Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk Factors and Complications of Acute Pancreatitis
Uploaded by
salome carpioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk Factors and Complications of Acute Pancreatitis
Uploaded by
salome carpioCopyright:
Available Formats
h
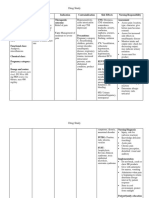
RISK FACTORS
COMPLICATIONS
PSEUDOCYST
INFECTION
Alcoholism KIDNEY FAILURE
Cholecystitis BREATHING PROBLEMS
Surgery involving DIABETES
or near the MALNUTRITION
PANCREATIC CANCER
pancreas
Viral hepatitis,
mumps, peptic
ulcer disease,
periarteritis
Hyperlipidemia,hy
percalcemia,
anorexia nervosa,
DIAGNOSIS BLOOD TEST
shock with ACUTE PANCREATITIS
CT SCAN
ischemia ABDOMINAL
Trauma to the ULTRASOUND
ENDOSCOPIC
ULTRASOUND
LABORATORY TEST MRI
Pancreatic enzymes
Serum amylase
Urine amylase
Serum lipase
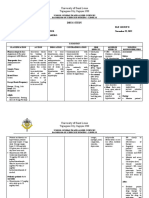
NURSING INTERVENTION
Pain and discomfort related
to edema, distention of the
pancreas, and peritoneal Altered body temperature
Deficient fluid intake related to
irritation related to infection as evidence
inadequate fluid intake vomiting
by raised in body
and temperature
diarrhea
and pulse rate.
Upper abdominal pain.
Abdominal pain that radiates to your back.
Tachycardia
Abdominal pain that feels worse after
Fever
eating.
Tenderness when touching the abdomen
Yellowing of the skin and eyes
(jaundice)
INDEPENDENT Assess skin turgor and oral mucous membranes for signs of
INDEPENDENT
dehydration
Assess pain Provide cool and calm environment to the patient
- Signs of dehydration are also detected through the skin. Skin of
-We must have a detailed baseline so we not only -know
Help provide
how
elderly a more
to treat
patients peaceful,
appropriately
losses quiet
elasticity, environment
hence forshould
skin turgor patientbe
but also to know if it has changed. (For example, a sudden relief
assessed overof the
painsternum recovery
in a patient
or on the inner thighs. Longitudinal
with appendicitis indicates rupture and an emergency.)
furrows may be noted along the tongue.
Windows and doors are open and air ventilation by fan are provided
Monitor fluid status in relation to dietary intake
- The general
Control pain: repositioning, heat/cold, medications purpose
(muscle of ventilation
relaxants, in buildings is to provide healthy air
analgesics)
- Most fluid comes into the body through drinking, water in food,
-Patients who are in pain have trouble participating in care, relaxing, sleeping, and
and water formed by oxidation of foods. Verifying if the patient is
healing. Do what is necessary to proactively treat the patient’s pain, and notify the
on a fluid restraint is necessary.
provider of changes or an inability to provide adequate relief.
Provide aseptic care to the patient
-To protect patients
Assess bowel movements (color, consistency, from
frequency, harmful bacteria and other pathogens during
amount)
Monitor and document temperature
medical procedures
-This will aid the provider in making clinical decisions significantly. It is decrease
- Febrile states essential body
to fluids by perspiration and
report bowel movement characteristics and frequency accurately
increased to aid in this
respiration. This is known as insensible water loss.
important decision making. This also ensures accurate intake and output recording.
Ensure adequate hydration; may require intravenous
Monitor
Recheckfluids
serum electrolytes
Vital and urine
signs for assess bodyosmolality,
temperatureand report
abnormal values
-Patients with abdominal pain may have- Vital
a diminished
signs areappetite,
useful in be NPO, oror monitoring medical problems
detecting
not want to drink fluids. Assess and promote appropriate
- Elevated bloodfluid
ureabalance,
nitrogen suggests fluid deficit. Urine specific
which may requiring notifying the provider of a decreased oral intakeisand
gravity likewise increased
need for intravenous fluids to maintain fluid balance.
Assess bowel sounds
Record the number and quality of stools
If fever found consistent provide cold sponge to the patient
-Essential to know their quality as a baseline and to routinely reassess to
- Regular monitoring with stool chart prevents constipation,
detect changes. If a patient had bowel sounds, - butUsually
nowsponging
does not,will
it isbring down the fever by one to two
urinary retention and delirium
degrees in
essential to detect that and notify the provider, as the patient may not thirty to forty-five minutes
experience any symptoms.
Facilitate normal bowel patterns DEPENDENT
-Abdominal pain can be due to issues withProvide
the GIAnti pyretic
tract. medication
Therefore, it’s as prescribed by physician.
essential to proactively address issues like nausea, vomiting, constipation, and
diarrhea as clinically appropriate. This can lessen
Record intake and output
-Patients with abdominal pain may not be taking in the necessary amount of
fluids or foods, or their urinary and/or bowel output may be lacking. Accurate I&O
is essential for appropriate clinical decision making.
Prevent infection
-Abdominal pain may have been caused by a pathogen (gastroenteritis, for
You might also like
- Ebook PDF Walk A Mile Experiencing and Understanding Diversity in Canada 2nd Edition by Theresa Anzovino PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Walk A Mile Experiencing and Understanding Diversity in Canada 2nd Edition by Theresa Anzovino PDFjames.price54897% (32)
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolDocument3 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy NCP GarganianDocument8 pagesAppendectomy NCP GarganianMa. Therese GarganianNo ratings yet
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument64 pagesNormal Spontaneous DeliveryMichellin Andres MarianoNo ratings yet
- Spiral ModelDocument2 pagesSpiral ModelLe Tran Uyen Thao (FGW HCM)No ratings yet
- Drug Study MethergineDocument2 pagesDrug Study MethergineJahmil DulatreNo ratings yet
- Dela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Document2 pagesDela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Atsu MiyaNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis & NPI - Edmalyn GozarDocument78 pagesAcute Appendicitis & NPI - Edmalyn GozarKM100% (1)
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDocument4 pagesTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting Nausea and VomitingDocument6 pagesNausea and Vomiting Nausea and VomitingTHERESA CLAIRE ENCINARESNo ratings yet
- Procreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableDocument9 pagesProcreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableShiela Mae GalisaNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin Tazobactam (Zosynpiperacillin)Document1 pagePiperacillin Tazobactam (Zosynpiperacillin)ENo ratings yet
- CAP Pneumonia CaseDocument46 pagesCAP Pneumonia CaseMatty FelNo ratings yet
- Levemir Product Insert PDFDocument11 pagesLevemir Product Insert PDFDegee O. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionTammy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Im Case Study 04Document49 pagesIm Case Study 04Shaine BalverdeNo ratings yet
- TrazodoneDocument20 pagesTrazodoneAjay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug Studyabulan100% (1)
- CarvedilolDocument2 pagesCarvedilolKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarielle Chua100% (1)
- GAT NCP Surgery WardDocument4 pagesGAT NCP Surgery WardDon Richard0% (1)
- Concept Map Worksheet Fatime Sanogo Jasgou1752Document1 pageConcept Map Worksheet Fatime Sanogo Jasgou1752Jasmyn RoseNo ratings yet
- Serving Sterile GownDocument2 pagesServing Sterile GownGelo BallartaNo ratings yet
- TramadolDocument2 pagesTramadoldwightciderNo ratings yet
- Drug PrilosecDocument1 pageDrug PrilosecSrkocher100% (1)
- NCP Episiotomy WoundDocument3 pagesNCP Episiotomy WoundJP2001No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJam CorrosNo ratings yet
- Janumet Drug StudyDocument4 pagesJanumet Drug Studykath bernardoNo ratings yet
- Post C-Section Delivery Care PlanDocument5 pagesPost C-Section Delivery Care Planᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩNo ratings yet
- Clinical Portrait Pertinent DataDocument9 pagesClinical Portrait Pertinent DataGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- MI BrochureDocument2 pagesMI BrochureAbedin Mehmedovic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension ManagementDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hypertension Managementbhavana100% (1)
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Subarachnoid HemorrhagicDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Subarachnoid HemorrhagicAshram Smart100% (1)
- Case Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiDocument12 pagesCase Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiHarlene Joyce ReyNo ratings yet
- BSN4D-SG2 DM Type2Document201 pagesBSN4D-SG2 DM Type2Charisse CaydanNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypercalcemia PathophysiologyBeverly PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- Medications To Continue at Home Exercise Treatments Health Teachings Outpatient Diet Sexuality/ SpiritualityDocument2 pagesMedications To Continue at Home Exercise Treatments Health Teachings Outpatient Diet Sexuality/ SpiritualityMae EstilloreNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin Tazobactam Dosage Mechanism Indications Side Effects NursingDocument1 pagePiperacillin Tazobactam Dosage Mechanism Indications Side Effects NursingAthena SaturdayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDiana MuañaNo ratings yet
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDocument7 pagesNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONo ratings yet
- Case Pre Ovarian CystDocument56 pagesCase Pre Ovarian Cystthesa1201No ratings yet
- NCM 114 Gerontology - WeeK 1Document38 pagesNCM 114 Gerontology - WeeK 1Jmarie Brillantes Popioco0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities for Sodium Bicarbonate AdministrationDocument2 pagesNursing Responsibilities for Sodium Bicarbonate AdministrationKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Problem: Pain at 6/10 For A "Sore Right Shoulder" Date Evaluated: December 14, 2020Document2 pagesProblem: Pain at 6/10 For A "Sore Right Shoulder" Date Evaluated: December 14, 2020florenzoNo ratings yet
- DRUG ANALYSIS TABLEDocument10 pagesDRUG ANALYSIS TABLEChanel BalinbinNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Trauma - 5Document12 pagesLower Limb Trauma - 5Renee RoSeNo ratings yet
- Examples of Therapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument6 pagesExamples of Therapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication TechniquesReya Mae OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Miglitol (Glyset)Document1 pageMiglitol (Glyset)ENo ratings yet
- Drug LovenoxDocument2 pagesDrug LovenoxSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for Effective Airway ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing Interventions for Effective Airway ManagementwaadNo ratings yet
- PNSSDocument2 pagesPNSSBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LDocument2 pagesSt. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Reteplase (MIRel)Document23 pagesReteplase (MIRel)Jhoann JamanilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionLovely San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Assessment - Docx CRUZDocument3 pagesPost Partum Assessment - Docx CRUZKariza PerdidoNo ratings yet
- Format, Drug StudyDocument23 pagesFormat, Drug StudyKrizzle Mae NeypesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ob WardDocument7 pagesDrug Study Ob WardKc DichosoNo ratings yet
- DRUGS Study BethanyDocument7 pagesDRUGS Study BethanyamirredNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Endoscopic Retrograde Signs and SymptomsDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test Endoscopic Retrograde Signs and Symptomssalome carpioNo ratings yet
- Brief Reflection on Herbs for HealingDocument3 pagesBrief Reflection on Herbs for Healingsalome carpioNo ratings yet
- Brief Reflection on Herbs for HealingDocument3 pagesBrief Reflection on Herbs for Healingsalome carpioNo ratings yet
- What Is Septic ShockDocument6 pagesWhat Is Septic Shocksalome carpioNo ratings yet
- NCP For MGDocument2 pagesNCP For MGsalome carpioNo ratings yet
- NCP For MGDocument2 pagesNCP For MGsalome carpioNo ratings yet
- Brief Reflection on Herbs for HealingDocument3 pagesBrief Reflection on Herbs for Healingsalome carpioNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis of CholelithiasisDocument7 pagesCase Analysis of Cholelithiasissalome carpioNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis of CholelithiasisDocument7 pagesCase Analysis of Cholelithiasissalome carpioNo ratings yet
- Business Planchapter07Document50 pagesBusiness Planchapter07salome carpioNo ratings yet
- A 6 Year Old Girl With Fever and Abdominal PainDocument1 pageA 6 Year Old Girl With Fever and Abdominal Painsalome carpioNo ratings yet
- NCP For HypothermiaDocument2 pagesNCP For Hypothermiasalome carpioNo ratings yet
- VSP - Vision 01Document1 pageVSP - Vision 01api-252555369No ratings yet
- Certificate of Readiness To Enter Higher Surgical Training 2021Document5 pagesCertificate of Readiness To Enter Higher Surgical Training 2021mNo ratings yet
- ADA10 SunflowerAlmondButterDocument1 pageADA10 SunflowerAlmondButterLi SchliemannNo ratings yet
- The Long Term Effects of Cyberbullying On Adolescent Mental HealthDocument27 pagesThe Long Term Effects of Cyberbullying On Adolescent Mental Healthnelrose NavascaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Cyberbullying To The Mental Health of The Grade 12 AbmDocument19 pagesThe Impact of Cyberbullying To The Mental Health of The Grade 12 AbmSerene RiegoNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle Activity 3 FinalDocument3 pagesCrossword Puzzle Activity 3 Finalapi-541744798No ratings yet
- Curative SARS-CoV-2 Test Results NegativeDocument2 pagesCurative SARS-CoV-2 Test Results Negativeluis torresNo ratings yet
- Tax Updates Under CREATE LawDocument4 pagesTax Updates Under CREATE LawSandy ArticaNo ratings yet
- PE - LVI - 13 - 270321 - Kanthi Swaroop, Joel LeeDocument8 pagesPE - LVI - 13 - 270321 - Kanthi Swaroop, Joel Leeveeveebakkup baccupNo ratings yet
- Definitions: The Social Determinants of Health. SummaryDocument4 pagesDefinitions: The Social Determinants of Health. SummaryS VaibhavNo ratings yet
- NRMP ResDocument128 pagesNRMP ResAlvi MuldaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Body and ConclusionDocument4 pagesIntroduction, Body and ConclusionDyemmmark PicazoNo ratings yet
- Sample ID: 88397031Document1 pageSample ID: 88397031Zorka DanyiNo ratings yet
- SS1 English Language Comprehension and Objective QuestionsDocument5 pagesSS1 English Language Comprehension and Objective QuestionsJoshua OshokpekhaNo ratings yet
- From Head To ToeDocument5 pagesFrom Head To Toeapi-500025821No ratings yet
- BL1761S-F GL1761S-FDocument9 pagesBL1761S-F GL1761S-FMin Htet KyawNo ratings yet
- Childhood BlindnessDocument6 pagesChildhood BlindnessMonika Diaz KristyanindaNo ratings yet
- GCS Assessment Aid ArabicDocument1 pageGCS Assessment Aid ArabicMohammed Ibrahim Yahya bonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4: Modifiable Risk Factors of Lifestyle Diseases: SmokingDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 4: Modifiable Risk Factors of Lifestyle Diseases: SmokingShimah100% (2)
- Insecticidal Activity of Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum) Extract On American Cockroach (Periplenata Americana)Document7 pagesInsecticidal Activity of Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum) Extract On American Cockroach (Periplenata Americana)heheeheheNo ratings yet
- Assignment Four Developments in Equine Care EssayDocument4 pagesAssignment Four Developments in Equine Care EssayEmma WalshNo ratings yet
- (Journal of Neurosurgery - Spine) Radiographic and Clinical Evaluation of Free-Hand Placement of C-2 Pedicle ScrewsDocument8 pages(Journal of Neurosurgery - Spine) Radiographic and Clinical Evaluation of Free-Hand Placement of C-2 Pedicle ScrewsVeronica Mtz ZNo ratings yet
- 2.12 ICS Forms ICS 206Document3 pages2.12 ICS Forms ICS 206mdrrmo sinait100% (1)
- Psychosocial Support PlanDocument2 pagesPsychosocial Support PlanGwendolyn Lalamonan AnganaNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan TovDocument8 pagesPeperiksaan TovNORLIYANA BINTI NORDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- 011 Exam Focus Dec 22Document25 pages011 Exam Focus Dec 22Moyooree BiswasNo ratings yet
- Situation of Drugs Use Among IDUsDocument52 pagesSituation of Drugs Use Among IDUsSuresh DhunganaNo ratings yet
- EVO-Hemp: Nature's Most Useful PlantDocument14 pagesEVO-Hemp: Nature's Most Useful PlantPreet SinghNo ratings yet