Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiovascular Drugs Classification
Uploaded by
MONIKA SINGHOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiovascular Drugs Classification
Uploaded by
MONIKA SINGHCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmaceutical Chemistry-II
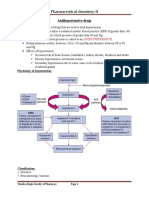
Cardiovascular drug
Cardiovascular drugs are those drugs that are used to treat various pathological conditions of the
cardiovascular system. These drugs comprise a huge arsenal of drugs that fight a broad list
of diseases in medical science i.e CVS diseases. Chemically these drugs are more or less like
some synthetic and some semi-synthetic versions of their natural crude sources.
Any agent that affects the function of the heart and blood vessels. Drugs that act on the
cardiovascular system are among the most widely used in medicine. Examples of disorders in
which such drugs may be useful include
hypertension (high blood pressure),
angina pectoris (chest pain resulting from inadequate blood flow through the coronary
arteries to the heart muscle),
heart failure (inadequate output of the heart muscle in relation to the needs of the rest of
the body),
arrhythmias (disturbances of cardiac rhythm)
Classification of Cardiovascular Drug
Basis of classification
In pharmacological classification, there is certain basis which we take into consideration while
classifying Them.they are;
The site of action.
Mechanism of action.
Chemical nature of the drug.
Nature of disease.
Here for general classification of cardiovascular drugs, we take nature of the disease as the basis
of classification. In other words, drugs are classified on the basis of cardiovascular Ailments that
they treat.
Cardiovascular Drugs Classification:
Cardiovascular agents are classified into the following five Drug classes.
1. Antihypertensive drugs
Monika Singh, faculty of Pharmacy Page 1
Pharmaceutical Chemistry-II
2. Anti-anginal drugs
3. Anti-congestive cardiac failure (CCF) drugs
4. Anti-arrhythmic drugs
5. Anti-hyperlipidemic drugs
Anti-hypertensive drugs
These are drugs used to lower B.P in hypertension. Hypertension is a very common disorder,
particularly past middle age. It is not a disease in itself But is an important risk factor for
cardiovascular mortality and morbidity. Drugs included in this category are
Beta-blocker
Alpha blockers
Direct vasodilators (hydralazine etc)
Diuretics
Ace-inhibitors
Calcium channel blockers
Angiotensin ii receptor blocker
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers
Anti-anginal drugs
These drugs are used for treating angina pectoris and myocardial infarction. These drugs include.
Coronary vasodilators (particularly Nitrites and Nitrates particularly organic nitrates)
Beta Blockers.
Calcium channel blockers.
Potassium channel opener.
Anti-platelet aggregation drugs.
Anti-Hyperlipidemias.
Antihyperlipidemic:
These drugs are used to decrease high lipids levels of fats and cholesterols. Chemically most of
These drugs are steroids in nature.
They are further classified as.
Cholesterolemic
Triglyceridemic
Monika Singh, faculty of Pharmacy Page 2
Pharmaceutical Chemistry-II
These drugs include "HMG-CoA reductase" inhibitors i.e pravastatin and fluvastatin.
Anti-CCF(congestive cardiac failure)
These drugs are used for treating congestive cardiac failure. They include.
Rennin angiotensin aldosterone system blockers
Beta-blockers
Diuretics
Direct acting vasodilators
Inotropic drugs
Aldosterone antagonist
Anti-arrhythmic drugs
They are used for treating arrhythmias like bradycardia and tachycardia. They are alpha blockers.
Anti-arrhythmic drugs are classified into following classes.
Class I antiarrhythmics:
Predominantly sodium channel blockers
Class II antiarrhythmics:
Class II antiarrhythmics are beta blockers i.e Propranolol, Metoprolol, Esmolol
Class III antiarrhythmics:
They are potassium channel blockers and block the outflow of k ions during repolarization of
cardiac cells. Amiodarone and dronedarone are examples.
Class IV antiarrhythmics
Class 4 antiarrhythmic includes calcium(Ca2+ ) channel blockers other than dipine class(only
diltiazem and verapamil).
Other antiarrhythmics
Digoxin and adenosine are classified as other antiarrhythmics. most of these are cardiac
glycosides.
Monika Singh, faculty of Pharmacy Page 3
You might also like
- Pharmacology of The Cardiovascular SystemsDocument4 pagesPharmacology of The Cardiovascular SystemsMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument17 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsGunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument9 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsBaqir BroNo ratings yet
- Choosing Blood Pressure MedicationsDocument8 pagesChoosing Blood Pressure MedicationsbhaskarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesPharmacology of The Cardiovascular SystemMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Medication Options For Stage 1 High Blood PressureDocument2 pagesMedication Options For Stage 1 High Blood PressureRoking KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 024 Heart Failure DrugsDocument7 pagesChapter - 024 Heart Failure DrugsthubtendrolmaNo ratings yet
- High Blood PressureDocument5 pagesHigh Blood PressureLeroy LoyNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument41 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsRwapembe StephenNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs: Dare OgunladeDocument18 pagesCardiovascular Drugs: Dare OgunladeNatik Bi IllahNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used To Treat Cardiovascular Diseases: HypertensionDocument35 pagesDrugs Used To Treat Cardiovascular Diseases: HypertensionAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Regulating BP with Adrenergic Blockers & DiureticsDocument16 pagesRegulating BP with Adrenergic Blockers & DiureticsSiti MunirahNo ratings yet
- Vasodilators and Antihypertensive Agents: An OverviewDocument18 pagesVasodilators and Antihypertensive Agents: An OverviewAbdiweli AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Types of Hypertension Pathophysiology Aims and Objectives Drugs Mechanism of Action Literature Review Materials AND MethodsDocument14 pagesTypes of Hypertension Pathophysiology Aims and Objectives Drugs Mechanism of Action Literature Review Materials AND MethodsMaram RanadeepNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive & Antianginal DrugsDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive & Antianginal Drugsdomememe1No ratings yet
- 7,8 - Antihypertensive DrugsDocument10 pages7,8 - Antihypertensive DrugsHusniya MehamedNo ratings yet
- Some Medical Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesSome Medical Questions and AnswersShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Acquired TTP - Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument16 pagesAcquired TTP - Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis - UpToDatepradeep danielNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument2 pagesDigoxinIsabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 35Document41 pagesChapter 35HannaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Effects of Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Review and UpdateDocument8 pagesPharmacological Effects of Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Review and UpdateSonalie IlapperumaNo ratings yet
- Farmacos AntihipertensivosDocument5 pagesFarmacos AntihipertensivosBrisniaSánchezNo ratings yet
- ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGDocument7 pagesANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGaarti sahuNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Pharmacology of Cardiovascular Drugs 0ct10Document12 pages1-Introduction To Pharmacology of Cardiovascular Drugs 0ct10Idrissou FmsbNo ratings yet
- 11 Anti Hypertensive 17-08-2023Document21 pages11 Anti Hypertensive 17-08-2023ashwin kNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure and Antidysrhythmic DrugsDocument38 pagesHeart Failure and Antidysrhythmic DrugsYza Belle RamoNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs GuideDocument52 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs GuideAlan LealNo ratings yet
- CVS PharmacologyDocument60 pagesCVS PharmacologyGølà Sèèñàà–baale irraaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive 2Document1 pageAntihypertensive 2Mylene MendozaNo ratings yet
- DOC-20240208-WA0014. (1)Document10 pagesDOC-20240208-WA0014. (1)Chippa ganeshNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs and Vasodilators: John W. SearDocument21 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs and Vasodilators: John W. SearIuliaUngurNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure MedicationDocument4 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Medicationiamfelix07No ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Agents GuideDocument3 pagesAntihypertensive Agents GuideCharles BayogNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PharmDocument6 pagesCardiac PharmJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure Medication Classes and Side EffectsDocument12 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Medication Classes and Side EffectsSARFRAZ ALINo ratings yet
- Merged 1 PDFDocument305 pagesMerged 1 PDFAhmed KurdiNo ratings yet
- Topic - Hyperte WPS OfficeDocument15 pagesTopic - Hyperte WPS OfficeVedant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants: Commonly Prescribed IncludeDocument8 pagesAnticoagulants: Commonly Prescribed IncludeRusmir GadzoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs (Veterinary Pharmacology)Document44 pagesCardiovascular Drugs (Veterinary Pharmacology)DR Muhammad Abdul BasitNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: Loretta Walker, PH.DDocument11 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: Loretta Walker, PH.DAdrian Jake LiuNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology PerfusionDocument1 pagePharmacology PerfusionkatrinasdNo ratings yet
- Understanding Common Heart Failure MedicationsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Common Heart Failure MedicationsEirene GaghaunaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology drug study guide for weeks 7 & 8Document2 pagesPharmacology drug study guide for weeks 7 & 8Todd Cole100% (1)
- Pharmacology Test 3 - Cardiovascular Drugs, Part I Flashcards - QuizletDocument10 pagesPharmacology Test 3 - Cardiovascular Drugs, Part I Flashcards - QuizletBhopesh Kadian0% (1)
- Anti Hypertensive Drugs .Document6 pagesAnti Hypertensive Drugs .Baqir BroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Cardiovascular DrugsDocument35 pagesChapter 17 Cardiovascular Drugsaisyahasrii_No ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: 2. Drug Regimens and TreatmentsDocument3 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias: 2. Drug Regimens and TreatmentskNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs - WsDocument45 pagesCardiovascular Drugs - WsCowox Post PartumNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: Dr/Azza Baraka Prof of Clinical Pharmacology Faculty of Medicine Alexandria UniversityDocument71 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: Dr/Azza Baraka Prof of Clinical Pharmacology Faculty of Medicine Alexandria UniversityMoonAIRNo ratings yet
- Pcol RevalidaDocument3 pagesPcol RevalidaNash IsmaelNo ratings yet
- 01 Hypertension - 2019 2020 PDFDocument122 pages01 Hypertension - 2019 2020 PDFbaraa abu sneineh100% (1)
- What Are The Toxicities of Amiodarone?: CardiologyDocument33 pagesWhat Are The Toxicities of Amiodarone?: Cardiologylakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System (Antihypertensive - Part-1)Document6 pagesDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System (Antihypertensive - Part-1)alialahmedy24No ratings yet
- Hyper MalindaDocument8 pagesHyper MalindaDewi RosalindaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Drug Classes GuideDocument31 pagesHypertension Drug Classes GuideTaikoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drug Classification ExplainedDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Drug Classification ExplainedJESSA MAE ASPENo ratings yet
- Assignments Pharmacodynamics 2 - Iffah Arizan (2219092) PDFDocument2 pagesAssignments Pharmacodynamics 2 - Iffah Arizan (2219092) PDFNur Iffah Hanna ArizanNo ratings yet
- This Is ItDocument6 pagesThis Is Itjagipeb439No ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]From EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Pharmaceutical chemistry-II: Antineoplastic AgentsDocument2 pagesPharmaceutical chemistry-II: Antineoplastic AgentsMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs ClassificationDocument5 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs ClassificationMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical chemistry-II: Antihypertensive DrugsDocument5 pagesPharmaceutical chemistry-II: Antihypertensive DrugsMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical chemistry-II: Cardiac GlycosideDocument3 pagesPharmaceutical chemistry-II: Cardiac GlycosideMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- BP202T Test - 1 Unit-IIDocument1 pageBP202T Test - 1 Unit-IIMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Deepak Verma Imran Ali Neha Verma Shivangi Tripathi: Name of Students Marks Obtained Out of 15Document1 pageDeepak Verma Imran Ali Neha Verma Shivangi Tripathi: Name of Students Marks Obtained Out of 15MONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- BP202T Test - 1 Unit-IIDocument1 pageBP202T Test - 1 Unit-IIMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Question bp202tDocument5 pagesPrevious Year Question bp202tMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Monika SinghDocument2 pagesMonika SinghMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Monika SinghDocument2 pagesMonika SinghMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- ABC First Aid GuideDocument0 pagesABC First Aid GuideNiti Ranjan DasNo ratings yet
- IdentifyDocument40 pagesIdentifyLeonard Kenshin LianzaNo ratings yet
- DR - Datten Bangun MSC - SPFK & DR - Tri Widyawati Msi, PHD Dept - Farmakologi & Therapeutik Fak - Kedokteran Usu MedanDocument50 pagesDR - Datten Bangun MSC - SPFK & DR - Tri Widyawati Msi, PHD Dept - Farmakologi & Therapeutik Fak - Kedokteran Usu MedanHabib Al KahfiNo ratings yet
- Amity College of Nursing: Nursing Care Plan ON Heart FailureDocument20 pagesAmity College of Nursing: Nursing Care Plan ON Heart Failurejyoti puniaNo ratings yet
- BIOL122 Exam Format and Case StudyDocument1 pageBIOL122 Exam Format and Case StudyHuge Lovely SmileNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Errors in TelehealthDocument8 pagesDiagnostic Errors in TelehealthKarina AuliaNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Notes For USMLE Step 2CKDocument16 pagesLast Minute Notes For USMLE Step 2CKJonathan B. Michaels100% (1)
- UNIT II MedicalDocument34 pagesUNIT II Medicalangelax1.1No ratings yet
- Lightspeed VCT PDFDocument24 pagesLightspeed VCT PDFlaura islas100% (1)
- Care Plan Unstable AnginaDocument4 pagesCare Plan Unstable Anginaالغزال الذهبي50% (6)
- Step 2 Medicine (UA) 2023 - Attempt Review6Document60 pagesStep 2 Medicine (UA) 2023 - Attempt Review6berdaderagaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction - Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and PathologyDocument54 pagesMyocardial Infarction - Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and PathologyMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument9 pagesDefinitionKhondokar ArafatNo ratings yet
- CH02 Data Mining A Closer LookDocument34 pagesCH02 Data Mining A Closer LookÜmit BüyükduruNo ratings yet
- Principles of Emergency NursingDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Emergency NursingShamera MahabassalNo ratings yet
- ACLS Drug TherapyDocument8 pagesACLS Drug TherapySahrensNo ratings yet
- Clinical: MCQ TestDocument47 pagesClinical: MCQ TestAhmed AlrkabeNo ratings yet
- Prevention Health..Document16 pagesPrevention Health..maliha ahmadNo ratings yet
- ICD 10 Penyakit KardiovaskularDocument20 pagesICD 10 Penyakit KardiovaskularMaya ShofiaNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument7 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromesAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- Rubidium Myocardial Perfusion ScanDocument2 pagesRubidium Myocardial Perfusion ScanRadlinkSingaporeNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment FormDocument1 pageRisk Assessment Formncd.bulacanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27Document17 pagesChapter 27Jessica nonyeNo ratings yet
- GordonsDocument46 pagesGordonsjaniel rose abeladoNo ratings yet
- Kardiomed-700-User ManualDocument87 pagesKardiomed-700-User ManualJulia TimakovaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Circulation: by Sridip HaldarDocument19 pagesCoronary Circulation: by Sridip HaldarPercy JacksonNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument7 pagesThesis On Coronary Heart Diseasetracyclarkwarren100% (1)
- Patient Decision Aid PDF 243780159 PDFDocument23 pagesPatient Decision Aid PDF 243780159 PDFJimboNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Cardiovascular Diseases Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)Document5 pagesPathophysiology: Cardiovascular Diseases Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)Grace Bernadine H. Ramos100% (1)
- SAMPLE NLE Style Questions 3 TESTDocument6 pagesSAMPLE NLE Style Questions 3 TESTIris AbogadoNo ratings yet
























































![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)