Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SED 3269 Module 1 - History of Astronomy
Uploaded by
Suiee Genriee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views24 pagesThis document outlines the module on the history of astronomy for the course SED 3269: Astronomy. It covers topics like the origins and branches of astronomy, contributions of ancient astronomers like those in Egypt and Greece, the Ptolemaic theory and Copernican model, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, Newton's law of universal gravitation, early telescope observations by Galileo, and modern developments in astronomy including space telescopes and citizen science.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the module on the history of astronomy for the course SED 3269: Astronomy. It covers topics like the origins and branches of astronomy, contributions of ancient astronomers like those in Egypt and Greece, the Ptolemaic theory and Copernican model, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, Newton's law of universal gravitation, early telescope observations by Galileo, and modern developments in astronomy including space telescopes and citizen science.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views24 pagesSED 3269 Module 1 - History of Astronomy
Uploaded by
Suiee GenrieeThis document outlines the module on the history of astronomy for the course SED 3269: Astronomy. It covers topics like the origins and branches of astronomy, contributions of ancient astronomers like those in Egypt and Greece, the Ptolemaic theory and Copernican model, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, Newton's law of universal gravitation, early telescope observations by Galileo, and modern developments in astronomy including space telescopes and citizen science.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
SED 3269: Astronomy
2nd Semester, Academic Year 2021 - 2022
Module 1: History of Astronomy
What is Astronomy?
- one of the oldest natural sciences;
- from the Greek word “astron” (star) and “nomia” (law or culture)
- branch of science that deals with the study of the stars and other celestial
phenomena outside of the Earth’s atmosphere;
- not to be confused with astrology which is a pseudo-science;
- commonly linked with astrophysics which deals with understanding the physical
and chemical characteristics and processes of astronomical phenomena.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Branches of Astronomy
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Ancient Astronomy (Egypt)
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Ancient Astronomy (Greece)
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Eratosthenes and Aristarchus
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Retrograde Motion of Planets
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
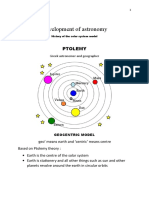
The Ptolemaic Theory
- introduced by Claudius Ptolemy in 2nd century AD to explain the heavens;
- used a system of deferents and epicycles to explain the motion of planets
in a circular orbit
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Complexity of the Ptolemaic Theory
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Copernicus and the Heliocentric Model
- re-introduced the heliocentric model of the Universe initially put forth by
Aristarchus in 1543 through his book De Revolutionibus which was published after
his death;
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Tycho Brahe and His Observations
- introduced a geo-heliocentric model;
- made detailed observations of the position of stars and planets from his
observatory, the Uraniborg;
- one of the best naked eye astronomers in history;.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Kepler and the Law of Planetary Motion
- Johannes Kepler served as the assistant of Tycho Brahe who inherited his
voluminous astronomical observations from which he based his laws of planetary
motion.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Kepler’s 1st Law of Planetary Motion
The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one
of the two foci.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Kepler’s 2nd Law of Planetary Motion
A line segment joining a planet and the Sun sweeps
out equal areas at equal intervals of time.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Kepler’s 3rd Law of Planetary Motion
The square of a planet’s orbital period is proportional to
the cube of the length of the semi-major axis of its orbit.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Isaac Newton and Universal Gravitation
- proposed the Universal Law of Gravitation which explains the reason for the
motion of the planets around the Sun.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
The Birth of the Telescope
- the first telescope is attributed to Hans Lippershey, a Dutch eyeglass maker in
1608;
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Galileo and His Telescope
- Galileo Galilei was one of the first to use the telescope for astronomical observations;
- he made observations of the Moon, discovered the phases of Venus, and moons of
Jupiter (eventually called the Galilean Moons);
- was condemned by the Roman Catholic Church for heretical views on the heliocentric
model, but was eventually pardoned in the 20th century.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Understanding the Stars with Spectroscopy
- spectroscopy allows us to understand the physical nature of stars despite their
distance from Earth.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Astronomy Across the EM Spectrum
- observing astronomical objects using
different parts of the EM spectrum allows us to
learn and understand other features.
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Modern Astronomy
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
The Birth of Space Telescopes
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Astronomy as a Citizen Science
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
Philippine Ethnoastronomy
SED 3269 - Astronomy Module 1: History of Astronomy
You might also like
- ModernPhysics Lesson 1Document24 pagesModernPhysics Lesson 1Abdullah AtiqNo ratings yet
- Earth Science MODULE 1 PDFDocument10 pagesEarth Science MODULE 1 PDFyhajj jamesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Modern Physics-Min PDFDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Modern Physics-Min PDFALURU VAISHNAVI 17BCE0017No ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Motion in Two and Three DimensionsDocument22 pagesChapter 3. Motion in Two and Three DimensionsAbdullatif AlOmairNo ratings yet
- The Particle Nature of MatterDocument2 pagesThe Particle Nature of MatterJohn Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Analytical Chemistry ModuleDocument22 pagesAnalyzing Analytical Chemistry ModuleMelliy100% (1)
- The Mirror Equation ExplainedDocument4 pagesThe Mirror Equation ExplainedJorge C. Bautista100% (1)
- Lab Activity No. 1 Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocument6 pagesLab Activity No. 1 Mendel and The Gene IdeaJohn Lesther PabiloniaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory and Structure QuizDocument3 pagesAtomic Theory and Structure QuizPradeep PatilNo ratings yet
- BTCH 1 Learning ModuleDocument33 pagesBTCH 1 Learning ModuleLOURDES W. UMILNo ratings yet
- Light - Independent Reaction 5Document46 pagesLight - Independent Reaction 5Dandena Gelmesa SobokaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Qtr1 Lesson 2Document2 pagesGrade 10 Qtr1 Lesson 2Niña Catubig - TangcalaganNo ratings yet
- Module 2 AtomDocument10 pagesModule 2 AtomJaenicaPaulineCristobalNo ratings yet
- BioPhysics Lab Activity 5Document4 pagesBioPhysics Lab Activity 5ANG, ROMAR CRISTIAN FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Notes 2020 PDFDocument16 pagesModern Physics Notes 2020 PDFNorthrop B2spiritNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Module 1Document35 pagesEnvironmental Science Module 1Hindrick Jumawan100% (1)
- Activity 5 Science Educ in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesActivity 5 Science Educ in The Philippinesgerald rupidoNo ratings yet
- 1st LESSON PLAN Earth ScienceDocument4 pages1st LESSON PLAN Earth ScienceLino Gayanilo100% (1)
- Activity #2 - ElectroscopeDocument4 pagesActivity #2 - ElectroscopeTUSHAR DASH0% (1)
- Science 9 Week 1Document18 pagesScience 9 Week 1lenNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 1Document3 pagesPerformance Task 1api-236548202No ratings yet
- QTR 2 Module 3 Other Living Things Besides Plants and AnimalDocument9 pagesQTR 2 Module 3 Other Living Things Besides Plants and AnimalNick Bantolo67% (3)
- Practice Problems 1 (Pressure, Gas Laws)Document3 pagesPractice Problems 1 (Pressure, Gas Laws)Jose Ruben SortoNo ratings yet
- LP Respiratory Act Bottled BalloonsDocument4 pagesLP Respiratory Act Bottled BalloonsRm Dela Serna SerniculaNo ratings yet
- Linear Coefficient of Expansion of MetalsDocument5 pagesLinear Coefficient of Expansion of MetalsRoselle Tura0% (1)
- Gen - Physics II LP Day#3Document3 pagesGen - Physics II LP Day#3MIKENo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentsengco_rizzajaneNo ratings yet
- PrefaceDocument3 pagesPrefaceditadniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Document5 pagesChapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Precious Aiverose EspinaNo ratings yet
- Addition of Vectors: By: Agustin A. PandomaDocument7 pagesAddition of Vectors: By: Agustin A. PandomaCharles SalinasNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter Long Test in ScienceDocument8 pagesFourth Quarter Long Test in ScienceJaysone De JesusNo ratings yet
- Human Karyotyping Lab #: Name: Date of Lab: Lab Partner/s: Due Date of LabDocument9 pagesHuman Karyotyping Lab #: Name: Date of Lab: Lab Partner/s: Due Date of LabLouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Definitions For Photosynthesis 1Document7 pagesDefinitions For Photosynthesis 1api-242369572No ratings yet
- OXIDATION NUMBERS AND NAMING CHEMICAL COMPOUNDSDocument6 pagesOXIDATION NUMBERS AND NAMING CHEMICAL COMPOUNDSAnton-ella RosanaNo ratings yet
- Charles Law ExplainedDocument3 pagesCharles Law ExplainedKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration ExplainedDocument57 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration ExplainedLeah Hope CedroNo ratings yet
- Angie Cream Banana Autopsy Lab ReportDocument1 pageAngie Cream Banana Autopsy Lab Reportapi-428117059No ratings yet
- CellsDocument18 pagesCellsapi-272901382No ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory PPTDocument29 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory PPTNanami MumuzunoNo ratings yet
- History of The Development of Atomic TheoryDocument27 pagesHistory of The Development of Atomic Theorysabaoonkhan329No ratings yet
- Science m1 Unit 2 g8Document13 pagesScience m1 Unit 2 g8Julia Geonzon Labajo100% (1)
- Final Exam Science 7 2018-2019Document2 pagesFinal Exam Science 7 2018-2019Bik BokNo ratings yet
- St. Peter's College of Ormoc: Astronomy College Unit AY 2020 - 2021Document7 pagesSt. Peter's College of Ormoc: Astronomy College Unit AY 2020 - 2021Kenneth Roy Matuguina100% (1)
- STK1211 Practical Analytical ChemistryDocument39 pagesSTK1211 Practical Analytical Chemistrylox agencyNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q3 Week4 MELC07 ASP Aceret, Dan Manayon Dan ManayoN AceretDocument10 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q3 Week4 MELC07 ASP Aceret, Dan Manayon Dan ManayoN AceretChristian Mart SoncioNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Explained in 40 CharactersDocument32 pagesQuantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Explained in 40 CharactersLALAINE NAANEPNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory TimelineDocument7 pagesCell Theory TimelineErwin AllijohNo ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument5 pagesApplicationArljarica PabunanNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument6 pagesSyllabushaileyparkNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter ExamDocument5 pagesScience 10 Quarter ExamlorenzfloresNo ratings yet
- Std11 Zoo EMDocument303 pagesStd11 Zoo EMElangovan PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Application of Radioactive Isotopes in Medical UsesDocument2 pagesApplication of Radioactive Isotopes in Medical UsesFana FaizalNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Question A.1Document8 pagesAnswer:: Question A.1SuvashreePradhan100% (1)
- Electric Fux WorksheetDocument1 pageElectric Fux Worksheetjovsky015No ratings yet
- STS LectureDocument415 pagesSTS LectureEdward Kenneth PantallanoNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument16 pagesAstronomyapi-3741779No ratings yet
- Historical Development of Space Exploration ModelsDocument11 pagesHistorical Development of Space Exploration ModelsMohd Fadzil Mohd ArifNo ratings yet
- What Is AstronomyDocument6 pagesWhat Is AstronomyRonnie PastranaNo ratings yet
- Semester 5 Open Course - I: (Problems Not Required)Document12 pagesSemester 5 Open Course - I: (Problems Not Required)kcameppadi123No ratings yet
- Development of AstronomyDocument11 pagesDevelopment of AstronomyNIK AZMAYATI BINTI ALI MoeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Rules and RegulationsDocument22 pagesLaboratory Rules and RegulationsSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Problem Set On Mendelian Inheritance, Genetic Ratios and ProbabilityDocument3 pagesProblem Set On Mendelian Inheritance, Genetic Ratios and ProbabilitySuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Exponential Population Growth's Impact on ClimateDocument4 pagesExponential Population Growth's Impact on ClimateDaniel NacordaNo ratings yet
- SHS Core - Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesSHS Core - Earth ScienceFeinrirNo ratings yet
- earthSCI PDFDocument160 pagesearthSCI PDFHersel May Isaiah NalamNo ratings yet
- Writing A Project Based Problem Based Learning PlanDocument28 pagesWriting A Project Based Problem Based Learning PlanSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Dominance Relations and Multiple Alleles Problem SetDocument1 pageDominance Relations and Multiple Alleles Problem SetSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Writing A Project Based Problem Based Learning PlanDocument28 pagesWriting A Project Based Problem Based Learning PlanSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Genetics Introduction Guide for StudentsDocument20 pagesGenetics Introduction Guide for StudentsSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives/Competencies: Code: S9Es-Iiie30: T-Calculator#Document3 pagesI. Objectives/Competencies: Code: S9Es-Iiie30: T-Calculator#Suiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 - The Student Who Thought He FailedDocument2 pagesCase Study 2 - The Student Who Thought He FailedSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis - RevisedDocument10 pagesItem Analysis - RevisedSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Overview of Ana ChemDocument8 pagesOverview of Ana ChemSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Mutations and chromosome variations in plantsDocument12 pagesMutations and chromosome variations in plantsSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Genetics Introduction Guide for StudentsDocument20 pagesGenetics Introduction Guide for StudentsSuiee GenrieeNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis Data Treatment and EvaluationDocument55 pagesStatistical Analysis Data Treatment and EvaluationJyl CodeñieraNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis Data Treatment and EvaluationDocument55 pagesStatistical Analysis Data Treatment and EvaluationJyl CodeñieraNo ratings yet
- Schools Division of Bulacan Caniogan High SchoolDocument13 pagesSchools Division of Bulacan Caniogan High SchoolTim Lopez IINo ratings yet
- Astrology BooksDocument6 pagesAstrology Booksmohosinawolia100% (3)
- De Thi Hoc Ky 2 Mon Tieng Anh Lop 9 Thi Diem Phong GD DT Thai Thuy Thai Binh Nam Hoc 2015 2016Document3 pagesDe Thi Hoc Ky 2 Mon Tieng Anh Lop 9 Thi Diem Phong GD DT Thai Thuy Thai Binh Nam Hoc 2015 2016Hương LêNo ratings yet
- DLP 7esDocument6 pagesDLP 7esSun JA100% (5)
- Sri LankaDocument35 pagesSri Lankabandarat100% (1)
- G6 Earth Science Revision Guide - 8Document16 pagesG6 Earth Science Revision Guide - 8Maria JiaNo ratings yet
- Research Report PowerPoint TemplatesDocument40 pagesResearch Report PowerPoint TemplatesNguyễn Thị Thanh HằngNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Solar SystemDocument3 pagesOrigin of The Solar SystemZercyNice Imbong CarreonNo ratings yet
- New Concepts of Space and Time: Milar, Francis Cyril S. Ocampo, Carl Francis MDocument41 pagesNew Concepts of Space and Time: Milar, Francis Cyril S. Ocampo, Carl Francis MCarl Francis Ocampo100% (1)
- 2.treatment With Vedic Astrology and Ayurveda-Mr. SApushpakirthiDocument15 pages2.treatment With Vedic Astrology and Ayurveda-Mr. SApushpakirthiSk MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Started With A Bang: Origin and Structure of The EarthDocument8 pagesStarted With A Bang: Origin and Structure of The EarthKowu BasyangNo ratings yet
- 050 MeteorologyDocument894 pages050 MeteorologykgyjuhiNo ratings yet
- DE THI THU TUYEN SINH LOP 10 (21) So3Document7 pagesDE THI THU TUYEN SINH LOP 10 (21) So335. Khánh Tâm 8/5No ratings yet
- AST251 Midterm 1.1Document7 pagesAST251 Midterm 1.1Alexander BaghramyanNo ratings yet
- Argala: Illustration: Define Primary Argala and Virodha Argala On Lagna For A Standard BirthDocument4 pagesArgala: Illustration: Define Primary Argala and Virodha Argala On Lagna For A Standard Birthsurinder sangarNo ratings yet
- Ancient SkiesDocument12 pagesAncient SkiesAnonymous HxLd544100% (1)
- Social Media Strategy Infographics by SlidesgoDocument27 pagesSocial Media Strategy Infographics by SlidesgoAdriana Huachaca EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Facts About SaturnDocument7 pagesFacts About SaturnGwyn CervantesNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Lesson 1 Mastery Assignment 2 - Elijah ShufordDocument10 pagesModule 3 Lesson 1 Mastery Assignment 2 - Elijah ShufordTawanda Boone-Shuford29% (7)
- Objective: GeographyDocument249 pagesObjective: GeographyDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Pak 10 Bab 11Document26 pagesPak 10 Bab 11Anastasia carolineNo ratings yet
- Pi in The Sky by Wendy Mass SAMPLEDocument26 pagesPi in The Sky by Wendy Mass SAMPLELizi BakradzeNo ratings yet
- Ufo Contact From Planet Koldas 1Document68 pagesUfo Contact From Planet Koldas 1jrospekNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers On The Space Vortex TheoryDocument11 pagesQuestions and Answers On The Space Vortex TheoryAchintya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Vaastu VidyaDocument73 pagesVaastu VidyaJithu Bayi100% (3)
- QF010-4th Quarter Learning Outcomes-Batanes ESDocument7 pagesQF010-4th Quarter Learning Outcomes-Batanes ESAna ConseNo ratings yet
- Wigley JupiterDocument2 pagesWigley JupiterPam WigleyNo ratings yet
- The Nine Grahas: - © Dr. Satya Prakash ChoudharyDocument3 pagesThe Nine Grahas: - © Dr. Satya Prakash ChoudharyDavid LorealNo ratings yet
- Heimat Presentation by SlidesgoDocument52 pagesHeimat Presentation by SlidesgoDaniela MiñonNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Lesikars Business Communication Connecting in A Digital World 13th EditionDocument6 pagesTest Bank Lesikars Business Communication Connecting in A Digital World 13th EditionRichard1LauritsenNo ratings yet