100% found this document useful (1 vote)
494 views45 pagesScaffolding Safety at Construction Site: Prepared by
This document provides information on scaffolding safety at construction sites. It defines scaffolding and describes the three main types: supported, suspended, and other scaffolds. It outlines the design load requirements for light, medium, and heavy duty scaffolds. It discusses hazards associated with scaffolding and provides general safety requirements including proper footing, guardrails, access, screening, and platforms. It also describes personal protective equipment for scaffolders.
Uploaded by
TulshidasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
494 views45 pagesScaffolding Safety at Construction Site: Prepared by
This document provides information on scaffolding safety at construction sites. It defines scaffolding and describes the three main types: supported, suspended, and other scaffolds. It outlines the design load requirements for light, medium, and heavy duty scaffolds. It discusses hazards associated with scaffolding and provides general safety requirements including proper footing, guardrails, access, screening, and platforms. It also describes personal protective equipment for scaffolders.
Uploaded by
TulshidasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Scaffolding Safety at Construction Site: Introduction to the presentation on scaffolding safety at construction sites, covering essential safety aspects and requirements.
- General Objectives of the Presentation: Describes the objectives of the presentation focused on safety in scaffolding usage and maintenance at construction sites.
- Definition of Scaffolding: Provides definition and categorization of scaffolding types according to OSHA standards.
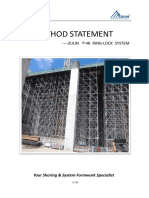
- Scaffold Types: Describes different scaffold types, including supported and suspended scaffolds, with examples.
- Design Load of Scaffolds: Explains different design loads for scaffolds categorized as light, medium, and heavy duty, specifying weight limits and dimensions.
- Introduction of Scaffolding Issues: Introduces common issues associated with scaffolding in construction and their impact on safety and productivity.
- Hazards In Scaffolding: Identifies primary hazards and faults in scaffolding usage leading to accidents and injuries.
- Safety In Scaffolding: Provides safety guidelines and best practices to avoid accidents while using scaffolding.
- Scaffolding General Requirements: Details general requirements and standards for safe erection and use of scaffolding, including footing, guardrails, and safe access.
- Scaffold Height and Support: Describes restrictions on scaffold height relative to support base dimensions.
- Supported Scaffolds: Explains platform support methods for stability including poles, frames, and outriggers.
- Different Parts of a Scaffold: Illustrates and labels the different parts and components of scaffolding structures.
- Common Faults: Identifies and illustrates common faults in scaffold materials and construction.
- Inspection Guidelines for Boards: Provides criteria for inspecting boards used in scaffolding to ensure safety and reliability.
- Scaffolder’s Personal Protective Equipment: Details the personal protective equipment required for scaffolders, including harnesses and gloves.
- Scaffolding Tools and Accessories: Lists essential tools and accessories for scaffolding construction and maintenance.
- Scaffold Tags: Explains the use of scaffold tags to indicate safety inspection status and instructions.
- Bad Practice Examples: Provides visual examples of bad practices in scaffold usage to warn against unsafe methods.
- Good Practice Examples: Illustrates good practice examples of scaffolding to promote safe usage and compliance.
- Conclusion: Concludes the presentation and invites questions from the audience on scaffolding safety.