Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment Activity: Test of Oils And: (Refer Only To The Translucent Test)
Uploaded by
Chryza Faith QuicoyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment Activity: Test of Oils And: (Refer Only To The Translucent Test)
Uploaded by
Chryza Faith QuicoyCopyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT ACTIVITY: TEST OF OILS AND
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l2QOi9mZoFc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3YCFwhPkYM
(REFER ONLY TO THE TRANSLUCENT TEST)
Table of Contents
Fats and oils are triesters of glycerol and higher fatty acids. At ordinary
temperatures, oils are liquids while fats are solids. Fats are present in gums,
oils and milk foods. They are insoluble in water sparingly soluble in alcohol
and soluble in chloroform. They serve as an excellent source of energy
providers to the body.
Aim:
To study some simple tests to identify the presence of oils and fats in the
given sample.
Theory:
Fats and oils are greasy in nature and on hydrolysis with aqueous or alcoholic
sodium or potassium hydroxide liberate glycerol. Fats and oils are of
vegetable or animal origin.
The following are the test to identify the presence of fats and oils.
1. Solubility test
2. Translucent spot test
3. Acrolein test
4. Baudouin test
5. Huble’s test
(a) Solubility Test:
Fats are soluble in organic solvents like chloroform, alcohol etc. It is insoluble
in water. So if the given sample forms an oily layer above the surface of the
water then fat is present. Partially soluble in alcohol and fully soluble in
chloroform than the presence of fat is confirmed.
Note: If the sample is miscible with chloroform and immiscible with water the
fat presence is confirmed.
(b) Translucent Spot Test:
In this test the given sample to be tested is rubbed between the folds of filter
paper. The appearance of translucent spot confirms the presence of fats in
the given sample.
Note: If there is presence of translucent spot then the presence of fats is
confirmed.
(c) Acrolein Test:
Fats and oils when heated with some crystals of potassium bisulfite KHSO4 in
a test tube. A pungent irritating odour or smell of acrolein confirms the
presence of fat or oil.
The chemical reaction is given below.
Note: If there is a pungent irritating odor then the presence of fats or oil is
confirmed.
(d) Baudouin Test:
Baudouin test is applied to distinguish between the desi ghee and vanaspati
ghee. Vanaspati ghee contains 5% sesame oil. Pure ghee does not contain
sesame oil. Fats and oils are treated with 5ml of concentrated hydrochloric
acid and 2% furfural solution in alcohol. After 5-10 minutes rose-red colour
appearance shows the presence of sesame oil in the given sample.
Note: This test is used to find out whether the given sample of desi ghee
contains vanaspati or not.
(e) Huble’s Test:
This test is used to know the degree of unsaturation in the given sample. Oils
on reaction with Huble’s reagent fads the violet colour of iodine then it is
unsaturated and if the colour persists then the given fat or oil is saturated.
Note: In this test various oils can be compared on the basis of unsaturation.
Precautions:
1. Handle the chemicals with care. Not to inhale chloroform since it has
anaesthetic effect.
2. Use droppers to take the reagents from the bottle.
3. While performing the experiment use hand gloves and lab aprons.
Materials Required:
1. Alcohol
2. Chloroform
3. Filter paper
4. Potassium bisulfate
5. Concentrated hydrochloric acid
6. Furfural solution
7. Test tubes
8. Test tube holder
9. Water bath
10. Dropper
11. Stirrer
12. Bunsen burner
Apparatus Setup:
Procedure:
Preparation of Reagent:
Huble’s reagent – Mix equal volumes of 7% mercury chloride in alcohol with
5% solution of iodine in 96% of alcohol.
(a) Solubility Test:
1. Take three test tubes which contains 5ml of given sample solution to
be tested.
2. Add 5ml of water to the first test tube and observe the solution.
3. To the second test tube add 5ml of alcohol.
4. To the third test tube add 5ml of chloroform.
5. Observe the change in solubility of the given sample.
6. If it is soluble in water then fat is absent, if its sparingly soluble in
ethanol then fat is present and same for chloroform.
(b) Translucent Spot Test:
1. Take the sample to be tested, press a little in the folds of the filter
paper.
2. On folding if there is the appearance of greasy spot indicates the
presence of oils or fats.
3. The spot grows larger on heating and drying the filter paper.
(c) Acrolein Test:
1. Take the sample to be tested in a test tube.
2. Add few crystals of potassium bisulfate to it.
3. Heat the mixture and observe the change in odour.
4. If there is pungent irritating odour then the presence of fate or oil is
confirmed.
(d) Baudouin Test:
1. Take 5ml of melted ghee in a test tube.
2. Add 5ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 2-3% of furfural solution
in alcohol to it.
3. Keep it aside for 5 to 10 minutes.
4. If there is the appearance of rose-red colour then the given ghee
contains vanaspati.
(e) Huble’s Test:
1. Take two test tube and add 3ml of chloroform in each.
2. Add cottonseed oil in one and linseed oil in the second test tube.
3. Shake the mixture well and add 3 drops of Huble’s reagent in each test
tube.
4. The violet colour of iodine fades away in linseed oil test tube while the
colour does not fade away in cottonseed oil.
5. This shows that linseed oil is more unsaturated than cotton seed oil.
Observations and Inference:
Solubility test If the sample is miscible with chloroform and immiscible with water
the fat presence is confirmed.
Translucent If there is presence of translucent spot then the presence of fats is
spot test confirmed.
Acrolein test If there is a pungent irritating odor then the presence of fats or oil is
confirmed.
Experiment Activity
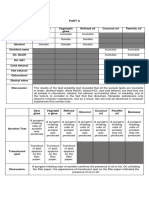
I. Make a table of the results on each test
Test Solvent Sample Observation
Desi ghee
Vegetable ghee
Solubility Water Immiscible with water
Refined oil
Test Desi ghee
Vegetable ghee
Ethanol It forms a lower layer
Refined oil
which dissolves on
heat
Desi ghee
Vegetable ghee
Chloroform Miscible with
Refined oil
chloroform
Test Sample Observation
Desi ghee Translucent spot appears
Vegetable ghee
Translucent Spot on the filter paper
Refined oil
Test
Desi ghee A pungent irritating odor of
II. Results and Discussion:
Vegetable ghee
Acrolein Test acrolein is produced
Refined oil
Baudouin Test Melted desi ghee No formation of rose-red
color
Melted vanaspati ghee Rose-red color appears
Huble’s Test Cotton seed oil Violet color does not fade
away
Linseed oil Violet color fade away
Based on the experiment, about the qualitative test of oils and fats the
results show that Solubility test is based on the property of lipid to dissolve
in different solvents. In the experiment of solubility test it shows that the
three samples which are desi ghee, vegetable ghee and refined oil. Using
the water as a solvent the samples showed immiscible which means oil or
fat is present. While, in alcohol the samples form a lower layer which
dissolves on heat this indicates the presence of oil or fats and in
chloroform the samples the result showed miscible which means oil or fat
is present.
The translucent test is a preliminary test for oils and fats which can be
detected by the appearance of a translucent and greasy spot. Most grease
or fat have a high boiling point. In the experiment, the result showed that
the three formed a translucent spot on the filter paper, which confirms the
presence of oil and fat on each sample.
In Acrolein Test, which is used to detect the presence of glycerol or fat.
When fat is treated strongly in the presence of a dehydrating agent such
as potassium bisulfate, the glycerol portion of the molecule is dehydrated
to form an unsaturated aldehyde, acrolein that has a pungent irritating
odor. The result showed in acrolein test, that all samples produced a
pungent irritating odor of acrolein which means there is a presence of oil or
fat in the samples.
Moreover, the Baudouin test is used to find out whether the given
sample of desi ghee contains vanaspati or not. In the experiment, the
result showed that in desi ghee there is no formation of rose-red color in
which it does not contain a sesame oil while, in vanasapati ghee it shows
rose-red color because of the presence of sesame oil. Also, Huble’s test
used to know the degree of unsaturation in the given sample. Oils and fats
on reaction with Huble's reagent fads the violet color of iodine then it is
unsaturated and if the color persists then the given fat or oil is saturated. In
the experiment, the results showed that in cotton seed oil, violet color
appears which means it is unsaturated while in linseed oil the color persist
which confirms that the given sample is more unsaturated.
We therefore conclude that the following experiments that we watched
enabled us to determine the presence and characteristics, as well as the
chemical properties of oils and fats. The analyst became more
knowledgeable about the presence of oils and fats in the following test that
were conducted.
III. Questions to Answer Tests of Oils and Fats
1. What are fats
Fat is an important part of our diet and it is important for our
health. It is one of the nutrients included in the foods we consume.
Fat is one of the most energy-dense foods. A gram of fat contains
nine kilocalories of energy. They are not water soluble. They're a
combination of lipids and fat-soluble vitamins. Although fat is
essential in our diet, eating too much of it can be harmful to your
health. There are several kinds of fats, some of which are better for
you than others. Fat is one of three primary macronutrients, along
with carbs and protein.
Fats serve a variety of functions in our bodies. Most people
have noted that they improve the taste of meals and assist
digestion. Fats supply energy to the body. There are several types
of fat, each of which performs a particular role. Saturated,
polyunsaturated, monounsaturated, and trans-fat are the four major
forms of fat. Some of these types are beneficial, while others are
detrimental. The bad fat is usually saturated fat since it raises blood
cholesterol levels, particularly LDL cholesterol, which leads to a rise
in heart disease, but saturated fats are also required for appropriate
alignment of growth factors in cells and organs. It's also a great
source of energy.
2. What is the difference between oils and fats?
Fats remains solid at room temperature. The fatty acid chains in
fats have a single bond. Since it has a single bond, there are
enough places for many hydrogen atoms to sit. So, as it is
saturated with hydrogen, it is called saturated fat. Considering it has
carbon bonds that are single, the molecular structure is robust and
strong. The intermolecular forces are not weak. Hence, a fat
remains solid where the binding is strong. Moreover, fats mainly
come from animal food but also through vegetable oil by process
called hydrogenation. Fats is unhealthy for human health, prone to
quick oxidation resulting in rancidity and it is responsible for high
cholesterol levels.
On the other hand, oils are liquid at room temperature. The oils
have double-bonded carbon atoms. Since it has double bonds,
there are not enough places for too many hydrogen atoms to sit.
So, it is not saturated with hydrogen. Thus, it is called unsaturated
fatty acid. Given that it has double bonds, the lack of hydrogen
atoms reduces the strength of the intermolecular forces. Hence, oils
remain liquid where the binding is not that strong. Also, oils mainly
come from plants or fish, healthy for human health, not that rancid
and eases high cholesterol levels.
3. How is the unsaturation in fats and oils determined?
The unsaturation in fats and oils determined by Houble’s drop
method. On the other hand, the amount of iodine that interacts with
the fat and oils is used to determine the degree of unsaturation. The
quantity of iodine that reacts is used to determine the fat and oils
iodine number, which indicates the degree of unsaturation in the fat
and oils.
4. What is the name of the compound formed when fats or
oils reacts with potassium bisulfate?
The acrolein is the compound formed when fats or oils reacts
with potassium bisulfate. When a fat is heated strongly in the
presence of a dehydrating agent such as KHSO 4, the glycerol
portion of the molecule is dehydrated to form the
unsaturated aldehyde or a acrolein which has the peculiar odor of
burnt grease.
5. Name the test used to test the presence of unsaturation in
fats and oils.
Huble’s test is used to test the presence of unsaturation in fats
and oils. This test determines the degree of unsaturation in oil or
fat. Huble's reagent interacts with an alcoholic iodine solution
including some mercuric chloride. If the oil or fat is unsaturated, the
violet color of iodine disappears during the process. The violet color
of iodine does not disappear when the oil or fat is saturated.
You might also like
- Exp. 4 Lipid Extraction and Lipid TestsDocument5 pagesExp. 4 Lipid Extraction and Lipid TestsEdchel67% (3)
- Activity 9 Lipids I.: CholesterolDocument8 pagesActivity 9 Lipids I.: CholesterolJasper Ian Tan JumalaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Test For LipidsDocument3 pagesQualitative Test For LipidsJeandra Villanueva100% (1)
- Lipids Lab ReportDocument9 pagesLipids Lab ReportRameesh IshakNo ratings yet
- Experiment #6Document11 pagesExperiment #6Tin-tin71% (7)
- HW5e Int Test Unit 2ADocument6 pagesHW5e Int Test Unit 2AСофия ЯрмакNo ratings yet
- Lab Report LipidsDocument5 pagesLab Report LipidsKhamis Tolentino100% (1)
- BSWM Ordinance No Segregation No CollectionDocument10 pagesBSWM Ordinance No Segregation No CollectionCharina Miclat100% (1)
- Expt. 5 Qualitative Test of LipidsDocument8 pagesExpt. 5 Qualitative Test of LipidsMary Ella Mae Pila100% (2)
- Alternative Uses of Sugarcane and Its Byproducts in AgroindustriesDocument55 pagesAlternative Uses of Sugarcane and Its Byproducts in AgroindustriesKasaimNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report On Feeding ProgramDocument6 pagesNarrative Report On Feeding ProgramAngelica Pastrana Dela Cruz87% (31)
- ACTIVITY NO. 5-Reactions of LipidsDocument12 pagesACTIVITY NO. 5-Reactions of LipidsReano Zendrix Perez AndresNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab Activity 5Document47 pagesBiochem Lab Activity 5Nafeesa Cadir100% (1)
- Lipids SOLVENT (Observations) Water Alcohol ChloroformDocument3 pagesLipids SOLVENT (Observations) Water Alcohol ChloroformEliza Cruz100% (1)
- Module 8 - BIOCHEM LABDocument5 pagesModule 8 - BIOCHEM LABStarrrNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Test of Oils and FatsDocument6 pagesLab Report Test of Oils and FatsKeth Samuel AdesasNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Oil and FatsDocument4 pagesQualitative Analysis of Oil and FatsMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Laboratory Activity No. 1: University of Perpetual Help System DALTA College of Medical TechnologyDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Laboratory Activity No. 1: University of Perpetual Help System DALTA College of Medical TechnologyKristine Joy Abellar ResuentoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 12Document2 pagesExperiment No. 12kokatedhananjay68No ratings yet
- Steps Carried Out Comparison: ObservationDocument9 pagesSteps Carried Out Comparison: ObservationJovan Paul DeldaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 ANALYSIS OF FATS AND OILSDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 5 ANALYSIS OF FATS AND OILSMissy Arabella PameNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Laboratory Report On Experiment 3: Test For LipidsDocument8 pagesBiochemistry Laboratory Report On Experiment 3: Test For LipidsDylan WhiteNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Test of Lipids Unsaturation Test For LipidsDocument12 pagesQualitative Test of Lipids Unsaturation Test For LipidsQasmNo ratings yet
- Formulas MsdsDocument2 pagesFormulas MsdsFaridah MagumparaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Qualitative Test For Lipid - ADocument5 pagesActivity No. 4 Qualitative Test For Lipid - APatricia Willyn DiosoNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Qualitative Test For LipidsDocument2 pagesGROUP 3 Qualitative Test For LipidsJennifer SorianoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 20 Group 1Document8 pagesLaboratory 20 Group 1Jamaica AciamajNo ratings yet
- Project-24: Study of Common Food Adulterants in Fat, Oil, Butter, Sugar, Turmeric Powder, Chilli Powder and PepperDocument4 pagesProject-24: Study of Common Food Adulterants in Fat, Oil, Butter, Sugar, Turmeric Powder, Chilli Powder and PepperMayank KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Lipids - "Fat": Trip Sa SBDocument3 pagesLipids - "Fat": Trip Sa SBYholzManioNo ratings yet
- The Characterization of Saponifiable LipidsDocument7 pagesThe Characterization of Saponifiable LipidsREYMAR CASAREONo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab ReportDocument4 pagesBiochem Lab ReportChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Activity 20Document10 pagesActivity 20Rane MandapatNo ratings yet
- BIO 024 Activity No. 11 Lipids BenavidezDocument4 pagesBIO 024 Activity No. 11 Lipids BenavidezZzzYayahzikNo ratings yet
- Baudouin TestDocument2 pagesBaudouin Testguialim99No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Laboratory Experiment #5 Oil and FatsDocument4 pagesBiochemistry Laboratory Experiment #5 Oil and Fatshyunjin is such a sweet heartNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument6 pagesLipidsFrancine Louisse Gealogo0% (1)
- BIO Lipid 2Document4 pagesBIO Lipid 2mhammadjalal70No ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Fixed Oils (Group 5)Document11 pagesActivity 4 - Fixed Oils (Group 5)Fabulously ShooktNo ratings yet
- M6 - Lipids TestDocument9 pagesM6 - Lipids Testlarry machonNo ratings yet
- Lopez, Azzia M. - bsn1-13 - (Bio 024) Lab Activity 11 - LipidsDocument4 pagesLopez, Azzia M. - bsn1-13 - (Bio 024) Lab Activity 11 - Lipidsallia LopezNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Group 2Document15 pagesLipids: Group 2JULIANNAH ATHENA MERCADONo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument13 pagesBiochemLilson De Guzman Bagbagay50% (2)
- Lipid Solubility Test: PrincipleDocument21 pagesLipid Solubility Test: PrincipleGresia FalentinaNo ratings yet
- Xt202000826@wmsu@edu - PH: Activity No. 5 Reaction of LipidsDocument5 pagesXt202000826@wmsu@edu - PH: Activity No. 5 Reaction of LipidsJohanna Marie GantalaoNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Experiment 5 Properties of Lipids Biochem LabDocument2 pagesGroup 5 Experiment 5 Properties of Lipids Biochem LabMiki CantaviejaNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument5 pagesLipidsmaggan donnaNo ratings yet
- The Same Results Happened With The Oil of Wintergreen. The Translucent Spot Did Not DisappearDocument3 pagesThe Same Results Happened With The Oil of Wintergreen. The Translucent Spot Did Not DisappearZerimar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Test For LipidDocument25 pagesTest For LipidJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For LipidsDocument6 pagesQualitative Tests For LipidsCorine RepatoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Biochemistry (BIO 462)Document3 pagesLab Report Biochemistry (BIO 462)Iman FarhaNo ratings yet
- Chem14lab Bsmt2a-2 Expt7Document5 pagesChem14lab Bsmt2a-2 Expt7RizhenNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 5 Lipids: IUG, Spring 2014 Dr. Tarek ZaidaDocument15 pagesLab Activity 5 Lipids: IUG, Spring 2014 Dr. Tarek ZaidaNaziefa JailaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 5 Qualitative Test For Fats and OilsDocument5 pagesLab Activity 5 Qualitative Test For Fats and OilsPatricia Willyn DiosoNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument16 pagesLipidsJonabel MacayNo ratings yet
- Activity # 6 LipidsDocument59 pagesActivity # 6 LipidsAebee AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Special Gates of Plant CellDocument12 pagesSpecial Gates of Plant CellChristian Dave CuetoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledMeena JeerhNo ratings yet
- TestforLipids ResearchLab3Document10 pagesTestforLipids ResearchLab3Mikaela Rome BigayNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 5 Lipids: IUG, 2016 Dr. Tarek ZaidaDocument17 pagesLab Activity 5 Lipids: IUG, 2016 Dr. Tarek ZaidaJohanna Marie GantalaoNo ratings yet
- BIO Lipid TestDocument5 pagesBIO Lipid Testmhammadjalal70No ratings yet
- Purifying Used Cooking OilDocument1 pagePurifying Used Cooking OilFelixNo ratings yet
- Analysis Exp 8Document4 pagesAnalysis Exp 8Chin T. OndongNo ratings yet
- Lab #17Document2 pagesLab #17jamesisaiahlallaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab Action of Amylase On Starch TemperatureDocument2 pagesBiochem Lab Action of Amylase On Starch TemperatureChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab ReportDocument4 pagesBiochem Lab ReportChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDocument2 pagesChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Lacking/Not Received Modules by The Subject Teacher in Entrepreneurship For Section Gemini For Finals Period S.Y. 2020-2021Document1 pageLacking/Not Received Modules by The Subject Teacher in Entrepreneurship For Section Gemini For Finals Period S.Y. 2020-2021Chryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesExperiment 9 - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Research CamiasDocument22 pagesResearch Camiasjustine chanNo ratings yet
- Fermented Seaweed SauceDocument8 pagesFermented Seaweed Sauceclaire qweenNo ratings yet
- NSSCO Syllabus Agr Nov2010.PdfpdfDocument38 pagesNSSCO Syllabus Agr Nov2010.PdfpdfpaulesNo ratings yet
- Effect of Spacing and Poultry Manure Rates On Growth, Yield and Quality of Cayenne Pepper (Capsicum Frutescens. L) in Southern Rain Forest of NigeriaDocument7 pagesEffect of Spacing and Poultry Manure Rates On Growth, Yield and Quality of Cayenne Pepper (Capsicum Frutescens. L) in Southern Rain Forest of NigeriaIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Fugalite Bio IN 2020Document8 pagesFugalite Bio IN 2020aasifNo ratings yet
- Kader Chapter 4Document9 pagesKader Chapter 4Gaganpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Strontium ChlorideDocument4 pagesStrontium ChlorideParvani PatankarNo ratings yet
- Impact Assessment of Good Agricultural Practices of Vegetable Farmers at Three Barangays of Roxas, IsabelaDocument41 pagesImpact Assessment of Good Agricultural Practices of Vegetable Farmers at Three Barangays of Roxas, IsabelaJacquiline NogalesNo ratings yet
- PIONIER 2076P Data SheetDocument1 pagePIONIER 2076P Data SheetAlexis GaydaNo ratings yet
- South Cotabato Life Science Team Research PaperDocument45 pagesSouth Cotabato Life Science Team Research PaperCedrick ManabatNo ratings yet
- Naturcomplet - G: Soil ImproverDocument1 pageNaturcomplet - G: Soil Improverchichu09No ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Agri-Fishery-ArtsDocument14 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Agri-Fishery-ArtsDechie NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Foods: DigestibilityDocument17 pagesEvaluation of Foods: DigestibilityMudasirNo ratings yet
- 1953 EconomicBiologyCollembolaDocument4 pages1953 EconomicBiologyCollembolabrandon arredondoNo ratings yet
- Commission Regulation Eu No 574 AmbrosiaDocument18 pagesCommission Regulation Eu No 574 AmbrosiaOk SunNo ratings yet
- Guide To Organic Certification-DikonversiDocument11 pagesGuide To Organic Certification-DikonversiBang LongNo ratings yet
- 32 ArticleText 50 1 10 201808031Document12 pages32 ArticleText 50 1 10 201808031eins sophia perwitaNo ratings yet
- Sticky Rice Tapai: Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Makassar State UniversityDocument6 pagesSticky Rice Tapai: Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Makassar State UniversityAyunda WfraaaNo ratings yet
- Mamun. Hort.509 ExamDocument10 pagesMamun. Hort.509 ExamnihanNo ratings yet
- FSSA - Stainless Steel Volute Pump PDFDocument7 pagesFSSA - Stainless Steel Volute Pump PDFBOYALFREDONo ratings yet
- MCQ Bank, Food TechnologyDocument10 pagesMCQ Bank, Food TechnologySuprabha DeyNo ratings yet
- Short Question AnswersDocument3 pagesShort Question AnswersYolanda HokerNo ratings yet
- 10 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 6 Page 110Document2 pages10 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 6 Page 110Tajinderpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Effect of Fermented Fish Waste (Gunapaselam) Application On The Soil Fertility With Special Reference To Trace Elements and The Growth Characteristics of Vigna Radiata.Document7 pagesEffect of Fermented Fish Waste (Gunapaselam) Application On The Soil Fertility With Special Reference To Trace Elements and The Growth Characteristics of Vigna Radiata.José Antonio MaquénNo ratings yet
- Jubilant Ingrevia Limited Annual Report 2021 22Document324 pagesJubilant Ingrevia Limited Annual Report 2021 22bapianshumanNo ratings yet
- MgCO3 Naikai Japan - Brocure & TDSDocument1 pageMgCO3 Naikai Japan - Brocure & TDSAreIf Cron BmxStreetNo ratings yet