Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) : John Marshall
Uploaded by
Tushar JadhavOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) : John Marshall
Uploaded by
Tushar JadhavCopyright:
Available Formats
Indus Valley Civilization (IVC)
John Marshall, the first scholar to use the term “Indus valley civilization”. The civilization
flourished between 2500 BC-1750 BC.
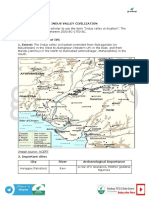
Geographical Extent of IVC
1. Extent: The Indus valley civilization extended from Sutkagandor (in Baluchistan) in
the West to Alamgirpur (Western UP) in the East; and from Mandu (Jammu) in the
North to Daimabad (Ahmednagar, Maharashtra) in the South.
Important cities
City River Archaeological Importance
A row of 6 Granaries, Mother
Harappa (Pakistan) Ravi
goddess figurines
Great Granary, Great bath,
Image of Pashupati
Mohenjodaro (Pakistan) Indus Mahadeva, Image of Bearded
man and Bronze image of a
woman dancer
Port city, Double burial,
Lothal (Gujarat) Bhogava
Terracotta horse figurines.
Chanhudaro (Pakistan) Indus The city without a citadel
Dholavira (Gujarat) Indus City divided into 3 parts.
Kalibangan (Rajasthan) Ghaggar Ploughed field
Banawali (Haryana) Ghaggar -
Sutkagandor (Pakistan) - -
Sukotada (Gujarat) - -
Town planning and Structure of IVC
• Grid system(Chess-board) of town planning
• Rectangular houses with brick-lined bathrooms and wells together with stairways
are found
• Use of Burnt bricks
• Underground drainage system
• Fortified citadel
Agriculture of Indus Valley Civilisation
• Hindon – Cotton – Major trade good – earliest people to produce Cotton.
• Proofs of Rice husk found
• Wheat and Barley were majorly cultivated
• Use of wooden plough. They had no idea about Iron implements.
Domestication of animals
• Oxens, Buffalo, Goats, Sheep and, Pigs were domesticated
• Asses and camels were used as Beasts of Burden
• Elephants and Rhino were known
• Remains of horse found in Surkotada and evidence of horse in Mohenjodaro and
Lothal are also found. But the civilization was not horse-centred.
Technology and crafts
• Bronze (Copper + tin) tools widely used
• Stone implements were still in vogue
• Potter’s wheel was put to full use
• Bronzesmiths, Goldsmiths, Boat-Making, Brick-laying etc were other occupations
commonly found
Trade during Indus Valley Civilisation
• Presence of granaries, weights and measures, seals and uniform script signifies
the importance of trade
• The barter system was widely prevalent
• Lothal, Sutkagendor were port cities used for conducting trade
• Trade destinations – Afghanistan, Iran and Central Asia. Contacts with
Mesopotamia civilization are also seen
Political organization during IVC
• Cultural homogeneity achieved through a strong central authority
• No temples or religious structures found. Harappa was possibly ruled by
Merchants class.
• Weapons are rarely found.
Religious practices during IVC
• Terracotta figure of Mother Goddess.
• Phallu and Yoni worship.
• Pashupati Mahadev seal found with the elephant, tiger, rhino and a bull
surrounding him with two deer near his feet.
Tree and animal worship during IVC
• Pipal tree worship was found.
• One horned Unicorn recognized as Rhino and the humped bull was commonly
worshipped.
• Use of Amulets to ward off ghosts and evil spirits.
• The lion was not known in Harappan culture.
The Harappan script
• Harappan script Pictographic in nature but not deciphered so far.
• They are recorded on seals and contains only a few words
• Harappan Script is the oldest script in Indian Sub-continent
Weights and Measures
• Use of standardized weights and measures to keep accounts of private property,
to indulge in trade and commerce etc.
• Weights are found in multiples of 16.
Harappan Pottery of IVC
• Well-developed Pottery techniques with elaborate designs of trees and circles.
• Redware pottery painted with black designs.
Seals of Indus Valley Civilisation
• Seals were used for the purpose of trade or worship. Images of animals such as
Buffalo, bull, tiger etc were found inscribed in the seals
Statue of IVC
• Discovery of Bronze statue of a naked woman and bearded man steatite statue
Terracotta figurines in IVC
• Terracotta – Fire baked earthen clay
• Used as toys or objects of worship
• Massive stone works were not found in Harappa which shows the poorly
developed artistic works made of stone
Origin, maturity, and end of IVC
• Pre-Harappan Settlements – Lower Sindh, Baluchistan and Kalibangan.
• Mature Harappa – 1900BC – 2550BC.
• Causes for the decline of Civilization.
• Decreasing fertility due to increasing salinity on the account of the expansion of
nearby desert.
• Sudden subsidence of uplift of land causing floods.
• Earthquakes caused changes in the course of Indus.
• Harappan culture destroyed by invading Aryans.
Post-urban Phase (1900BC – 1200BC)
• Sub-Indus Culture
• Primarily chalcolithic
• Development of Ahar Culture, Malwa Culture and Jorwe Culture at various
phases in post-Harappan Civilization.
You might also like
- John Marshall, The First Scholar To Use The Term "Indus Valley Civilization". TheDocument5 pagesJohn Marshall, The First Scholar To Use The Term "Indus Valley Civilization". TheMonikaNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization 64Document7 pagesIndus Valley Civilization 64Team RaagNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) : Harappan CivilisationDocument5 pagesIndus Valley Civilization (IVC) : Harappan Civilisation11B sskgNo ratings yet
- 040 REXODAS History Ancient History English Printable BY REXODASDocument110 pages040 REXODAS History Ancient History English Printable BY REXODASMehdiNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument10 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationShivani MauryaNo ratings yet
- Ancient India Mains Notes COMPLETEDocument67 pagesAncient India Mains Notes COMPLETEsanvicky1991No ratings yet
- Ancient & MedievalDocument34 pagesAncient & Medievalvn balaji goparajuNo ratings yet
- Ancient HistoryDocument42 pagesAncient Historyreema malikNo ratings yet
- Ancient History 1 Pre Historic and Indus ValleyDocument25 pagesAncient History 1 Pre Historic and Indus ValleyKomal SangwanNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric India: From Palaeolithic to Harappan CivilisationDocument25 pagesPrehistoric India: From Palaeolithic to Harappan Civilisation21-23 M Sai kumar reddyNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilisation: 2500 BC - 1750 BC (750 YRS)Document18 pagesIndus Valley Civilisation: 2500 BC - 1750 BC (750 YRS)Chinmay JenaNo ratings yet
- Ancient HistoryDocument45 pagesAncient HistorySana MariyamNo ratings yet
- Harappan CivilizationDocument7 pagesHarappan Civilizationbilbobaggings0% (1)
- Indian HistoryDocument33 pagesIndian HistoryTiwaan02No ratings yet
- Ancient Indian History: Indus Valley CivilizationDocument45 pagesAncient Indian History: Indus Valley CivilizationMiniNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilisation 721693295269990Document47 pagesIndus Valley Civilisation 721693295269990paonemechNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization Ancient Indian History Notes For UPSC PDFDocument2 pagesIndus Valley Civilization Ancient Indian History Notes For UPSC PDFVasupilli VennelaNo ratings yet
- Ancient India - 1Document132 pagesAncient India - 1raja varmanNo ratings yet
- Art & Culture - Sunya Prelims Notes 2024Document145 pagesArt & Culture - Sunya Prelims Notes 2024Jacob JrNo ratings yet
- Attachment Lecture 6 Indus Valley Civilization Lyst8867Document19 pagesAttachment Lecture 6 Indus Valley Civilization Lyst8867Rishabh AroraNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument56 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationGopal KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument20 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationvickybal347No ratings yet
- Ancient India Part-1Document32 pagesAncient India Part-1arunNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument7 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationRamjan SkNo ratings yet
- Twitter Assignment AMCDocument144 pagesTwitter Assignment AMCTarun PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Ancient India History OverviewDocument64 pagesAncient India History OverviewKaran PatelNo ratings yet
- AI 1 - Indus Valley CivilizationDocument4 pagesAI 1 - Indus Valley CivilizationArun PrasathNo ratings yet
- General Studies - I: Section - I: History and Cultural Heritage (India and Karnataka)Document9 pagesGeneral Studies - I: Section - I: History and Cultural Heritage (India and Karnataka)Manju KiranNo ratings yet
- 1.indus Valley CivilizationDocument11 pages1.indus Valley CivilizationAbhijitNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilisationDocument3 pagesIndus Valley Civilisationnewcontrol testNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indus Valley Civilization: The First Major South Asian CultureDocument4 pagesAncient Indus Valley Civilization: The First Major South Asian Cultureகாட்டு வாசிNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Smart PDF by GV SirDocument64 pagesAncient History Smart PDF by GV SirMohit1 Mj1100% (1)
- Major Sites of Indus Valley Civilization Ancient History Notes For Upsc 8974a305Document6 pagesMajor Sites of Indus Valley Civilization Ancient History Notes For Upsc 8974a305ManojNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument10 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationsubhajit ghoshNo ratings yet
- His Notes PDFDocument37 pagesHis Notes PDFvivekNo ratings yet
- His Notes PDFDocument37 pagesHis Notes PDFMushtaq KasbaNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument4 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationShreyaa Lakshmi Prasanta BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument4 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationbaravikumarNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization & Vedic Age - English - 1562065959 - English - 1579160381Document7 pagesIndus Valley Civilization & Vedic Age - English - 1562065959 - English - 1579160381kevinNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument4 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationanupanup2019No ratings yet
- Indian History - Revision PDFDocument54 pagesIndian History - Revision PDFAnimesh Hazarika100% (1)
- Session 02 Sindhu-Sarasvati CivilizationDocument33 pagesSession 02 Sindhu-Sarasvati Civilizationrevati chandakNo ratings yet
- Careerwill: Ancient HistoryDocument30 pagesCareerwill: Ancient HistoryGouthamshastri Gadicharla50% (2)
- 1 Bricks BeadsDocument35 pages1 Bricks BeadsShreyash RanjanNo ratings yet
- Ancient IndiaDocument62 pagesAncient IndiaVipul RajputNo ratings yet
- Ancient India Important Facts of Indian HistoryDocument7 pagesAncient India Important Facts of Indian HistoryRaymond ZoliansangaNo ratings yet
- History of Indus Valley CivilizationDocument19 pagesHistory of Indus Valley CivilizationAquib IrshadNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Mod 2 I VCDocument8 pagesAncient History Mod 2 I VCShubham KhokerNo ratings yet
- History Revision Notes (Eng) by RaMo SirDocument19 pagesHistory Revision Notes (Eng) by RaMo Sirdick kumarNo ratings yet
- Harappan Civilization Brief NoteDocument9 pagesHarappan Civilization Brief Notearshitagupta2004No ratings yet
- Lec 1.1 Ivc PDFDocument33 pagesLec 1.1 Ivc PDFChaitanya siriNo ratings yet
- ConstiDocument70 pagesConstiVed PrakashNo ratings yet
- History of India - INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATIONDocument31 pagesHistory of India - INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATIONBinayak MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- PDF Indian CultureDocument354 pagesPDF Indian CultureABCDEFNo ratings yet
- Ancient India The Prehistoric PeriodDocument48 pagesAncient India The Prehistoric Periodmkprabhu100% (1)
- Gujarat Administrative Services Prelims Full Syllabus History Indus Valley CivilizationDocument9 pagesGujarat Administrative Services Prelims Full Syllabus History Indus Valley CivilizationAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- IVCDocument4 pagesIVCrupalm02No ratings yet
- Ancient India for Kids - Early Civilization and History | Ancient History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandAncient India for Kids - Early Civilization and History | Ancient History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesNo ratings yet
- The Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India, Volume 4From EverandThe Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India, Volume 4No ratings yet
- EchallanDocument2 pagesEchallanTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- सूचना शिष्यवृत्ती 2021-22Document5 pagesसूचना शिष्यवृत्ती 2021-22Tushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth Rahuri: College of Agriculture, Babhulgaon Course - Wise Result SheetDocument2 pagesMahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth Rahuri: College of Agriculture, Babhulgaon Course - Wise Result SheetTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth Rahuri: College of Agriculture, Babhulgaon Course - Wise Result SheetDocument2 pagesMahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth Rahuri: College of Agriculture, Babhulgaon Course - Wise Result SheetTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth Rahuri: College of Agriculture, Babhulgaon Course - Wise Result SheetDocument2 pagesMahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth Rahuri: College of Agriculture, Babhulgaon Course - Wise Result SheetTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- DEG111 Course Explores Democracy, Elections and GovernanceDocument84 pagesDEG111 Course Explores Democracy, Elections and GovernanceTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of SRP EL ENTO-406Document3 pagesEvaluation of SRP EL ENTO-406Tushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Morphology of MushroomDocument11 pagesMorphology of MushroomTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Student Training MinutesDocument2 pagesStudent Training MinutesTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- 5 6071355646387684434Document2 pages5 6071355646387684434Tushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- CISF - Central Industrial Security ForceDocument2 pagesCISF - Central Industrial Security ForceTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University, KolhapurDocument20 pagesShivaji University, KolhapurTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. (Hons) Agriculture Semester Course LayoutDocument40 pagesB.Sc. (Hons) Agriculture Semester Course LayoutTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Agrochemicals: Course No: Ele-Ssac-364Document31 pagesCourse Title: Agrochemicals: Course No: Ele-Ssac-364Tushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Course No.: HORT-366 Course Title: Post - Harvest Management and Value Addition of Fruits and Vegetables. Course Credits: 1+1 2 Books RecommendedDocument32 pagesCourse No.: HORT-366 Course Title: Post - Harvest Management and Value Addition of Fruits and Vegetables. Course Credits: 1+1 2 Books RecommendedTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- BS PublicationDocument34 pagesBS PublicationTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Notes On Course Title-Rural Sociology and Educational PsychologyDocument55 pagesSyllabus: Notes On Course Title-Rural Sociology and Educational PsychologyTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- WRTN RSLT CDS II 2015 EnglDocument36 pagesWRTN RSLT CDS II 2015 EnglChagan LalNo ratings yet
- RECRUITMENT ADVERTISEMENT FOR VARIOUS POSTSDocument5 pagesRECRUITMENT ADVERTISEMENT FOR VARIOUS POSTSTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Dht5Hy-9029/.35.9O9/0 3.: Ztgt. FfaDocument2 pagesDht5Hy-9029/.35.9O9/0 3.: Ztgt. FfaTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Admission Process Centerwise College Details For Spot Admission RoundDocument8 pagesAdmission Process Centerwise College Details For Spot Admission RoundTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Aeco 341 PDFDocument134 pagesAeco 341 PDFMunna GuptaNo ratings yet
- Scanned by CamscannerDocument15 pagesScanned by CamscannerTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Documents, Emails and Letters Regarding Agricultural IssuesDocument4 pagesDocuments, Emails and Letters Regarding Agricultural IssuesTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Farm Machinery and Power: C. No. AENG 251 2 (1+1)Document111 pagesFarm Machinery and Power: C. No. AENG 251 2 (1+1)Tushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Aeco 341 PDFDocument134 pagesAeco 341 PDFMunna GuptaNo ratings yet
- Course File: Department of AgronomyDocument37 pagesCourse File: Department of AgronomyTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- WRTN RSLT CDS II 2015 EnglDocument36 pagesWRTN RSLT CDS II 2015 EnglChagan LalNo ratings yet
- Bhandare Ritesh Unit AttatchmentDocument30 pagesBhandare Ritesh Unit AttatchmentTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Vardhaman TextilesDocument96 pagesVardhaman TextilesRathinakumar Natarajan100% (1)
- Prominent Brahmins in Indian Politics, Military and SciencesDocument7 pagesProminent Brahmins in Indian Politics, Military and SciencesDil90100% (1)
- Temples in INDIA and RemediesDocument16 pagesTemples in INDIA and RemediesSSha100% (2)
- Concept of DeathDocument51 pagesConcept of DeathUday DokrasNo ratings yet
- MahavamsaDocument378 pagesMahavamsaAnonymous 87cpqABhUNo ratings yet
- Puja Sankalpam PDFDocument1 pagePuja Sankalpam PDFxs11167% (3)
- TamilDocument6 pagesTamilAnonymous ITc6Lyp0kjNo ratings yet
- Vision For Sikh WomenDocument7 pagesVision For Sikh WomenHarpreet Singh100% (1)
- Sasura Bada Paisawala - WikipediaDocument3 pagesSasura Bada Paisawala - WikipediasoftdinaNo ratings yet
- (Final Result) (SSC CGL 2015) Rank Wise - All Posts (Rohit Lee)Document411 pages(Final Result) (SSC CGL 2015) Rank Wise - All Posts (Rohit Lee)AbhishekNo ratings yet
- 2023 Kelas VIIIDocument12 pages2023 Kelas VIIIHmj Ilmu KeolahragaanNo ratings yet
- Lab Technician PositionsDocument38 pagesLab Technician Positionsashok98909090No ratings yet
- The Vimanika ShastraDocument181 pagesThe Vimanika ShastraVaishali Thambukesavalu100% (7)
- RS CJ 2017 21082017Document16 pagesRS CJ 2017 21082017Ashish ChandaheNo ratings yet
- 3rd Class GKDocument4 pages3rd Class GKsujeet panditNo ratings yet
- Sudra Was Artisan and LabourerDocument10 pagesSudra Was Artisan and LabourerAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NepalDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Nepalsbaral_un100% (1)
- KamathDocument166 pagesKamathCuriosityShopNo ratings yet
- Bannanje Lectures ListDocument6 pagesBannanje Lectures Listapi-24465548750% (2)
- Mahatma Gandhi's ValuesDocument12 pagesMahatma Gandhi's ValuestiwarigulshriyaNo ratings yet
- Chakra Systems (Archive) - Hindu Dharma ForumsDocument15 pagesChakra Systems (Archive) - Hindu Dharma Forumstigerlo75100% (1)
- 1st To 30 JulyDocument34 pages1st To 30 JulyKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Nielit Calicut Common Application Form For M.Tech in Embedded Systems (ES) & Electronics Design Technology (EDT) 2017Document3 pagesNielit Calicut Common Application Form For M.Tech in Embedded Systems (ES) & Electronics Design Technology (EDT) 2017ADARSHNo ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 3Document51 pages08 - Chapter 3Saurabh JainNo ratings yet
- Dyczkowski Mark S G Inner Pilgrimage of The Tantra 59pDocument59 pagesDyczkowski Mark S G Inner Pilgrimage of The Tantra 59pAnkam Nirmala Jagadeesh100% (2)
- Annu Jalais Forest of Tigers PDFDocument255 pagesAnnu Jalais Forest of Tigers PDFArkadeb BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- The Partition and LiteratureDocument20 pagesThe Partition and LiteratureMoshei KhanNo ratings yet
- Regional Languages of PakistanDocument3 pagesRegional Languages of PakistanMAWiskillerNo ratings yet
- AbhivadayeDocument24 pagesAbhivadayesrikanth_krishnamu_3No ratings yet
- PaySlip IR-31027 SurajDocument1 pagePaySlip IR-31027 SurajPrashant SwamiNo ratings yet