Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BOW in SCIENCE Pages Deleted
BOW in SCIENCE Pages Deleted
Uploaded by
Abel Emmanuel Solitario Cabrales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesBOW in SCIENCE Pages Deleted
BOW in SCIENCE Pages Deleted
Uploaded by
Abel Emmanuel Solitario CabralesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Page 137 of 349
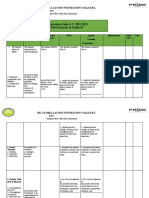
GRADE 9 – SCIENCE
Most Essential Learning No. of Days
Quarter Learning Competencies
Competencies (MELC) Taught
Quarter 1
Explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work
1 together to transport nutrients, gases, and other 10
molecules to and from the different parts of the body.
Infer how one’s lifestyle can affect the functioning of
2 5
respiratory and circulatory systems.
Describe the location of genes in chromosomes. 2
3 Explain the different patterns of Non-Mendelian inheritance. 10
Relate species extinction to the failure of populations of
4 organisms to adapt to abrupt changes in the
environment. 3
Differentiate basic features and importance of
5 10
photosynthesis and respiration.
Quarter 2
Describe how Bohr model of the atom improved
2
Rutherford`s atomic model
Explain how the Quantum Mechanical Model of the atom
6 4
describes the energies and positions of the electrons
Explain the formation of ionic and covalent bonds. 4
Recognize different types of compounds (ionic or
covalent) based on their properties such as melting point,
7 6
hardness, polarity, and electrical and thermal
conductivity.
Explain properties of metals in terms of their structure. 2
8 Explain how ions are formed. 4
Explain how the structure of the carbon atom
9 affects the type of bonds it forms. 5
Recognize the general classes and uses of organic
10 4
compounds.
11 Use the mole concept to express mass of substances. 4
Determine the percentage composition of a compound
12 5
given its chemical formula and vice versa.
Quarter 3
Describe the different types of volcanoes 2
Describe the different types of volcanoes and volcanic
13 5
eruption.
Differentiate between active and inactive volcanoes. 5
14 Explain what happens when volcanoes erupt. 6
Illustrate how energy from volcanoes may be tapped for
15 5
human use.
Explain how different factors affect the climate of an area.
16 5
Describe certain climatic phenomena that occur on a
17 3
global level.
Infer the characteristics of stars based on the
2
characteristics of the Sun.
Infer that the arrangement of stars in a group
2
(constellation) does not change.
Observe that the position of a constellation changes in the
3
course of a night.
Show which constellations may be observed at different
18 2
times of the year using models.
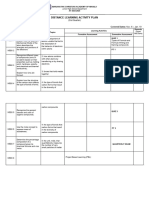
Quarter 4
Describe the horizontal and vertical motions of a
19
projectile; 6
Investigate the relationship between the angle of release
20 1
and the height and range of the projectile;
Examine effects and predict causes of collision- related
2
damages/injuries;
Page 138 of 349
Most Essential Learning No. of Days
Quarter Learning Competencies
Competencies (MELC) Taught
Relate impulse and momentum to collision of objects (e.g.,
21 2
vehicular collision);
Explain energy transformation in various activities/events
4
(e.g., waterfalls, archery, amusement rides);
Infer that the total momentum before and after collision is
22 4
equal;
Infer that the total mechanical energy remains the same
3
during any process;
Explain why machines are never 100-percent efficient; 2
Perform activities to demonstrate conservation of
23 3
mechanical energy;
24 Construct a model to demonstrate that heat can do work; 3
Infer that heat transfer can be used to do work, and that
2
work involves the release of heat.
Explain how heat transfer and energy transformation make
25 3
heat engines like geothermal plants work ; and
Explain how electrical energy is generated, transmitted,
26 5
and distributed.
You might also like
- BOW ScienceDocument10 pagesBOW ScienceRUTH MIASCONo ratings yet
- Hem Actsheet: Redox Equilibria IV - Redox TitrationsDocument3 pagesHem Actsheet: Redox Equilibria IV - Redox TitrationsAya ZhNo ratings yet
- 8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersDocument1 page8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersClaire LNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod7 The-Mole-Concept VerfinalDocument25 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod7 The-Mole-Concept VerfinalAbel Emmanuel Solitario Cabrales100% (1)
- Least Learned CompetenciesDocument6 pagesLeast Learned CompetenciesMichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DLP Q1W2Document7 pagesPhysical Science DLP Q1W2junar asentista50% (2)
- Polarographic Analysis and Its Importance in Pharmaceutical Field PDFDocument17 pagesPolarographic Analysis and Its Importance in Pharmaceutical Field PDFAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Q2 - Mod4 - CARBON ATOM A UNIQUE ONE - VerFinalDocument24 pagesScience 9 - Q2 - Mod4 - CARBON ATOM A UNIQUE ONE - VerFinalAbel Emmanuel Solitario CabralesNo ratings yet
- Fall2022PHAR128 AnalChem1CH0Student ALLDocument87 pagesFall2022PHAR128 AnalChem1CH0Student ALLErsin TukenmezNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science2Document2 pagesIntegrated Science2Earn8348100% (1)
- Least Mastered Skills Science 6Document2 pagesLeast Mastered Skills Science 6Jazel Ann Pantaleon100% (2)
- Science 9 - Q2 - Mod5 - USES-OF-ORGANIC-COMPOUNDS - VerFinalDocument22 pagesScience 9 - Q2 - Mod5 - USES-OF-ORGANIC-COMPOUNDS - VerFinalAbel Emmanuel Solitario Cabrales100% (1)
- Process Validation (Version 3)Document39 pagesProcess Validation (Version 3)AhckarawinThummaneeNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Bow ScienceDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Bow ScienceValir JanNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod8 Percentage-composition-Of-compounds VerfinalDocument28 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod8 Percentage-composition-Of-compounds VerfinalAbel Emmanuel Solitario Cabrales100% (1)
- CG Science 9 MelcsDocument4 pagesCG Science 9 MelcsDanilo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Curriculum GuideDocument4 pagesScience 10 Curriculum Guideclay adrian67% (3)
- Physical Science DLL1Document8 pagesPhysical Science DLL1Gracie O. ChingNo ratings yet
- RDT RESULTS IN Science 9Document3 pagesRDT RESULTS IN Science 9Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Bow 2021 2022Document2 pagesGrade 9 Bow 2021 2022catherine mojicaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Subject Overview 2023 2024Document5 pagesSCIENCE 9 Subject Overview 2023 2024Paulo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Post-Test Result in Grade 9 - Sy 2021-2022Document2 pagesPost-Test Result in Grade 9 - Sy 2021-2022Angelita MenesesNo ratings yet
- Bow ScienceDocument2 pagesBow ScienceAnn Rose PelayoNo ratings yet
- GRADE-8 Most Essential Learning Competencies Budget of Work School Year 2020-2021Document2 pagesGRADE-8 Most Essential Learning Competencies Budget of Work School Year 2020-2021Rosita CayananNo ratings yet
- Target Pembelajaran Hasil Rekonstruksi Kompetensi Mata Pelajaran IpaDocument19 pagesTarget Pembelajaran Hasil Rekonstruksi Kompetensi Mata Pelajaran Iparomy subiyantoroNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 TOS - 2nd Quarter-UnifiedDocument2 pagesGrade 9 TOS - 2nd Quarter-Unifiedadelfa.montesNo ratings yet
- Bol ScienceDocument8 pagesBol ScienceKarina CorrosNo ratings yet
- Science 10 BowDocument10 pagesScience 10 BowGERRY CHEL LAURENTENo ratings yet
- Budget of Works For The Most Essential Learning Competencies Subject: Earth and Life Science Grade: 11 Time Allotment: 60 Minutes/DayDocument5 pagesBudget of Works For The Most Essential Learning Competencies Subject: Earth and Life Science Grade: 11 Time Allotment: 60 Minutes/DayHarold Nalla HusayanNo ratings yet
- BOW in SCIENCEDocument5 pagesBOW in SCIENCELESLIE JOY ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Science 8 3rd Quarter Curriculum GuideDocument3 pagesScience 8 3rd Quarter Curriculum GuideJerica Joy BundocNo ratings yet
- For F2FDocument4 pagesFor F2FRjay NagilNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Implementation MatrixDocument11 pagesCurriculum Implementation MatrixReymart VillapeñaNo ratings yet
- SCI 9 2nd QTRDocument4 pagesSCI 9 2nd QTRBenson CornejaNo ratings yet
- A&P Unit IDocument4 pagesA&P Unit IArianna MenissianNo ratings yet
- Budget of WorkDocument2 pagesBudget of WorkChelsie May ReyesNo ratings yet
- Science 9 3rd Quarter Curriculum GuideDocument4 pagesScience 9 3rd Quarter Curriculum GuideJerica Joy BundocNo ratings yet
- Physical Science (None Lab) : TimeDocument7 pagesPhysical Science (None Lab) : Timeatz KusainNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Budget of Work Level: Grade 10 Subject Group: Subject: EnglishDocument8 pagesDepartment of Education: Budget of Work Level: Grade 10 Subject Group: Subject: Englishfloramie rellonNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Budget of Work Level: Grade 10 Subject Group: Subject: EnglishDocument8 pagesDepartment of Education: Budget of Work Level: Grade 10 Subject Group: Subject: Englishfloramie rellonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Yearly Planner f4 2013Document22 pagesChemistry Yearly Planner f4 2013adiyudi7No ratings yet
- G10 TOS DiagnosticDocument1 pageG10 TOS DiagnosticJr CapanangNo ratings yet
- Vertical Articulation 2020Document4 pagesVertical Articulation 2020Naty HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Science Ariculation of TopicsDocument10 pagesScience Ariculation of TopicsArlance Sandra Marie MedinaNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work - Q3Document2 pagesBudget of Work - Q3Michelle AglipayNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet - 5 MelcDocument6 pagesAnswer Sheet - 5 MelcJemuel LuminariasNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification Earth and Life ScienceDocument6 pagesTable of Specification Earth and Life SciencegraceromajNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Q2 - MATTER - MELCs Unpacked InventoryDocument8 pagesGrade 9 Q2 - MATTER - MELCs Unpacked InventoryMerry Chris TabliganNo ratings yet
- Least Learned Rank Most LearnedDocument4 pagesLeast Learned Rank Most LearnedRenalyn F. AndresNo ratings yet
- Science-7 TOS DATDocument3 pagesScience-7 TOS DATryan anthony manubayNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education National Capital Region Division of Taguig and PaterosDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education National Capital Region Division of Taguig and PaterosSherren Marie NalaNo ratings yet
- Target Pembelajaran Hasil Rekonstruksi Kompetensi Mata Pelajaran IpaDocument23 pagesTarget Pembelajaran Hasil Rekonstruksi Kompetensi Mata Pelajaran IpaulfaNo ratings yet
- Tos Advanced Chemistry q1Document3 pagesTos Advanced Chemistry q1CHRISTIAN RHEY NEBRENo ratings yet
- Bol Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesBol Physical ScienceEaea OjorpNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan G8 June-July2Document3 pagesLesson Plan G8 June-July2sunitak115No ratings yet
- Periodic Properties Hazari SirDocument9 pagesPeriodic Properties Hazari Sirriaz.atom4No ratings yet
- Enabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Document49 pagesEnabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Zea May BiasNo ratings yet
- Chem 31 (Upm)Document7 pagesChem 31 (Upm)Patricia Gayle JacildoNo ratings yet
- K To 12 CG Melcs Merged/ Clustered RetainedDocument1 pageK To 12 CG Melcs Merged/ Clustered RetainedMarfe MontelibanoNo ratings yet
- AllChapterQuestions PDFDocument23 pagesAllChapterQuestions PDFKim Na NaNo ratings yet
- Bow Science 9Document8 pagesBow Science 9diana rose cabilinNo ratings yet
- PS Module 2 PDFDocument10 pagesPS Module 2 PDFChelle GandiaNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: Potential and Kinetic EnergyDocument2 pagesLearning Module: Potential and Kinetic EnergyJoyR.AlotaNo ratings yet
- Test Plan in Science 9 First Quarter Examinatio1Document6 pagesTest Plan in Science 9 First Quarter Examinatio1Archie Borja delos ArcosNo ratings yet
- AST251 Lecture 2Document3 pagesAST251 Lecture 2Alexander BaghramyanNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 2 Important Questions em 216263 PDFDocument6 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 2 Important Questions em 216263 PDFRoman Varadha RajNo ratings yet
- Tos DRRMDocument7 pagesTos DRRMBRENDEL SACARISNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aspects of Membrane Permeability: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesFrom EverandCellular Aspects of Membrane Permeability: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod6 Organic-Compounds VerfinalDocument30 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod6 Organic-Compounds VerfinalAbel Emmanuel Solitario CabralesNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - q2 - Mod2 - Chemical Bonding Properties of Compounds - VerfinalDocument39 pagesScience 9 - q2 - Mod2 - Chemical Bonding Properties of Compounds - VerfinalAbel Emmanuel Solitario CabralesNo ratings yet
- Radiation-Curable Coatings: 150 HillDocument46 pagesRadiation-Curable Coatings: 150 HillAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Chemistry 12thDocument2 pagesPre Board Chemistry 12thSyed Raza Hassan GardeziNo ratings yet
- Lesson+Check Energy+and+States+of+Matter SEDocument4 pagesLesson+Check Energy+and+States+of+Matter SEAbdelrhman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wall System KS1000 AWP: Product DataDocument24 pagesWall System KS1000 AWP: Product DataNemanja VistaćNo ratings yet
- List of Pesticides Tolerances and Exemptions For PesticideDocument12 pagesList of Pesticides Tolerances and Exemptions For PesticideSales SaddiqiaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Alkaloid Structures I. Isolation Characterization and Physical MethodsDocument6 pagesDetermination of Alkaloid Structures I. Isolation Characterization and Physical Methodsgeovani2No ratings yet
- Flame PhotometreDocument9 pagesFlame PhotometreMuhammad Arslan AkramNo ratings yet
- Wastewater TreatmentDocument10 pagesWastewater Treatmentهاجر صالح جبارNo ratings yet
- Paint Specification No.: SSPC: The Society For Protective CoatingsDocument5 pagesPaint Specification No.: SSPC: The Society For Protective CoatingsanoopkumarNo ratings yet
- ARCAIR (MSDS) COPPERCLAD POINTED ELECTRODES Expires 16-07-02Document3 pagesARCAIR (MSDS) COPPERCLAD POINTED ELECTRODES Expires 16-07-02PubcrawlNo ratings yet
- GOC Neet Key NotesDocument40 pagesGOC Neet Key Notesiampriyatiwarii890No ratings yet
- Integrated Science 2020Document7 pagesIntegrated Science 2020Jâmãçy BräthwåítèNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12TH ProjectDocument12 pagesChemistry 12TH Projectamitmurmu3330No ratings yet
- Surface Tension: Cohesive and Adhesive ForcesDocument6 pagesSurface Tension: Cohesive and Adhesive ForcesAbdelrahman Abo AufNo ratings yet
- Powerfix Set15Document2 pagesPowerfix Set15Darwin AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Tyrosinase Inhibition From Green Tea (Camellia Sinensis (L.) Kuntze) GelDocument7 pagesTyrosinase Inhibition From Green Tea (Camellia Sinensis (L.) Kuntze) GelSandra MegantaraNo ratings yet
- Di ReportDocument4 pagesDi ReportStudent Access SLMC-IMNo ratings yet
- Nitofill WS60: Constructive SolutionsDocument2 pagesNitofill WS60: Constructive SolutionsrayNo ratings yet
- Review On Thermal Properties of Nanofluids - Recent Developments PDFDocument31 pagesReview On Thermal Properties of Nanofluids - Recent Developments PDFmahesh dNo ratings yet
- Licta March 2024 Paper 2 A Level Chemistry Marking GuideDocument14 pagesLicta March 2024 Paper 2 A Level Chemistry Marking Guidenkafor7No ratings yet
- Klein,: Organic ChemistryDocument41 pagesKlein,: Organic ChemistryMark BakalanNo ratings yet
- IASA Technical TrainingDocument88 pagesIASA Technical TrainingXavier DiazNo ratings yet
- Bulan Februari 2022Document45 pagesBulan Februari 2022Yogie 1290No ratings yet
- Kimyasal Tepk - Müh 1Document8 pagesKimyasal Tepk - Müh 1Merve YönyülNo ratings yet
- BORANG BQ 2019 BP EditDocument5 pagesBORANG BQ 2019 BP EditSyamsul 7511No ratings yet
- REVISED SR SEC Chemistry 2020 21Document8 pagesREVISED SR SEC Chemistry 2020 21jacobNo ratings yet