Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 1 - Review
Unit 1 - Review
Uploaded by
m soo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document provides a review of key topics in physiology including:
1) Word roots commonly found in physiology and their meanings.
2) The major organ systems of the body and their functions as well as homeostasis and control systems.
3) The primary tissue types and structures like junctions and epithelia.
4) Compartmentalization of the body into cavities and fluid spaces.
5) Methods of communication in the body including chemical signaling, receptors, and signal transduction pathways.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a review of key topics in physiology including:
1) Word roots commonly found in physiology and their meanings.
2) The major organ systems of the body and their functions as well as homeostasis and control systems.
3) The primary tissue types and structures like junctions and epithelia.
4) Compartmentalization of the body into cavities and fluid spaces.
5) Methods of communication in the body including chemical signaling, receptors, and signal transduction pathways.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageUnit 1 - Review
Unit 1 - Review
Uploaded by
m sooThis document provides a review of key topics in physiology including:
1) Word roots commonly found in physiology and their meanings.
2) The major organ systems of the body and their functions as well as homeostasis and control systems.
3) The primary tissue types and structures like junctions and epithelia.
4) Compartmentalization of the body into cavities and fluid spaces.
5) Methods of communication in the body including chemical signaling, receptors, and signal transduction pathways.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
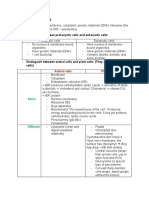
Biol 273 – Unit 1 Review
Word Roots for Physiology:
anti- against extra- outside lumen inside of a hollow structure
-ase enzyme epi- over para- near, close
auto- self homo- same poly- many
bi- two hydro- water post- after
-crine a secretion hyper- above, excess pre- before
de- without, lacking hypo- beneath, not enough pro- before
endo- inside, within inter- between retro- backward or behind
exo- outside intra- within trans- through, across
Physiology:
What are the organ systems of the body? What is the function of each organ system?
What are the main themes in physiology?
What is homeostasis? What are control systems for homeostasis? What are Cannon’s postulates?
Tissues:
What are the primary tissue types?
Describe the structure and function of the following types of junctions, and where you are likely to find them:
gap junctions, tight junctions, anchoring junctions
What are some types of epithelia and their functions?
What is the basal lamina (basement membrane), and what is its function?
What is mean by ‘excitable’ when referring to tissues?
Body Compartmentalization:
What are the three major body cavities? What separates them? What major organs are found in each?
What is a lumen? What do we mean when we say that for some organs, the lumen is essentially an extension of the
external environment?
What are the two main fluid compartments of the body? Can they be further subdivided into three compartments?
Communication:
Differentiate between local and long-distance communication strategies in the body.
Distinguish between chemical and electrical communication methods.
What are target cells / tissues?
List the basic methods of cell-cell communication.
Distinguish between paracrine and autocrine signals.
What are hormones? Why don’t all cells react to hormones circulating in the body?
Why do some cells respond to a chemical signal and others ignore it?
How do chemical signals interact with receptors? What factors determine the location of a receptor protein within a cell
for a given ligand?
List differences in the mechanisms for hydrophilic versus hydrophobic signal molecules.
What are the major categories of membrane receptors?
What is meant by signal transduction across a cell membrane? When is this necessary? What is a second messenger?
Why do we call signal transduction pathways ‘cascades’?
What is signal amplification in a signal transduction pathway?
What are GPCRs (G-protein coupled receptors)? How do they work? What types of ligands bind to them?
Describe examples of pathways involving GPCRs working via a) cAMP and b) lipid-derived second messengers.
Distinguish between agonists and antagonists.
You might also like
- AnaPhy Reviewer PrelimsDocument7 pagesAnaPhy Reviewer Prelimsysa hernandezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer AnaphysDocument42 pagesReviewer AnaphysReed YangNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System and Chemical Communication: (Link To Chapter 16, Essential Cell Biology)Document9 pagesEndocrine System and Chemical Communication: (Link To Chapter 16, Essential Cell Biology)NikhilBalajiNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Exam Review QuestionsDocument17 pagesAP Biology Exam Review Questionsdstaples7100% (10)
- AutophagyDocument7 pagesAutophagymikikiNo ratings yet
- Module 1A - Ch.1 (Cells, Tissues and Homeostasis) 2023Document24 pagesModule 1A - Ch.1 (Cells, Tissues and Homeostasis) 2023futurebiologist00pNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For FinalDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For Finalkwrrm99r8fNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: HomeostasisDocument8 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: HomeostasisSheená EspañolNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology General: What Is LifeDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology General: What Is LiferenjiniNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lecture 1 To 8Document8 pagesANAPHY Lecture 1 To 8mi yaNo ratings yet
- RIZALDocument7 pagesRIZALKaren Joy BaloloNo ratings yet
- A p2 Lesson 1Document10 pagesA p2 Lesson 1api-257062466No ratings yet
- Organ SystemDocument9 pagesOrgan SystemMaycee ʚĭɞNo ratings yet
- Physiology: Instructor: Department of Physiology and Patophysiology Room NoDocument45 pagesPhysiology: Instructor: Department of Physiology and Patophysiology Room Nogvu71No ratings yet
- Prelecture Questions 2Document7 pagesPrelecture Questions 2kaslana kianaNo ratings yet
- Gen Physiology 2015Document423 pagesGen Physiology 2015cathlynjoy.marsamoloNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- CHAPTER1SGDocument5 pagesCHAPTER1SGNicole BrassingtonNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument66 pagesIntroductionDagmawe ZewengelNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument44 pagesNervous SystemSarathebestshowNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Human OrganismDocument4 pages1 - The Human Organismdanielle stephanieNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument14 pagesCharacteristics of Living OrganismsMai Hoa GranatiNo ratings yet
- Structure Level Assignment KeanneDocument2 pagesStructure Level Assignment KeanneJerome GaribayNo ratings yet
- 1 The Human Organism 2020 08 14 at 8.06.43 PMDocument63 pages1 The Human Organism 2020 08 14 at 8.06.43 PMeam somarNo ratings yet
- BioSci Lab Quiz 1 To 4Document11 pagesBioSci Lab Quiz 1 To 4Elvira MirajulNo ratings yet
- What Is Physiology?: Chapter ContentsDocument4 pagesWhat Is Physiology?: Chapter ContentsWahaj KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio ReviewerCaptain YooNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - The Human BodyDocument8 pagesLesson 1 - The Human BodyGilmar ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Endocrin e SystemDocument18 pagesEndocrin e SystemEthan Dreiz BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document42 pagesDocument 5mmbakk :0No ratings yet
- (ANAPHY) Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pages(ANAPHY) Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyPearl FllominNo ratings yet
- NM - Chapter 3 - Extra ClassDocument55 pagesNM - Chapter 3 - Extra Classyashvi.maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Support TheoriesDocument4 pagesSupport TheoriesAbegail Ines BernalNo ratings yet
- RT 105 Prelim NotesDocument20 pagesRT 105 Prelim NotesLouiseNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyDocument8 pagesThe Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Prelim ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnaphy Prelim ReviewerJamaica TuellaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument13 pagesHomeostasisSanchezNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Theory - WorksheetDocument9 pagesWEEK 1 - Theory - WorksheetRajal PratapNo ratings yet
- Happ Chapter 1Document9 pagesHapp Chapter 1Raniel SilimNo ratings yet
- L1. Exploring Life-2024Document39 pagesL1. Exploring Life-2024Cedric HastingsNo ratings yet
- Ana & Physio (EE Reviewer)Document8 pagesAna & Physio (EE Reviewer)Katrina Tuazon MisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 OutlineDocument5 pagesChapter 5 OutlineShirley PinedaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Outline of Lecture: Module 1Document22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Outline of Lecture: Module 1Jes CmtNo ratings yet
- Cells Study Guide 2020 KEYDocument4 pagesCells Study Guide 2020 KEYLaarni GeeNo ratings yet
- BIOS-251 Anatomy and Physiology With Lab Self-Test (40) - RRDocument5 pagesBIOS-251 Anatomy and Physiology With Lab Self-Test (40) - RRkariukisimonmeritNo ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: 02.03 Early Cells: Key Questions and Terms NotesDocument4 pagesBiology Notebook: 02.03 Early Cells: Key Questions and Terms NotesAloni CampbellNo ratings yet
- Biology: /duringDocument15 pagesBiology: /duringBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 - Mod6B - Lesson2 - Gas Exchange With The Environment and Circulation The Internal Transport SystemDocument20 pagesELS Q2 - Mod6B - Lesson2 - Gas Exchange With The Environment and Circulation The Internal Transport SystemRenz Christian BrobioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument17 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyPamela Spam100% (1)
- Human Anatomy Major Organs of The BodyDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy Major Organs of The BodyKert trocioNo ratings yet
- 1.homeostasis and Homeodynamism (Life and Hemostasis)Document23 pages1.homeostasis and Homeodynamism (Life and Hemostasis)HarshilPatelNo ratings yet
- Intro To PhysiologyDocument86 pagesIntro To PhysiologyMelissa LouiseNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYSIO TransesDocument75 pagesANAPHYSIO Transesjasonenmanuel10No ratings yet
- L1 - Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument52 pagesL1 - Characteristics of Living OrganismsAditya MishraNo ratings yet
- MPDFDocument1 pageMPDFManav PARMARNo ratings yet
- NFPA 24-2013 Standpipe Test AttachmentDocument2 pagesNFPA 24-2013 Standpipe Test AttachmentPatrick John PaguioNo ratings yet
- TC NotesDocument46 pagesTC Notesbelej40682No ratings yet
- Paz M., International Handbook of Earthquake Engineering Codes, Programs, and Examples, 1994 PDFDocument557 pagesPaz M., International Handbook of Earthquake Engineering Codes, Programs, and Examples, 1994 PDFErikEspino100% (2)
- LTE Speech Traffic Dimenshioning For VoipDocument6 pagesLTE Speech Traffic Dimenshioning For VoipRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- AST Ascentia M5160X 166MMX NotebookDocument4 pagesAST Ascentia M5160X 166MMX NotebookBranislav TanevskiNo ratings yet
- Sharp Lc-60 Le 630 U-A - lc-60 Le 6300 U-A-b - lc-70 Le 735 U - PWB - Unit - EditionDocument38 pagesSharp Lc-60 Le 630 U-A - lc-60 Le 6300 U-A-b - lc-70 Le 735 U - PWB - Unit - EditionRabshaqa100% (1)
- SW423 Basic Psychology For Social WorkDocument3 pagesSW423 Basic Psychology For Social WorkSudeep TamangNo ratings yet
- Petrol Filling StationsDocument20 pagesPetrol Filling StationsAdel A. Abdelaziz100% (1)
- Solon Belleville Springs CatalogDocument72 pagesSolon Belleville Springs CatalogKamasani PraveenaNo ratings yet
- Ais FlowchartDocument7 pagesAis FlowchartTangkua NasaNo ratings yet
- V - TM Storyteller Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesV - TM Storyteller Cheat SheetJulioNo ratings yet
- Duct DesignDocument42 pagesDuct DesignSanu ThomasNo ratings yet
- Final Disertation Copy PrintDocument74 pagesFinal Disertation Copy PrintBhalvindrakumar MaranNo ratings yet
- SP0407 Commissioning Tests For HV UG CablesDocument13 pagesSP0407 Commissioning Tests For HV UG Cablesyavuz772100% (4)
- MPQ RankedDocument11 pagesMPQ Rankedblack jackNo ratings yet
- Smbj5.0a Smbj170a DiodesDocument6 pagesSmbj5.0a Smbj170a DiodesAhmed Sherif CupoNo ratings yet
- Fortnightly Subjective Test-4: Integrated Classroom Course For Olympiads and Class-IX (2021-2022)Document5 pagesFortnightly Subjective Test-4: Integrated Classroom Course For Olympiads and Class-IX (2021-2022)Atharva AhireNo ratings yet
- Chap 01 Marlin 2023Document34 pagesChap 01 Marlin 2023Phillip WeyersNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 The School CultureDocument8 pagesUnit 5 The School CultureJC CambriNo ratings yet
- JKBT Radhae Ebook Guide V 1 .7Document28 pagesJKBT Radhae Ebook Guide V 1 .7AshokNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras: 1. (3 MarksDocument11 pagesPythagoras: 1. (3 MarksSemaNo ratings yet
- Plant Inspection-API InspectionDocument5 pagesPlant Inspection-API InspectionTina Miller100% (1)
- Epson L805 BrochureDocument4 pagesEpson L805 Brochureavijit_deNo ratings yet
- User Manual: AS2000+ Portable GPS TrackerDocument13 pagesUser Manual: AS2000+ Portable GPS TrackerMarcio CamargosNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Unit 1 Communication Skills NotesDocument5 pagesClass 9 Unit 1 Communication Skills Notessuryanshkharwar59No ratings yet
- CEN For Natural StoneDocument25 pagesCEN For Natural StonePaulNo ratings yet
- Endangered Species ProjectDocument4 pagesEndangered Species ProjectAMULYA MISHRANo ratings yet
- SERIES 599-Y2000: Features Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesSERIES 599-Y2000: Features Product DescriptionluismcmcNo ratings yet
- TestBank Evans Ba2 Tif Ch01Document18 pagesTestBank Evans Ba2 Tif Ch01Khaleel AbdoNo ratings yet