Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A243 Final Examination 2B
A243 Final Examination 2B
Uploaded by
Idris Jeffrey MangueraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A243 Final Examination 2B
A243 Final Examination 2B
Uploaded by
Idris Jeffrey MangueraCopyright:
Available Formats
A243 Final Examination
I. Write J if the statement is TRUE and H if the statement is FALSE. Erasures are not allowed. (20pts)
1. The JFET always operates with a reverse-biased gate-to-source pn junction.
2. The channel resistance of a JFET is always constant.
3. The gate-to source voltage of an n-channel JFET must be negative.
4. ID becomes zero at the pinch-off voltage.
5. VGS has no effect on ID.
6. The JFET is a square-law device because of the mathematical expression of its transfer characteristic curve.
7. The D-MOSFET can be operated in two modes.
8. An E-MOSFET operates in the depletion mode.
9. A D-MOSFET has a physical channel and an E-MOSFET has an induced channel.
10. MOSFETs must be handled with care.
11. A bipolar junction transistor has three terminals.
12. The three regions of a BJT are base, emitter and cathode.
13. For operation in the linear or active region, the base-emitter junction of a transistor is forward-biased.
14. Two types of BJT are npn and pnp.
15. The base and the collector current are approximately equal.
16. The dc voltage gain of a transistor is designated 𝛽𝐷𝐶 .
17. Cutoff and saturation are the two normal states of a linear transistor amplifier.
18. When a transistor is saturated, the collector current is maximum.
19. Amplification is the output voltage divided by the input current.
20. A transistor in cutoff acts as an open switch.
II. Circuit analysis. Show complete and detailed solutions. Express all answers in two significant decimal
places for your calculations. Use graphing paper if necessary. Enclose all final answers in a box. (70 pts)
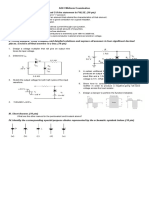
1. For the network shown below:
a. Draw the dc equivalent circuit. (5 pts)
b. Find the dc voltages VB, VCB, and VCE. (15 pts)
c. Draw the ac equivalent circuit. (5 pts)
d. Determine re. (5 pts)
2. Find VS. (15 pts)
3. Determine the quiescent values of ID and VGS. (25 pts)
You might also like
- Two-Way Power Source Chicken Egg IncubatorDocument35 pagesTwo-Way Power Source Chicken Egg IncubatorIdris Jeffrey Manguera100% (4)
- Module 6 - Communications CircuitsDocument26 pagesModule 6 - Communications CircuitsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On TransistorsDocument5 pagesRevision Notes On TransistorsvproNo ratings yet
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 4 - BJT BiasingDocument4 pagesEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 4 - BJT Biasingdonatello84100% (1)
- Unit - 6 AMPLIFIERS: Small Signal LowDocument23 pagesUnit - 6 AMPLIFIERS: Small Signal LowAzImmNo ratings yet
- True FalseDocument5 pagesTrue FalseShuvodip Das50% (2)
- ECE111 - Analog Electronics: Sandeep Saini Gaurav ChatterjeeDocument100 pagesECE111 - Analog Electronics: Sandeep Saini Gaurav ChatterjeeAAYUSH SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics & Telecom Engineering EDC-1 Question Bank For IA-02 A.Y 2021-22Document7 pagesDepartment of Electronics & Telecom Engineering EDC-1 Question Bank For IA-02 A.Y 2021-22Pratik BhalakeNo ratings yet
- Ee 211 Chapter 3Document19 pagesEe 211 Chapter 3RickNo ratings yet
- Lab - Vi: Name - Kushagra Sagar ROLL NUMBER - 2021BCS0105Document10 pagesLab - Vi: Name - Kushagra Sagar ROLL NUMBER - 2021BCS0105Kushagra SagarNo ratings yet
- ECE Experiment No.5Document11 pagesECE Experiment No.5John Wilben Sibayan ÜNo ratings yet
- TRAN2Document27 pagesTRAN2Hamad H.ANo ratings yet
- Fundamental of ElectronicsDocument6 pagesFundamental of ElectronicsAbdihamid bin-mohamoudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ele IDocument27 pagesChapter 3 Ele Ibiruk satnawNo ratings yet
- BJT With BIASING CONFIGSDocument5 pagesBJT With BIASING CONFIGSTristan Paul Guerra OrodioNo ratings yet
- Et502 Power ElectronicDocument66 pagesEt502 Power ElectronicKelvin Yip100% (1)
- Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument4 pagesDepartment of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & TechnologyMeowNo ratings yet
- BJT Lab ExperimentDocument8 pagesBJT Lab ExperimentRizwan LatifNo ratings yet
- Exp05-2019 368Document13 pagesExp05-2019 368Mohammad alhaboob2030No ratings yet
- Coimbatore Institute of TechnologyDocument3 pagesCoimbatore Institute of TechnologyMani BharathiNo ratings yet
- Lab # 08Document7 pagesLab # 08Zulfiqar AliNo ratings yet
- V DR - RR&DR - SR Techincal University Lab Manual: EltechDocument25 pagesV DR - RR&DR - SR Techincal University Lab Manual: EltechadiprasanthNo ratings yet
- Superconductor and SemiconductorsDocument45 pagesSuperconductor and SemiconductorsChand BikashNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument37 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorTauseef AhmadNo ratings yet
- Analog Lab ManualDocument57 pagesAnalog Lab ManualMukesh Sahu100% (1)
- EE201Document12 pagesEE201Iqmal Shah PutraNo ratings yet
- Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationDocument30 pagesSmall-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationAbraham JyothimonNo ratings yet
- Single-Stage BJT Amplifiers: Experiment-2Document19 pagesSingle-Stage BJT Amplifiers: Experiment-2karan007_mNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document9 pagesUnit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Gunjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lab.5 Power ElectronicsDocument7 pagesLab.5 Power Electronicsbaig79No ratings yet
- 20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Document7 pages20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Usama MughalNo ratings yet
- To Study The Characteristics of A Common Emitter NPN (Or PNP) Transistor & To Find Out The Values of Current & Voltage GainsDocument11 pagesTo Study The Characteristics of A Common Emitter NPN (Or PNP) Transistor & To Find Out The Values of Current & Voltage GainsAman AhamadNo ratings yet
- Electronics - 1 Lecture 13Document37 pagesElectronics - 1 Lecture 13rizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Unit 9: Electronic Devices: Question BankDocument4 pagesUnit 9: Electronic Devices: Question BankNathanianNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document10 pagesLab 8Mike AlbertNo ratings yet
- Lecture11!11!12284 MosfetDocument28 pagesLecture11!11!12284 Mosfetshivali.vannarathNo ratings yet
- To use a multimeter to (a) identify base of a multimeter (b) distinguish between non and pop type transistors (c) see the unidirectional flow of current in case of a diode and an LED (d) check whether a given electronic component (ex- diode, transistor, or IC) is in working orderDocument5 pagesTo use a multimeter to (a) identify base of a multimeter (b) distinguish between non and pop type transistors (c) see the unidirectional flow of current in case of a diode and an LED (d) check whether a given electronic component (ex- diode, transistor, or IC) is in working orderAurora Aurealis50% (2)
- Basic Electronics PracticalDocument9 pagesBasic Electronics Practicalasfadare100% (2)
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition Boylestad Test Bank 1Document13 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition Boylestad Test Bank 1julia100% (36)
- Edc Lab Manuals Third SemesterDocument56 pagesEdc Lab Manuals Third SemesterSprout GigsNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 2022-3Document4 pagesStudy Guide 2022-3Diego AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Electronics 2Document69 pagesElectronics 2joeNo ratings yet
- IA FormatDocument2 pagesIA Formatpatilvk2003No ratings yet
- Edc Unit 3 TransistorDocument17 pagesEdc Unit 3 TransistorsrinivasNo ratings yet
- BJT Transistor As A SwitchDocument12 pagesBJT Transistor As A SwitchRoaa AlfakeehNo ratings yet
- What Is BJT and Its ExplanationDocument5 pagesWhat Is BJT and Its ExplanationJerick De LaraNo ratings yet
- To Use A Multimeter To (A) Identify Base of Transistor, (B)Document6 pagesTo Use A Multimeter To (A) Identify Base of Transistor, (B)aff bearNo ratings yet
- DEVICE EXP 5 STUDENT MANUAL NewDocument6 pagesDEVICE EXP 5 STUDENT MANUAL NewPial Hassan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- II BTECH - I SEM - ECE - EDC - THEORY & QUIZ QUESTIONS - MID 2 - Students PDFDocument19 pagesII BTECH - I SEM - ECE - EDC - THEORY & QUIZ QUESTIONS - MID 2 - Students PDFK SrinuNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 AnalogIC ECE4A - SetBDocument8 pagesQuiz1 AnalogIC ECE4A - SetBNiel Joshua I. LozadaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 03Document54 pagesLecture Week 03عبدالله قيس محمود الحيدريNo ratings yet
- Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationDocument30 pagesSmall-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationTaufique ZamanNo ratings yet
- Problems BJT Operation and IVDocument2 pagesProblems BJT Operation and IVMd. Nymur Rahman HemelNo ratings yet
- Bab 3-bjtDocument80 pagesBab 3-bjtNoor Hanisah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Electronics-I (EEE 231) : Syed Bilal JavedDocument68 pagesElectronics-I (EEE 231) : Syed Bilal JavedNihala KhalidNo ratings yet
- Recap On CH - 11 of G - 11 With TGDocument5 pagesRecap On CH - 11 of G - 11 With TGKhin Khin ThanNo ratings yet
- BJT AC Analysis Part 1 PDFDocument9 pagesBJT AC Analysis Part 1 PDFnupur kesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document10 pagesActivity 6Ultima_SarinNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - ECELXM1L - Lab04Document5 pagesGroup 8 - ECELXM1L - Lab04Hannah VisitacionNo ratings yet
- Review of BJTS, Jfets and MosfetsDocument26 pagesReview of BJTS, Jfets and MosfetsSundar RajaduraiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- 61 ECEP433 Communications 3 - Transmission Media and Antenna SystemsDocument3 pages61 ECEP433 Communications 3 - Transmission Media and Antenna SystemsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP353 SyllabusDocument2 pagesECEP353 SyllabusIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A 243 MT Exam 20202021 CDocument1 pageA 243 MT Exam 20202021 CIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP 353 Quiz # 1Document1 pageECEP 353 Quiz # 1Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A243 Midterm ExaminationDocument1 pageA243 Midterm ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECE313 Quiz 1 Ee 3 eDocument2 pagesECE313 Quiz 1 Ee 3 eIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECE313 Quiz 1 Ece 3 FDocument2 pagesECE313 Quiz 1 Ece 3 FIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- The Electronics Engineering ProfessionDocument41 pagesThe Electronics Engineering ProfessionIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP353 (Signals, Spectra, Signal Processing) Midterm ExaminationDocument1 pageECEP353 (Signals, Spectra, Signal Processing) Midterm ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Course Code Course Title Date Effective: Date Revised: Prepared By: Approved By: Page No.Document3 pagesCourse Code Course Title Date Effective: Date Revised: Prepared By: Approved By: Page No.Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A353 (Fundamentals of Electronic Communications) Midterm ExaminationDocument1 pageA353 (Fundamentals of Electronic Communications) Midterm ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP351L Activity 2Document1 pageECEP351L Activity 2Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP433 Activity 2Document1 pageECEP433 Activity 2Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A353q1 Set BDocument2 pagesA353q1 Set BIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Principles of CommunicationsDocument174 pagesLecture Notes in Principles of CommunicationsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- M113 Quiz 1Document1 pageM113 Quiz 1Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Y N X (N: ECEP 353 Quiz # 2Document1 pageY N X (N: ECEP 353 Quiz # 2Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A353q1 Set ADocument2 pagesA353q1 Set AIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet