Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ECE 313 Quiz #1 Solutions
Uploaded by
Idris Jeffrey MangueraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE 313 Quiz #1 Solutions
Uploaded by
Idris Jeffrey MangueraCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME: ____________________________________________________ Score: ______________
ECE 313 Quiz # MT-01
I. TRUE/FALSE. Write F if the statement is correct and T if the statement is incorrect. Any form of erasure is not allowed.
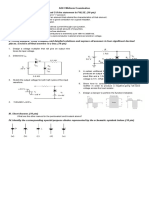
1. An atom is the smallest particle in an element. 17. PIV stands for positive inverse voltage.
2. An electron is a negatively charged particle. 18. Each diode in a full-wave rectifier conducts for the
3. An atom is made up of electrons, protons and neutrons. entire input cycle.
4. Electrons are part of the nucleus of an atom. 19. A bridge rectifier uses four diodes.
5. Valence electrons exist in the outer shell of an atom. 20. In a bridge rectifier, two diodes conduct during each
6. Crystals are formed by the bonding of atoms. half cycle of the input.
7. Silicon is a conductive material. 21. A diode limiter is also known as a clipper.
8. All diodes have one pn junction. 22. The purpose of a clamper is to remove a dc level from a
9. The p and n regions in a diode are formed by a process waveform.
called ionization. 23. Voltage multipliers use diodes and capacitors.
10. The two regions of a diode are the anode and the 24. The zener diode normally operates in reverse
collector. breakdown.
11. A diode can conduct in two directions with equal ease. 25. A zener diode can be used as a voltage regulator.
12. A diode conducts current when forward-biased. 26. There is no current when a zener is in reverse
13. When reverse-biased, a diode ideally appears as a short. breakdown.
14. Two types of current in a diode are electron and hole. 27. The varactor diode is used as a variable capacitor.
15. A basic half-wave rectifier consists of one diode. 28. The LED is based on the process of electroluminescence.
16. The diode in a half-wave rectifier conducts for half the 29. The photodiode operates in reverse bias.
input cycle. 30. The light emitted by a laser diode is monochromatic.
II. PROBLEM SOLVING. Use the back of this paper for your solutions and answers.
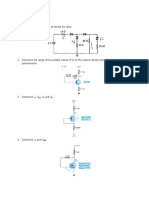
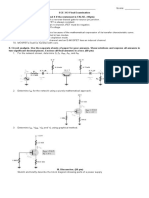
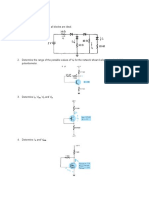
1. In the circuit, D1 and D2 are ideal diodes. Find ID1 and ID2.
2. Show how to connect the diodes in a bridge-type rectifier in order to produce a negative-going full-wave voltage across the load
resistor.
3. Sketch Vo
4. Design a clamper to perform the function indicated.
5. The Zener diode in the voltage regulator circuit has V Z = 18.6 V at a minimum IZ of 15 mA. If Vi = 24±3 V and RL varies from 250 Ω to
2kΩ, find the maximum value of R to maintain regulation.
III. ESSAY. Place your answer in the space provided below.
1. How is reverse current in a junction produced?
2. What is the simplest way to visualize a diode?
You might also like
- ECE313 Quiz 1 Ece 3 FDocument2 pagesECE313 Quiz 1 Ece 3 FIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Ip 2Document3 pagesIp 2Choiril AthoNo ratings yet
- Diode Applications and TypesDocument6 pagesDiode Applications and TypesRifky OfficialNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors & Diodes: Jaesung JangDocument20 pagesSemiconductors & Diodes: Jaesung JangSyed ShahmeerNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors & Diodes: Jaesung JangDocument20 pagesSemiconductors & Diodes: Jaesung JangVaratha RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document25 pagesChapter 2Bizuayehu Ze GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Crystal Diode Rectifier GuideDocument8 pagesCrystal Diode Rectifier GuideS M JOYNo ratings yet
- Chap 6Document8 pagesChap 6S M JOYNo ratings yet
- STP211 ELECTRONICS NOTE PART 3 & 4Document8 pagesSTP211 ELECTRONICS NOTE PART 3 & 4SOFTY SOFTYNo ratings yet
- University Institute of Engineering Electrical EngineeringDocument37 pagesUniversity Institute of Engineering Electrical EngineeringShyam GagliyaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diode ModuleDocument19 pagesSemiconductor Diode ModuleAkashi SeijuroNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: PhysicsDocument8 pagesChapter Six: Physicssaed cabdiNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Class 12 NotesDocument10 pagesSemiconductor Class 12 NotesgraphiccmemesNo ratings yet
- Full Summary (Floyd) Final EditDocument9 pagesFull Summary (Floyd) Final EditJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- Edc - 2 Marks With AnswerDocument0 pagesEdc - 2 Marks With AnswerJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- Lesson PLan Demo FinalDocument3 pagesLesson PLan Demo FinalPatricia Ann Contreras MercadoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits 2 Mark Questions - Solved Unit 1Document60 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits 2 Mark Questions - Solved Unit 1priya88_recNo ratings yet
- CPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 7, Chapter 24Document47 pagesCPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 7, Chapter 24dheerajbhagwatNo ratings yet
- Eto Handout1 DiodeDocument20 pagesEto Handout1 DiodedawitNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Powered byDocument5 pagesTransistor: Powered bynarayanansahaana545No ratings yet
- Electronics Device Circuit Lab SheetDocument27 pagesElectronics Device Circuit Lab Sheetjimfinch512No ratings yet
- Postrero - Notes 2 - Final QuizDocument9 pagesPostrero - Notes 2 - Final QuizALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- EDC 2 Marks All Five UnitsDocument31 pagesEDC 2 Marks All Five Unitsksreddy2002No ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Semiconductor DiodesDocument28 pagesLecture 2: Semiconductor DiodesgokulphdNo ratings yet
- 2 Lecture 2 Diode B Stad - CH - 01Document66 pages2 Lecture 2 Diode B Stad - CH - 01peter brownNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument91 pagesDiodesMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS: SEMICONDUCTORS, PN JUNCTION DIODEDocument4 pagesELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS: SEMICONDUCTORS, PN JUNCTION DIODEmuthaiNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors 1Document16 pagesSemiconductors 1Rohit SwamiNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Diode Rangkaian Penyearah Setengah GelombangDocument9 pagesAplikasi Diode Rangkaian Penyearah Setengah GelombangIndra PutraNo ratings yet
- Active Electronic Components 1Document43 pagesActive Electronic Components 1Kanchana SenadheeraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part ADocument17 pagesChapter 1 Part APrasad ChandramohananNo ratings yet
- Exam RevisionDocument61 pagesExam RevisionRachul heenimNo ratings yet
- Makalah Dioda Kel 5Document7 pagesMakalah Dioda Kel 5sara yulidaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document72 pagesModule 4Kshitiz RastogiNo ratings yet
- Semi ConductorDocument8 pagesSemi ConductorSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- EI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersDocument16 pagesEI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersASPCN 2017No ratings yet
- K00192 - 20180906092258 - W2b&3-SFE3013-PN JUNCTION-SVDocument42 pagesK00192 - 20180906092258 - W2b&3-SFE3013-PN JUNCTION-SVJohnNo ratings yet
- DJM2032 - Electronic SystemDocument19 pagesDJM2032 - Electronic SystemphyrdowsNo ratings yet
- W3-PN Junction-SvDocument43 pagesW3-PN Junction-Svizz isalahNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearDocument27 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearT ThirumuruganNo ratings yet
- CGE535 Chapter 2: Electronic Devices and TransducersDocument71 pagesCGE535 Chapter 2: Electronic Devices and TransducersAzizul HakimNo ratings yet
- International Islamic University Islamabad: Project ReportDocument9 pagesInternational Islamic University Islamabad: Project ReportPow dowtowNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Diode CircuitsDocument29 pagesUnit 1 Diode Circuitseee3 semNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode-2Document45 pagesPN Junction Diode-2RAUNAK GARGNo ratings yet
- EI2203 EDC 2marksDocument14 pagesEI2203 EDC 2marksBhanu KodaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Three Semiconductor Diodes: Outlines 3.2 PN Junction Diodes 3.3 Application of DiodesDocument33 pagesChapter - Three Semiconductor Diodes: Outlines 3.2 PN Junction Diodes 3.3 Application of DiodesAbrha FtsumNo ratings yet
- Discussion For The Most Part, in Performing This Experiment, We Only Used Diodes of Different Kinds, Multimeters, and A Power SupplyDocument2 pagesDiscussion For The Most Part, in Performing This Experiment, We Only Used Diodes of Different Kinds, Multimeters, and A Power SupplyEj HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Full Summary (Floyd)Document8 pagesFull Summary (Floyd)Adrian BagayanNo ratings yet
- 1 DiodesDocument30 pages1 DiodesSUCHIN AnandNo ratings yet
- EE 211 CHAPTER 2 Part2Document22 pagesEE 211 CHAPTER 2 Part2RickNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction DiodeDocument32 pagesP-N Junction Diodesashi_s2No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 & 4 Special - Purpose - Diodes and BJTsDocument50 pagesChapter 3 & 4 Special - Purpose - Diodes and BJTsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Module 04 Electronics Fundamentals Aircraft License ComDocument70 pagesModule 04 Electronics Fundamentals Aircraft License ComMohamad Nadzmi100% (1)
- Ec-8261 Electronic Devices: Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument21 pagesEc-8261 Electronic Devices: Two Mark Questions and Answersmadhupavi_2007100% (1)
- APLIKASI DIODE RANGKAIAN PENYEARAHDocument11 pagesAPLIKASI DIODE RANGKAIAN PENYEARAHIndra PutraNo ratings yet
- Study Guide EE225 Ver1Document6 pagesStudy Guide EE225 Ver1aonNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsFrom EverandNonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonFrom EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Module 6 - Communications CircuitsDocument26 pagesModule 6 - Communications CircuitsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Communications CircuitsDocument26 pagesModule 6 - Communications CircuitsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Two-way solar and grid powered chicken egg incubatorDocument35 pagesTwo-way solar and grid powered chicken egg incubatorIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument33 pagesNewtons Laws of Motionapi-237070241No ratings yet
- Module 3 - Amplitude ModulationDocument11 pagesModule 3 - Amplitude ModulationYanna Marie Porlucas MacaraegNo ratings yet
- ECEP353 SyllabusDocument2 pagesECEP353 SyllabusIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- 61 ECEP433 Communications 3 - Transmission Media and Antenna SystemsDocument3 pages61 ECEP433 Communications 3 - Transmission Media and Antenna SystemsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP353 SyllabusDocument2 pagesECEP353 SyllabusIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Two-Way Power Source Chicken Egg IncubatorDocument35 pagesTwo-Way Power Source Chicken Egg IncubatorIdris Jeffrey Manguera100% (4)
- TOS Template 7Document1 pageTOS Template 7Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP353 SyllabusDocument2 pagesECEP353 SyllabusIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECEP 353 Quiz # 1Document1 pageECEP 353 Quiz # 1Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A243 Completion ExaminationDocument1 pageA243 Completion ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- 61 ECEP433 Communications 3 - Transmission Media and Antenna SystemsDocument3 pages61 ECEP433 Communications 3 - Transmission Media and Antenna SystemsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- JFET Final ExamDocument1 pageJFET Final ExamIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- JFET Final ExamDocument1 pageJFET Final ExamIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A222 Completion ExaminationDocument1 pageA222 Completion ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- ECE313 FTExam 2 K 17Document1 pageECE313 FTExam 2 K 17Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A243 Final Examination 2021Document1 pageA243 Final Examination 2021Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- TOS Template 7Document1 pageTOS Template 7Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A243 Final Examination 2021Document1 pageA243 Final Examination 2021Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A 243 MT Exam 20202021 CDocument1 pageA 243 MT Exam 20202021 CIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- V V I V V I β: A222 Final ExaminationDocument2 pagesV V I V V I β: A222 Final ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Semiconductor Diodes CircuitsDocument1 pageMidterm Exam Semiconductor Diodes CircuitsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A243 Completion ExaminationDocument1 pageA243 Completion ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- A222 Completion ExaminationDocument1 pageA222 Completion ExaminationIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- IEEE defines key antenna termsDocument8 pagesIEEE defines key antenna termsRoberto CostantiniNo ratings yet
- Amta5 8 Applying Tungsten Inert Gas Tig Welding TechniquesDocument115 pagesAmta5 8 Applying Tungsten Inert Gas Tig Welding TechniquesAbu RectifyNo ratings yet
- Friction Stir Welding GuideDocument20 pagesFriction Stir Welding GuideCebrac ItatibaNo ratings yet
- Fretting Fatigue On Thread Root of Premium Threaded ConnectionsDocument10 pagesFretting Fatigue On Thread Root of Premium Threaded ConnectionsJesus ZilchNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Part 2: Basic Components of Spectroscopic InstrumentationDocument17 pagesTopic 1 Part 2: Basic Components of Spectroscopic InstrumentationDeevanesh Gengatharan100% (1)
- Mems GyroscopeDocument18 pagesMems GyroscopeKurian ThomasNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum Poster ProjectDocument2 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum Poster Projectapi-279403490No ratings yet
- Nikon Tseries CloseupDocument5 pagesNikon Tseries Closeupdergi100% (1)
- Design of Pressure Vessel by Group 4Document46 pagesDesign of Pressure Vessel by Group 4anteneh tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Flir t530 Technical DataDocument9 pagesFlir t530 Technical DataSatyam S MohantaNo ratings yet
- The 5.56 X 45mm - 2008 - A Chronology of Development (Part 19) - by Daniel WattersDocument36 pagesThe 5.56 X 45mm - 2008 - A Chronology of Development (Part 19) - by Daniel Wattersblowmeasshole1911No ratings yet
- Temperature of A TIG Welder: Introduction To WeldingDocument4 pagesTemperature of A TIG Welder: Introduction To WeldinghammadNo ratings yet
- HP Officejet Pro Products: NEW NEW NEW NEW NEW NEWDocument2 pagesHP Officejet Pro Products: NEW NEW NEW NEW NEW NEWSayanna HydNo ratings yet
- Optic ProblemsDocument7 pagesOptic ProblemsmariosisaNo ratings yet
- Experiment On LaserDocument4 pagesExperiment On LaserSiddharth GautamNo ratings yet
- Catalog Samyang 2013Document24 pagesCatalog Samyang 2013mariosapereiraNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesSemiconductor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaChâu Vĩnh LợiNo ratings yet
- MGP Paranoia - GM Screen BackDocument1 pageMGP Paranoia - GM Screen BackAurik FreyNo ratings yet
- Module-5 (Cat.B1.1) Dec-18 Dgca Paper With Ans PDFDocument15 pagesModule-5 (Cat.B1.1) Dec-18 Dgca Paper With Ans PDFMegha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Eet 10 Lighting Technology and Methods of CalculationDocument10 pagesEet 10 Lighting Technology and Methods of CalculationLinus AbokiNo ratings yet
- Canadian Board of Examiners Biomed Study Guide Revised January 2010 PDFDocument31 pagesCanadian Board of Examiners Biomed Study Guide Revised January 2010 PDFSyed Atif MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Chinmaya Sahu@vit Ac inDocument97 pagesChinmaya Sahu@vit Ac inRishyavandhan VNo ratings yet
- Upright Microscope Eclipse NiDocument15 pagesUpright Microscope Eclipse NiluroguitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Standards of MeasurementDocument18 pagesChapter 1: Standards of MeasurementStelwin FernandezNo ratings yet
- European Pharmacopoeia Optical Rotation and Refractive IndexDocument1 pageEuropean Pharmacopoeia Optical Rotation and Refractive IndexAlejaMedranoNo ratings yet
- Ikon PDFDocument6 pagesIkon PDFJoseph Sidhom SnadaNo ratings yet
- The #1 Factory Automation Company Drive Systems OverviewDocument9 pagesThe #1 Factory Automation Company Drive Systems OverviewPatricio Alarcon CastroNo ratings yet
- Applications of Electromagnetic RadiationDocument4 pagesApplications of Electromagnetic Radiationapi-377210189% (9)
- Microscope ProjectDocument6 pagesMicroscope ProjectAnubhooti SinghNo ratings yet
- Study On Holograms Laser Engraving ProcessDocument5 pagesStudy On Holograms Laser Engraving ProcessBenexSpecNo ratings yet