0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views28 pagesDiesel Engine Lubrication Insights
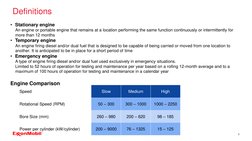
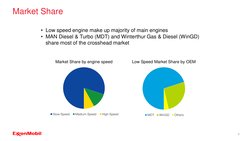
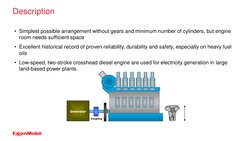
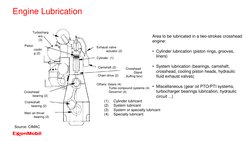
The document discusses lubrication for different types of diesel engines. It provides an overview of the low-speed, medium-speed, and high-speed diesel engine markets. For low-speed engines, it describes the typical characteristics like rotational speed, bore size, and power output. It also discusses lubrication needs for different engine components and recommends Mobil lubricant products. For medium-speed engines, it compares characteristics to low-speed engines and discusses lubrication systems and selecting the proper lubricant based on engine builder requirements.
Uploaded by
Brian ASCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views28 pagesDiesel Engine Lubrication Insights
The document discusses lubrication for different types of diesel engines. It provides an overview of the low-speed, medium-speed, and high-speed diesel engine markets. For low-speed engines, it describes the typical characteristics like rotational speed, bore size, and power output. It also discusses lubrication needs for different engine components and recommends Mobil lubricant products. For medium-speed engines, it compares characteristics to low-speed engines and discusses lubrication systems and selecting the proper lubricant based on engine builder requirements.
Uploaded by
Brian ASCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Industry Overview
- Low Speed Diesel Engine
- Medium Speed Diesel Engine
- High Speed Diesel Engine