Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 9 Elaborate
Uploaded by
TrishaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 9 Elaborate
Uploaded by
TrishaCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY OF CEBU - BANILAD
Gov. M. Cuenco Ave, Cebu City, 6000 Philippines
College of Nursing
Telephone No: (032) 231- 8631
NCM 106 – Pharmacology
Course Outputs /Assessment of Learning for CILO # 1
Written Outputs (Mental Models, Group Activity and Reflection Journal)
Name of Student : Trisha Faye Y. Pasay________ Yr.& Sec. : BSN 2 - A____ __
Module/Topic : Module 9 – Elaborate _______ Date : 12/12/2021______
I. Create a Drug Study on Endocrine Drugs that are commonly used in clinical
settings. Utilize the drug study template.
a. Medical Ward (Internal & Non-communicable) Service Ward (3 Medications)
b. Surgical Ward – Male/Female (3 Medications)
c. Pediatric Non-Critical) Ward (2 Medication)
II. Briefly organize and bring together main ideas. Explain in your own words.
(50 – 150 words for each question)
1. TC, a 32-year-old patient, was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus after the birth of
her first child; her blood glucose level was 180 mg/dL. Her serum glucose level
has been maintained within the normal range with metformin 500 mg/day.
A. It is given that after giving birth to baby, a 32-year-old patient, TC has been
diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. The sugar level of the patient was 180
milligram per deciliter. The serum glucose level is managed with metformin
of 500 milligrams per day. The effectiveness of the oral glucose load is more
when compared to insulin. Therefore, patient TC is recommended to take an
oral antidiabetic drug instead of insulin. Metformin is a compound of
biguanide. This medication acts by decreasing the hepatic production of
glucose from the stored glycogen. Metformin medication helps in decreasing
the formation of serum glucose after the consumption of meal. Hyperglycemia
is being controlled with the help of this medication.
B. Metformin is under the class of drugs called biguanides. Metformin helps to
control the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood. It decreases the amount of
glucose one absorbs from food and the amount of glucose made by the liver.
It is indicated in type 2 diabetes. You should not give it with type 1 diabetes,
people with prediabetes over the age 60 and not with stage 4 or 5 kidney
disease. Metformin should not be used by patients with an estimated
glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 30 mL/minute/1.73 m2 and starting
Pharmacology Module 1st Semester S.Y. 2021- 2022 UCBC Page 1
UNIVERSITY OF CEBU - BANILAD
Gov. M. Cuenco Ave, Cebu City, 6000 Philippines
College of Nursing
Telephone No: (032) 231- 8631
metformin in patients with an eGFR between 30-45 mL/minute/1.73 m2 is not
recommended.
C. Regular monitoring is a particularly helpful way to manage the patient’s
diabetes and help control her blood sugar, so it's important to know how to
properly use the home glucometer device. If one has type 1 diabetes, type 2
diabetes, latent autoimmune diabetes in adults, or were diagnosed with
gestational diabetes during pregnancy, a major part of a patient’s treatment
plan should be regularly testing the blood glucose levels with a glucometer.
Frequent glucometer use can help patient: check how controlled her blood
sugar is and whether it's high or low, recognize patterns when she is more
likely to have a spike or crash in glucose, see how her glucose levels respond
after exercise or in times of stress, monitor the effects of diabetes medications
and other therapies and assess how well she is meeting specific treatment
goals.
D. When patient TC became pregnant, she will not be able to take antidiabetic
medication as a way to control blood sugar because the safety of using these
medications during pregnancy has not been established. It means that it can be
harmful to the pregnant woman and more especially to the developing fetus,
which is why the doctor will probably have to switch to insulin immediately.
The drug of choice for the management of diabetes in pregnancy is insulin
which was decided based on high efficacy and safety since there is lack of any
well-studied alternative medication in pregnancy. The reason why physicians
stick to insulin as a treatment of choice for diabetes in pregnancy because it is
the only standard for treatment when lifestyle measures do not maintain
glycemic control during pregnancy.
E. Human insulin is under a class of medications called hormones. Human insulin
is used to take the place of insulin that is normally produced by the body.
Human insulin is available in two forms, a short acting (regular) form and an
intermediate acting (NPH) form. Some examples of human insulin are:
• Regular (short acting): Humulin S, Actrapid, Insuman Rapid
• NPH (intermediate acting): Humulin I, Insuman basal, Insulatard
• Premixed human insulins: Humulin M2, M3 and M5, Insuman Comb
15, 25 and 50
These insulins have four advantages over highly purified animal insulins: they
induce lower titers of circulating insulin antibodies; their subcutaneous
injection is associated with fewer skin reactions; they are absorbed more
rapidly from the injection site; and less degradation occurs at the site of
injection.
Pharmacology Module 1st Semester S.Y. 2021- 2022 UCBC Page 2
UNIVERSITY OF CEBU - BANILAD
Gov. M. Cuenco Ave, Cebu City, 6000 Philippines
College of Nursing
Telephone No: (032) 231- 8631
F. Before administering the insulin, wash your hands, put on gloves, and clean
the injection site with an alcohol swab. Now you are ready to inject the insulin,
choosing between two injection techniques: inserting the needle into the skin
at a 90-degree or at a 45-degree angle. Insulin should be injected into the fat
just underneath the skin rather than into muscle, which can lead to quicker
insulin action and greater risk of low blood sugar. The stomach, thighs,
buttocks, and upper arms are common injection sites because of their higher
fat content.
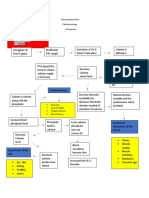
G. Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin, also known as isophane insulin,
is an intermediate-acting insulin given to help control blood sugar levels in
people with diabetes.
Pros
• Available over the counter without a prescription, but usually also
covered by many insurance plans
• Insulin works quite well to lower her blood sugar. When used
correctly, it'll lower blood sugar every time she will use it and prevent
the harmful, long-term effects of high sugar levels on her organs and
blood vessels.
• Starting insulin early in the treatment of type 2 diabetes can keep her
body's insulin-producing cells working and slow down the worsening
of her diabetes.
• Can be used even if she has liver or kidney problems, unlike many
other blood sugar-lowering medications
Cons
• Patient must be comfortable with checking her blood sugar regularly
to take insulin
• She must be comfortable giving herself injections
• Can cause weight gain and fat buildup
• Has higher risk of low blood sugar compared to medications taken by
mouth
• Can cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), especially if she doesn’t
take it every day or have a random meal and exercise schedule
• Only available as a brand name, so it can be expensive
H. A hypoglycemic reaction, also called an insulin reaction, insulin shock, or low
blood sugar reaction, occurs when blood glucose drops to a point where the
individual becomes confused and disoriented. Symptoms of low blood sugar
reaction can be divided into two general stages. The first stage, usually
occurring early in a reaction, can include shakiness, sweating, nervousness,
fast pulse, dizziness, headache, and pale skin color. Symptoms may appear
suddenly. The second, more advanced stage of hypoglycemia, includes
mood/behavior changes, confusion, poor coordination, and difficulty in
speaking.
Pharmacology Module 1st Semester S.Y. 2021- 2022 UCBC Page 3
UNIVERSITY OF CEBU - BANILAD
Gov. M. Cuenco Ave, Cebu City, 6000 Philippines
College of Nursing
Telephone No: (032) 231- 8631
I. What should be included in patient teaching?
Patient teaching should include:
• Education in insulin therapy, including reasons for insulin
treatment, contraindications, complications, and appropriate
aftercare
• Education on use of the equipment used in the procedure and its
safe disposal
• An understanding of different insulin’s, their action and safe dose
adjustments
• Discuss the process of starting insulin with the patient; encourage
the patient to have a family member present if they so desire
A step-by-step approach is provided to teaching the patient the basics about
starting insulin. The provider or staff performing the teaching should check off
each item as it is completed to document teaching.
References:
• Bryant, E. (n.d.). HYPOGLYCEMIA. Nfb.Org. Retrieved December 12, 2021, from
https://nfb.org//images/nfb/publications/vod/vsum9911.htm
• Comerford, K. C., & Durkin, M. T. (2021). Nursing 2021 drug handbook. 41st edition. Philadelphia:
Wolters Kluwer.
• Doenges, Marilynn E., Moorhouse, Mary Frances, Murr, Alice C. (2014). Nursing care plans:
guidelines for individualizing client care across the life span (9th). Philadelphia: F.A. Davis
Company.
• Karch, A. M. (2017). Focus on nursing pharmacology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
• Karch, A. M. (2014). 2014 Lippincott's nursing drug guide. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer
Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Pharmacology Module 1st Semester S.Y. 2021- 2022 UCBC Page 4
UNIVERSITY OF CEBU - BANILAD
Gov. M. Cuenco Ave, Cebu City, 6000 Philippines
College of Nursing
Telephone No: (032) 231- 8631
• Kee, J. LeFever, Hayes, E. R., & McCuistion, L. E. (2015). Pharmacology: A Patient-Centered Nursing
Process Approach. 8th edition. St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier/Saunders.
• Manzella, D. (2021, September 25). 10 Steps for Using a Glucometer. Verywell Health.
Retrieved December 12, 2021, from https://www.verywellhealth.com/how-to-use-a-
glucometer-1087304
• Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER). (2020, March 13).
Hypoglycemia - Symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved December 11, 2021, from
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hypoglycemia/symptoms-causes/syc-
20373685
• NANDA International & Herdman, T. H. (2012). NANDA International Nursing diagnoses:
Definitions and classification 2012-14. Wiley-Blackwell.
• National Library of Medicine. (2021, December 6). Metformin: MedlinePlus Drug Information.
Medlineplus.Gov. Retrieved December 12, 2021, from
https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a696005.html
• The Global Diabetes Community. (2019, January 15). Human Insulin. Diabetes.Co.Uk.
Retrieved December 12, 2021, from https://www.diabetes.co.uk/insulin/human-
insulin.html
Pharmacology Module 1st Semester S.Y. 2021- 2022 UCBC Page 5
UNIVERSITY OF CEBU - BANILAD
Gov. M. Cuenco Ave, Cebu City, 6000 Philippines
College of Nursing
Telephone No: (032) 231- 8631
Prepared by:
Trisha Faye Y. Pasay
Students Signature over
Printed Name
Submitted to:
Lemuel C. Candelasa, EdD(c) ,MAN,RN
ProfeAmeliaor – Pharmacology
Pharmacology Module 1st Semester S.Y. 2021- 2022 UCBC Page 6
You might also like
- Practical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersFrom EverandPractical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus DefinitionDocument4 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus DefinitionTempoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Considerations for Patients with DiabetesDocument7 pagesNursing Considerations for Patients with Diabeteslanguha NgatiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesSummary of Product Characteristicsorly villalonNo ratings yet
- Oral RevalidaDocument39 pagesOral Revalidajunathancortez123No ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesDiabetes MellitusNoviley Amor TianiaNo ratings yet
- History of Present IllnessDocument4 pagesHistory of Present Illnessegabe386No ratings yet
- Antidiabetic AgentDocument5 pagesAntidiabetic AgentChamique Gelle Kerlin C LingayoNo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic Agents: Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesAntidiabetic Agents: Diabetes MellitusRatika SariNo ratings yet
- Hayatt Univesity College. Faculty of Medicine. Family Medicine. Mohamed Gassim Mohamed. Insulin ManagementDocument14 pagesHayatt Univesity College. Faculty of Medicine. Family Medicine. Mohamed Gassim Mohamed. Insulin ManagementMohammed GassimNo ratings yet
- Lantus (Insulin Glargine)Document3 pagesLantus (Insulin Glargine)ENo ratings yet
- INSULIN CONTROLS BLOOD GLUCOSEDocument7 pagesINSULIN CONTROLS BLOOD GLUCOSEMIR SARTAJNo ratings yet
- The Diabetes Handbook by DK - Parte3Document20 pagesThe Diabetes Handbook by DK - Parte3CarlosPutnamNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Study GuideDocument4 pagesDiabetes Study GuideNicole Brassington0% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus in Paediatric Age: Topics CoveredDocument13 pagesDiabetes Mellitus in Paediatric Age: Topics Coveredlotp12No ratings yet
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Diabetes Mellitus Key PointsDocument6 pagesLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Diabetes Mellitus Key PointsDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Insulin and Antidiabetic Drugs: Prof - DR Asya RehmanDocument23 pagesInsulin and Antidiabetic Drugs: Prof - DR Asya RehmanGareth BaleNo ratings yet
- Insulin injection and pump options for diabetes patientsDocument7 pagesInsulin injection and pump options for diabetes patientsSourav DasNo ratings yet
- Presentation TomorrowDocument8 pagesPresentation TomorrowRafik LakhdarNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument34 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAru VermaNo ratings yet
- DM Ppt. NewDocument26 pagesDM Ppt. NewRio Ramon HilarioNo ratings yet
- Insulin AdministrationDocument15 pagesInsulin Administrationmec17No ratings yet
- Manejo de La DMGDocument5 pagesManejo de La DMGsandymejiaNo ratings yet
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin Drug StudyRai Hanah92% (13)
- Dr. Dr. I Wayan Bikin Suryawan SpA (K) - Type II DM Whats New On ManagementDocument34 pagesDr. Dr. I Wayan Bikin Suryawan SpA (K) - Type II DM Whats New On ManagementajescoolNo ratings yet
- Novolin R SQ (Regular Insulin)Document3 pagesNovolin R SQ (Regular Insulin)ENo ratings yet
- Managing Diabetes in Preschool Children - ISPAD 2017Document19 pagesManaging Diabetes in Preschool Children - ISPAD 2017Sandra ContrerasNo ratings yet
- GDM DrugsDocument13 pagesGDM DrugsAnkur YadavNo ratings yet
- What Is DiabetesDocument9 pagesWhat Is Diabeteskdubb90No ratings yet
- Novolog (Insulin Aspart)Document3 pagesNovolog (Insulin Aspart)ENo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic Agents GuideDocument19 pagesAntidiabetic Agents GuideJames SoeNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument9 pagesDiabetesMsPocketbook HoarderNo ratings yet
- DIABETESDocument29 pagesDIABETESVinnes Ann InfanteNo ratings yet
- Monsalud - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMonsalud - Drug StudyJanielle Christine MonsaludNo ratings yet
- Effective Use of Insulin: PreviewDocument6 pagesEffective Use of Insulin: Previewprad1973No ratings yet
- Diabetes Treatment: Dr. Chavan P.R. Pharm DDocument73 pagesDiabetes Treatment: Dr. Chavan P.R. Pharm DAvel ChandNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Medications W2023Document39 pagesDiabetes Medications W2023Alyssa Camille EbisonNo ratings yet
- DR Shahjada Selim: Assistant Professor Department of Endocrinology, BSMMU Organizing Secretary, BESDocument63 pagesDR Shahjada Selim: Assistant Professor Department of Endocrinology, BSMMU Organizing Secretary, BESABDUL BARINo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesPharmacology - Endocrine System22bgu0805msNo ratings yet
- New Technologies and Therapies in The Management of DiabetesDocument8 pagesNew Technologies and Therapies in The Management of DiabetesArhaMozaNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose-Insulin Administration-Study GuideDocument8 pagesBlood Glucose-Insulin Administration-Study GuideChandra MuraliNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 - Inpatient Management of Diabetes and HyperglycemiaDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 7 - Inpatient Management of Diabetes and HyperglycemiaenesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyRhanne Bolante100% (1)
- NCLEX Endocrine Questions: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Priority for Diabetic PatientsDocument21 pagesNCLEX Endocrine Questions: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Priority for Diabetic Patientsjpornmany100% (6)
- DIABETES - WHEN TO START INSULINDocument4 pagesDIABETES - WHEN TO START INSULINJovankaNo ratings yet
- ICF FinalDocument36 pagesICF FinalCyntia MontalvoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Medication 2017Document10 pagesDiabetes Medication 2017Nicolas Mauricio Rodriguez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Dietetik TerjemahDocument8 pagesDietetik TerjemahAsrori MuhofiNo ratings yet
- Cdho Assignment 2 Type 1 DiabetesDocument10 pagesCdho Assignment 2 Type 1 Diabetesapi-596913754No ratings yet
- Sansulin N Suspensi injeksi 100 IU,mL_Rekombinan Insulin Manusia_DKI0708100343A1_2016Document2 pagesSansulin N Suspensi injeksi 100 IU,mL_Rekombinan Insulin Manusia_DKI0708100343A1_2016Budi MakmurNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - DiabetesDocument9 pagesGroup 2 - DiabetesJasper VictoryNo ratings yet
- Insulin: Mert Aygüler 13O2O2O32Document16 pagesInsulin: Mert Aygüler 13O2O2O32deryaaaNo ratings yet
- Readings (Insulin) - RetuyaDocument20 pagesReadings (Insulin) - RetuyaFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: TreatmentDocument25 pagesType 1 Diabetes Mellitus: TreatmentironNo ratings yet
- CH 32Document8 pagesCH 32Elizabeth PetersenNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Management of Infants and Children With DiabetesDocument10 pagesPerioperative Management of Infants and Children With DiabetesRamesh lal ShahNo ratings yet
- Pediatric & Diabetes Case StudyDocument3 pagesPediatric & Diabetes Case Studydsaitta108100% (2)
- Diabetes for Primary Care: A Step By Step ApproachFrom EverandDiabetes for Primary Care: A Step By Step ApproachNo ratings yet
- Specialized Fields of Community Health NursingDocument1 pageSpecialized Fields of Community Health NursingTrishaNo ratings yet
- Cally PDFDocument34 pagesCally PDFTrishaNo ratings yet
- University of Cebu - BaniladDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cebu - BaniladTrishaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14Document10 pagesLesson 14TrishaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Control ProgramsDocument2 pagesQuiz Control ProgramsTrishaNo ratings yet
- CHN by PairDocument5 pagesCHN by PairTrishaNo ratings yet
- CV for RN Position at UC-MED HospitalDocument2 pagesCV for RN Position at UC-MED HospitalTrishaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health Nursing - Helping People Get Back to Work QuicklyDocument1 pageOccupational Health Nursing - Helping People Get Back to Work QuicklyTrishaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument76 pagesUntitledTrishaNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec FinalsDocument51 pagesMCN Lec FinalsTrishaNo ratings yet
- Pasay - Rle Lab InstrumentsDocument10 pagesPasay - Rle Lab InstrumentsTrishaNo ratings yet
- Specialized Fields of Community Health NursingDocument1 pageSpecialized Fields of Community Health NursingTrishaNo ratings yet
- University of Cebu Nursing Organizational ChartsDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cebu Nursing Organizational ChartsTrishaNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Activity On Anxiety EDITABLEDocument7 pagesAsynchronous Activity On Anxiety EDITABLETrishaNo ratings yet
- Feeding techniques for babies with cleft lip or palateDocument14 pagesFeeding techniques for babies with cleft lip or palateTrishaNo ratings yet
- 114 SF QuizDocument7 pages114 SF QuizTrishaNo ratings yet
- MCN LecDocument461 pagesMCN LecTrishaNo ratings yet
- JEJE ExtractedDocument1 pageJEJE ExtractedTrishaNo ratings yet
- HANDLING DELIVERIESDocument396 pagesHANDLING DELIVERIESTrishaNo ratings yet
- Maternal MidtermDocument253 pagesMaternal MidtermTrishaNo ratings yet
- Rle MidtermDocument77 pagesRle MidtermTrishaNo ratings yet
- Delivery Definitions and StagesDocument29 pagesDelivery Definitions and StagesTrisha100% (1)
- Essential Bed Making TechniquesDocument672 pagesEssential Bed Making TechniquesTrisha100% (1)
- Membership FeeDocument1 pageMembership FeeTrishaNo ratings yet
- Rle MergeDocument7 pagesRle MergeTrishaNo ratings yet
- 96 333 1 PBDocument2 pages96 333 1 PBTrishaNo ratings yet
- Pasay and PudeDocument1 pagePasay and PudeTrishaNo ratings yet
- Email Signature in Gmail Moodle ReadyDocument9 pagesEmail Signature in Gmail Moodle ReadyTrishaNo ratings yet
- MT Quiz 1 2Document6 pagesMT Quiz 1 2TrishaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2TrishaNo ratings yet
- T10 FinDocument12 pagesT10 FinalejandraNo ratings yet
- X-ray, luminescent and transilluminating diagnostics in periodontal diseaseDocument2 pagesX-ray, luminescent and transilluminating diagnostics in periodontal diseaseHERO RescueNo ratings yet
- MSDS Pro-Kleen 302Document8 pagesMSDS Pro-Kleen 302Wirdaniati EmiliaNo ratings yet
- The Periodontal Pocket: Intended Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesThe Periodontal Pocket: Intended Learning OutcomesREHAB ABBASNo ratings yet
- Cram Reviewer MusculoskeletalDocument32 pagesCram Reviewer MusculoskeletalGwynthselle SalazarNo ratings yet
- N 509 MaterialsDocument128 pagesN 509 MaterialsgdomagasNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3. Handling and Mass Production of Biological Control AgentsDocument5 pagesExercise 3. Handling and Mass Production of Biological Control AgentsRoxan AngonNo ratings yet
- Running Head: QSEN 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: QSEN 1Mariam AbedNo ratings yet
- الميكروبيولوجى والتحكم فى العدوىDocument115 pagesالميكروبيولوجى والتحكم فى العدوىmahmoud salahNo ratings yet
- Hypoparathyroidism PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypoparathyroidism PathophysiologymaricarNo ratings yet
- Manual For Dental TechniciansDocument186 pagesManual For Dental Techniciansstabik96% (23)
- NCP Activity NavidasDocument2 pagesNCP Activity NavidasFran LanNo ratings yet
- Kounis Syndrome A Pediatric PerspectiveDocument10 pagesKounis Syndrome A Pediatric PerspectiveAna Belén Artero CastañoNo ratings yet
- What Is Nano Silver - Nano Silver PDFDocument2 pagesWhat Is Nano Silver - Nano Silver PDFvijuNo ratings yet
- Cataract Qustion and AnswersDocument90 pagesCataract Qustion and AnswersVaishnavi MNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - 1. Research Overview TranscriptDocument13 pagesModule 2 - 1. Research Overview TranscriptpatrickfvlboltNo ratings yet
- Session 10. Review of Centric Records RECORDSDocument25 pagesSession 10. Review of Centric Records RECORDSbaraa.abdulrahman.23No ratings yet
- Neet Ug Absolute Biology Vol 2Document22 pagesNeet Ug Absolute Biology Vol 2Rakesh Agarwal0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Normal Microbial Flora and Pathogenic Bacteria HardDocument14 pagesChapter 5 Normal Microbial Flora and Pathogenic Bacteria HardRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Eat Yourself Smart: Britain Faces Airlift DeadlineDocument64 pagesEat Yourself Smart: Britain Faces Airlift DeadlineNidhi BhartiNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Relationships Professional Communication Skills For Nurses 6Th Edition Arnold Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesInterpersonal Relationships Professional Communication Skills For Nurses 6Th Edition Arnold Test Bank Full Chapter PDFhungden8pne100% (11)
- Podcast Script "Hustle Culture" OPENING: Haiii I'am Hidayah Malika and Welcome To Speak Up' PodcastDocument3 pagesPodcast Script "Hustle Culture" OPENING: Haiii I'am Hidayah Malika and Welcome To Speak Up' PodcastMas'adatul HidayahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Marker Sem 5Document42 pagesCardiac Marker Sem 5novi pujiNo ratings yet
- 13 AntibioticsAntiRetroviralsAIDS PDFDocument90 pages13 AntibioticsAntiRetroviralsAIDS PDFjenniferluzonNo ratings yet
- NP1 - ToprankDocument16 pagesNP1 - ToprankAllaiza Cristille100% (1)
- Sia DH FinalDocument26 pagesSia DH FinalJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Traditional Zootherapeutic Uses in The Treatment of Asthma by The Ethnic Groups of Assam, IndiaDocument5 pagesTraditional Zootherapeutic Uses in The Treatment of Asthma by The Ethnic Groups of Assam, IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- CariesCare-International Consensus-Manuscript BDJ-corrected 12062019Document13 pagesCariesCare-International Consensus-Manuscript BDJ-corrected 12062019pocket4love4yeahNo ratings yet
- Provisional Admit Card Cum Call LetterDocument3 pagesProvisional Admit Card Cum Call Lettersravikumar sNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for diagnosing and treating hypothyroidismDocument43 pagesGuidelines for diagnosing and treating hypothyroidismJoseAbdalaNo ratings yet