Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adaptation Typology
Uploaded by
VAISHALI SHARMA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThis document provides an overview of common types of adaptation options identified in the EACC Adaptation typology. It defines 12 different categories of adaptation, including anticipatory, autonomous, hard, high-regrets, low-regrets, maladaptive, planned, private, public, reactive, soft, and win-win/no-regrets adaptation. For each category, it provides a brief definition and examples.
Original Description:
Original Title
Adaptation_Typology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of common types of adaptation options identified in the EACC Adaptation typology. It defines 12 different categories of adaptation, including anticipatory, autonomous, hard, high-regrets, low-regrets, maladaptive, planned, private, public, reactive, soft, and win-win/no-regrets adaptation. For each category, it provides a brief definition and examples.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageAdaptation Typology
Uploaded by
VAISHALI SHARMAThis document provides an overview of common types of adaptation options identified in the EACC Adaptation typology. It defines 12 different categories of adaptation, including anticipatory, autonomous, hard, high-regrets, low-regrets, maladaptive, planned, private, public, reactive, soft, and win-win/no-regrets adaptation. For each category, it provides a brief definition and examples.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Economics of Climate Resilient Development
Module 2: How to Adapt Framework Overview
Step 3: Identify Adaptation Options
EACC Adaptation typology
Term Definition Example Source
Purchasing
Anticipatory/pro-active Adaptation that occurs before the effects of climate insurance,
adaptation change are evident. increasing capacity
of resevoirs
Adaptation that does not constitute a conscious response
to climatic stimuli, but rather is triggered by ecological
Shift in biological
Autonomous adaptation changes in natural systems and by market or welfare IPCC
diversity
changes in human systems. Also referred to as
spontaneous adaptation
Adaptation measures that usually imply the use of specific
Hard adaptation technologies and actions involving capital goods, such as Building a seawall World Bank
dikes, seawalls and reinforced buildings.
Involves decisions on large-scale planning and
investments with high irreversibility. In view of the
considerable consequences at stake, the significant Construction of
High-regrets adaptation investment costs and the long-lived nature of the long-lived World Bank
infrastructure, uncertainties in future climate projections infrastructure
play a crucial role when making decisions about whether
to implement high-regret adaptation measures.
Installing larger
Adaptation actions where moderate levels of investment
diameter drains to
increase the capacity to cope with future climate risks.
Low-regrets adaptation deal with expected World Bank
Typically, these involve over-specifying components in
increases in
new builds or refurbishment projects.
rainfall intensity
Actions which tend to increase vulnerability to climate Allowing
change. Maladaptive actions and processes often include development in
Maladaptation planned development policies and measures that deliver flood zones or low- UNDP
short-term gains or economic benefits but lead to elevation coastal
exacerbated vulnerability in the medium to long-term. areas
Adaptation that occurs due to conscious intervention or Relocating due to
Planned adaptation
preparation. sea-level rise
Adaptation that is initiated and implemented by
Private adaptation individuals, households or private companies. Private
adaptation is usually in the actor's rational self-interest.
Adaptation that is initiated and implemented by Changes in
Public adaptation governments at all levels. Public adaptation is usually national policies or World Bank
directed at collective needs. laws
Changing cropping
Adaptation that occurs after the effects of climate change patterns due to
Reactive adaptation World Bank
are evident. shortened growing
season
Adaptation measures that focus on information, capacity
Change in land
Soft adaptation building, policy and strategy development, and
zoning laws UNDP
institutional arrangements.
Measures that contribute to both climate change Measures that deal
mitigation and adaptation and wider development with climate
objectives, e.g., business opportunities from energy variability (e.g.,
Win-win adaptation/no-
efficiency measures, sustainable soil and water long-term weather World Bank
regrets adaptation
management, etc. That is, they constitute adaptation forecasting and
measures that would be justifiable even in the absence of early warning
climate change. systems)
You might also like
- History of The Philippine Folk DanceDocument2 pagesHistory of The Philippine Folk DanceRommel Villaroman Esteves79% (34)
- Senior Practical-Research-2-Q1-Module8 For PrintingDocument17 pagesSenior Practical-Research-2-Q1-Module8 For PrintingEustass Kidd67% (3)
- ENG8 Q3 MOD5 Using Parallel StructureDocument21 pagesENG8 Q3 MOD5 Using Parallel StructureIvy Joy San Pedro100% (2)
- RSVPselling Sales Aptitude Test PDFDocument7 pagesRSVPselling Sales Aptitude Test PDFBharadwaja JoshiNo ratings yet
- WATCHERS GUIDE 17apri19 EditDocument26 pagesWATCHERS GUIDE 17apri19 EditThomas Vincent PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Climate Change AdaptationDocument9 pagesClimate Change AdaptationXimena PachecoNo ratings yet
- TQM and Business ExcellenceDocument8 pagesTQM and Business ExcellencearcherselevatorsNo ratings yet
- Thesis Profile - Final PDFDocument109 pagesThesis Profile - Final PDFElias Hizkeal67% (6)
- National Adaptation Plan: ExecutiveDocument32 pagesNational Adaptation Plan: ExecutiveEka Dyana100% (1)
- Belgian National Adaptation Plan 2017-2020 (2016)Document40 pagesBelgian National Adaptation Plan 2017-2020 (2016)Climate Change BelgiumNo ratings yet
- Adaptation and Mitigation in Urban AreasDocument7 pagesAdaptation and Mitigation in Urban AreasVittaya Ruangrit100% (1)
- Adaptation NregaDocument48 pagesAdaptation NregaNarender SinghNo ratings yet
- Ten Key Requirements For A Systemic Approach To Climate AdaptationDocument21 pagesTen Key Requirements For A Systemic Approach To Climate AdaptationM SidinaNo ratings yet
- BR Fing: How Integrated Monitoring and Evaluation Systems Can Help Countries Address Climate ImpactsDocument4 pagesBR Fing: How Integrated Monitoring and Evaluation Systems Can Help Countries Address Climate ImpactsNebojsa RedzicNo ratings yet
- PUB100449Document9 pagesPUB100449oneforalltraderNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Adaptation StrategiesDocument6 pagesClimate Change Adaptation StrategiesFloria ShilaNo ratings yet
- Habitat International: Elisabeth M. Hamin, Nicole GurranDocument8 pagesHabitat International: Elisabeth M. Hamin, Nicole GurranWorkagegne SolomonNo ratings yet
- Preparing For The Day After Tomorrow - Frameworks For Climate ChanDocument13 pagesPreparing For The Day After Tomorrow - Frameworks For Climate ChanJaija J JayanNo ratings yet
- Articulo Bayesian NetworkDocument6 pagesArticulo Bayesian NetworkIván GómezNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Department of Budget and Management Climate Change CommissionDocument22 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Department of Budget and Management Climate Change CommissionjoancuteverNo ratings yet
- National Policy On Climate Change NPCCDocument19 pagesNational Policy On Climate Change NPCCAMBROSENo ratings yet
- 08 Philippines RecabarDocument19 pages08 Philippines Recabargracel angela tolejanoNo ratings yet
- Adaptation Planning For Climate Change Concepts, Assessment Approaches, and Key LessonsDocument11 pagesAdaptation Planning For Climate Change Concepts, Assessment Approaches, and Key LessonsClement KwangNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem-Based Adaptation: An Approach Responding To Climate HazardsDocument2 pagesEcosystem-Based Adaptation: An Approach Responding To Climate HazardsΡομίρ ΓιάνκκιλNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Integrated Assessment Models IAMsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Integrated Assessment Models IAMsVishnu ChNo ratings yet
- Researh Paper - Anubhuti SinghalDocument5 pagesResearh Paper - Anubhuti SinghalAnubhuti SinghalNo ratings yet
- Adaptation To Climate Change in The Context of Sustainable DevelopmentDocument30 pagesAdaptation To Climate Change in The Context of Sustainable Developmentadmin.maldivesNo ratings yet
- Ps AppaDocument6 pagesPs AppaDaniel RabascallNo ratings yet
- Climate Smart Aquaculture ToolkitDocument76 pagesClimate Smart Aquaculture ToolkitZinabu Tunu JilloNo ratings yet
- BR Fing: Calling For Business Unusual: Mechanisms For Delivering ChangeDocument4 pagesBR Fing: Calling For Business Unusual: Mechanisms For Delivering ChangeGhassan HawilyNo ratings yet
- ALN-Competency-Framework 2021 Final PDFDocument83 pagesALN-Competency-Framework 2021 Final PDFRafael OsunaNo ratings yet
- Pp161-192CC2008Ch6 Adaptation ConsequencesDocument32 pagesPp161-192CC2008Ch6 Adaptation ConsequencesCIO-CIONo ratings yet
- 10 SROCC AnnexI-Glossary FINALDocument28 pages10 SROCC AnnexI-Glossary FINALAnisa NurfitrianiNo ratings yet
- Revised Climate Marker Handbook - FINALDocument34 pagesRevised Climate Marker Handbook - FINALpooriya zamaniNo ratings yet
- CCA in Health Sector - OktaDocument11 pagesCCA in Health Sector - OktaLarva KuningNo ratings yet
- Zevenbergen Flood Resilience 2Document8 pagesZevenbergen Flood Resilience 2HamzaNo ratings yet
- Chapt 5Document20 pagesChapt 5Alrick Bulosan SablayNo ratings yet
- Philippines Summary CcaDocument40 pagesPhilippines Summary CcaNELSON NISPEROSNo ratings yet
- Zevenbergen Flood Resilience 2Document8 pagesZevenbergen Flood Resilience 2PearlNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0957178712000409 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0957178712000409 MainAUDLEY THANIA T SNo ratings yet
- PROKLIM PUSLUH 22 APRIL 2022 - CompressedDocument38 pagesPROKLIM PUSLUH 22 APRIL 2022 - CompressedhelmyNo ratings yet
- Innovation Insights NBS Climate ResilienceDocument24 pagesInnovation Insights NBS Climate ResiliencevaiaNo ratings yet
- Iucn Glossary of Definitions - enDocument83 pagesIucn Glossary of Definitions - enAnwita JhaNo ratings yet
- Zurich Climate Change Whitepaper PDFDocument21 pagesZurich Climate Change Whitepaper PDFValerio ScaccoNo ratings yet
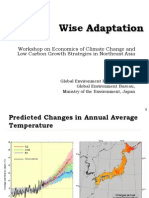
- Wise AdaptationDocument16 pagesWise AdaptationTA7465No ratings yet
- Climate Change 2023Document6 pagesClimate Change 2023melinda tannousNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Overview of Vulnerability and Adaptation FrameworksDocument47 pagesIntroduction and Overview of Vulnerability and Adaptation FrameworksMohamad soltaniNo ratings yet
- IF11827Document3 pagesIF11827sandra venturaNo ratings yet
- Adelphi Giz 2012 Msme Climate Risk StudyDocument110 pagesAdelphi Giz 2012 Msme Climate Risk StudyNiraj ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Climate Resilience-Definition From WikipediaDocument13 pagesClimate Resilience-Definition From WikipediaWalaa MahrousNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Adaptationin New Zealand NZCCChigh 1Document17 pagesClimate Change Adaptationin New Zealand NZCCChigh 1Vincent WilburNo ratings yet
- Resilience in ArchitectureDocument4 pagesResilience in Architecturer...No ratings yet
- Factsheet NCCAP 2011 2016Document8 pagesFactsheet NCCAP 2011 2016Michael SiaNo ratings yet
- Nature Docs 5Document7 pagesNature Docs 5Kasun HerathNo ratings yet
- Adaptation Responses and Vulnerability To Climate ChangeDocument12 pagesAdaptation Responses and Vulnerability To Climate ChangeBloodNo ratings yet
- Econ of AdaptationDocument11 pagesEcon of AdaptationppayonggNo ratings yet
- Business Climate Resilience: Thriving Through The TransformationDocument32 pagesBusiness Climate Resilience: Thriving Through The TransformationSaniy Amalia PriscilaNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument17 pagesBiotechnologyHameed arghandewalNo ratings yet
- Department of Defense Climate Adaptation PlanDocument32 pagesDepartment of Defense Climate Adaptation PlanCFHeatherNo ratings yet
- Salvador Resilience Strategy EnglishDocument27 pagesSalvador Resilience Strategy EnglishLucas OliveiraNo ratings yet
- IiedDocument4 pagesIiedMallik ArjunNo ratings yet
- TOO4TO Module 3 / Climate Change and Sustainability: Part 2Document34 pagesTOO4TO Module 3 / Climate Change and Sustainability: Part 2TOO4TONo ratings yet
- Leadership 1BDocument7 pagesLeadership 1BVarun AnilNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles EN v2 - 0Document8 pages10 Principles EN v2 - 0kamalmuraNo ratings yet
- What Is Climate Change?: PerspectivesDocument4 pagesWhat Is Climate Change?: PerspectivesCyanide048No ratings yet
- 17725IIEDDocument4 pages17725IIEDDea DharaNo ratings yet
- Tunisia in a Changing Climate: Assessment and Actions for Increased Resilience and DevelopmentFrom EverandTunisia in a Changing Climate: Assessment and Actions for Increased Resilience and DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- UseOfForceReviewBoard FINAL MolinaART2017 002Document11 pagesUseOfForceReviewBoard FINAL MolinaART2017 002LynsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document19 pagesChapter 18deysiNo ratings yet
- Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal DECISION NO. 945/15Document8 pagesWorkplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal DECISION NO. 945/15Franco DiLenaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan English PanelDocument3 pagesYearly Plan English PanelMahirah OthmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Solutions - 155Document5 pagesAssignment Solutions - 155Prof OliviaNo ratings yet
- Math Module 3.1 PDFDocument20 pagesMath Module 3.1 PDFHazer SaludezNo ratings yet
- Consumers in The Circular Economy: November 2019Document15 pagesConsumers in The Circular Economy: November 2019Eryck PangindianNo ratings yet
- Highway Traffic Analysis and DesignDocument7 pagesHighway Traffic Analysis and DesignROHIT GUPTA0% (1)
- Listening Skill Language InstructionDocument2 pagesListening Skill Language InstructionAinul MardhyahNo ratings yet
- Detailed Process For The Submission of Online Academic Counselor ApplicationDocument4 pagesDetailed Process For The Submission of Online Academic Counselor ApplicationnileshmsawantNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Theoretical Framework - LectureDocument13 pagesWeek 4 - Theoretical Framework - LectureRayan Al-ShibliNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Evaluation On School ReadinessDocument3 pagesMonitoring and Evaluation On School ReadinessArlene TubanNo ratings yet
- Opening The Sales CallDocument10 pagesOpening The Sales CallDIWAKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- BSBOPS501 - Assessment Task 1 Written Questions TemplateDocument7 pagesBSBOPS501 - Assessment Task 1 Written Questions TemplatebeaNo ratings yet
- Spain TodayDocument249 pagesSpain TodayJason ShilcockNo ratings yet
- Selectionguidelines PDFDocument23 pagesSelectionguidelines PDFTamilselvanNo ratings yet
- The Dark Side of AlliancesDocument15 pagesThe Dark Side of AlliancesOleksandra MalichenkoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Numeracy Skills AssessmentDocument4 pagesGuidelines For Numeracy Skills Assessmentcherry pastoralNo ratings yet
- Excellent Good Fair Needs Improvement PoorDocument2 pagesExcellent Good Fair Needs Improvement PoorAroma EyreNo ratings yet
- Cerificate No 7 To 100 PDFDocument124 pagesCerificate No 7 To 100 PDFanilNo ratings yet
- Music 9 Q3 M1Document3 pagesMusic 9 Q3 M1HPLaptop ReymarkNo ratings yet
- Motivation WorksheetDocument4 pagesMotivation WorksheetDragutescu Maria ElizaNo ratings yet
- Kobelco - Fullline Brochure Full Size ExcavatorsDocument8 pagesKobelco - Fullline Brochure Full Size ExcavatorsErlanda MaulanaNo ratings yet