Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unpacking of The Learning Standards
Uploaded by
Myla Rose AcobaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unpacking of The Learning Standards
Uploaded by
Myla Rose AcobaCopyright:
Available Formats
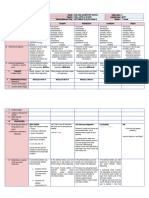
UNPACKING OF THE LEARNING STANDARDS
Subject: _________________ Grade Level: ____________ Teacher: _______________________________________
Chapter/Unit: ____________________________________
Quarter Period: ___________________________________
Content Standard Restated Content Standard Performance Standard Restated Performance Standard
The learners demonstrate an understanding of: The learner demonstrates The learners shall be able to: The learners shall be able to
understanding of key concepts of formulate and solve practical
key concepts Measures of Variation measures of variation in daily life. formulate and solve practical problems involving problems involving measures of
measures of variation in daily life. variation in daily life.
Big Ideas: Big Ideas:
Variation Practical problems
Acquisition: Students will learn… Transfer Goal:
Students will learn the key concepts of variation through , estimating the standard The learners will measures problems involving variations in daily life.
deviation of a population, based on sampledata. and solving problems involving measures of
variation in daily life.
Making Meaning: Students will understand… GRASPS:
Students will understand that probability is essential in nature of chance and variation Goal - to be able to solve practical problems
in daily life in order to be efficient. Role - Learners,
Audience - Mathematics Teachers
Situation -
Product - Practical Problems
Standards -
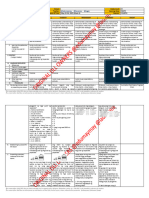
Learning Competencies
No. of
Competencies based on CG Deficiency
teachin No. of
(Arrange the competencies in order Words are ambiguous? A-M-T Focus Question linked
g hours No explicit connections among standards? Restated/Enhanced Competency teachin
based on the need of the curriculum based Missing standards? g hours Classification to School’s PVMGO
map) on CG Needs to breakdown the processes involve?
Illustrates an experiment, 1. Illustrates an experiment, outcome, sample
outcome, sample space and event 4 4 Acquisition
space and event
Counts the number of occurrences 4 4
2. Counts the number of occurrences of an
of an outcome in an experiment:
outcome in an experiment: (a) table; (b) tree Making
(a) table; (b) tree diagram; (c)
diagram; (c) systematic listing; and (d) Meaning
systematic listing; and (d)
fundamental counting principle.
fundamental counting principle.
Finds the probability of a simple 4 4 Making
3. Finds the probability of a simple event.
event. Meaning
Illustrates an experimental 4 4
4. Illustrates an experimental probability and Making
probability and a theoretical
a theoretical probability. Meaning
probability.
Solves problems involving 4 5. Solves problems involving probabilities of 4
probabilities of simple events. Transfer
simple events.
Added Competency/ies (those that are missing skills such as transfer competency)
Nota Bene: Mark the competencies considered as power competencies with asterisk (*)
You might also like
- DLL LC54 Fourth - Day1-4Document4 pagesDLL LC54 Fourth - Day1-4CM TumabieneNo ratings yet
- Math 8 DLL 4th Quarter Week 8 LC 54Document5 pagesMath 8 DLL 4th Quarter Week 8 LC 54Cesar Abajo Lingolingo Jr.No ratings yet
- DLL LC54 Fourth - Day5-6Document5 pagesDLL LC54 Fourth - Day5-6Rod Kennedy BergonioNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 9 Q1 Week 1Document5 pagesDLL Math 9 Q1 Week 1MarlaFirmalinoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Math 7 (1st-4th)Document15 pagesCurriculum Map Math 7 (1st-4th)Carmi Formentera LuchavezNo ratings yet
- Math 8 DLL 4th Quarter Week 7 LC 54Document4 pagesMath 8 DLL 4th Quarter Week 7 LC 54Cesar Abajo Lingolingo Jr.No ratings yet
- DLL For Math 8 4thQDocument4 pagesDLL For Math 8 4thQrolando palacio100% (1)
- DLL - math8SPhLC54 - FOURTH - 8th WeekDocument4 pagesDLL - math8SPhLC54 - FOURTH - 8th WeekMaricel Tarenio MacalinoNo ratings yet
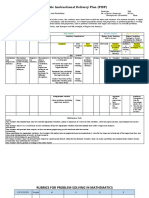
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Document3 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Arniel LlagasNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 5 MathDocument11 pagesDLL Week 5 Mathcarl justin de diosNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 9 Q1 Week 2Document5 pagesDLL Math 9 Q1 Week 2MarlaFirmalino100% (2)
- Stat&Prob 3rd Week 4Document3 pagesStat&Prob 3rd Week 4Mark Lenon VerdaderoNo ratings yet
- G10 Unit 1 Ext - STD Periodic Phenomena Unit PlannerDocument4 pagesG10 Unit 1 Ext - STD Periodic Phenomena Unit PlannerYueping ShanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PDFDocument6 pagesLesson Plan PDFFlorita LagramaNo ratings yet
- DLL - MATH - 3 - Q4 - W4 - Solves Routine and Non-Routine Problems Involving Capacity Measure - @edumaymay@lauramos@angieDocument7 pagesDLL - MATH - 3 - Q4 - W4 - Solves Routine and Non-Routine Problems Involving Capacity Measure - @edumaymay@lauramos@angiejimNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesI. ObjectivesDeorena CagadasNo ratings yet
- BM 12 PT 2 - Activity SheetDocument3 pagesBM 12 PT 2 - Activity SheetkweenNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document11 pagesWeek 4Coco LlameraNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 10 Week 1Document4 pagesDLL Grade 10 Week 1Jaymar SarvidaNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4Document3 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4renliejanepNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - SyllabusDocument4 pagesGroup 1 - SyllabusAnna Katherine ArsolonNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. Objectivesanon_874462606No ratings yet
- WHLP Math 7 Q1 W5Document3 pagesWHLP Math 7 Q1 W5MMC HUMSS 11No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: ObjectivesDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: ObjectivesErwin B. NavarroNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics-4 - Q2 Njov. 7-11Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics-4 - Q2 Njov. 7-11Mavic SilvaNo ratings yet
- New DLL Blank FormDocument9 pagesNew DLL Blank FormHero MirasolNo ratings yet
- G5 Week2 DLL in Math With 2C2I1R Pedagogical ApproachDocument8 pagesG5 Week2 DLL in Math With 2C2I1R Pedagogical ApproachRichard Bareng SNo ratings yet
- DLL9 2ndQuarterWeek4Document3 pagesDLL9 2ndQuarterWeek4Ramon CasildoNo ratings yet
- Cabuloan National High School: Week 3Document8 pagesCabuloan National High School: Week 3Pia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- LDM Course 2 (Module 2)Document6 pagesLDM Course 2 (Module 2)LEONARDO BAÑAGANo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 4 - Q2 - W1Document3 pagesDLL - Math 4 - Q2 - W1Marie MontanaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map: First QuarterDocument2 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map: First QuarterTwinkz Oberio BarcomaNo ratings yet
- DLP 4thDocument7 pagesDLP 4thCelmariza AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Revised Gen. Math Adaptive-Curriculum-July 2021Document5 pagesRevised Gen. Math Adaptive-Curriculum-July 2021Nika BellosilloNo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 4 - Q2 - W1Document5 pagesDLL - Math 4 - Q2 - W1Allyza Fae DavidNo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 9 - Q1 - W2.1Document5 pagesDLL - Math 9 - Q1 - W2.1MarlaFirmalino94% (17)
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W6Document6 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W6MarichanLoocNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics-5 Q1 W8Document10 pagesDLL Mathematics-5 Q1 W8Alberto SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Grade-10-4th-Quarter-Week 4 2023 4Document2 pagesGrade-10-4th-Quarter-Week 4 2023 4ROLLY APDO100% (1)
- DLL - Mathematics 4 - Q2 - W1Document5 pagesDLL - Mathematics 4 - Q2 - W1Alliah Jessa PascuaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Gen Math-Week 4Document5 pagesDLL - Gen Math-Week 4Jennelyn JacintoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 4 - Q2 - W1Document5 pagesDLL - Math 4 - Q2 - W1Prints CharmingNo ratings yet
- DLL - Gen Math-Week 3Document5 pagesDLL - Gen Math-Week 3Jennelyn JacintoNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 5 q1 w6Document9 pagesDLL Mathematics 5 q1 w6Delta Delta SieraNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument9 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogJessmiel LabisNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 5 q1 w9Document8 pagesDLL Mathematics 5 q1 w9Gesaly Ocena BorromeoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W7Document6 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W7JOSHUA CARRERA100% (1)
- The Sum Ans Product of The Roots of Quadratic EquationsDocument5 pagesThe Sum Ans Product of The Roots of Quadratic EquationsNono, Kathleen Joyce I.No ratings yet
- Q1 W4 MathDocument15 pagesQ1 W4 MathBernadeth SanchezNo ratings yet
- Dll... Math (Sept.5-9,2016) RevisedDocument5 pagesDll... Math (Sept.5-9,2016) RevisedFlorecita CabañogNo ratings yet
- Week 4 MATHDocument5 pagesWeek 4 MATHCharles lbaoNo ratings yet
- GRADE - VI - Daily Lesson Log June (Week 1) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument5 pagesGRADE - VI - Daily Lesson Log June (Week 1) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayRicaSanJose100% (1)
- Grades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I. Objectives Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument19 pagesGrades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I. Objectives Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayRichimon Remigio Licerio100% (2)
- DLL MathDocument9 pagesDLL MathEllanie Pujalte MontebonNo ratings yet
- Stat 2Document6 pagesStat 2demrickNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 5 q1 w8Document10 pagesDLL Mathematics 5 q1 w8claire cabatoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 10 - Q3Document3 pagesDLL - Math 10 - Q3Ronnel Manilag Atienza92% (12)
- RUBRICDocument1 pageRUBRICMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument1 pageLetterMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Variables Prob DistributionDocument3 pagesVariables Prob DistributionMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- RRL RelatedDocument2 pagesRRL RelatedMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Subject Description: at The End of The Course, The Students Must Be Able To Apply Concepts and Solve Problems Involving Conic Sections, Systems ofDocument5 pagesSubject Description: at The End of The Course, The Students Must Be Able To Apply Concepts and Solve Problems Involving Conic Sections, Systems ofMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Auto LetterDocument2 pagesAuto LetterMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Cidam (Random - Hypo)Document12 pagesCidam (Random - Hypo)Myla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Making A Poster Rubric 1Document1 pageMaking A Poster Rubric 1Myla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- The Slums Reaction Paper PDFDocument2 pagesThe Slums Reaction Paper PDFharperboy0921100% (2)
- 2021MATHADVHO3.5 - Unit Performance Task Template Design ThinkingDocument1 page2021MATHADVHO3.5 - Unit Performance Task Template Design ThinkingMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument10 pagesPerformance TaskRhea Glipo100% (2)
- 1st Quarter Exam 2020 (Mapeh 8, Econ, Pre-Cal)Document5 pages1st Quarter Exam 2020 (Mapeh 8, Econ, Pre-Cal)Myla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Introduction On Applied Economics: Learning TargetsDocument8 pagesIntroduction On Applied Economics: Learning TargetsMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Sample Diary Curriculum Map SUBJECT: Mathematics QUARTER: Fourth Quarter Grade Level: 7 TOPIC: Measures of VariationDocument2 pagesSample Diary Curriculum Map SUBJECT: Mathematics QUARTER: Fourth Quarter Grade Level: 7 TOPIC: Measures of VariationMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- IDENTIFICATION. Identify The Following Questions Being Asked. (2 Points Each)Document5 pagesIDENTIFICATION. Identify The Following Questions Being Asked. (2 Points Each)Myla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Module MR. BACCAYDocument44 pagesGrade 8 Module MR. BACCAYMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- CSUKs Algorithm Writing Guide and WorkbookDocument73 pagesCSUKs Algorithm Writing Guide and Workbooksaimaagarwal220508No ratings yet
- Gas Ab 1Document24 pagesGas Ab 1John Leonard FazNo ratings yet
- Applying Finite Element Based Limit Load Analysis Methods To Structures Under Dynamic LoadsDocument5 pagesApplying Finite Element Based Limit Load Analysis Methods To Structures Under Dynamic LoadsM Afif HidayatNo ratings yet
- Proc ReportDocument7 pagesProc ReportrajeshdatastageNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Circuits Objective QuestionsDocument9 pagesDigital Logic Circuits Objective Questionssundar_mohan_2100% (2)
- UTS Bahasa Inggris AnalisisDocument4 pagesUTS Bahasa Inggris AnalisisCuapCuapIndyNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Tubular Flow Reactor - ManuscriptDocument8 pagesLab 4 - Tubular Flow Reactor - ManuscriptppppNo ratings yet
- A Study of Association Between Fingernail Elements and OsteoporosisDocument11 pagesA Study of Association Between Fingernail Elements and OsteoporosisangelikjoliehNo ratings yet
- Lectures On Communicative AlgebraDocument64 pagesLectures On Communicative Algebramimi_loveNo ratings yet
- Present ValueDocument11 pagesPresent ValueJazine John AmbajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document34 pagesChapter 8Ummu Fahmi FikriyantoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument11 pagesPhysicszap_123No ratings yet
- Scavenger Hunt Multiplying and Dividing ExponentsDocument20 pagesScavenger Hunt Multiplying and Dividing ExponentsRoss HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Second LawDocument32 pagesChapter 7-Second LawIsrael EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- ANNDocument37 pagesANNSohan ReddyNo ratings yet
- 271 - AI Lect Notes PDFDocument128 pages271 - AI Lect Notes PDFkiransangeetaNo ratings yet
- Ensemble Learning Algorithms With Python Mini CourseDocument20 pagesEnsemble Learning Algorithms With Python Mini CourseJihene BenchohraNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis JD - CR - GS - FinalDocument185 pagesPHD Thesis JD - CR - GS - FinalmvillabrNo ratings yet
- 1st 4 PagesDocument5 pages1st 4 PagesAn Neh GynNo ratings yet
- Block Cipher PrinciplesDocument5 pagesBlock Cipher PrinciplesSatya NarayanaNo ratings yet
- FPGA Simon Game With VGA PDFDocument46 pagesFPGA Simon Game With VGA PDFBryan ToapaxiNo ratings yet
- Counting Trees Using Segmentation and Vectorization in SAGA GisDocument6 pagesCounting Trees Using Segmentation and Vectorization in SAGA GisCassie SmithNo ratings yet
- DICE ManualDocument102 pagesDICE ManualMarcela Barrios RiveraNo ratings yet
- Branson 1965 PDFDocument16 pagesBranson 1965 PDFTatiane MagaNo ratings yet
- Basic Technical Mathematics With Calculus Si Version Canadian 10th Edition Washington Solutions ManualDocument39 pagesBasic Technical Mathematics With Calculus Si Version Canadian 10th Edition Washington Solutions Manualpatentlymoietypuhae100% (14)
- Valuation of SecuritiesDocument31 pagesValuation of Securitiesmansi sainiNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagrams and Probability W S 2Document4 pagesVenn Diagrams and Probability W S 2api-314332531No ratings yet
- MELC 2 Use Conditionals in Expressing ArgumentsDocument2 pagesMELC 2 Use Conditionals in Expressing ArgumentsMar Sebastian100% (1)
- Nav Arch QP Updated November 2022Document60 pagesNav Arch QP Updated November 2022Saurabh Singh RawatNo ratings yet