Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculating transient voltages/currents in 1st order circuits
Uploaded by
Lars ReijndersOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculating transient voltages/currents in 1st order circuits
Uploaded by
Lars ReijndersCopyright:
Available Formats
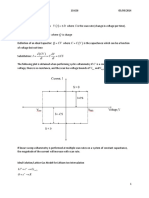
Recipe to calculate transient voltages vx(t) or currents ix(t) in 1st order circuits
Besides resistors and constant voltage and/or current sources, these circuits have one inductor or
one capacitor (and a switch, or a voltage source resp. current source that generates a stepped
voltage resp. stepped current).
i= 0 → C open
Step 1: For t = 0 − : steady state → C
v=
L 0 → L short
( ) ( ) ( )
Calculate vC 0− , i L 0− and the required unknown voltage v X 0− or current i X 0 − . ( )
v=
+
+
C (0 ) vC (0− ) → voltage source
Step 2: For t = 0 :
i L (0 + ) i L (0 − ) → current source
=
Calculate the required unknown voltage v X 0+ or current i X 0 + . ( ) ( )
Step 3: For t > 0 : use either the differential equation method (see step 3a) or the step-by-step
method (see step 3b).
Step 3a:(Differential equation method)
Use nodal analysis (or KVL in case of a single loop)
t
with iC (t ) = C C
dv (t )
dt
or =
1
L0
( )
i L (t ) i L 0 + + ∫ v L (τ ) dτ
(In case of an inductor take the first derivative of the resulting expression, to get rid of the
integral.)
dx
This will lead to a 1st order differential equation of shape + ax =
B.
dt
Solution: x (t= )
B
a
+ Ke − at where = K x 0+ −
B
a
( ) ( )
(with x 0+ found in step 2).
Now the required unknown voltage v X ( t ) or current i X ( t ) can be found.
Step 3b:(Step-by-step method)
i= 0 → C open
For t = ∞ : steady state → C
v=
L 0 → L short
Calculate the required unknown voltage v X ( ∞ ) or current i X ( ∞ ) .
Calculate the Thévenin equivalent resistance RTh , ‘seen’ from C or L
L
→ τ RThC=
= or τ
RTh
Now the required unknown voltage v X ( t ) or current i X ( t ) can be found:
( ( )
) v X ( ∞ ) + v X 0+ − v X ( ∞ ) e − t /τ
v X (t= )
i X (t )= i X ( ∞ ) + ( i (0 ) − i
X
+
X ( ∞ ) ) e −t /τ
You might also like
- Measurement System BehaviorDocument39 pagesMeasurement System BehaviorM. Sya'banur RozaqNo ratings yet
- TelegrphDocument4 pagesTelegrphimohammadghiyasiNo ratings yet
- Wave EquationDocument18 pagesWave EquationBibekNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Write UpDocument10 pagesTransmission Line Write UpAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 2Document15 pagesStudy Unit 2Gontse SempaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-3 Dynamic CharacteristicsDocument24 pagesChapter 2-3 Dynamic Characteristicsmekinjemal999No ratings yet
- Problem 2.28 PDFDocument2 pagesProblem 2.28 PDFKauê BrittoNo ratings yet
- OscillationDocument33 pagesOscillationchinmoy duttaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1003Document4 pagesLecture 1003YocobSamandrewsNo ratings yet
- 08 Differential Equations - Second Order LDE ApplicationsDocument25 pages08 Differential Equations - Second Order LDE ApplicationsRemo Rubian EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion: 8.01 Week 12D1Document23 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion: 8.01 Week 12D1Deepak AwasthiNo ratings yet
- This Is The Standard Lorentz Transformation Applied To The 4-Vector Differential DV, With DV The Space Conponent and DV The Time PartDocument9 pagesThis Is The Standard Lorentz Transformation Applied To The 4-Vector Differential DV, With DV The Space Conponent and DV The Time PartPraveen Dennis XavierNo ratings yet
- Akhil Math IA Properties of AC CircuitsDocument12 pagesAkhil Math IA Properties of AC CircuitsJordy Van KollenburgNo ratings yet
- Properties of The Wave Equation On RDocument12 pagesProperties of The Wave Equation On RElohim Ortiz CaballeroNo ratings yet
- TheoriesDocument4 pagesTheorieskratos9879No ratings yet
- Peirce Heat Conduction With Time DependentDocument6 pagesPeirce Heat Conduction With Time DependentLuis PeralesNo ratings yet
- 22 Assignment2Document7 pages22 Assignment2Akash KumarNo ratings yet
- 20122013assignment - 6.pdf 2012/2013 (Assignment 6) : TU Delft - Offshore & Dredging Engineering - Structural DynamicsDocument6 pages20122013assignment - 6.pdf 2012/2013 (Assignment 6) : TU Delft - Offshore & Dredging Engineering - Structural DynamicsShashank BabuNo ratings yet
- Problem 2.22 PDFDocument2 pagesProblem 2.22 PDFKauê BrittoNo ratings yet
- Natural and Step Responses For RLC Circuits: A D X DT DX DTDocument2 pagesNatural and Step Responses For RLC Circuits: A D X DT DX DTfarazhumayunNo ratings yet
- Programa: 1. Introdução Aos Circuitos Eléctricos 2. Grafos e Circuitos Resistivos LinearesDocument25 pagesPrograma: 1. Introdução Aos Circuitos Eléctricos 2. Grafos e Circuitos Resistivos LinearesPedro FernandesNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument9 pagesNotesAtharv AryaNo ratings yet
- Homework 3: ANSWERS provides infinitely many solutionsDocument4 pagesHomework 3: ANSWERS provides infinitely many solutionskrishnaNo ratings yet
- MCG 4308 Lec 4Document25 pagesMCG 4308 Lec 4Nadjet AkloucheNo ratings yet
- MCG 4308 Lec 4Document25 pagesMCG 4308 Lec 4Nadjet AkloucheNo ratings yet
- Controllability and Observability Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesControllability and Observability Lecture NotesfghstrhNo ratings yet
- Physics With Mathematica Fall 2013 Exercise #1 27 Aug 2012Document12 pagesPhysics With Mathematica Fall 2013 Exercise #1 27 Aug 2012Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Lecture Chapter 06 2024S WuDocument54 pagesCircuit Lecture Chapter 06 2024S Wudavidyang19995No ratings yet
- A Talk On Variable Separable MethodDocument53 pagesA Talk On Variable Separable Method30 Chaman JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Problem 2.35 PDFDocument3 pagesProblem 2.35 PDFKauê BrittoNo ratings yet
- Engr 213 Final 2009Document2 pagesEngr 213 Final 2009akabaka123No ratings yet
- EE16B HW 2 SolutionsDocument15 pagesEE16B HW 2 SolutionsSummer YangNo ratings yet
- How to find inertia tensor of 3D solid body from triangle meshDocument6 pagesHow to find inertia tensor of 3D solid body from triangle meshJesus Alfredo LMNo ratings yet
- Transient Analysis - First Order CircuitsDocument11 pagesTransient Analysis - First Order CircuitseugeneNo ratings yet
- 1 Transverse Vibration of A Taut String: 1.138J/2.062J/18.376J, WAVE PROPAGATIONDocument4 pages1 Transverse Vibration of A Taut String: 1.138J/2.062J/18.376J, WAVE PROPAGATIONabolfazl sanchoolyNo ratings yet
- 1 Problem Statement: Advanced Theory of Vibrations (AE 721) Assignment No. 4Document7 pages1 Problem Statement: Advanced Theory of Vibrations (AE 721) Assignment No. 4Ali BaigNo ratings yet
- Wave Equations SolverDocument14 pagesWave Equations SolverWilson LimNo ratings yet
- m257 316 Assigment5 12 Supplementary Problems SolutionsDocument9 pagesm257 316 Assigment5 12 Supplementary Problems SolutionsSanchez DavidNo ratings yet
- Interconnect Delay Models: EE695K VLSI InterconnectDocument16 pagesInterconnect Delay Models: EE695K VLSI InterconnectSuyash SinghNo ratings yet
- W3 L1 Slides PDFDocument13 pagesW3 L1 Slides PDFYeison Fabian Fernández MarinNo ratings yet
- EE263 Homework 3 SolutionsDocument16 pagesEE263 Homework 3 SolutionsLucky DeltaNo ratings yet
- Expressions for free response of simple RC, RLC circuitsDocument4 pagesExpressions for free response of simple RC, RLC circuitssrinvas_107796724No ratings yet
- Mathematics For Engineers PDF Ebook-1026-1030Document5 pagesMathematics For Engineers PDF Ebook-1026-1030robertodjoko001No ratings yet
- Strauss PDEch 4 S 1 P 3Document4 pagesStrauss PDEch 4 S 1 P 3Rudi JuliantoNo ratings yet
- MA 201: One Dimensional Wave Equation Lecture - 13Document16 pagesMA 201: One Dimensional Wave Equation Lecture - 13Sahrish AsifNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 PDFDocument16 pagesLecture7 PDFMato KankarašNo ratings yet
- CDS270-I Lecture2Document13 pagesCDS270-I Lecture2sab238633No ratings yet
- EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations: Solutions To Differential Equations of Motion For Vibrating SystemsDocument8 pagesEN40: Dynamics and Vibrations: Solutions To Differential Equations of Motion For Vibrating SystemsMilad RadNo ratings yet
- X Denote The Proportion of Susceptible y Denote The Proportion of CarriersDocument1 pageX Denote The Proportion of Susceptible y Denote The Proportion of CarriersneetiNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Accuracy and Stability For U C UDocument12 pages5.2 Accuracy and Stability For U C UEfstathios SiampisNo ratings yet
- Ntegration in Ractice: HapterDocument1 pageNtegration in Ractice: HapterLuis SalgadoNo ratings yet
- DQ I DT Q: Notes by MIT Student (And MZB)Document9 pagesDQ I DT Q: Notes by MIT Student (And MZB)PALANI R CHENo ratings yet
- Unit - IVDocument56 pagesUnit - IVharikaranNo ratings yet
- 0054 Handout 5Document8 pages0054 Handout 5zcaptNo ratings yet
- MIT presentation(physics-mecahanics)Document22 pagesMIT presentation(physics-mecahanics)mevlana3992No ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document3 pagesQuiz 1AnupNo ratings yet
- TD3 SolutionDocument3 pagesTD3 Solutionboulahdour.ayoub.g55No ratings yet
- Continuous Systems: P ChandramouliDocument43 pagesContinuous Systems: P ChandramouliPranav RaveendranNo ratings yet
- CONDUCTIONDocument19 pagesCONDUCTIONNwose Emmanuel N.No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- 5ECA0 Class 3: Equivalent Circuits (CH 5)Document81 pages5ECA0 Class 3: Equivalent Circuits (CH 5)Lars ReijndersNo ratings yet
- Recipe For Thévenin v1.1Document1 pageRecipe For Thévenin v1.1Lars ReijndersNo ratings yet
- Recipe For Nodal Analysis v1.2Document1 pageRecipe For Nodal Analysis v1.2Lars ReijndersNo ratings yet
- Recipe For Superposition v1.1Document1 pageRecipe For Superposition v1.1Lars ReijndersNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 Gyrator GuideDocument11 pagesLab 12 Gyrator GuideJulio César GuardiolaNo ratings yet
- Manual Electrical Engineering Lab 2: PoliteknikDocument7 pagesManual Electrical Engineering Lab 2: Politeknikae7678No ratings yet
- Schematic_Inversor 12V para 220V - 300W + PCI_2022-01-31Document1 pageSchematic_Inversor 12V para 220V - 300W + PCI_2022-01-31maurilioctbaNo ratings yet
- KA2201Document4 pagesKA2201Shriniwas SalunkeNo ratings yet
- Wien S Bridge Oscillator Using Op Amp PDFDocument19 pagesWien S Bridge Oscillator Using Op Amp PDFTarun BarthwalNo ratings yet
- IPD2400 Block DiagramDocument1 pageIPD2400 Block DiagramBradyXuerebNo ratings yet
- Norton's Theorem Explained in 40 CharactersDocument28 pagesNorton's Theorem Explained in 40 CharactersCyrus wendell P. De sosaNo ratings yet
- Amp Ka2206b DatasheetDocument6 pagesAmp Ka2206b DatasheetCristiano FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Cmos Differential AmplifierDocument8 pagesCmos Differential Amplifierparth aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Eletronics Lab Report - BJT AmplifierDocument3 pagesEletronics Lab Report - BJT AmplifierThan Lwin Aung50% (12)
- How the Origin 5 Amp Mods Improved Tone and Reduced DistortionDocument3 pagesHow the Origin 5 Amp Mods Improved Tone and Reduced DistortionowirwojNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document4 pagesSheet 2Ahmed GamalNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Wiring For 120V Unit: Service Diagram, Combined Bassman 100T Power Amp PCB AssyDocument4 pagesPower Supply Wiring For 120V Unit: Service Diagram, Combined Bassman 100T Power Amp PCB AssymidexNo ratings yet
- Lic Project Report Vinod GroupDocument12 pagesLic Project Report Vinod GroupPavase SumitNo ratings yet
- 18 Ec 421Document3 pages18 Ec 421Srujana PurohitNo ratings yet
- In Fulfillment of Diploma in Computer Engineering Of: Shri Swami Vivekanand Shikshan SansthaDocument7 pagesIn Fulfillment of Diploma in Computer Engineering Of: Shri Swami Vivekanand Shikshan SansthaRingtones WorldsNo ratings yet
- Very Low Phase Noise Vackar VFODocument4 pagesVery Low Phase Noise Vackar VFOShiva Prasad100% (2)
- Chapter 7Document46 pagesChapter 7Deivasigamani SubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Amplifier Frequency ResponseDocument33 pagesUnit - 2 Amplifier Frequency ResponsePrasadNo ratings yet
- Questions From Last Year Papers Chapter Wise Semiconductor: Explain P Type SemiconductorDocument4 pagesQuestions From Last Year Papers Chapter Wise Semiconductor: Explain P Type Semiconductornandkishor joshiNo ratings yet
- AmplifiersDocument4 pagesAmplifiersRed David BallesterosNo ratings yet
- 07 Voltage RegulatorsDocument20 pages07 Voltage RegulatorsAman MalikNo ratings yet
- Alarm CircuitDocument2 pagesAlarm Circuitamit281276No ratings yet
- Thevenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits: ECE 205 Prof. Ali KeyhaniDocument5 pagesThevenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits: ECE 205 Prof. Ali Keyhaniumar khan0% (1)
- Notes on Relaxation Oscillators Physics 120Document2 pagesNotes on Relaxation Oscillators Physics 120rishiNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Log BookDocument18 pagesLab 1 - Log BookNipuna WijeruwanNo ratings yet
- NESCOM TEST (2nd Shift) (16.02.2021)Document4 pagesNESCOM TEST (2nd Shift) (16.02.2021)Abdul Rehman100% (1)
- A 180 NM Low Power CMOS Operational Amplifier: Ketan J. Raut R. Kshirsagar A. BhagaliDocument4 pagesA 180 NM Low Power CMOS Operational Amplifier: Ketan J. Raut R. Kshirsagar A. BhagaliAnika TahsinNo ratings yet
- PDF Active Tilt Eq PCB - CompressDocument1 pagePDF Active Tilt Eq PCB - CompressDaniel OfoeNo ratings yet
- Parts List From Pacific SemicondutorsDocument7 pagesParts List From Pacific SemicondutorsNeville McBeanNo ratings yet