Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reflection Paper - Sotto - John Uriel
Uploaded by
John SottoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reflection Paper - Sotto - John Uriel
Uploaded by
John SottoCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics - It encompasses the study of matter, its motion and behavior along with energy and
force.
• Classical Physics - It primarily deals with different laws of motion and gravitation
• Modern Physics - is primarily centered around the two theories of relativity and quantum
mechanics.
• Nuclear Physics - This is a branch of physics that is concerned with the constituents, structure,
behavior and interactions of atomic nuclei.
• Atomic Physics - It is concerned with the composition of the atom apart from the nucleus.
• Mechanical Physics - is concerned with understanding the motion of material objects and how
they are influenced by forces
• Mechanics - Mechanics is a branch of physics that focuses on the movement and motion of
physical objects under a force and when at rest.
• Acoustics - is a branch of physics that studies sound.
• Thermodynamics - is a branch of physics concerned with heat and other forms of energy.
• Astrophysics - is a subset of astronomy that primarily studies celestial objects and their
composition by applying the laws and principles of physics to explain the phenomenon.
Optics - is a significant Science branch of physics that studies light and its properties.
Wave - is a disturbance that moves energy from one place to another.
Electromagnetic Spectrum - is the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to
frequency or wavelength.
Light Interactions - are fundamentally quantum electrodynamical, and in many cases, are
described as quantum transitions by electrons, accompanied by the emission, absorption or
scattering of quanta of the electromagnetic field in vacuum.
• Reflected - electromagnetic radiation/light bounces off the surface of the object.
• Absorbed - energy from the electromagnetic radiation/light is taken up/‘soaked up’ by the
object
• Transmitted - when the light moves through the object.
• Diffracted - the spreading/bending of light as it goes through openings or around the edges of
objects.
• Refracted - the bending of transmitted light as it travels across the boundary of one material
into another material in which its speed is different.
Lens - is a transparent device with two curved surfaces, usually made of glass or plastic, that
uses refraction to form an image of an object.
Mirrors - which have curved surfaces designed to reflect rays, also form images.
Ray Diagram - is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a person to view a
point on the image of an object.
You might also like
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentsengco_rizzajaneNo ratings yet
- What Type of Subject Is Physics?Document3 pagesWhat Type of Subject Is Physics?Darry BlanciaNo ratings yet
- FisicsDocument2 pagesFisicssalomon.pupoNo ratings yet
- IntroductoryDocument14 pagesIntroductorymohammad amaraNo ratings yet
- q3 PPT Physics and Its BranchesDocument19 pagesq3 PPT Physics and Its BranchesesperancillababyNo ratings yet
- Outline of PhysicsDocument56 pagesOutline of Physicsaditya00012No ratings yet
- Outline of Physics: Physics - Natural Science That Involves The Study of MatterDocument11 pagesOutline of Physics: Physics - Natural Science That Involves The Study of MatterroyNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes TemplateDocument1 pageCornell Notes TemplateZurielle LuboaNo ratings yet
- Physics and Its BranchesDocument6 pagesPhysics and Its Branchesphysics_freak100% (3)
- Forging New Generations of EngineersDocument28 pagesForging New Generations of EngineersDarshan MbNo ratings yet
- Particles of Matter Have Space Between ThemDocument2 pagesParticles of Matter Have Space Between ThemDeepak Raj100% (2)
- Phyiscs StuffDocument1 pagePhyiscs StuffredinfinitexNo ratings yet
- DictionaryDocument6 pagesDictionaryRaven AmparoNo ratings yet
- Physical WorldDocument15 pagesPhysical WorldKashyap PatelNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Physics Notes QuestionsDocument100 pages1st Year Physics Notes QuestionsAnwar Textiles100% (1)
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To General Physics & Scientific MethodDocument24 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To General Physics & Scientific MethodJamicah Nicole SolisNo ratings yet
- GEN P6 ReviewerDocument11 pagesGEN P6 ReviewerSTO. DOMINGO, Aneka MaghintayNo ratings yet
- Guia Physics ChrisDocument2 pagesGuia Physics ChrisAndres AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Cabang Ilmu Fisika (Pertemuan 2)Document22 pagesCabang Ilmu Fisika (Pertemuan 2)alfi_hamidahNo ratings yet
- Passing PhysicsDocument6 pagesPassing PhysicsAkhilesh KishunNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Welcome ToDocument5 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Welcome ToFlorelen GarbeNo ratings yet
- NovelDocument2 pagesNovelMeaniizz KpNo ratings yet
- Principle of Food AnalysisDocument60 pagesPrinciple of Food AnalysisMuzahid IslamNo ratings yet
- General PhysicsDocument3 pagesGeneral PhysicsPablo IskomorinoNo ratings yet
- General Physics ReviewerDocument9 pagesGeneral Physics ReviewerSTO. DOMINGO, Aneka MaghintayNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument17 pagesSCIENCENIÑA JANE BARREDONo ratings yet
- The Scope of PhysicsDocument23 pagesThe Scope of PhysicsDeane Marc TorioNo ratings yet
- Types of Waves EnergyDocument4 pagesTypes of Waves Energyjayson pintorNo ratings yet
- Armalyn Simora IVDocument2 pagesArmalyn Simora IVNylamra AromisNo ratings yet
- Sci8 1stqtrDocument6 pagesSci8 1stqtr10B-21 Harry VillaluzNo ratings yet
- 2 Major Fields of Physics: 1. Classical Physics - Physics That Does Not Make Use of Quantum Mechanics or The Theory ofDocument2 pages2 Major Fields of Physics: 1. Classical Physics - Physics That Does Not Make Use of Quantum Mechanics or The Theory ofDennis VillasNo ratings yet
- Tarja Kallio-Tamminen - Dynamic Universe Andthe Conception of RealityDocument25 pagesTarja Kallio-Tamminen - Dynamic Universe Andthe Conception of Reality939392No ratings yet
- Physics ConceptsDocument1 pagePhysics Conceptstemp manNo ratings yet
- Physical World: Genius Physics Class XIDocument2 pagesPhysical World: Genius Physics Class XIAryan MahajanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction, Big Bang Theory FormationDocument29 pagesLesson 1 Introduction, Big Bang Theory FormationxylemNo ratings yet
- Definition of Mathematics, Physics, and EngineeringDocument7 pagesDefinition of Mathematics, Physics, and EngineeringBrandon DaseNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument5 pagesPHYSICSHarris AbdulganiNo ratings yet
- Intro Branches of PhysicsDocument9 pagesIntro Branches of PhysicsZenda Marie Facinal SabinayNo ratings yet
- OptDocument3 pagesOptklkl mnkNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument1 pagePHYSICSzoya last nameNo ratings yet
- Branches of PhysicsDocument2 pagesBranches of PhysicsYrrej Onivol OnazolNo ratings yet
- Lorentz TransformationDocument19 pagesLorentz TransformationSehrish MalikNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument94 pagesOpticsshahadaljobouryNo ratings yet
- Radiation: Information From The CosmosDocument56 pagesRadiation: Information From The Cosmosglydel fedelicioNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument3 pagesPhysical ScienceRIALINE SACOPONNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1illumination and General Lighting SystemDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Part 1illumination and General Lighting Systemmahato4120No ratings yet
- Physics Part Two Dictionary - Natural Science: Grow Your Vocabulary, #37From EverandPhysics Part Two Dictionary - Natural Science: Grow Your Vocabulary, #37No ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument2 pagesPhysics NotesPaula Castellar FandosNo ratings yet
- 5aba10f2e4b037820c381f3b 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341Document9 pages5aba10f2e4b037820c381f3b 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341Prenshi ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- The Basic Theories of LightDocument33 pagesThe Basic Theories of LightJan Fern HistorilloNo ratings yet
- Physics Class XI SCDocument13 pagesPhysics Class XI SCAyush Abhinandan RathNo ratings yet
- Magnet Magnetic Field Electric Current: Electromagnet Is A Type ofDocument5 pagesMagnet Magnetic Field Electric Current: Electromagnet Is A Type ofChris Loidz GanadoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysicsDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Physicsahmdhjw24No ratings yet
- Rad PhysicsDocument5 pagesRad PhysicsSoleil SierraNo ratings yet
- Physics Class NotesDocument2 pagesPhysics Class Notesainur.seidullaNo ratings yet
- Senior High School A.Y 2020 - 2021 Modern Physics: RELATIVITY I. Modern PhysicsDocument8 pagesSenior High School A.Y 2020 - 2021 Modern Physics: RELATIVITY I. Modern PhysicsKyle Cedric MitalNo ratings yet
- Physics - Laws of Motion-LightDocument4 pagesPhysics - Laws of Motion-LightLara BalangiaoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 q2 With TOSDocument6 pagesSCIENCE 10 q2 With TOSGrace Mary Tedlos BoocNo ratings yet
- Seismic Principles: - Chapter 1Document13 pagesSeismic Principles: - Chapter 1Mahardika Aji KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Light QuizDocument2 pagesLight QuizZariya GabrielleNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument37 pagesPadhle 10th - Light - Reflection & Refractionved bhaskerNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Light and OpticsDocument71 pagesUnit-4 Light and OpticsjeyaselvamuruganNo ratings yet
- TG - Science 10 - Q2 PDFDocument137 pagesTG - Science 10 - Q2 PDFKristian Lapasaran100% (4)
- 0708 Optics Mirrors and LensesDocument21 pages0708 Optics Mirrors and LensesPedro AldrinerNo ratings yet
- Nilsson 2015Document10 pagesNilsson 2015JOHAN SEBASTIAN SANTANA GILNo ratings yet
- RF-IR Stealth (Techniques/Benefits)Document50 pagesRF-IR Stealth (Techniques/Benefits)Himanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- Surface QualityDocument35 pagesSurface Qualityroyce_ss75% (4)
- Experiment No.1 Measurement of Length, Mass, Volume and DensityDocument3 pagesExperiment No.1 Measurement of Length, Mass, Volume and DensityRichard SerquinaNo ratings yet
- A New Concept of Headlight Light Guide HeadlampDocument7 pagesA New Concept of Headlight Light Guide Headlampkeval patelNo ratings yet
- Cbjescco11 PDFDocument10 pagesCbjescco11 PDFneomatrix70No ratings yet
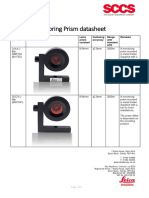
- SCCS Monitoring Prism Datasheet: Reflector (SAP#) Leica Prism Constant Centering Accuracy Range With Standard ATR RemarksDocument9 pagesSCCS Monitoring Prism Datasheet: Reflector (SAP#) Leica Prism Constant Centering Accuracy Range With Standard ATR RemarksP DNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Sapkal Knowledge HubDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Sapkal Knowledge HubMaqsood 9682619146No ratings yet
- Inf Geo4310 2009 Lecture 5Document18 pagesInf Geo4310 2009 Lecture 5Rohith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Metamaterial-Based Patch Antenna With Wideband RCS Reduction and Gain Enhancement Using Improved Loading MethodDocument8 pagesMetamaterial-Based Patch Antenna With Wideband RCS Reduction and Gain Enhancement Using Improved Loading MethodTanvi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Radar Cross Section Reduction: April 2013Document17 pagesRadar Cross Section Reduction: April 2013Ahmed RamiNo ratings yet
- Newport Projects in Optics - Good For Literature ReviewDocument88 pagesNewport Projects in Optics - Good For Literature ReviewEngr SalimNo ratings yet
- Gonioscopy1 PDFDocument74 pagesGonioscopy1 PDFhestisuzetaNo ratings yet
- HSP Physics f4 2Document27 pagesHSP Physics f4 2Staff SmkaaNo ratings yet
- CRIMINALISTICS EditedDocument70 pagesCRIMINALISTICS EditedOnin RelacionNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 4Document7 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 4fordalNo ratings yet
- Grade: Vii M.MARKS: 90 Date: TIME: 2Hrs 30 MinDocument7 pagesGrade: Vii M.MARKS: 90 Date: TIME: 2Hrs 30 MinJacob ChakolaNo ratings yet
- S3 Physics - 201617 - Light - STUDENT - 2016augDocument92 pagesS3 Physics - 201617 - Light - STUDENT - 2016augjeannieqintszyanNo ratings yet
- Selina Refraction-of-Light-at-Plane-SurfacesDocument51 pagesSelina Refraction-of-Light-at-Plane-SurfacesOverRush Amaresh100% (1)
- National Curriculum of Bangladesh HSC Physics Syllabus PDFDocument4 pagesNational Curriculum of Bangladesh HSC Physics Syllabus PDFfahim faisal100% (1)
- Fiber Optic Lab ManualDocument68 pagesFiber Optic Lab Manualregio122No ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Grade VIII ScienceDocument63 pagesLaboratory Manual For Grade VIII SciencedeeptiNo ratings yet