Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Classifications for Arthritis & Gout
Uploaded by
Cindy100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
20 views3 pagesThis document discusses drug classifications and examples for treating gout and arthritis. It outlines several classes of drugs including anti-gout agents like allopurinol and febuxostat that inhibit uric acid synthesis, cholchicine which impacts granulocytes, and probenecid, pegloticase, and lesinurad which change uric acid into inert substances. It also discusses common medications for arthritis like acetaminophen, NSAIDs, glucosamine therapy, steroid injections, and non-steroid injections. For rheumatoid arthritis, it recommends aggressive use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate for best long-term outcomes
Original Description:
Original Title
Bone & Joint Medication Cheat Sheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses drug classifications and examples for treating gout and arthritis. It outlines several classes of drugs including anti-gout agents like allopurinol and febuxostat that inhibit uric acid synthesis, cholchicine which impacts granulocytes, and probenecid, pegloticase, and lesinurad which change uric acid into inert substances. It also discusses common medications for arthritis like acetaminophen, NSAIDs, glucosamine therapy, steroid injections, and non-steroid injections. For rheumatoid arthritis, it recommends aggressive use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate for best long-term outcomes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
20 views3 pagesDrug Classifications for Arthritis & Gout
Uploaded by
CindyThis document discusses drug classifications and examples for treating gout and arthritis. It outlines several classes of drugs including anti-gout agents like allopurinol and febuxostat that inhibit uric acid synthesis, cholchicine which impacts granulocytes, and probenecid, pegloticase, and lesinurad which change uric acid into inert substances. It also discusses common medications for arthritis like acetaminophen, NSAIDs, glucosamine therapy, steroid injections, and non-steroid injections. For rheumatoid arthritis, it recommends aggressive use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate for best long-term outcomes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
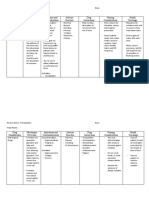
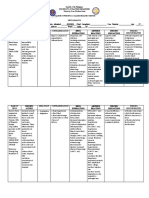
Drug Classifications & Examples Dosing & Considerations
Anti-Gout or Uricosic Agents Xanthine Oxidase
Xanthine Oxidase - used to inhibit inflammation, prevent synthesis of uric acid and must not disrupt the biosynthesis of vital
- Allopurinol purines
- Febuxostat - ADR- Hypersensitivity rash (higher in blacks/hispanics)
- Allopurinol can be used for renal impairment
Cholchicine
Cholchicine
- impacts granulocytes reducing deposit of uric formulation
Probenecid, Pegloticase, and Lesinurad - Anti-inflammatory & pain medication
- Mostly used as prophylactic or during acute attack
- ADRs: myopathy, weakness, neuropathy and malabsorption of B12
* all not used in pregnancy & in children
(except of uricemia of malignancy) Probenecid, Pegloticase, and Lesinurad
* Can precipitate renal stones - impacts uric acid excretion or change it into inert substances thus reducing deposits and deposition retarded.
* ADRs: GI disturbances and peptic ulcer - Probenecid is sulfa based & only used in pregnancy.
- Drug of choice for older adults.
Arthritis Acetaminophen
- Acetaminophen - 1st ordered drug; overuse or sudden change in activity can created inflammatory response requiring NSAIDs.
- NSAIDs - Can be used for up-to moderate pain
- Glucosamine Therapy NSAIDs
- Arthritis Steroid injection - Lowest dose for pain relief is best
- Non-steroid injection - Topical NSAIDs (votary 1%) is safer than oral therapy and benefits of being applied to region of high
discomfort. Less GI effects
Glucosamine Therapy
- takes months for full effects
- Has an anti-inflammatory and touted as safer than NSAIDs
Arthritis Steroid Injections
- used in conjunction for physical therapy, oral medications, weight loss and overall gradual activity increases.
- Injections to joint increase risk for osteomyelitis.
- Four injections per year.
Non-steroid injections
- Hyalurone and other viscous solutions are intended to supplement synovial fluid in larger joints
- Not endorsed by major specialities societies.
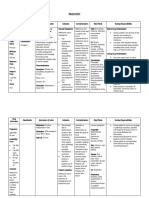
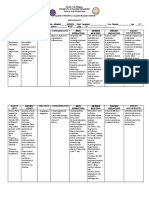
Drug Classifications & Examples Dosing & Considerations
Rheumatoid Arthritis DMARDs
- Aggressive movement toward use of - Nonbiological: Methotrexate
disease modifying antirheumatic drugs - Methotrexate
(DMARDs) creates the best long-term - Inhibits cytokine activity and purine production
outcomes - Take 6 weeks for full effects
- Smoking increase risk and progression - Can be mixed with other DMARDs
- Contraceptive use for longer than 7 years - Pregnancy Category X
be “protective” for a few years. - ADRs: GI distress, Stomatitis, Folic acid deficiency, Photodermatitis,
- First line- DMARDs - Monitoring
- Kidney
- Liver
- Platelet
- Education
- Wash urine-contaminated clothing separately
- Hydrochlorquine (Plaquenil)
- Doesn’t cause bone marrow suppression like others in the group
- Significant corneal deposits and retinal degeneration (Requires yearly eye examination & self-
monitoring with amsler grid for more frequent monitoring)
- Used for malaria before newer drugs
- Minocycline
- Tetracycline family of medication
- Best used in mild, early disease
- ADRs: photodermatitis
- Never used in pregnancy
- Janus Kinase Inhibitor
- Used for moderate-sever RA
- Prefer over parenteral biologicals
- Helps with bone erosion
- May not decrease synovitis
- Increase risk for infections
- Biological (Not started until failure of non-biologicals and progression to moderate-severe RA)
- Strong immunosuppressive properties. Increase risk for infections, cancers, site reactions
- There are 2 types:
- TNF-alpha inhibitor (Etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab)
- Non-Alpha TNF inhibitor (abatacept, rituximab)
- Remember patient cannot receive any active/live vaccination.
- ADRs: Steven-johnson, renal compromise, and progressive multifocal leukoencaphalopathy
- Bio-similar- same clinical endpoints as the biologics. Not generic versions. Can only be used for same FDA
approved indications.
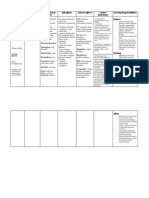
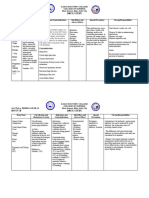
Drug Classifications & Examples Dosing & Considerations
Osteoporosis Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator (Raloxifene (Evista))
- Diagnosed when bone density is 2.5 SD - Have estrogenic effects on bone
below average - Protective against breast cancer
- Increased at risk for fractures especially Biphosphonates (Alendronate (Fosomax), Risedronate (Actonel))
at areas of stress. - Reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast activity —> increasing bone density
- Medications that increase risk for - No longer used for preventative therapy
osteoporosis - First line therapy for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis
- Glucocorticoids- 5 mg/day > 3 months - First line therapy for men older than age 70 years with osteoporosis
- Anticonvulsant - Instruct patient to remain upright after taking medication for 30 minutes with a full glass of water.
- LT PPI - ADR: Esophageal/Gastric Upset, Hyoocalcemia, Hypophospatemia, CV: A-Fib, arthralgia, myalgia,
- Heavy tobacco or alcohol use headache, Pathological fractures & Osteonecrosis of jaw
- Aromatase inhibitor - Caution: renal impairment, Heart failure, liver disease and active GI problems
- Treatment - Drug interaction: Ranitidine- increase bioavailability
- Selective estrogen receptor modulator Calcium & Vitamin D
- Biphosphonates - Prevents and treat osteoporosis
- Calcium & Vitamin D - Include low-impact bone-strengthening exercise
- Estrogen Estrogen
- Low dose maintain bone mineral density
Monitoring
- Measure Bone Mineral Density
- 10% loss = double the fracture risk
- DEXA is gold standard
- Baseline evaluation for all women older than 65 y.o
Education
- Role of diet, caffeine, alcohol and smoking on risk for developing osteoporosis
- Importance of adequate calcium and vitamin D intake regardless of treatment.
You might also like
- Ketorolac, Metoclopramide, and Cefuroxime Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesKetorolac, Metoclopramide, and Cefuroxime Nursing ConsiderationsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- IX. Drug StudyDocument4 pagesIX. Drug StudykingpinNo ratings yet
- Azathioprine - Frequent:: Anti-Inflammatory Immunosuppressive That Can Decrease Joint Damage and DisabilityDocument3 pagesAzathioprine - Frequent:: Anti-Inflammatory Immunosuppressive That Can Decrease Joint Damage and DisabilityJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Docusate, Trimetazidine, Salbutamol, and Spironolactone drug chartDocument8 pagesDocusate, Trimetazidine, Salbutamol, and Spironolactone drug chartzhapper2002No ratings yet
- Medication Dosage and Availability Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Action Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility DoseDocument3 pagesMedication Dosage and Availability Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Action Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Dosebambem aevanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MBDocument29 pagesDrug Study MBk4jggjtnz5No ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyJay Ann Joy PerudaNo ratings yet
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSDanica EspejoNo ratings yet
- Drug STXDocument2 pagesDrug STXSarah CarreteroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Chart - DM MedsDocument7 pagesEndocrine Chart - DM MedsrhondaNo ratings yet
- FamotidineDocument2 pagesFamotidinenikki shein bullongNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyZhaira LilangNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen drug information and nursing considerationsDocument1 pageAcetaminophen drug information and nursing considerationsnikki shein bullongNo ratings yet
- DRUG CelecoxibDocument2 pagesDRUG CelecoxibrholiboiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Hernandez 2nd semDocument3 pagesDrug Study Hernandez 2nd semhernandezmarianneroseNo ratings yet
- E.-Drug-Study-Report BevDocument2 pagesE.-Drug-Study-Report BevPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesDrugstudy Mefenamic Acidmikaela_magsinoNo ratings yet
- Aspirin and Other SalicylatesDocument6 pagesAspirin and Other SalicylatesCristine ChubiboNo ratings yet
- DTR PneumoniaDocument16 pagesDTR PneumoniaGUNPLANo ratings yet
- Anti-Inflammatory Antiarthritis and Related AgentsDocument10 pagesAnti-Inflammatory Antiarthritis and Related AgentsJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- WARD MaleDocument4 pagesWARD MaleDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Analgesics Fact SheetDocument6 pagesAnalgesics Fact SheethulaoshuNo ratings yet
- DS (Ibuprofen)Document6 pagesDS (Ibuprofen)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Difflam Drug StudyDocument1 pageDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid - Cuevas2Document2 pagesMefenamic Acid - Cuevas2Cuevas, Ryan Roy B.No ratings yet
- Jumex Tablet Selegiline Hydrochloride Sanofi-Aventis M SDN BHD 5 DEC 2017 ENG 1Document2 pagesJumex Tablet Selegiline Hydrochloride Sanofi-Aventis M SDN BHD 5 DEC 2017 ENG 1TQINNo ratings yet
- Waiters Morphine PDFDocument2 pagesWaiters Morphine PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Drug Study AssignmentDocument1 pageDrug Study AssignmentDaniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AssignmentDocument1 pageDrug Study AssignmentDaniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Brand Name Generic Name Classification Dosage Action MechanismDocument4 pagesDrug Study Brand Name Generic Name Classification Dosage Action MechanismJudith D. DSantosNo ratings yet
- Jacob Unit V PharmaDocument4 pagesJacob Unit V PharmaNikky Rossel FloresNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Prescribing GuidanceDocument1 pageIrritable Bowel Syndrome Prescribing Guidancetom8989No ratings yet
- Magnesium OxideDocument1 pageMagnesium Oxidefaithsamp6No ratings yet
- EsomeprazoleDocument2 pagesEsomeprazolekpanggat100% (2)
- AcetheminophenDocument1 pageAcetheminophenJoshua AndrewNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern SamarDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University Town, Northern SamarJosef Angelo PoldoNo ratings yet
- Antacid Drug AnalysisDocument2 pagesAntacid Drug AnalysisJosef Angelo PoldoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementNathanielle Keith PENASONo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument2 pagesDrug Study FinalFrancesca Marie CapawanNo ratings yet
- Managing Pain: Non-Opioid and Multimodal ApproachesDocument26 pagesManaging Pain: Non-Opioid and Multimodal ApproachesJenna DantNo ratings yet
- Gantala Drug Stusy-TabhsoDocument8 pagesGantala Drug Stusy-TabhsoHey it's FerdyNo ratings yet
- I. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesI. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Considerationscyn yana0723No ratings yet
- DRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDocument1 pageDRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac drug info: dosage, mechanism, indications, contraindications, adverse effectsDocument2 pagesKetorolac drug info: dosage, mechanism, indications, contraindications, adverse effectsRona PieNo ratings yet
- Erythromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesErythromycin Drug StudyJude LabajoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SurgeryDocument1 pageDrug Study SurgerygorgeazNo ratings yet
- Buscopan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesBuscopan Drug StudyMarc BantilanNo ratings yet
- 7endocrine DrugsDocument2 pages7endocrine DrugsSOFIA ALYSSA MARIE ABUDENo ratings yet
- Analgesic & Anti Inflammatory DrugsDocument39 pagesAnalgesic & Anti Inflammatory DrugschicagomdNo ratings yet
- SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)Document1 pageSSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)Mike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Mfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Negatil Tablet: What Is in This LeafletDocument2 pagesNegatil Tablet: What Is in This LeafletEe JoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study - ParacetamolNE TdrNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 203Document3 pagesDrug Study 203Daniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Geria)Document7 pagesDrug Study (Geria)nicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MCL or TechDocument7 pagesDrug Study MCL or TechKyra Lalaine Angub CervantesNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyJude LabajoNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Beating the Benzo Blues: Getting off BenzodiazapinesFrom EverandBeating the Benzo Blues: Getting off BenzodiazapinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Yunnan Baiyao Guide: Yunnan Baiyao Stops Bleeding, Relieves Pain, Improves Blood Flow, Treats Cancer in Dogs and Other AilmentsFrom EverandYunnan Baiyao Guide: Yunnan Baiyao Stops Bleeding, Relieves Pain, Improves Blood Flow, Treats Cancer in Dogs and Other AilmentsNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Classification of Heart FailureDocument2 pagesTreatment and Classification of Heart FailureShannon RamsumairNo ratings yet
- Management of DiabetesDocument1 pageManagement of DiabetesTwinkle SalongaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument2 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseShrestha AnjivNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument9 pagesCardiac Study GuideJane DiazNo ratings yet
- (Oxford Specialty Training - Revision Texts) Bessant, Rupa - The Pocketbook For PACES-Oxford University Press (2012)Document892 pages(Oxford Specialty Training - Revision Texts) Bessant, Rupa - The Pocketbook For PACES-Oxford University Press (2012)basocdovnch100% (2)
- Pohon Masalah AnsietasDocument16 pagesPohon Masalah AnsietasDeva NatarummandaNo ratings yet
- Spond Ylo ArthritisDocument58 pagesSpond Ylo ArthritisirsyadilfikriNo ratings yet
- Metadichol: Rheumatoid Arthritis A Case StudyDocument4 pagesMetadichol: Rheumatoid Arthritis A Case StudyDr P.R. RaghavanNo ratings yet
- 2033 Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument48 pages2033 Rheumatoid Arthritisdinaarzina100% (1)
- Ankylosing Spondylitis...Document6 pagesAnkylosing Spondylitis...mfahrizaNo ratings yet
- Final Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument58 pagesFinal Rheumatoid ArthritisShivalingaiah GirishNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulator 2014Document56 pagesImmunomodulator 2014LeilybadryaNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument19 pagesGeneral Principles of Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisSakinah Ginna RNo ratings yet
- Management of Severe Ulcerative Colitis: DR - Siddharth SinghDocument21 pagesManagement of Severe Ulcerative Colitis: DR - Siddharth SinghLohith VakacherlaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Inflammatory Antiarthritis and Related AgentsDocument10 pagesAnti-Inflammatory Antiarthritis and Related AgentsJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Psoriatic Arthritis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument14 pagesPsoriatic Arthritis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDhany karubuyNo ratings yet
- Enfermedad Inflamatoria IntestinalDocument24 pagesEnfermedad Inflamatoria Intestinalnicolas cuellarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Treatment of Fever in AdultsDocument24 pagesPathophysiology and Treatment of Fever in AdultsCosmina GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- ESPGHAN 52nd Annual Meeting Abstracts.1 PDFDocument1,248 pagesESPGHAN 52nd Annual Meeting Abstracts.1 PDFiuliaNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Rheumatology Association Recommendations for Diagnosis and Management of Axial Spondyloarthritis 2021Document15 pagesIndonesian Rheumatology Association Recommendations for Diagnosis and Management of Axial Spondyloarthritis 2021Rahmanu ReztaputraNo ratings yet
- Diabetes y Quistes RenalesDocument11 pagesDiabetes y Quistes RenalesJairo StragaNo ratings yet
- TNF InhibitorsDocument1 pageTNF InhibitorsSam RassamNo ratings yet
- 2033 Rheumatoid Arthritis 14-1 PDFDocument48 pages2033 Rheumatoid Arthritis 14-1 PDFAfif Al FatihNo ratings yet
- Scms 6s 6-16 Hawaiisppl v9Document28 pagesScms 6s 6-16 Hawaiisppl v9Michele CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis - Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2020Document19 pagesInvasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis - Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2020MICHAEL AMARILLO CORREANo ratings yet
- FSR Physicians Protocol1Document32 pagesFSR Physicians Protocol1Nishtha SinghalNo ratings yet
- Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors in Patients With Takayasu Arteritis: Experience From A Referral Center With Long-Term FollowupDocument5 pagesTumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors in Patients With Takayasu Arteritis: Experience From A Referral Center With Long-Term FollowupMikhail PisarevNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Sistem Organ-RADocument54 pagesFarmakoterapi Sistem Organ-RAMayZulFathulainNo ratings yet
- Role of Dmards in Ra-Psa-Sp2019Document94 pagesRole of Dmards in Ra-Psa-Sp2019GregNo ratings yet
- AbbVie Generics LawsuitDocument248 pagesAbbVie Generics LawsuitRobert GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoporosis: A Case Study: ArticleDocument5 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoporosis: A Case Study: ArticleSha HerNo ratings yet
- 744Document16 pages744Ruxandra DanuletNo ratings yet
- TNF Research PDFDocument882 pagesTNF Research PDFniluh suwasantiNo ratings yet
- Chron Skin Allergy Oct 2010Document32 pagesChron Skin Allergy Oct 2010shannon3458No ratings yet
- Multiple Clinical and Business Milestones in 2014 for Immune PharmaceuticalsDocument21 pagesMultiple Clinical and Business Milestones in 2014 for Immune PharmaceuticalsSusan LaskoNo ratings yet