0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pagesNitroglycerin Drug Study
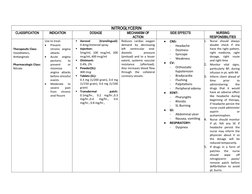
Nitroglycerin is used to treat chronic angina attacks, acute angina pectoris, and moderate to severe pain from chronic anal fissure. It works by reducing cardiac oxygen demand and lowering blood pressure. Common side effects include headache, dizziness, hypotension, and flushing. Nursing responsibilities include carefully checking dosage and administration, monitoring vital signs during treatment, informing patients of potential side effects like headache, and monitoring for side effects to report to the physician.
Uploaded by
Beatrizz P GellaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pagesNitroglycerin Drug Study
Nitroglycerin is used to treat chronic angina attacks, acute angina pectoris, and moderate to severe pain from chronic anal fissure. It works by reducing cardiac oxygen demand and lowering blood pressure. Common side effects include headache, dizziness, hypotension, and flushing. Nursing responsibilities include carefully checking dosage and administration, monitoring vital signs during treatment, informing patients of potential side effects like headache, and monitoring for side effects to report to the physician.
Uploaded by
Beatrizz P GellaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd