32 pagesEvolution PDFShiella Mae Baltazar BulauitanNo ratings yet
- Examview - Biology Yearly Benchmark Assessment Sy14-15 Wo AnsDocument10 pagesExamview - Biology Yearly Benchmark Assessment Sy14-15 Wo Ansapi-232424041No ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering by Inamdar PDFDocument462 pagesBiochemical Engineering by Inamdar PDFKuo Sarong60% (5)
- General Biology 1 2023 ExamDocument22 pagesGeneral Biology 1 2023 Examrolly baloNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksFelix SimsungNo ratings yet
- A Review of Cleanroom Microflora Types, Trends, and Patterns.Document14 pagesA Review of Cleanroom Microflora Types, Trends, and Patterns.Sean NamNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Structure and FunctionRahila AkramNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System-Final PDFDocument57 pagesThe Nervous System-Final PDFCarlo Makiling100% (1)
- Biology Staar Review Stations Day 3Document12 pagesBiology Staar Review Stations Day 3api-267841335No ratings yet
- CH 7 Part I TESTDocument7 pagesCH 7 Part I TESTlshawNo ratings yet
- Biochem Introduction A PDFDocument107 pagesBiochem Introduction A PDFDaevy Toribio AmdosNo ratings yet
- Origin of Life On EarthDocument20 pagesOrigin of Life On EarthJulieanne Nirus Jumarang VeranoNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Exam - LE - 10 - 11Document5 pagesCell Bio Exam - LE - 10 - 11tinateacherbkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 TESTDocument4 pagesChapter 14 TESTPak RisNo ratings yet
- Cell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsDocument10 pagesCell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsFirdaus Asha'riNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Stages & PhasesDocument11 pagesCell Cycle Stages & PhasesJessie Katrisha TayagNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesCells and TissuesLouise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- Imaging in Drug Discovery and Early Clinical Trials 2005 PDFDocument389 pagesImaging in Drug Discovery and Early Clinical Trials 2005 PDFAnkush BiswasNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissuesDocument18 pagesCell and Tissuesalvin jr ayugatNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument17 pagesPlant Cellrjjain07No ratings yet
- Cell Parts Practice Quiz StudentDocument4 pagesCell Parts Practice Quiz StudentAngel AugustineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Sep 10) - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument56 pagesLecture 3 (Sep 10) - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesRhomoneNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Earth Sci and BioDocument10 pagesReviewer Earth Sci and BioCHELSIE KAITLYN DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Science Scope and SequenceDocument5 pages6th Grade Science Scope and Sequenceapi-261880769No ratings yet
- Practice Chapter TestDocument4 pagesPractice Chapter Testhossam mohamedNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Summative TestDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Summative TestAnna Liza CarrascalNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Document1 pageQUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Tego Shei Harumi100% (1)
- Cell Organelles Assessment Ch 6 and 8Document3 pagesCell Organelles Assessment Ch 6 and 8cshining330% (1)
- Cell Transport Test ReviewDocument3 pagesCell Transport Test ReviewJohn Kevin NocheNo ratings yet
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocument21 pagesBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: Type A: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesHuman Reproduction: Type A: Multiple Choice Questionsriya sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Mol Biol Guide - Structure, Membranes, OriginDocument2 pagesCell and Mol Biol Guide - Structure, Membranes, Originjessie4466No ratings yet
- Cell Division Reinforcement WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Division Reinforcement WorksheetАлександър Антоан Николов50% (2)
- Biology EvolutionDocument22 pagesBiology EvolutionBrasa Y. de AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Porifera & CnidariaDocument25 pagesLab 10 Porifera & Cnidariadraykid100% (1)
- Diffusion and Osmosis ExperimentDocument3 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis ExperimentstjustinsNo ratings yet
- Organ Systems Cloze ReadDocument1 pageOrgan Systems Cloze Readapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System To BirthDocument11 pagesHuman Reproductive System To BirthDEEBANNo ratings yet
- Bio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit OneDocument7 pagesBio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit OneTammy SmithNo ratings yet
- 08 Lion Elephant Energy From MacromoleculesDocument8 pages08 Lion Elephant Energy From MacromoleculesJonghyun (Justin) YangNo ratings yet
- Answers Are Here:: Pwxwtkrlxvzh6Wlwagrsc/Edit?Usp SharingDocument10 pagesAnswers Are Here:: Pwxwtkrlxvzh6Wlwagrsc/Edit?Usp SharingCharlotte KimNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Diffusion Lab-1Document7 pagesOsmosis Diffusion Lab-1api-1658690000% (1)
- Cell Structure and IonDocument14 pagesCell Structure and IonNur NaNa100% (1)
- Math Project G7aDocument1 pageMath Project G7aShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Grade 8ADocument1 pageGrade 8AShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Completing The Sentence Unit 1Document2 pagesCompleting The Sentence Unit 1Shimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Synonyms and Antonymsunit1Document1 pageSynonyms and Antonymsunit1Shimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Practice B: Frequency Tables, Stem-and-Leaf Plots, and Line PlotsDocument2 pagesPractice B: Frequency Tables, Stem-and-Leaf Plots, and Line PlotsShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- ImpDocument1 pageImpShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Proper Adjectives HW PDFDocument2 pagesProper Adjectives HW PDFrachelNo ratings yet
- Grade 4BDocument1 pageGrade 4BShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Practice C: Congruent FiguresDocument2 pagesPractice C: Congruent FiguresShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Grammar Work Sheet On Verb Phrases + Complete Subjects and PredicatesDocument3 pagesGrammar Work Sheet On Verb Phrases + Complete Subjects and PredicatesShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Mental Health USADocument4 pagesCOVID-19 Mental Health USAShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Spatial and Themes QuestionsDocument5 pagesSpatial and Themes QuestionsShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- ImpDocument1 pageImpShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography WorksheetDocument1 pagePhysical Geography WorksheetShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Organization of LivingthingsDocument2 pagesOrganization of LivingthingsShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Graphic Organizer For Western World ProjectDocument1 pageGraphic Organizer For Western World ProjectShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Factor Worksheet - PDF (HW)Document2 pagesFactor Worksheet - PDF (HW)Shimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- European Colonization of North AmericaDocument11 pagesEuropean Colonization of North AmericaShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- ImpDocument1 pageImpShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Science Organization of Living ThingDocument2 pagesScience Organization of Living ThingShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Essay Between Washington and ArizonaDocument3 pagesCompare and Contrast Essay Between Washington and ArizonaShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Spatial and Themes QuestionsDocument5 pagesSpatial and Themes QuestionsShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography WorksheetDocument1 pagePhysical Geography WorksheetShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Integrated Projects and STEAM G7Document5 pagesIntegrated Projects and STEAM G7Shimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Abdulrahman Introduction and ConclusionDocument1 pageAbdulrahman Introduction and ConclusionShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Factoring Worksheet: List All The Factors of The Given NumbersDocument2 pagesFactoring Worksheet: List All The Factors of The Given NumbersShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Subject and Predicate g7Document1 pageSubject and Predicate g7Shimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- El-Shimaa Samir: ProfileDocument1 pageEl-Shimaa Samir: ProfileShimaa SamirNo ratings yet
- Biology Class XII 2023-24 TBSE Pre BoardsDocument5 pagesBiology Class XII 2023-24 TBSE Pre BoardsquiahmaxfrancisNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Aberrations (Reprint of Cytogenetic and Genome Research 2004) by G. Obe (Editor), A. T. Natarajan (Editor)Document397 pagesChromosome Aberrations (Reprint of Cytogenetic and Genome Research 2004) by G. Obe (Editor), A. T. Natarajan (Editor)alokNo ratings yet
- Antibody-Alpha-Smooth Muscle ActinDocument5 pagesAntibody-Alpha-Smooth Muscle ActinLauraNiiñoMartínezNo ratings yet
- FSC Notes Biology Part 1 Chapter 4 The CellDocument19 pagesFSC Notes Biology Part 1 Chapter 4 The CellGhulam Qasim QaisraniNo ratings yet
- 1112283stock2075 3 17Document5 pages1112283stock2075 3 17cds nepalNo ratings yet
- For DemonstrationDocument34 pagesFor DemonstrationJovanie LudiomanNo ratings yet
- Mpharm 2 Sem Advanced Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics mph202 2019Document1 pageMpharm 2 Sem Advanced Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics mph202 2019Anshika Khatri100% (1)
- Question 2Document14 pagesQuestion 2ANIS HUMAIRA ABDUL HAFIZNo ratings yet
- Types of ElectrophoresisDocument3 pagesTypes of ElectrophoresisSridharan VNo ratings yet
- Materi 1 Dr. Apt. Diana Laila Ramatillah, M.farmDocument32 pagesMateri 1 Dr. Apt. Diana Laila Ramatillah, M.farmDimas RfNo ratings yet
- Microbial Growth Factors and Control Methods in VitroDocument31 pagesMicrobial Growth Factors and Control Methods in VitroBryan JanierNo ratings yet
- Biological WarfareDocument7 pagesBiological WarfareBakhtawar ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Ben-Nissan, Sharon - 2014 - Regulating The 20S Proteasome Ubiquitin-Independent Degradation PathwayDocument24 pagesBen-Nissan, Sharon - 2014 - Regulating The 20S Proteasome Ubiquitin-Independent Degradation PathwayZyxonnNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology & Biosafety Bill, 2012Document63 pagesBiotechnology & Biosafety Bill, 2012Magelah Peter GwayakaNo ratings yet
- Ud7 (I) : Molecular Cloning: Dra Maria V. MonserratDocument32 pagesUd7 (I) : Molecular Cloning: Dra Maria V. MonserratAngela MarNo ratings yet
- Cell FoldableDocument2 pagesCell Foldableapi-310503032No ratings yet
- Genomics GeneticsDocument40 pagesGenomics Geneticssazaki224No ratings yet
- 7.16DNA WorksheetDocument8 pages7.16DNA WorksheetVanessa JuatcoNo ratings yet
- Fetalix: Fetal-Inspired Biomaterials For IVD RegenerationDocument13 pagesFetalix: Fetal-Inspired Biomaterials For IVD RegenerationHugo PrazeresNo ratings yet
- 100mL・30mL: For pluripotent stem cell stirred suspension cultureDocument2 pages100mL・30mL: For pluripotent stem cell stirred suspension cultureRupal Charaniya HiraniNo ratings yet
- Bacteria and Archaea Are Both Single-Celled Prokaryotes.: Key ConceptDocument61 pagesBacteria and Archaea Are Both Single-Celled Prokaryotes.: Key Conceptmomo connorNo ratings yet
- 02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsDocument38 pages02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsLaeliaMunawarohNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of TB - Handout (Final) 4-08Document3 pagesPharmacotherapy of TB - Handout (Final) 4-08Ahmedshaker21No ratings yet
- StudentDocument11 pagesStudent김예진No ratings yet
- Evolution Facts Mechanisms ConstraintsDocument3 pagesEvolution Facts Mechanisms ConstraintsZianaly JeffryNo ratings yet