Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Original Article: Aamir Jalal Al-Mosawi
Uploaded by
asclepiuspdfsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Original Article: Aamir Jalal Al-Mosawi
Uploaded by
asclepiuspdfsCopyright:
Available Formats
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A Girl from Canada with Severe Cerebral Palsy
Associated with Hydrocephalus and Mutation
of Kinase D-Interacting Substrate of 220-KDa
(KIDINS220) Gene: A New Syndrome with Unique
Brain Imaging Findings and a Therapeutic Challenge
Aamir Jalal Al-Mosawi
Advisor and expert trainer, The National Training and Development Center, Iraqi Ministry of Health,
Baghdad, Iraq
ABSTRACT
Background: Cerebral palsy is a heterogeneous neurologic condition caused by abnormalities of brain development or damage
affecting mostly regions controlling movements, balance, and posture. The brain abnormalities and damage causing cerebral
palsy are characteristically non-progressive, but lead to permanent abnormalities of movements, posture, and limitation of
mobility. Kinase D-interacting substrate of 220 kDa (KIDINS220), a trans-membrane protein that is essential for growth
mediating pathways in the nervous system. Heterozygous KIDINS220 truncating variants affecting protein’s C-terminus
have been reported only in few unrelated children who had spastic paraplegia, mental retardation, nystagmus, and obesity. A
homozygous, more N-terminal truncating variant in KIDINS220 gene has been reported to be associated with enlarged brain
ventricles and limb contractures in three fetuses from a consanguineous family. Patients and methods: The family of a girl
who developed severe cerebral palsy caused by hydrocephalus, and had mutation of kinase D-interacting substrate of 220-
kDa (Kidins220), consulted us about the possible therapies her condition. Unique brain imaging abnormalities are described,
and the relevant literatures were reviewed with aim of suggesting possible evidence-based therapies. Results: A 33-month
old girl from Canada had cerebral palsy dominated by spasticity and caused hydrocephalus. The girl had slight nystagmus,
and was also thought to experience sometimes dystonia. During the first 18 months of life, her head was enlarging, and
Brain MRI showed dilated lateral ventricles, hypoplastic basal ganglia and inferior vermis, agenesis of septum pelucidum,
thin corpus collosum. Before surgery (endoscopic third ventriculostomy) at 19 months of age, her head circumference was
above the 99th percentile. Her head stabilized after the surgery. Literature review suggested the possible usefulness of the
use multi-factorial therapies including cerebrolysin, citicoline, piracetam, and pyritinol, and based on our extensive clinical
experience we suggested an initial one-month therapeutic course. Conclusion: In this paper, a new genetic syndrome is
described. The syndrome is associated with mutation of KIDINS220 gene, cerebral palsy, hydrocephalus, nystagmus, and
unique brain imaging findings including hypoplastic basal ganglia and inferior vermis, agenesis of septum pelucidum, and
thin corpus collosum.
Key words: New genetic syndrome, mutation of KIDINS220 gene, cerebral palsy, hydrocephalus, nystagmus.
Address for correspondence:
Aamir Jalal Al-Mosawi, Advisor and expert trainer, The National Training and Development Center, Iraqi Ministry of
Health. Baghdad, Iraq.
DOI: 10.33309/2639-913X.040105
© 2021 The Author(s). This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 4.0 license.
Journal of Clinical Research in Radiology • Vol 4 • Issue 1 • 2021 22
Al-Mosawi: Hydrocephalus and Mutation of Kinase D-Interacting Substrate of 220-KDa (KIDINS220) Gene
INTRODUCTION During the first 18 months of life, her head was enlarging,
and Brain MRI showed dilated lateral ventricles, hypoplastic
C
erebral palsy is a heterogeneous neurologic condition basal ganglia and inferior vermis, agenesis of septum
caused by abnormalities of brain development pelucidum, thin corpus collosum
or damage affecting mostly regions controlling
movements, balance, and posture. The brain abnormalities
and damage causing cerebral palsy are characteristically
non-progressive, but lead to permanent abnormalities of
movements, posture, and limitation of mobility. [1, 2, 3, 4].
We reported the occurrence of various brain imaging
abnormalities in children with cerebral palsy including brain
atrophy, periventricular leukomalacia, arachnoid cyst, and
cerebellar atrophy/cerebellar hypoplasia [5-15].
Kinase D-interacting substrate of 220 kDa (KIDINS220), a
trans-membrane protein that is essential for growth mediating
pathways in the nervous system. Heterozygous KIDINS220
truncating variants affecting protein’s C-terminus have been
reported only in few unrelated children who had spastic
paraplegia, mental retardation, nystagmus, and obesity.
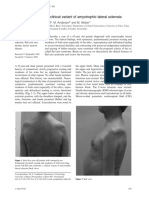
Figure 1. 33-month old girl from Canada who had cerebral
palsy dominated by spasticity
A homozygous, more N-terminal truncating variant in
KIDINS220 gene has been reported to be associated with
Before surgery (endoscopic third ventriculostomy) at 19
enlarged brain ventricles and limb contractures in three
months of age, her head circumference was above the 99th
fetuses from a consanguineous family [16].
percentile. Her head stabilized after the surgery.
PATIENTS AND METHODS She was receiving baclofen 10 mg at bed time, gabapentin,
and omprezole for gastro-esophageal reflux.
The family of a girl who developed severe cerebral palsy
caused by hydrocephalus, and had mutation of kinase Literature review suggested the possible usefulness of the use
D-interacting substrate of 220-kDa (Kidins220), consulted multi-factorial therapies including cerebrolysin, citicoline,
us about the possible therapies her condition. Unique brain piracetam, and pyritinol, and based on our extensive clinical
imaging abnormalities are described, and the relevant experience we suggested an initial one-month therapeutic
literatures were reviewed with aim of suggesting possible course [1-15].
evidence-based therapies.
The Initial Therapeutic Course Primarily Aimed at
RESULTS 1-Improving posture and spontaneous movement by providing
adequate muscle relaxation which hopefully results in easier
The 33-month old girl from Canada was studied during correction of the flexion deformity at the ankle.
October, 2021 (Figure-1). She had cerebral palsy dominated
by spasticity and caused hydrocephalus. She had significant 2-Repairing brain which can result in improved brain function
delay in gross motor, fine motor, speaking, and was unable that can be manifested early by improvement in head control,
to sit unassisted and had poor head control. She was unable and sometimes may result an early cognitive improvement
to neither roll, crawl, sit, nor stand. Spasticity had already which can be associated with improved speech and a better
associated with flexion deformity at the ankle which was understanding of simple speech. Improvement in nystagmus
correctable. However, the child was able to recognize the may occur early.
face of the mother, and was smiling, and responding to her
name. She was starting to make some sounds with words, na, Our suggested evidence-based treatment included withdrawal
ma. She also had slight nystagmus. The girl was also thought of gabapentin, and the gradual increase of baclofen to 20 mg
to experience sometimes dystonia. daily in 4 divided doses during the first month of treatment.
23 Journal of Clinical Research in Radiology • Vol 4 • Issue 1 • 2021
Al-Mosawi: Hydrocephalus and Mutation of Kinase D-Interacting Substrate of 220-KDa (KIDINS220) Gene
Initially, Baclofen 5 mg is given three times a day, and Kinase D-interacting substrate of 220 kDa (KIDINS220), a
increased to 4 times a day on day-8. Diazepam 2 mg daily at trans-membrane protein that is essential for growth mediating
bed time is added at day 14, and continued. pathways in the nervous system. Heterozygous KIDINS220
truncating variants affecting protein’s C-terminus have been
In addition, Cerebrolysin 2 ml given by intramuscular reported only in few unrelated children who had spastic
injection daily every other day during the morning hours (15 paraplegia, mental retardation, nystagmus, and obesity.
doses over one month). Oral Citicoline syrup 2 ml (200mg)
daily in the morning was also prescribed. A homozygous, more N-terminal truncating variant in
KIDINS220 gene has been reported to be associated with
DISCUSSION enlarged brain ventricles and limb contractures in three
fetuses from a consanguineous family [16].
Neuroimaging studies showing enlarged ventricles suggest
the diagnosis of hydrocephalus in the presence of head CONCLUSION
enlargement. However, as early as 1996, the work of
Campistol and colleagues suggested that in the absence of In this paper, a new genetic syndrome is described. The
macrocephaly, brain images showing slight ventricular dilation, syndrome is associated with mutation of KIDINS220 gene,
normotensive hydrocephalus, hydrocephalus with irregular cerebral palsy, hydrocephalus, nystagmus, and unique brain
limits, subcortical atrophy or periventricular heterotopia may imaging findings including hypoplastic basal ganglia and
indicate residual periventricular leukomalacia [17]. inferior vermis, agenesis of septum pelucidum, and thin
corpus collosum.
From Spain reviewed 250 patients with cerebral palsy, and
reported their brain imaging findings which included atrophy
in 38.8%, hydrocephalus in 29.4%, ischemia in 14.9%, ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
hemorrhage in 11.6%, and no abnormalities in 23.8% [18].
The author would like to express his gratitude for the family
From the United Kingdom reviwed patients with cerebral of the patients who willingly accepted publishing the photo
of their child.
palsy born in 1966-1991 in the counties of Merseyside and
Cheshire, UK, and reported an important association between
cerebral palsy and hydrocephalus [19]. REFERENCES
Reviewed 1104 patients (663 males, 441 females) with 1. Al Mosawi AJ. Dramatic effect of nandrolone decanoate on
cerebral palsy were born during the period from 1991 to 1999 motor development in cerebral palsy. Arch Dis Child 2008;
93(11) :( Suppl II):A338-A339.
in three areas (Isère Region, French Alps; Funen County,
2. Al Mosawi AJ. A novel therapeutic approach for the treatment
Denmark; Northern Region, England). They found that the of cerebral palsy (Ed). LAP Lambert Academic Publishing,
most common cerebral anomalies were primary microcephaly Germany, 2017.
which was observed in 26.5%, and congenital hydrocephalus 3. Al Mosawi AJ. A novel therapeutic approach for the treatment
which was observed in 17.3% [20]. of brain atrophy (Ed). LAP Lambert Academic Publishing,
Germany, 2017.
Reported brain MRI and CT-scan findings in 129 children 4. Al Mosawi AJ. New therapies for the treatment of spastic
(86 males, 43 females; aged 2-18 years) who had various cerebral palsy (Ed). LAP Lambert Academic Publishing,
Germany, 2019.
types of cerebral palsy. 100 patients (77.52%) had CT-scan
5. Al-Mosawi AJ. New therapies for the treatment of spastic
and 29 patients (22.48%) had MRI. 19 patients (14.72%) cerebral palsy. Med J Clin Trials Case Stud (ISSN: 2578-4838)
had normal MRI and CT-scan. Ventriculomegaly which 2019; 3(2): 000209. USA. DOI: 10.23880/mjccs-16000209.
indicates hydrocephalus in the presence of head enlargement 6. Al-Mosawi AJ. The pattern of cerebral palsy in Iraqi children.
was the most common findings and occurred in 38 patients, Med Life Clin. 2019; 1(1):1001.
followed by focal infarct which was observed in 28 patients, 7. Al-Mosawi AJ. The pattern of cerebral palsy in Iraqi children.
periventricular leukomalacia was observed in 17 patients, 1st ed., Saarbrücken; LAP Lambert Academic Publishing: 2019
(ISBN: 978-620-0-09427-8).
cortical and cortical/subcortical atrophy was observed in 13
8. Al-Mosawi AJ. New Therapies for the treatment of ataxic
patients, basal ganglia lesions was observed in 12 patients, cerebral palsy caused by kernicterus. EC Clinical and Medical
and cortical migration and organization problems were Case Reports March 18, 2020; 3(4): 26-31.Doi: 10. 5281/
observed in 12 patients [21]. zenodo.3892208.
Journal of Clinical Research in Radiology • Vol 4 • Issue 1 • 2021 24
Al-Mosawi: Hydrocephalus and Mutation of Kinase D-Interacting Substrate of 220-KDa (KIDINS220) Gene
9. Al-Mosawi AJ. The experience with the use of nandrolone 17. Campistol Plana J, Escofet Soteras C, Póo Argüelles P.
decanoate and pyritinol in children with cerebral palsy. Open Leucomalacia periventricular: diagnóstico retrospectivo en
Access Journal of Biogeneric Science and Research (ISSN: niños con diplejía espástica [Periventricular leukomalacia: its
2692-1081) July 6, 2020; 2(3):1-3 Doi: 10.46718/ retrospective diagnosis in children with spastic diplegia]. An
JBGSR.2020.01.000 051. Esp Pediatr 1996 Jun; 44(6):553-6. PMID: 8849097 [Article
10. Al-Mosawi AJ. Cerebral palsy: A unique illustrated in Spanish].
experience. Medico Research Chronicles (ISSN: 2394- 18. Bringas-Grande A, Fernández-Luque A, García-Alfaro C,
3971) 2020 September 8; 7 (4):2017-239. Doi: 10.26838/ Barrera-Chacón M, Toledo-González M, Domínguez-Roldá
MEDRECH.2020.7.4.441. JM. Paralisis cerebral infantil: estudio de 250 casos [Cerebral
11. Al-Mosawi AJ. Congenital Externally Communicating palsy in childhood: 250 cases report]. Rev Neurol 2002 Nov
1-15; 35(9):812-7. PMID: 12436377 [Article in Spanish].
Porencephaly Presenting as Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy:
19. Pharoah PO. Prevalence and pathogenesis of congenital
Imaging Study of a Rare Condition. SunKrist Journal of anomalies in cerebral palsy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed
Neonatology and Pediatrics January 18, 2021; 3 (1):1-4.Doi: 2007 Nov; 92(6):F489-93. Doi: 10.1136/adc.2006.107 375.
10.5281/zenodo.4515510. PMID: 17428819.
12. Al-Mosawi AJ. The early treatment of a boy from Virginia with 20. Rankin J, Cans C, Garne E, Colver A, Dolk H, Uldall P, Amar
ataxic cerebral palsy. Journal of Pediatrics and Child Health E, Krageloh-Mann I. Congenital anomalies in children with
2021 May 22; 2 (4): 1-5. Doi: 10.5281/ zenodo. 4777413 . cerebral palsy: a population-based record linkage study. Dev
13. Al-Mosawi AJ. Cerebral palsy: An illustrated ground-breaking Med Child Neurol 2010 Apr; 52(4):345-51.Doi: 10.1111/j.
experience. Scholar’s press: 2020 (ISBN: 978-613-8-93772). 1469-8749.2009. 03415.x. PMID: 19737295.
14. Al-Mosawi AJ. Mózgowe porażenie dziecięce: Ilustrowane 21. Grigore I, Diaconu G. Corelaşii clinico-radiologice în paralizia
cerebrală [Clinical and radiologic correlations in cerebral palsy].
przełomowe doświadczenie: Medycyna oparta na dowodach
Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 2010 Jul Sep; 114(3):748-52.
(Polish Edition). Wydawnictwo Nasza Wiedza September 16,
PMID: 21243802 [Article in Romanian].
2020 (ISBN-10: 6202762136, ISBN-13: 978-620 276 2 137).
15. Al-Mosawi AJ. Cerebrale parese: Een geïllustreerde
baanbrekende ervaring: Bewijsgerichte geneeskunde (Dutch
Edition) .Uitgeverij Onze Kennis : September 16, 2020 (ISBN- How to cite this article: Al-Mosawi AJ. A Girl from Canada
10 : 6202762128, ISBN-13 : 978-6202762120). with Severe Cerebral Palsy Associated with Hydrocephalus
16. El-Dessouky SH, Issa MY, Aboulghar MM, Gaafar HM, and Mutation of Kinase D-Interacting Substrate of 220-
Elarab AE, Ateya MI, Omar HH, Beetz C, Zaki MS. Prenatal
KDa (KIDINS220) Gene: A New Syndrome with Unique
delineation of a distinct lethal fetal syndrome caused by a
homozygous truncating KIDINS220 variant. Am J Med Genet
Brain Imaging Findings and a Therapeutic Challenge. J
A 2020 Dec; 182 (12): 2867-2876. Doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61858. Clin Res Radiol 2021;4(1):22-25.
PMID: 32909676. DOI: 10.33309/2639-913X.040105
25 Journal of Clinical Research in Radiology • Vol 4 • Issue 1 • 2021
You might also like
- Front Pediatr 2022 - Cerebral Oxygenation and Metabolism After Hypoxia-IschemiaDocument9 pagesFront Pediatr 2022 - Cerebral Oxygenation and Metabolism After Hypoxia-IschemiaCharlie CharcapeNo ratings yet
- The Use of Citicoline in Pediatric Neurology and Pediatric PsychiatryDocument2 pagesThe Use of Citicoline in Pediatric Neurology and Pediatric PsychiatryAamir Jalal Al-MosawiNo ratings yet
- 324-Article Text-681-1-10-20220531Document11 pages324-Article Text-681-1-10-20220531Violine MartaliaNo ratings yet
- Ma 2020Document12 pagesMa 2020daelCohenNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Cerebral PalsyDocument16 pagesRecent Advances in Cerebral PalsyTasyaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics in Pediatric NeurologyDocument6 pagesThesis Topics in Pediatric Neurologykarenoliverbaltimore100% (1)
- Espina Bifida 2022Document7 pagesEspina Bifida 2022Edwin Fabian Paz UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Uses of Cerebrolysin in Pediatric NeuropsychiatryDocument4 pagesClinical Uses of Cerebrolysin in Pediatric NeuropsychiatryAamir Jalal Al-MosawiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: Nature Reviews Disease Primers January 2016Document25 pagesCerebral Palsy: Nature Reviews Disease Primers January 2016Firdaus BillyNo ratings yet
- The Use of Piracetam and Cerebrolysin in The Treatment of Agenesis of Corpus Callosum With ColpocephalyDocument5 pagesThe Use of Piracetam and Cerebrolysin in The Treatment of Agenesis of Corpus Callosum With ColpocephalyAamir Jalal Al-MosawiNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Pediatric Neurological Emergency Book NEWDocument174 pagesHandbook of Pediatric Neurological Emergency Book NEWAyidhNo ratings yet
- TE MRIs For Very Preterm Infants-2017Document18 pagesTE MRIs For Very Preterm Infants-2017tNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: Nature Reviews Disease Primers January 2016Document25 pagesCerebral Palsy: Nature Reviews Disease Primers January 2016Zerry Reza SyahrulNo ratings yet
- Thapa 2009Document3 pagesThapa 2009Pedro Banho da RosaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: A Mini Review: Amrita Kumari, S. YadavDocument10 pagesCerebral Palsy: A Mini Review: Amrita Kumari, S. YadavMahfud HidayatNo ratings yet
- SpinaBifida ManagementDocument4 pagesSpinaBifida ManagementDimple GoyalNo ratings yet
- Steroids and Injury To Dev BrainDocument18 pagesSteroids and Injury To Dev Brainseemee23820No ratings yet
- TG Case 1 - Congenital 2012Document17 pagesTG Case 1 - Congenital 2012Galih Nadhova Imana LiverpudlianNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Iv Spina BifidaDocument7 pagesBahan Ajar Iv Spina Bifidaanon_800290919No ratings yet
- Neural Tube Defects: Group 1Document28 pagesNeural Tube Defects: Group 1imneverwrong2492100% (1)
- Jurnal Internasional 1Document5 pagesJurnal Internasional 1As karNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Ischemia Deteriorates White Matter, Brain Organization, and FunctionDocument10 pagesPrenatal Ischemia Deteriorates White Matter, Brain Organization, and FunctionJakssuel AlvesNo ratings yet
- A432 4 FullDocument2 pagesA432 4 FullArturo ArturoNo ratings yet
- MedBack MyelomeningoceleDocument3 pagesMedBack MyelomeningoceleJulia Rei Eroles IlaganNo ratings yet
- Cognitiveand Neuropsych Fxin Childrenwith CPDocument7 pagesCognitiveand Neuropsych Fxin Childrenwith CPAida RosellNo ratings yet
- (2018) Dandy-Walker Malformation-Like Condition Revealed by Refractory Schizophrenia A Case Report and Literature ReviewDocument8 pages(2018) Dandy-Walker Malformation-Like Condition Revealed by Refractory Schizophrenia A Case Report and Literature Reviewamaral.medicineschoolNo ratings yet
- Caringforthechildwith Spinabifida: Brandon G. Rocque,, Betsy D. Hopson,, Jeffrey P. BlountDocument13 pagesCaringforthechildwith Spinabifida: Brandon G. Rocque,, Betsy D. Hopson,, Jeffrey P. Blountyoussef alaouiNo ratings yet
- Encefalopatia Neonatal PDFDocument13 pagesEncefalopatia Neonatal PDFVanessa RomeroNo ratings yet
- Graham 2016Document25 pagesGraham 2016Constanzza Arellano LeivaNo ratings yet
- AANAbstract Myocl DystDocument2 pagesAANAbstract Myocl Dystpratap chandNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Administration of EndotoxinDocument7 pagesIntrauterine Administration of EndotoxinMaria SilvaNo ratings yet
- General PresentationDocument306 pagesGeneral PresentationJamie IllmaticNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument10 pagesSpina BifidamartirezdawncelineNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy ReviewDocument11 pagesCerebral Palsy ReviewYERNYNo ratings yet
- Spontaneuous Down Beat Nystagmus - JNRPDocument4 pagesSpontaneuous Down Beat Nystagmus - JNRPAshok Vardhan Reddy TNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument20 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptJosephine D CarandangNo ratings yet
- J Child Neurol 2001 Fennell 58 63Document6 pagesJ Child Neurol 2001 Fennell 58 63Elena GatoslocosNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System AbnormalitiesDocument56 pagesCentral Nervous System AbnormalitiesApin PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Approach To MacrocephalyDocument15 pagesApproach To MacrocephalywarunkumarNo ratings yet
- New Developments in The Management of NarcolepsyDocument19 pagesNew Developments in The Management of Narcolepsypeppers226647dndsh34No ratings yet
- A Case Report of Obsessive-Compulsive DisorderDocument6 pagesA Case Report of Obsessive-Compulsive DisorderfonsoalNo ratings yet
- Perspective: Age-Related Decline in Neurogenesis: Old Cells or Old Environment?Document6 pagesPerspective: Age-Related Decline in Neurogenesis: Old Cells or Old Environment?Fahmi IsmailNo ratings yet
- Daadi Et Al. 2010Document8 pagesDaadi Et Al. 2010matteo.tripodi.mtNo ratings yet
- Fulltext Ajcds v4 Id1060Document5 pagesFulltext Ajcds v4 Id1060Malik IbrahimNo ratings yet
- NrneurolDocument11 pagesNrneurolshaima nasimNo ratings yet
- Bab I Pendahuluan: Persistent Vegetative State in Head InjuryDocument17 pagesBab I Pendahuluan: Persistent Vegetative State in Head InjuryNindy Novela RitongaNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Steroids and The Developing Brain: Current TopicDocument4 pagesAntenatal Steroids and The Developing Brain: Current TopicPatrick RamosNo ratings yet
- Large Siza HeadDocument8 pagesLarge Siza HeaddyahNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: A Mini Review: January 2012Document11 pagesCerebral Palsy: A Mini Review: January 2012andreas kevinNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: A Mini Review: January 2012Document11 pagesCerebral Palsy: A Mini Review: January 2012andreas kevinNo ratings yet
- Burns 2008Document12 pagesBurns 2008Monesh-BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- CDP Choline (Citicoline Nicholin) Therapy On Some Cases of Children With Organic Brain SyndromeDocument5 pagesCDP Choline (Citicoline Nicholin) Therapy On Some Cases of Children With Organic Brain SyndromeSandyNo ratings yet
- Limperopoulos Bolduc09 Neurodevelopmental Outcomes After CB Injury REVIEWDocument12 pagesLimperopoulos Bolduc09 Neurodevelopmental Outcomes After CB Injury REVIEWEccoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Malformation of Nervous System PPT Sesi 1Document22 pagesCongenital Malformation of Nervous System PPT Sesi 1Brandedlovers Onlineshop100% (1)
- Caffeine and Brain Development in Very Preterm InfantsDocument9 pagesCaffeine and Brain Development in Very Preterm Infantspaopics arevaloNo ratings yet
- Bennet Et Al., 2012Document12 pagesBennet Et Al., 2012matteo.tripodi.mtNo ratings yet
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis in Chicken Pox: Case ReportDocument2 pagesAcute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis in Chicken Pox: Case ReportCorneliu VladNo ratings yet
- Metabolic and Genetic Disorders Mimicking Cerebral Palsy: Review ArticleDocument9 pagesMetabolic and Genetic Disorders Mimicking Cerebral Palsy: Review ArticleCarlosErnestoBolañosAlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum Disorder: Bioregenerative Medicine With Stem Cell TherapyFrom EverandAutism Spectrum Disorder: Bioregenerative Medicine With Stem Cell TherapyNo ratings yet
- Epigenetic Regulation in the Nervous System: Basic Mechanisms and Clinical ImpactFrom EverandEpigenetic Regulation in the Nervous System: Basic Mechanisms and Clinical ImpactNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Profile of Honey On Staphylococcus Aureus Isolated From Surgical Wound in Awomamma General HospitalDocument5 pagesAntibacterial Profile of Honey On Staphylococcus Aureus Isolated From Surgical Wound in Awomamma General HospitalasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Acute Pneumonia and The Hidden Effect of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesAcute Pneumonia and The Hidden Effect of AntibioticsasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Hemorrhage and Ischemic Stroke in The Same Brain: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesSimultaneous Hemorrhage and Ischemic Stroke in The Same Brain: A Case ReportasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Anti Mullerian Hormone and Its RelevanceDocument2 pagesAnti Mullerian Hormone and Its RelevanceasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Semi-Split Bulk Filling Technique: A Key To Achieve Occlusal Bulk-Fill Resin Composite Restorations Free of Postoperative Sensitivity and PainDocument3 pagesSemi-Split Bulk Filling Technique: A Key To Achieve Occlusal Bulk-Fill Resin Composite Restorations Free of Postoperative Sensitivity and PainasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Frequency Distribution of ABO, Rhesus Blood Groups and Haemoglobin Genotypes Among Students of University of Port Harcourt, Rivers State, NigeriaDocument5 pagesFrequency Distribution of ABO, Rhesus Blood Groups and Haemoglobin Genotypes Among Students of University of Port Harcourt, Rivers State, NigeriaasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Adrenal Function in COVID-19Document4 pagesAssessment of Adrenal Function in COVID-19asclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Splenic Tuberculosis - A Rare PresentationDocument3 pagesSplenic Tuberculosis - A Rare PresentationasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Cryptococcus Gattii and Its Distinctive Yeast Morphology in Cerebrospinal Fluid CytologyDocument4 pagesCryptococcus Gattii and Its Distinctive Yeast Morphology in Cerebrospinal Fluid CytologyasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Angiomyofibroblastoma Presenting As Labia Minora CystDocument3 pagesAngiomyofibroblastoma Presenting As Labia Minora CystasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Bio 212 GDocument11 pagesBio 212 GhugoivanstNo ratings yet
- Case Study 6 - JimDocument1 pageCase Study 6 - Jimginabobina3337238No ratings yet
- Ictal TachycardiaDocument10 pagesIctal TachycardiaMaulidina AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Evelline Priscillia P 405140047 Pemicu 1 NeuroDocument105 pagesEvelline Priscillia P 405140047 Pemicu 1 NeurovlinkhoeNo ratings yet
- EEG Lecture Introduction To EEGDocument62 pagesEEG Lecture Introduction To EEGSada Twins100% (2)
- Neuromuscular Disorders 2016Document68 pagesNeuromuscular Disorders 2016Alberto MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Headache PAINDocument1 pageHeadache PAINOmarNo ratings yet
- Therapy (LLL)Document432 pagesTherapy (LLL)Biruk DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Fas CaseDocument2 pagesFas Caseanon_378668477No ratings yet
- 04.0 HydrocephalusDocument41 pages04.0 HydrocephalusBaraka SayoreNo ratings yet
- Michael J. Fox: Get To Know The Amazing Story BehindDocument5 pagesMichael J. Fox: Get To Know The Amazing Story BehindTRIXIA MAY ELEVADONo ratings yet
- Penatalaksanaa Terapi Wicara Pada Kasus Motor Speech DisorderDocument23 pagesPenatalaksanaa Terapi Wicara Pada Kasus Motor Speech DisorderAnggita AlifviaNo ratings yet
- 4 - The Unsteady BookeeperDocument4 pages4 - The Unsteady Bookeeperkvguan7090No ratings yet
- NIHSS Answer KeyDocument4 pagesNIHSS Answer KeyNathalie Caraca100% (3)
- 19 Neuromuscular DisordersDocument39 pages19 Neuromuscular DisordersSara 'Yaa SaraaNo ratings yet
- Live Streaming - Pre Recorded Paralel PDFDocument2 pagesLive Streaming - Pre Recorded Paralel PDFdrjohny kambuNo ratings yet
- Advertisement - GMC Nagpur Final PDFDocument15 pagesAdvertisement - GMC Nagpur Final PDFharkalshripadNo ratings yet
- AphasiaDocument14 pagesAphasiahafida rayni100% (1)
- 5 Idiopathic Diseases: Arranged By: Aryana Budiawan Septian Hidayat Zaki Fahrul AziDocument14 pages5 Idiopathic Diseases: Arranged By: Aryana Budiawan Septian Hidayat Zaki Fahrul AziZaki Azki TigabelasNo ratings yet
- NeuropathyDocument5 pagesNeuropathyAMAN RAJNo ratings yet
- Botulinum ToxinDocument29 pagesBotulinum Toxinbluecrush1100% (1)
- DysphasiaDocument2 pagesDysphasiatini0211No ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project Class 12thDocument20 pagesBiology Investigatory Project Class 12thsupercelldarshil100% (1)
- Restauración FuncionalDocument22 pagesRestauración FuncionalConstanza Vargas GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Migraine-Associated VertigoDocument12 pagesMigraine-Associated Vertigotaufik.abdiNo ratings yet
- Dua Kasus Multipel Sklerosis Dengan Tipe Yang Berbeda Di Rsup M. Djamil, PadangDocument7 pagesDua Kasus Multipel Sklerosis Dengan Tipe Yang Berbeda Di Rsup M. Djamil, PadangNurul Fitriana IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Upaya Meningkatkan Bicara Anak Autis Melalui Pendekatan Floortime Partiwi Ngayuningtyas AdiDocument6 pagesUpaya Meningkatkan Bicara Anak Autis Melalui Pendekatan Floortime Partiwi Ngayuningtyas Adim aldidsNo ratings yet
- A 62 Yr Old Patient From Akmeemana Presenting With Limb WeaknessDocument48 pagesA 62 Yr Old Patient From Akmeemana Presenting With Limb WeaknessSamapriya Pasan HewawasamNo ratings yet
- Teleconsult Call SummaryDocument2 pagesTeleconsult Call SummaryJhade Ann CayanesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination and Management of Impairments in VariousDocument34 pagesClinical Examination and Management of Impairments in Variousmukesh pokharelNo ratings yet