Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Yr10 t3 2018
Uploaded by
mark smithOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Yr10 t3 2018
Uploaded by
mark smithCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT FOR CURRICULUM,
RESEARCH, INNOVATION AND LIFELONG LEARNING
Directorate for Learning and Assessment Programmes Track 3
Educational Assessment Unit
Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2018
YEAR 10 BIOLOGY TIME: 2 hours
Name: _____________________________________ Class: _______________
Section A Section B
Question
No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5
Max
7 8 7 10 8 8 7 15 15 15 15 15
mark
TOTAL
Actual MARK
mark
85% Theory Paper 15% Practical 100% Final Score
Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018 Page 1 of 11
Section A: This section carries 55 marks. Answer all questions in this section.
1. A person went for a medical check-up and had the chest X-ray image below taken.
trachea
a. i. Structure ‘X’ forms part of a set of bones found in the chest. Name this set of
bones.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. List two functions of these bones.
______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
iii. Name the muscles that control the movement of these bones.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
b. The X-ray image shows a tube called trachea.
i. Explain how the trachea stays upright and does not collapse.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. Explain why the trachea has to divide in two smaller tubes called bronchi.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
iii. Give one reason why the trachea has to be blocked when a food bolus is
swallowed.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
Total: 7 marks
Page 2 of 11 Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018
2. Below are three possible food chains showing how the energy, captured by 50kg
of green plants, may end up in humans.
A B C
Human Human Human
Fish
Cows
Insects
50 kg
Green
Plants
a. For food chain ‘C’,
i. state the number of trophic levels;
____________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. name the secondary consumer.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
b. Name and explain which one of the three food chains would allow the highest
amount of energy to be transferred to humans.
_________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________ (1, 1)
c. In the space below, draw a pyramid of biomass representing food chain ‘B’.
(2)
d. Explain why the production of beef (cow meat) in food chain ‘B’ would be more
efficient if cows are kept indoors in a controlled environment.
_________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________ (2)
Total: 8 marks
Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018 Page 3 of 11
3. The diagram below shows a transverse section through a part of a pea plant.
a. i. State which plant structure is shown in the diagram.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. Explain how the diagram confirms your answer to part (a.i.).
____________________________________________________________ (1)
iii. List two ways how this structure assists plants in carrying out photosynthesis.
______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
b. i. On the diagram above, label with a ‘Y’ a tissue through which food is
transported to the rest of the plant. (1)
ii. Explain why it is important for this tissue to reach the bottom parts of the
plant.
______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
Total: 7 marks
4. Lisa wears an electronic activity tracker on her
wrist. Among other things, this device tracks the
heart rate. An app on Lisa’s smartphone produces
graphs with the data it receives from this device.
The screenshot on the following page shows Lisa’s
heart beat rate per minute on the ‘Y’ axis against
the time of day on the ‘X’ axis, over a period of 24
hours from midnight to midnight.
Page 4 of 11 Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018
a. i. Give the approximate time of day when Lisa went for a run.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. Support your answer with evidence from the graph.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
iii. Give a biological explanation for the data recorded by the activity tracker at
the time of the run.
______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
b. i. At rest, Lisa has a heartbeat of around 62 beats per minute. From the graph
identify a period during which Lisa was sleeping.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. Name one body function for which the heart is required to stay active even
when at rest.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
c. The heart contracts by means of a distinct kind of muscle called cardiac muscle.
i. List two properties specific to the cardiac muscle that make it suitable for its
function.
______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
ii. Explain how the thickness of the cardiac muscle differs between the right and
the left ventricles, giving a reason for your answer.
______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
Total: 10 marks
Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018 Page 5 of 11
5. The diagram below shows a section of the digestive system.
X
stomach
gall
bladder
duodenum
a. i. Name the fluid produced in structure ‘X’ and stored in the gall bladder.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. Explain how this fluid helps the duodenum regulate the pH effectively.
______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
b. Explain how both structures ‘X’ and ‘Y’ help in the efficient breakdown of lipids in
the duodenum.
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________ (3)
c. Explain how structure ‘Y’ helps the duodenum perform a digestive breakdown
similar to that performed by the stomach.
_________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________ (2)
Total: 8 marks
Page 6 of 11 Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018
6. The two setups below were used to measure the rate of aerobic respiration in
seeds. In both setups, seeds were placed into an air tight test-tube in the
presence of potassium hydroxide (KOH). A drop of dye was placed into a thin
glass capillary-tube as shown.
Setup A Setup B
drop drop
of dye of dye
Germinating Dead
seeds seeds
a. Define ‘aerobic respiration’.
_________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________ (2)
b. Explain the aim behind using dead seeds in ‘Setup B’.
_______________________________________________________________ (1)
c. KOH removes the gas produced by germinating seeds. Name this gas.
_______________________________________________________________ (1)
d. In ‘Setup A’ the drop of dye is expected to move towards the test-tube. Explain
why.
_________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________ (2)
e. Describe the change in results you would expect in ‘Setup A’ if:
i. the experiment is done in a much colder environment.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. anaerobic organisms are used instead of seeds.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
Total: 8 marks
Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018 Page 7 of 11
7. During one stage in the production of mozzarella cheese, the enzyme rennin is
added to milk together with an adequate amount of citric acid at a temperature of
40oC.
a. Explain the role of enzymes in chemical reactions.
_________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________ (2)
b. Explain the effect on the production of mozzarella cheese if the following mistakes
take place during the process:
i. temperature is increased to 80oC.
______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
ii. a reduced amount of citric acid is used.
______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
c. The amount of rennin used in the process is relatively low. Explain why.
_______________________________________________________________ (1)
Total: 7 marks
Page 8 of 11 Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018
Section B: This section carries 45 marks. Answer question 1 and any other two
questions. Write your answers on the separate A4 sheet provided.
1. Quinoa’s nutritional value.
Chenopodium quinoa, known as quinoa, is a plant that has been cultivated and
consumed by humans for the last 7,000 years.
Quinoa has potential health benefits and exceptional nutritional value. It has a high
concentration of protein with all essential amino acids being available. It is also rich
in unsaturated fatty acids.
The table below compares the nutritional value of 100g of Quinoa to the
equivalent mass of rice, wheat and corn.
Energy Proteins Carbo- Lipids Unsaturated Fibre
Food
(kcals) (g) hydrates (g) (g) fatty acids (g) (g)
Quinoa 120 4.4 21.3 1.92 1.61 2.8
Rice 130 2.38 28.59 0.21 0.12 0.3
Wheat 113 3.6 25.12 0.66 0.35 4.23
Corn 96 3.41 20.98 1.5 0.98 2.4
Quinoa also contains vitamins such as Vitamin C, and minerals such as calcium.
Quinoa is a sustainable food, as it requires less water and needs less land to grow
than the equivalent amount of wheat, corn or rice. Besides it could be cultivated in
different environments. For these reasons, many countries worldwide are growing
quinoa thus reducing the need for transportation which helps the global community
in the effort to reduce pollution.
adapted from:
https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/quinoa-chenopodium-quinoa-willd-from-nutritional-value-to-potential-health-benefits-an-integrative-review-
2155-9600-1000497.php?aid=72704
a. Provide one reason why quinoa is more beneficial to young teenagers than the
other 3 foods. (1)
b. Explain the advantage of quinoa having ‘all essential amino acids available’. (2)
c. i. Out of the 4 foods mentioned in the table above, name the one that is the
least suitable to help a person suffering from constipation. (1)
ii. Give a reason for your answer. (1)
d. i. Explain why a diet rich in quinoa could help a poor community to reduce the
risks of children suffering from rickets. (1)
ii. Name one other vitamin-deficiency disorder that can be prevented by
consuming quinoa. (1)
e. i. Quinoa has a high amount of unsaturated fatty acids. Name the molecule that
joins fatty acids to form a fat molecule. (1)
ii. Give one use of lipids in the human body. (1)
f. All of the foods in the table above contain a high amount of carbohydrates. Explain
in full the role of the mouth in the breakdown of carbohydrates. (3)
g. Quinoa needs less water than most plants. Name one use of water as a reagent in
plants. (1)
h. ‘Reducing the need for transportation … helps the global community in the effort
to reduce pollution’. Explain this statement. (2)
Total: 15 marks
Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018 Page 9 of 11
2. Haemodialysis is a treatment given to patients whose kidneys have both failed.
Blood is pumped out of the body and passed through filters with very small pores
similar to what happens in kidney nephrons. It is then pumped back into the body.
a. Explain why haemodialysis treatment is not required by patients who have suffered
failure in only one kidney. (1)
b. i. Explain why blood cells and proteins will not be lost during haemodialysis. (1)
ii. Name the structure in the nephron that does not allow blood cells and proteins
to be filtered out. (1)
iii. Name the process that separates proteins from soluble substances in the
structure you named above. (1)
c. i. During haemodialysis blood is passed in contact with a solution of sugar and
salts. Explain what will happen if this solution has too little sugar and salt. (3)
ii. Name the part of the nephron that reabsorbs the glucose in the filtrate. (1)
d. In haemodialysis, unwanted blood substances accumulate in the machine before
filtered blood is returned to the patient.
i. Name one substance that will accumulate in the machine. (1)
ii. Explain what happens to unwanted substances in the kidney from the moment
they leave the nephron until they are expelled from the body. (3)
e. Some haemodialysis patients have to be given a dose of anti-diuretic hormone
(ADH). Explain the role of ADH in healthy individuals. (3)
Total: 15 marks
3. At Buskett, a sooty mould is often seen growing on Bay Laurel leaves. Sooty
moulds are black powdery moulds that cover leaf blades of infected plants, thus
blocking sunlight.
a. i. Describe the effect of blocking sunlight from leaves. (2)
ii. Explain how epidermal cells are adapted not to block light to underlying cells.
(1)
iii. Name two types of cells that would use any light that manages to pass
through. (2)
iv. Name the chemical found in most plant cells that is able to trap energy from
light. (1)
b. Describe an experiment you would carry out to demonstrate the effect of blocking
light on leaves. (5)
c. Sooty mould grows as a consequence of juices (sap) that escape from the leaf
through the pores open for transpiration.
i. List three effects of transpiration to the plant. (3)
ii. Name the pores that allow transpiration to take place. (1)
Total: 15 marks
Page 10 of 11 Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018
4a. Pneumonia is an infection of the alveoli, where they become full of fluid and blood
cells in an attempt to kill microbes causing the infection.
i. Name the type of blood cells that attempt to kill the microbes. (1)
ii. List two methods by which these blood cells can kill microbes. (2)
iii. Name another defence mechanism adopted by blood. (1)
b. i. The diagram below shows a large amount of fluid covering most of the surface
area of the infected alveoli. The fluid makes the alveolar walls thicker. Explain
the effect this will have on the efficiency of the alveoli affected with pneumonia
when compared to the healthy alveoli. (3)
fluid and blood
cells in alveoli
thickened
alveolar walls
ii. Explain why alveoli should have a dense capillary network around them. (1)
iii. Name the major blood vessel that sends blood to this network of capillaries.(1)
c. If pneumonia spreads, it can infect and inflame the pleural membrane. This causes
a lot of pain, especially upon breathing in.
i. State where the pleural membrane is found. (1)
ii. Explain why the inflammation causes pain upon breathing in. (2)
d. Cigarette smokers have a much higher chance of developing pneumonia. Name
three chemicals found in cigarettes or their smoke and give one effect of each on
the human body. (3)
Total: 15 marks
5. Compare and contrast:
a. the terms community and population. (3)
b. dentition in herbivores and carnivores. (4)
c. the structure and function of arteries and veins. (4)
d. adaptations of leaves of plants living in dry and leaves of plants living in humid
conditions. (4)
Total: 15 marks
Biology – Year 10 – Track 3 – 2018 Page 11 of 11
You might also like
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyNo ratings yet
- Bio QuestionsDocument12 pagesBio QuestionsYasmine CaparNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Biology Form IV Exam Guide and QuestionsDocument11 pagesBiology Form IV Exam Guide and Questionsmark smithNo ratings yet
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Organismal BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Organismal BiologyNo ratings yet
- B Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023Document12 pagesB Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Biology (Form 4) - Test 1 (2019)Document12 pagesBiology (Form 4) - Test 1 (2019)Kordell leydNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Exam OverviewDocument10 pagesBiology Form 4 Exam Overviewmark smithNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2023Document12 pagesYear 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- 0610/42 Biology: DC (ST/CT) 166141/1Document32 pages0610/42 Biology: DC (ST/CT) 166141/1Thapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Biology Questions ExplainedDocument9 pagesMultiple-Choice Biology Questions ExplainedAaron LiuNo ratings yet
- A03 Data AnalysisDocument19 pagesA03 Data Analysisleocarlton0700No ratings yet
- Proteinsand Enzymes Part 2Document94 pagesProteinsand Enzymes Part 2dfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Photosynthesis QPDocument35 pages4.1 Photosynthesis QPZaynab Ameenah KhanNo ratings yet
- Sce Form 2Document22 pagesSce Form 2williamkong123No ratings yet
- Exercise Digestive System PDFDocument22 pagesExercise Digestive System PDFIzudin Hasan86% (7)
- Academic Window BIOLOGY 7 PDFDocument15 pagesAcademic Window BIOLOGY 7 PDFsidharth balaji sridharanNo ratings yet
- Junior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2007 Biology PaperDocument10 pagesJunior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2007 Biology PapershahirahNo ratings yet
- 3.7.4 Populations in Ecosystems Pack 2Document79 pages3.7.4 Populations in Ecosystems Pack 2savinbusinesswomanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Photosynthesis QPDocument33 pages4.1 Photosynthesis QPNirashaNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit One Cells TutorialDocument10 pagesCape Biology Unit One Cells Tutorialakeisha kingNo ratings yet
- Practical Techniques Booklet Qm1hekDocument49 pagesPractical Techniques Booklet Qm1hekzena Al-SarawanNo ratings yet
- Organisation Foundation HigherDocument135 pagesOrganisation Foundation HigherSơnSơnNo ratings yet
- SC Paper 2 Yr 5 (2022)Document6 pagesSC Paper 2 Yr 5 (2022)SHEELA A/P ARUMUGAM MoeNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - QuestionsDocument57 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - QuestionsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- B F3 Annual 2023Document18 pagesB F3 Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- 4.1c Cell Biology HigherDocument64 pages4.1c Cell Biology HigherJayasri JeevaNo ratings yet
- Biology Worksheet OneDocument14 pagesBiology Worksheet Onetevin_prawlNo ratings yet
- Application Questions Nx8jamDocument22 pagesApplication Questions Nx8jamdovidNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2Document88 pagesGenetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2kafiazabit200No ratings yet
- Mid Term f4 2008-Paper 2Document7 pagesMid Term f4 2008-Paper 2hamzah79No ratings yet
- Week 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804Document36 pagesWeek 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- WS 2 IG I BiologyDocument4 pagesWS 2 IG I BiologyRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane of Host CellDocument8 pagesCell Membrane of Host CellAshique FarhadNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Assessment Booklet: Marks 1'9 Time Allowed 165 MinutesDocument39 pagesTopic 5 Assessment Booklet: Marks 1'9 Time Allowed 165 MinutesHayley Camenzuli100% (1)
- Cell Cycle Extra Q and MSDocument14 pagesCell Cycle Extra Q and MSKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1Document8 pagesBiology Paper 1paqurette3No ratings yet
- RP - Food TestsDocument17 pagesRP - Food TestsNeel MutagiNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Biology STPM 2011 PDFDocument6 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Biology STPM 2011 PDFben0706No ratings yet
- Enzyme Blood Exam QsDocument9 pagesEnzyme Blood Exam Qsmichael.quinn729No ratings yet
- Sda Term 2 TestDocument13 pagesSda Term 2 TestHope MaboteNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2010 P2Document16 pagesCSEC Biology June 2010 P2Joy Boehmer100% (1)
- Biology MES 2013Document12 pagesBiology MES 2013Al-Ashmal FoolchandNo ratings yet
- Biology June/July Paper: Application QuestionsDocument14 pagesBiology June/July Paper: Application QuestionsCHUA MING XIU HCINo ratings yet
- Populations in Ecosystems Summer Holiday Homework QsDocument11 pagesPopulations in Ecosystems Summer Holiday Homework QsSohail AliNo ratings yet
- SMK Bukit Jambul Science Mid-Year ExamDocument10 pagesSMK Bukit Jambul Science Mid-Year ExamhusnaihsanNo ratings yet
- Exams 2022 Paper 3 SCDXPKDocument39 pagesExams 2022 Paper 3 SCDXPKQueen Bee (Tt)No ratings yet
- Food Tests Exam QsDocument8 pagesFood Tests Exam QsAleNo ratings yet
- May Pen High School Mid Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 3Document8 pagesMay Pen High School Mid Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 3CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- SPIRAL CL 8 SWT 2020 21 26 12 19 FinalDocument106 pagesSPIRAL CL 8 SWT 2020 21 26 12 19 FinalISHAAN GOYALNo ratings yet
- Set 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Document17 pagesSet 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- 9th class biology PBA PAPERDocument9 pages9th class biology PBA PAPERhadiabdul56755No ratings yet
- Biology - Higher Level: Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations CommissionDocument16 pagesBiology - Higher Level: Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations CommissionDiaa SaberNo ratings yet
- Shreya WorksheetDocument4 pagesShreya WorksheetRahulNo ratings yet
- Practical Skills QuestionsDocument62 pagesPractical Skills QuestionshftuuNo ratings yet
- BiologyMock 2Document36 pagesBiologyMock 2backup14gNo ratings yet
- GANDHI SCHOOL ANCOL Biology Mock Test 2Document10 pagesGANDHI SCHOOL ANCOL Biology Mock Test 2Roselyn TrixieNo ratings yet
- Energy in The Ecosystem WebquestDocument4 pagesEnergy in The Ecosystem Webquestapi-327342342No ratings yet
- Earth's Structure and Tectonic ActivityDocument6 pagesEarth's Structure and Tectonic Activitymark smithNo ratings yet
- O Level Chemistry BookDocument68 pagesO Level Chemistry Bookmark smithNo ratings yet
- (Old) F4T3 STBIO - Enzymes & PH, Digestion, Respiration & Gas ExchangeDocument33 pages(Old) F4T3 STBIO - Enzymes & PH, Digestion, Respiration & Gas Exchangemark smithNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision NotesDocument20 pagesQuick Revision NotesYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of Life: Bil - Ye R 10 - Tra 3Document7 pagesChemicals of Life: Bil - Ye R 10 - Tra 3mark smithNo ratings yet
- Test On Diversity of LifeDocument6 pagesTest On Diversity of Lifemark smithNo ratings yet
- Earth's Structure and Tectonic ActivityDocument6 pagesEarth's Structure and Tectonic Activitymark smithNo ratings yet
- Earth's Structure and Tectonic ActivityDocument6 pagesEarth's Structure and Tectonic Activitymark smithNo ratings yet
- PDFBiology F3 T3 - Study NotesDocument49 pagesPDFBiology F3 T3 - Study Notesmark smithNo ratings yet
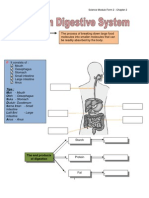
- Human Digestive System GuideDocument18 pagesHuman Digestive System Guidemark smithNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Worksheet Ch. 6 Section 2: Name: . DateDocument4 pagesEnzymes Worksheet Ch. 6 Section 2: Name: . DateOlivia ScallyNo ratings yet
- Energy & Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument30 pagesEnergy & Respiration and Gas Exchangemark smithNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and The Excretory SystemDocument21 pagesHomeostasis and The Excretory Systemmark smithNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition and PhotosynthesisDocument21 pagesPlant Nutrition and Photosynthesismark smithNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument9 pagesEnzymesmark smithNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Exam OverviewDocument10 pagesBiology Form 4 Exam Overviewmark smithNo ratings yet
- Biology f4 t3 2014 MsDocument5 pagesBiology f4 t3 2014 Msmark smithNo ratings yet
- ME 251 Lecture 1Document20 pagesME 251 Lecture 1Seth AnkamahNo ratings yet
- Telemecanique Integral 32 Motor StarterDocument52 pagesTelemecanique Integral 32 Motor StarterJaime IxtaNo ratings yet
- Rear Axle ShaftsDocument4 pagesRear Axle ShaftsMaria AparecidaNo ratings yet
- Monorail HC Overhead Track Scale: Technical ManualDocument30 pagesMonorail HC Overhead Track Scale: Technical ManualRicardo Vazquez SalinasNo ratings yet
- Abandonship Drill and LSA Training With Newly Join CrewDocument3 pagesAbandonship Drill and LSA Training With Newly Join CrewSashNo ratings yet
- Chain Surveying InstrumentsDocument5 pagesChain Surveying InstrumentsSachin RanaNo ratings yet
- Those Who Serve - Stephen Melillo (Score)Document22 pagesThose Who Serve - Stephen Melillo (Score)Fernando RamiresNo ratings yet
- Fire Warden Training: Richard Hagger - ConsultantDocument61 pagesFire Warden Training: Richard Hagger - ConsultantRichard Hagger100% (2)
- Syllabus 2020Document4 pagesSyllabus 2020asdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis of The Origin of LanguageDocument6 pagesHypothesis of The Origin of LanguageJefferson KagiriNo ratings yet
- Band 2 eDocument58 pagesBand 2 eIonaş Claudia Ramona100% (1)
- Range Safety Regulations and DocumentsDocument11 pagesRange Safety Regulations and Documentsjakehunter24No ratings yet
- Unit Ii, Lesson 4: Qualitative Research in Different Areas of KnowledgeDocument6 pagesUnit Ii, Lesson 4: Qualitative Research in Different Areas of KnowledgeJessy RoseNo ratings yet
- LA36300 Circuit Breaker Data SheetDocument2 pagesLA36300 Circuit Breaker Data SheetALEJANDRO DOMINGUEZNo ratings yet
- Manual Liebert PSADocument12 pagesManual Liebert PSAMatthew CannonNo ratings yet
- Cobra 4 Far DynacordDocument4 pagesCobra 4 Far DynacordDaniel SfichiNo ratings yet
- Jaguar Land-Rover: A Customer Centric OrganizationDocument15 pagesJaguar Land-Rover: A Customer Centric OrganizationAnmol Shukla100% (1)
- 5S Office OrganizationDocument14 pages5S Office Organizationthuy linh phamNo ratings yet
- History of Nano FiltrationDocument42 pagesHistory of Nano FiltrationKieran Sexton100% (2)
- Math10 Q2 Mod24 WritingtheEquationofaCircleandDeterminingtheCenterandRadiusofaCircle V3-1Document19 pagesMath10 Q2 Mod24 WritingtheEquationofaCircleandDeterminingtheCenterandRadiusofaCircle V3-1Bridget SaladagaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report FACTDocument16 pagesInternship Report FACTBennetHailinkNo ratings yet
- Bar Code Label Requirements, Compatibility, and UsageDocument22 pagesBar Code Label Requirements, Compatibility, and Usagelarrylegend33No ratings yet
- MCQs in Oral Surgery by Babu SParmarDocument517 pagesMCQs in Oral Surgery by Babu SParmarAmr KhattabNo ratings yet
- Types of DisasterDocument22 pagesTypes of DisasterKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Greenheck Facilities Guide - Locations and Details in Schofield & Mosinee WIDocument1 pageGreenheck Facilities Guide - Locations and Details in Schofield & Mosinee WIRicardo Ruy PeñaNo ratings yet
- Tips On Fatigue - NAVWEPS 00-25-559Document123 pagesTips On Fatigue - NAVWEPS 00-25-559Mark Evan SalutinNo ratings yet
- Catalogo RobinsonDocument8 pagesCatalogo RobinsonclerigonsaNo ratings yet
- LP in ArtsDocument6 pagesLP in ArtsBilindaNo ratings yet
- U1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1Document4 pagesU1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1jonahNo ratings yet
- My Heart Sings Praises - Line UpDocument4 pagesMy Heart Sings Praises - Line UpAnthony JimenezNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesFrom EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Younger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationFrom EverandYounger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Darwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeFrom EverandDarwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (523)
- Fearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageFrom EverandFearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)