Professional Documents
Culture Documents
شابتر 3
Uploaded by
Feras ArafatOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
شابتر 3
Uploaded by
Feras ArafatCopyright:
Available Formats
An-Najah National University
College of Engineering
Statics-61110
Chapter [3]
Equilibrium
Dr. Sameer Shadeed
1 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Chapter Objectives
Students will be able to:
1. Draw a free body diagram (FBD)
2. Apply equations of equilibrium to solve 2D
and 3D problems
2 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Applications
For a spool of
given weight,
what are the
forces in cables
AB and AC ?
3 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Applications
For a given
cable strength,
what is the
maximum
weight that can
be lifted ?
4 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Applications
A steel beam is
used to support roof
joists
How can we
determine the support
reactions at A and B ?
Again, how can we make use of an idealized model
and a free body diagram to answer this question?
5 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
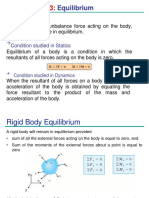
Equilibrium in Two Dimension (2D)
When a body is in equilibrium, the resultant
of all forces acting on it is zero
Thus, the resultant force R and the resultant
moment M are both zero
6 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Free Body Diagram (FBD)
The Free body Diagram is a diagrammatic
representation of the isolation of a single body
from all surrounding bodies
The Free Body Diagram is one of the most
important things for you to know how to draw
and use
The Free Body Diagram is the most
important single step in the solution of problems
in mechanics
7 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Free Body Diagram (FBD)
What and Why
What ?
It is a drawing that shows all external forces
acting on the particle
Why ?
It helps you write the equations of equilibrium
used to solve for the unknowns (usually forces
or angles)
8 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Modeling The Action of Forces
in 2D Analysis
9 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Modeling The Action of Forces
in 2D Analysis
10 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Modeling The Action of Forces
in 2D Analysis
11 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Construction of Free Body
Diagrams
1. Imagine the system to be isolated or cut free from
its surroundings
2. Show all the forces that act on the system
Active forces: They want to move the system
Reactive forces: They tend to resist the motion
3.Identify each force and show all known
magnitudes and directions
4. Show all unknown magnitudes and/or directions
as variables
12 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Examples of Free Body
Diagrams
13 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Examples of Free Body
Diagrams
14 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Free Body
Diagram
Exercises
15 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Free Body
Diagram
Exercises
16 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Draw A complete and Correct
Free Body Diagram
17 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Draw A complete and Correct
Free Body Diagram
18 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Equilibrium Conditions
When a body is in equilibrium, the
resultant of all forces and moments
acting on it is zero
For two dimensional force system (2D),
the equations of equilibrium may be
written in scalar form as
19 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Categories of Equilibrium
The
categories of
force
systems
acting on
bodies in two
dimensional
equilibrium
are
summarized
as follows:
20 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Constraints and Statical
Determinacy
Redundant Constraints: When a body has
more supports than necessary to hold it in
equilibrium, it becomes statically indeterminate
Redundant: Supports which can be removed
without destroying the equilibrium condition of
the body
A problem that is statically indeterminate has
more unknowns than equations of equilibrium
21 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Constraints and Statical
Determinacy
Bodies which are supported by the minimum
number of constraints necessary to ensure
equilibrium configuration are called statically
determinant
For such bodies the equilibrium equations are
sufficient to determine the unknown external forces
In some cases, there may be as many unknown
reactions as there are equations of equilibrium
However, if the supports are not properly
constrained, the body may become unstable for
some loading cases
22 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Adequacy of Constraints
23 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Steps For Solving 2D
Equilibrium Problems
1. If not given, establish a suitable x-y
coordinate system
2. Draw a free body diagram (FBD) of the
object under analysis
3. Apply the three equations of equilibrium to
solve for the unknowns
24 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Important Notes
1. If we have more unknowns than the number of
independent equations, then we have a statically
indeterminate situation. We cannot solve these
problems using just statics
2. The order in which we apply equations may affect the
simplicity of the solution. For example, if we have two
unknown vertical forces and one unknown horizontal
force, then solving ∑FX = 0 first allows us to find the
horizontal unknown quickly
3. If the answer for an unknown comes out as negative
number, then the sense (direction) of the unknown
force is opposite to that assumed when starting the
problem
25 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 1
26 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 1 (Solution)
27 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 1 (Solution)
28 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 1 (Solution)
29 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 2
30 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 2 (Solution)
31 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 2 (Solution)
32 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 3
33 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 3 (Solution)
34 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 3 (Solution)
35 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 4
36 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 4 (Solution)
37 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 4 (Solution)
38 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Equilibrium in Three
Dimensions (3D)
As stated earlier, when a body is in equilibrium, the
net force and the net moment equal zero (∑ ∑F = 0 and
∑M = 0)
These two vector equations can be written as six
scalar equations of equilibrium. These are
39 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Free Body Diagram (FBD)
The FBD is the only reliable method for
disclosing all forces and moments which
should be included in our equilibrium
equations
In 3D the FBD serves the same essential
purpose as it does in 2D and should always
be drawn
40 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Modeling The Action of
Forces in 3D Analysis
41 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Modeling The Action of
Forces in 3D Analysis
42 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Categories of Equilibrium in 3D
43 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Categories of Equilibrium in 3D
44 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 5
45 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 5 (Solution)
46 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 5 (Solution)
47 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 5 (Solution)
48 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 6
49 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 6 (Solution)
50 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 6 (Solution)
51 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 6 (Solution)
52 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 7
53 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 7 (Solution)
54 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 7 (Solution)
55 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
Example 7 (Solution)
56 Static Notes 2013 [Equilibrium] Dr. Sameer Shadeed
You might also like
- Nonlinear Dynamic in Engineering by Akbari-Ganji’S MethodFrom EverandNonlinear Dynamic in Engineering by Akbari-Ganji’S MethodNo ratings yet
- شابتر 5Document87 pagesشابتر 5Feras ArafatNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect Linear Algebra (EBOOK): With 500 ExercisesFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect Linear Algebra (EBOOK): With 500 ExercisesNo ratings yet
- شابتر 4Document82 pagesشابتر 4Feras ArafatNo ratings yet
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- شابتر 2Document89 pagesشابتر 2Feras ArafatNo ratings yet
- شابتر 7Document29 pagesشابتر 7Feras ArafatNo ratings yet
- Statics-61110: Chapter (1) ChapterDocument23 pagesStatics-61110: Chapter (1) ChapterFeras ArafatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statics - EquilibriumDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Statics - EquilibriumAjinkya KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Load and Stress AnalysisDocument23 pagesChapter - 3: Load and Stress AnalysissandeshlikesNo ratings yet
- شابتر 6Document36 pagesشابتر 6Feras ArafatNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium in 3D Lecture Note 1Document4 pagesEquilibrium in 3D Lecture Note 1venkatarao HanumanthuNo ratings yet
- 1 - Topic 06 - 2D Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocument10 pages1 - Topic 06 - 2D Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyHenry SchofieldNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Rigid BodyDocument41 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid BodyJaya KarthigaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 03:: EquilibriumDocument15 pagesChapter No. 03:: EquilibriumAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium: Part A: Equilibrium in Two DimensionsDocument50 pagesEquilibrium: Part A: Equilibrium in Two DimensionsChakkarat ProyseepaiNo ratings yet
- Greens Theorem Part 2Document9 pagesGreens Theorem Part 2Desmond NjikeNo ratings yet
- KA20903 - Lecture 1 Introduction To Mechanics of SolidsDocument6 pagesKA20903 - Lecture 1 Introduction To Mechanics of SolidsKit Meng LimNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Equilibrium 2DDocument10 pages2.1 Equilibrium 2DEster shilumeNo ratings yet
- WWW Engin Brown Edu Courses En3 Notes Statics Equilibrium EqDocument52 pagesWWW Engin Brown Edu Courses En3 Notes Statics Equilibrium EqArunachalam NarayananNo ratings yet
- 001.principle of StaticsDocument3 pages001.principle of StaticsCIELO OTADOYNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Week 1aDocument7 pagesDynamics Week 1adonatchangeNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 (Stress and Strain)Document27 pagesTopic 3 (Stress and Strain)Peter AdamNo ratings yet
- AA 9 Checking Out Stress States With Mohrs CircleDocument53 pagesAA 9 Checking Out Stress States With Mohrs CircleHatem AbdelnabiNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis GerritvisserDocument11 pagesModal Analysis GerritvisserSathiyaseelan SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Equilibriumequationofequilibrium 131201132649 Phpapp01Document28 pagesEquilibriumequationofequilibrium 131201132649 Phpapp01Raghu BhatNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11: Deformation of C-BarDocument10 pagesExercise 11: Deformation of C-Barjdial9664No ratings yet
- Chap. 1 General Principles: What Is Mechanics? What Is Statics? MechanicsDocument4 pagesChap. 1 General Principles: What Is Mechanics? What Is Statics? Mechanicsrj2263No ratings yet
- Free Body Diagram and Quasi-Static, Two-Dimensional Load Analysis Free BodyDocument10 pagesFree Body Diagram and Quasi-Static, Two-Dimensional Load Analysis Free Bodyabdo alsyedNo ratings yet
- Structural ANALYSIS Stability and Degrees of IndeterminacyDocument5 pagesStructural ANALYSIS Stability and Degrees of IndeterminacyDaVenki100% (1)
- Module 5-Intro To Engr MechDocument7 pagesModule 5-Intro To Engr MechPradeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument26 pagesLecture 3 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodieskeempee meeraNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction: Review of Basic Concepts in Mechnics Lecture 2: EquilibriumDocument3 pagesModule 1: Introduction: Review of Basic Concepts in Mechnics Lecture 2: EquilibriumSaurabh MishraNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction: Review of Basic Concepts in Mechnics Lecture 2: EquilibriumDocument3 pagesModule 1: Introduction: Review of Basic Concepts in Mechnics Lecture 2: EquilibriumEldho VargheseNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks Motion AnalysisDocument37 pagesSolidWorks Motion AnalysisAnonymous rI9NBeE5No ratings yet
- SolidWorks Motion Study TutorialDocument37 pagesSolidWorks Motion Study TutorialVega R JoseNo ratings yet
- 5 External Reliability: Robustness Analysis Final ReportDocument23 pages5 External Reliability: Robustness Analysis Final ReportMul YaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter Statics, Lecture Notes, Chapter 5Document74 pagesChapter Statics, Lecture Notes, Chapter 5RayanNo ratings yet
- Team 2b H2Document33 pagesTeam 2b H2Ivan AlbertosNo ratings yet
- CN Chap05 - Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocument13 pagesCN Chap05 - Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyJohn Mark Manalo RosalesNo ratings yet
- 13 Determinacy and Kinematic Stability Notes Sp04Document8 pages13 Determinacy and Kinematic Stability Notes Sp04Aarna JainNo ratings yet
- Lec7 Flexibility Method and Stiffness MethodDocument34 pagesLec7 Flexibility Method and Stiffness MethodVasu Dev VkmNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 1Document16 pagesCh-5 1Noor BasheerNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis - FeaDocument33 pagesStress Analysis - Feaaap1100% (3)
- RatchetingDocument20 pagesRatchetingAllan Marbaniang100% (1)
- Idealization of Supports and Distributed LoadsDocument6 pagesIdealization of Supports and Distributed LoadsAbhishek AroraNo ratings yet
- 03 Equilibrium 3DDocument18 pages03 Equilibrium 3DMuzammil Ahmed Khan tareenNo ratings yet
- 2 Statics of Particles - 2Document10 pages2 Statics of Particles - 2gamue08No ratings yet
- 4 Equilibrium of Bodies 2dDocument21 pages4 Equilibrium of Bodies 2dFadlanbunglonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Internal Loadings and StressesDocument22 pagesLecture 1 Internal Loadings and Stresseskyle vincent0% (1)
- Fatigue Failure Analysis - Learn EngineeringDocument3 pagesFatigue Failure Analysis - Learn Engineeringpavan317No ratings yet
- Make It Stand, Prevost Et AlDocument10 pagesMake It Stand, Prevost Et AlRamonaTamaraNarkevicius-FleischerNo ratings yet
- AMOS Note - Week 10-11 (Mod-IV)Document105 pagesAMOS Note - Week 10-11 (Mod-IV)Arupananda PrustyNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strain - Plane Stress and Plane StrainDocument5 pagesStress and Strain - Plane Stress and Plane StrainPretheesh Paul CNo ratings yet
- 0054 Handout 4Document4 pages0054 Handout 4zcaptNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Equilibrium: Learning Outcomes For This ChapterDocument15 pagesChapter 3 - Equilibrium: Learning Outcomes For This ChapterLetshego Itumeleng MoahloliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document22 pagesLecture 4نصرت سعد نصرتNo ratings yet
- L04 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies AnswerDocument46 pagesL04 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies Answertony tangNo ratings yet
- Principal Stresses and PlanesDocument5 pagesPrincipal Stresses and PlanesGanesh PeketiNo ratings yet
- شابتر 6Document36 pagesشابتر 6Feras ArafatNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.: (5) Experiment Name: Continuous Operation: Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems LabDocument1 pageExperiment No.: (5) Experiment Name: Continuous Operation: Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems LabFeras ArafatNo ratings yet
- Ex8 Sequence Operation of Double-Acting P.C.A (Pneumatic Control) PDFDocument1 pageEx8 Sequence Operation of Double-Acting P.C.A (Pneumatic Control) PDFFeras ArafatNo ratings yet
- Ex7 Speed Control (Latching Relay Circuit) PDFDocument1 pageEx7 Speed Control (Latching Relay Circuit) PDFFeras ArafatNo ratings yet
- Studio Photography PresentationDocument16 pagesStudio Photography Presentationapi-248078730No ratings yet
- Expansion Joint in CAESARDocument5 pagesExpansion Joint in CAESARkaruna346No ratings yet
- Material Constitution of RockDocument24 pagesMaterial Constitution of RockPandu Deya AnankeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document16 pagesChapter 2Nur Anira AsyikinNo ratings yet
- Dialab Autolyzer 450Document2 pagesDialab Autolyzer 450Niraj Silwal100% (1)
- Introduction To KinematicsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Kinematicsdhilip_sacetNo ratings yet
- EMPDS - First Review Seprator DesignDocument30 pagesEMPDS - First Review Seprator DesignnawarsNo ratings yet
- FORM U-5 MANUFACTURERS DATA REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SHEET SHELL-AND-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGERS Edit2017Document2 pagesFORM U-5 MANUFACTURERS DATA REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SHEET SHELL-AND-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGERS Edit2017Ashish PatelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Chapter 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3 Chapter 3Danial AimanNo ratings yet
- TB50SE13Document11 pagesTB50SE13Novianto RachmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1 GENERAL:-Concrete Is One of The Foremost Versatile Building Materials. It Will Be Cast ToDocument51 pagesChapter-1: 1.1 GENERAL:-Concrete Is One of The Foremost Versatile Building Materials. It Will Be Cast ToNAVEEN ROYNo ratings yet
- Chap-2 PropertiesDocument82 pagesChap-2 PropertieskushNo ratings yet
- Metodo de Losc ComponenetesDocument14 pagesMetodo de Losc ComponenetesFrey EspadaNo ratings yet
- Emulsiones (Sativay)Document15 pagesEmulsiones (Sativay)Cesar DuqueNo ratings yet
- NS Refractory Repair Spray TechnologyDocument7 pagesNS Refractory Repair Spray TechnologyZaini MahdiNo ratings yet
- Oregon Scientific wmr88Document11 pagesOregon Scientific wmr88Flavio MazziniNo ratings yet
- Precast Driven Pile 450x450-350x350Document55 pagesPrecast Driven Pile 450x450-350x350civixxNo ratings yet
- Dupont SurlynDocument2 pagesDupont SurlynpackagingNo ratings yet
- Anna University of Technology Chennai: Affiliated InstitutionsDocument42 pagesAnna University of Technology Chennai: Affiliated InstitutionsSAGUNTHVELNo ratings yet
- Minfc25885 Is 733 Grade 63400Document4 pagesMinfc25885 Is 733 Grade 63400pavankumarankad81No ratings yet
- Are They Pour Lines or Cold Joints - tcm45-348413Document4 pagesAre They Pour Lines or Cold Joints - tcm45-348413محمد كاشف جاويدNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Soundness of Aggregates by Freezing and ThawingDocument3 pagesSoundness of Aggregates by Freezing and ThawingEvert RiveraNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Storage For HVAC SystemsDocument3 pagesThermal Energy Storage For HVAC SystemsmohdnazirNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Chapter7 2020 Part1Document45 pagesLecture - Chapter7 2020 Part1Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Manual 26260: Governing Fundamentals and Power ManagementDocument76 pagesManual 26260: Governing Fundamentals and Power Managementmarius_1959No ratings yet
- 2009 H2 Physics - YJC PDFDocument58 pages2009 H2 Physics - YJC PDFEndi FendiNo ratings yet
- Resina - TDS - 10200005 - EN - EN-WEICON-F2Document2 pagesResina - TDS - 10200005 - EN - EN-WEICON-F2kakonauta1No ratings yet
- Boiling MechanismDocument16 pagesBoiling MechanismherawanadifNo ratings yet
- CT Design ParametersDocument6 pagesCT Design ParametersMike Rowen BanaresNo ratings yet