Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marfan Syndrom1
Uploaded by
Amala Fay ChavezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marfan Syndrom1
Uploaded by
Amala Fay ChavezCopyright:
Available Formats
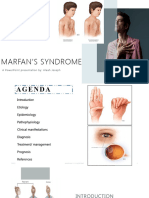
Marfan Syndrome Visual difficulties
Flat feet
(Arachnodactyly) Learning disability
Thin, narrow face
Marfan syndrome is a heritable condition that
Hypotonia
affects the connective tissue. The primary
purpose of connective tissue is to hold the Joint laxity
body together and provide a framework for Highly arached palate
growth and development. Crowded teeth
Dislocation of lens
Relatively rare disorder characterized by Malformed cornea
elongation of bones associated abnormalities Retinal detachment
of eyes and cardiovascular system.
Complications
Marfan syndrome affects men, women, and
Dilated aortic root
children, and has been found among people
Dissecting aortic aneurysm
of all races and ethnic backgrounds. It is
estimated that at least 1 in 5,000 people. Aortic rupture
Bacterial endocarditis
Heart failure
Marfan syndrome is named after Antoine
Mitral valve prolapsed
Marfan, the French doctor who first described
Frequent palpations
the disorder in 1896.
High blood
Pneumothorax
Etiology Scoliosis
Marfan syndrome is a genetic disorder. A Diagnostic tests
mutation, or change, in the gene that controls
Physical examination
how the body makes fibrillin causes Marfan
Echocardiogram
syndrome. Fibrillin is a protein that plays a
Eye examination
major role in your body's connective tissue. X-ray
Doppler echo test
Signs and Symptoms MRI
CT scan
Marfan syndrome often affects the long bones of Biopsy
the body. This can lead to signs, or traits, such as: CBC
Blood chemistry
Long, lanky frame Urine analysis
Long thin ribs
Arm span significantly greater than body Nursing Diagnoses
height
Long, spidery fingers (arachnodactyly) Risk for injury
Funnel chest Risk for infection
Scoliosis Knowledge deficit
Anxiety Nursing Interventions
Activity intolerance
Disturbance in self-esteem 1. Observe safety precautions all the time,
Fear keep side rails up all the time.
Fatigue 2. Observe cleanliness and sterility all the
Disturbed body image time to avoid possible contamination and
Impaired physical mobility spread of infection.
3. Provide correct information about the
Treatment disease process, complications and possible
treatment.
4. Encourage patient to acknowledge and to
Marfan syndrome has no cure. However, express feelings to be relieved from anxiety.
treatments can help delay or prevent 5. Ascertain ability to stand and move about
complications, especially when started early.
and degree of assistance necessary or use of
equipment.
Marfan syndrome can affect many parts of your
body, including your heart, bones and joints, eyes, 6. Discover patient’s inner abilities and help
nervous system, and lungs. The type of treatment to improve them to boost up their self-esteem.
you receive will depend on your signs and 7. Provide rest periods, avoid unnecessary
symptoms. disturbance.
8. Improve other qualities and help the
Surgery patient accept their problems and help them
comfort them.
If your aorta stretches, it's more likely to tear (a
condition called aortic dissection). To prevent this,
your doctor may recommend surgery to repair or
replace part of your aorta.
Surgery may involve:
A composite valve graft. For this surgery,
part of the aorta and the aortic valve are
removed. The aorta is replaced with a
man-made tube called a graft. A man-
made valve replaces the original valve.
Aortic valve-sparing surgery. If your aortic
valve is working well, your doctor may
recommend valve-sparing surgery. For
this surgery, your doctor replaces the
enlarged part of your aorta with a graft.
Your aortic valve is left in place.
You might also like
- Technical ReportDocument184 pagesTechnical Reportomen2ng88% (17)
- MANAURITE XM Material PDFDocument8 pagesMANAURITE XM Material PDFkbc404No ratings yet
- Nursing OncologyDocument208 pagesNursing OncologyfelxhuNo ratings yet
- Asme Section II A Sa-435 Sa-435mDocument4 pagesAsme Section II A Sa-435 Sa-435mAnonymous GhPzn1xNo ratings yet
- Oral RevalidaDocument14 pagesOral RevalidaAyaBasilioNo ratings yet
- OSPE Peads Medicine: Tetralogy of FallotDocument54 pagesOSPE Peads Medicine: Tetralogy of FallotKamran MallickNo ratings yet
- AMPUTATION LESSON PLANDocument7 pagesAMPUTATION LESSON PLANdhanasundariNo ratings yet
- Company & Project Information for Electrical, Instrumentation ServicesDocument28 pagesCompany & Project Information for Electrical, Instrumentation ServicesMrudul PatilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology BrainDocument21 pagesAnatomy & Physiology BrainAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- Preventing and Explaining NCDs Like Diabetes, Asthma and CancerDocument9 pagesPreventing and Explaining NCDs Like Diabetes, Asthma and CancerMaricris ArsibalNo ratings yet
- Marfan Syndrome PresentationDocument36 pagesMarfan Syndrome PresentationSivajothyNo ratings yet
- Marfan SyndromeDocument6 pagesMarfan SyndromeNurhidayu PauziNo ratings yet
- Nursing OncologyDocument131 pagesNursing Oncologyapi-3818438100% (5)
- The Marfan's SyndromeDocument2 pagesThe Marfan's SyndromeEdceleen AbsalonNo ratings yet
- Junctional ArrythmiasDocument14 pagesJunctional ArrythmiasCapitain Clou DofusNo ratings yet
- Marfan's Syndrome-Embryology & HistologyDocument13 pagesMarfan's Syndrome-Embryology & HistologyDark Melanin Fineapple XoXoNo ratings yet
- Marfan Syndrome With Atypical PresentationDocument4 pagesMarfan Syndrome With Atypical PresentationaiNo ratings yet
- Cam MidtermDocument6 pagesCam MidtermEarl Dave FarNo ratings yet
- I. Duane Syndrome (DS) : Genetic DisordersDocument7 pagesI. Duane Syndrome (DS) : Genetic DisordersJules ErinNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular DisordersDocument43 pagesNeuromuscular DisordersReem 10No ratings yet
- Radiographic Assessment of Congenital Malformations of The Upper ExtremityDocument17 pagesRadiographic Assessment of Congenital Malformations of The Upper ExtremityZoe GraceNo ratings yet
- Noonan Syndrome (Am Fam Physician. 2014 PDFDocument7 pagesNoonan Syndrome (Am Fam Physician. 2014 PDFKhalila DiantiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Congenital Deformities Bone and Joint InfectionDocument16 pages1.2 Congenital Deformities Bone and Joint InfectionRohit kumar Saravana kumarNo ratings yet
- Marfan Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMarfan Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Oncology AssignmentDocument18 pagesOncology AssignmentAngeline EspinasNo ratings yet
- Congential 3 Musculoskeletal 3 Neurological 3 Abusive DisordersDocument7 pagesCongential 3 Musculoskeletal 3 Neurological 3 Abusive DisordersNichole CollinsNo ratings yet
- Levels of Prevention Primary Secondary TertiaryDocument3 pagesLevels of Prevention Primary Secondary Tertiarymyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Prenatal Diagnosis Fetal Therapy and UltrasoundDocument14 pagesObstetrics Prenatal Diagnosis Fetal Therapy and UltrasoundRodrerick De lafuentesNo ratings yet
- Bandal 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomaDocument25 pagesBandal 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomasharedNo ratings yet
- Marfan's Syndrome - NIHDocument2 pagesMarfan's Syndrome - NIHTracy MagpocNo ratings yet
- PHACE Syndrome Case Report Highlights Rare ConditionDocument4 pagesPHACE Syndrome Case Report Highlights Rare ConditionÍtalo EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Treatment Timing and Multidisciplinary Approach in Apert SyndromeDocument6 pagesTreatment Timing and Multidisciplinary Approach in Apert SyndromeJulio AbarzuaNo ratings yet
- Amputation: Lesson Plan On ONDocument7 pagesAmputation: Lesson Plan On ONdhanasundariNo ratings yet
- Care Repoport AnjirDocument26 pagesCare Repoport AnjirqonitaNo ratings yet
- Marfan SyndromeDocument4 pagesMarfan SyndromenafasyaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems: Diseases and DisordersDocument16 pagesHuman Body Systems: Diseases and DisordersLena EmataNo ratings yet
- Marfan Syndrome PresentationDocument5 pagesMarfan Syndrome PresentationDorji WangdiNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Band Sequence: A SMFM Consult Series GuideDocument2 pagesAmniotic Band Sequence: A SMFM Consult Series GuideRamos Zavala Julio CesarNo ratings yet
- Adhesive CapsulitisDocument7 pagesAdhesive CapsulitisMariane GumbanNo ratings yet
- All CancersDocument23 pagesAll CancersericNo ratings yet
- Marfan Syndrome: Clinical CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesMarfan Syndrome: Clinical CharacteristicsRômulo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument2 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisSid GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ascaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalDocument21 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalPatricia CabisonNo ratings yet
- Semionov Imaging of Thoracic WallDocument13 pagesSemionov Imaging of Thoracic Walllaila.forestaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AcccidentDocument46 pagesCerebrovascular AcccidentFatin AmirahNo ratings yet
- Copy Oncology 1Document57 pagesCopy Oncology 1Brielle ShoppNo ratings yet
- Most Common Malignant Primary Tumor in Childhood: Malignanttumors RhabdomyosarcomaDocument2 pagesMost Common Malignant Primary Tumor in Childhood: Malignanttumors RhabdomyosarcomaMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Delantar 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomaDocument26 pagesDelantar 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomasharedNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument4 pagesConnective TissuePaola Elizabeth González MartínezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cerebral PalsyDocument43 pagesUnderstanding Cerebral Palsydareen tolentinoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 36Document3 pagesCHAPTER 36Samantha QuintoNo ratings yet
- Management of Snake Bite in India: Shibendu Ghosh, Prabuddha MukhopadhyayDocument6 pagesManagement of Snake Bite in India: Shibendu Ghosh, Prabuddha MukhopadhyaychandanNo ratings yet
- 醫科Document85 pages醫科Jason LinNo ratings yet
- MS FinalsDocument114 pagesMS FinalsMylene Grace ElarcosaNo ratings yet
- Endoscopy - : Brain Station CasesDocument4 pagesEndoscopy - : Brain Station CasesflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Marfan's Syndrome and The Heart: ReviewDocument6 pagesMarfan's Syndrome and The Heart: Reviewmuthiadewi31No ratings yet
- Management of SnakebiteDocument67 pagesManagement of SnakebiteHui TingNo ratings yet
- 2012 The Patient History - Evidence Based Appoach-368-376 PDFDocument9 pages2012 The Patient History - Evidence Based Appoach-368-376 PDFJoseph AndradeNo ratings yet
- BEprepared&beatitDocument2 pagesBEprepared&beatitRikki Marc ArnoldNo ratings yet
- DR G Avinash Rao Fellow in Hand and Microsurgery: ArthrogryposisDocument74 pagesDR G Avinash Rao Fellow in Hand and Microsurgery: Arthrogryposisavinashrao39100% (1)
- Marfan's Disease PamphletDocument8 pagesMarfan's Disease PamphletMark Thomas JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Special NeedsDocument4 pagesManagement of Patients With Special NeedsSophia MolinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Neurologic Examination: Section 3Document15 pagesChapter 1 - The Neurologic Examination: Section 3gus_lionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Fibro-sarcoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Fibro-sarcoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- NedaDocument2 pagesNedaAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- IV FluidDocument1 pageIV FluidAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and Design MethodsDocument765 pagesSystem Analysis and Design MethodsKarthik VkNo ratings yet
- IV FluidDocument1 pageIV FluidAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- Philippine Macroeconomic PresentationDocument68 pagesPhilippine Macroeconomic PresentationAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- Pre TestDocument7 pagesPre TestAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- 20 Issues Facing the ChurchDocument5 pages20 Issues Facing the ChurchAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- ArcticleDocument2 pagesArcticleAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- 8A CardiovascularFinalwithdxDocument50 pages8A CardiovascularFinalwithdxGlenn Daryll SantosNo ratings yet
- Logistic Management: A Supply Chain ImperativeDocument33 pagesLogistic Management: A Supply Chain Imperativekirk1985No ratings yet
- Normal Vital SignsDocument3 pagesNormal Vital SignsDianne CabanaNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument26 pagesStaffingAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- ParaphernaliaDocument3 pagesParaphernaliaAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- Anticancer DrugsDocument83 pagesAnticancer DrugsAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument26 pagesStaffingAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument2 pagesSystemic Lupus ErythematosusAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- DATASHEET Transistor 13003ADDocument4 pagesDATASHEET Transistor 13003ADCarlos MoraNo ratings yet
- Sizing PSV Broady Valvitalia-R4Document18 pagesSizing PSV Broady Valvitalia-R4Anggun RushNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle Cer 002Document2 pagesWater Cycle Cer 002api-434008934No ratings yet
- Syllabus For TR Supervisors Quality AssurnaceDocument67 pagesSyllabus For TR Supervisors Quality Assurnaceadnanlibra194No ratings yet
- For Student-General Chemistry I - Module 6 - Phan Tai HuanDocument41 pagesFor Student-General Chemistry I - Module 6 - Phan Tai HuanEsat Goceri100% (1)
- Users Manual: Documenting Process CalibratorDocument134 pagesUsers Manual: Documenting Process CalibratorSilvaa60No ratings yet
- MandrakeDocument6 pagesMandrakeEmry Kamahi Tahatai KereruNo ratings yet
- Men FootwearDocument442 pagesMen FootwearAbhishekNo ratings yet
- SR-21 SniperDocument6 pagesSR-21 SniperBaba HeadquaterNo ratings yet
- Oval Lake Hospital: Managing Your Data With Data ToolsDocument7 pagesOval Lake Hospital: Managing Your Data With Data ToolsJacob SheridanNo ratings yet
- Biosystems Engineering BS CurriculumDocument2 pagesBiosystems Engineering BS CurriculumAsiiimweNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency 2.45 GHZ Low Power Hybrid Junction Rectifier For RF Energy HarvestingDocument4 pagesHigh Efficiency 2.45 GHZ Low Power Hybrid Junction Rectifier For RF Energy HarvestingPrakash SunnyNo ratings yet
- Cascade Control: 25.1 Master and Slave LoopsDocument10 pagesCascade Control: 25.1 Master and Slave Loopsdeepak pandeyNo ratings yet
- Internal II BEEE QPDocument1 pageInternal II BEEE QPsivaNo ratings yet
- March 31-Drugs PDFDocument10 pagesMarch 31-Drugs PDFfan-a-tykNo ratings yet
- NAS810 Protection of Fluid Lines & EquipDocument1 pageNAS810 Protection of Fluid Lines & EquipfdhgjklNo ratings yet
- CJ1M Programming ManualDocument381 pagesCJ1M Programming ManualherpadianaNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric and Pumped Storage, Tidal, WaveDocument62 pagesHydroelectric and Pumped Storage, Tidal, WavePrince AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Official All Things Turmeric PPT GuidebookDocument14 pagesOfficial All Things Turmeric PPT Guidebookapi-507527047No ratings yet
- Chennai Public School: CH 3 Coordinate Geometry Multiple AssessmentDocument3 pagesChennai Public School: CH 3 Coordinate Geometry Multiple Assessment11F10 RUCHITA MAARANNo ratings yet
- 1Document36 pages1Abrvalg_1No ratings yet
- Tle Grade7 8 - CARPENTRYDocument10 pagesTle Grade7 8 - CARPENTRYdonna geroleoNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Case and Duct SystemDocument11 pagesCh.2 Case and Duct Systemcpt.ghostNo ratings yet
- Chords ListDocument5 pagesChords ListakshayNo ratings yet
- 2021 SC Hurricane GuideDocument16 pages2021 SC Hurricane GuideWMBF News100% (1)
- EA PSC Substation Earthing Course Leaflet PSC006CL MAR15Document2 pagesEA PSC Substation Earthing Course Leaflet PSC006CL MAR15David RothwellNo ratings yet