Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bromide - For IR: Colorimetry
Uploaded by
Lia KimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bromide - For IR: Colorimetry
Uploaded by
Lia KimCopyright:
Available Formats
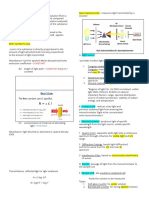
Clinical Chemistry Laboratory – Spectrophotometer ♥ K.A.S.
A, RMT, IMT ♥
COLORIMETRY Monochromator – isolates specific
wavelengths of light
- Involves the Beer’s law o PRISM – triangular or wedged piece
- The constituent measured is colored of transparent material
a. Glass prism – for VIS
BEER’S LAW
b. Quartz prism – for UV
- States that the CONCENTRATION of an analyte
c. Sodium chloride or potassium
is DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL to the amount of
bromide – for IR
light ABSORBED
o GRATING – grooved piece of
- States that the CONCENTRATION of an analyte
transparent material which may
is INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL to the logarithm
contain about 3000 or more grooves
of light TRANSMITTED
per mm. Each groove functions as an
ABSORBANCE
individual prism.
- Amount of light blocked by the solution
TRANSMITTANCE Exit slit – controls the amount of light that
- Ratio of the transmitted light to the incident passes through the cuvette
light Cuvette/analytical cell/absorption cell –
holds the solution whose concentration is to
𝟏𝟎𝟎 be assayed
A = abc = −𝒍𝒐𝒈 %𝑻 = 2 – log %T
o Aluminosilicate glass – strong acidic
o A = absorbance/optical density
solutions; resistant to etching
o a = coefficient of absorptivity
o Borosilicate glass – for strong
o b = path length of cuvet
alkaline solutions
o c = concentration of the analyte
o Quartz or plastic – for UV; glass is not
o %T = percent transmittance
recommended because it blocks the
VISUAL COLORIMETRY passage of UV light
- The color intensity of the solution is matched Photodetector – measures the intensity of
against a standard solution the light from the solution
- Less precise because it relies on the human o Barrier layer cell – operate on the
eye for interpretation principle that when light falls on
- Example: Dubowski (Duboscq) colorimeter certain metals, electron flows in
proportion to the intensity of light
o Photomultiplier tubes – electron
PHOTOELECTRIC COLORIMETRY
tubes capable of converting light
- Involves the use of a photoelectric device or
energy into an electric signal
detector to measure light intensity
Readout device – numerically presents the
(independent of wavelength)
absorbance or percent transmittance
SPECTROPHOTOMER
- Used to measure the light transmitted by a BLANK CORRECTION
solution to determine the concentration of the Blanking – ensures the accuracy of the results by
light-absorbing substance in the solution eliminating interfering substances inherent with the
sample or the reagent
COMPONENTS OF SPECTROPHOTOMETER 1. Reagent blank – corrects for the absorbance
Light Source – provides the radiant energy interference caused by the color of the
o UV reagent
o VIS 2. Sample blank – used to correct non-specific
o IR absorbance of substances in the sample
Entrance Slit – minimizes stray light emitted (hemoglobin, bilirubin, lipids)
by the lamp and prevents scattered light 3. Water blank – sets the spectrophotometer
from entering the monochromator at zero absorbance
You might also like
- Exam Style Answers 12 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 12 Asal Physics CBAnshul Shah50% (2)
- Instrumentation Lecture IV MidtermsDocument15 pagesInstrumentation Lecture IV MidtermsArmie Joy ManingatNo ratings yet
- CC LAB SpectrophotometerDocument2 pagesCC LAB SpectrophotometerNichole T.No ratings yet
- Electronic Spectroscopy UV-VisibleDocument28 pagesElectronic Spectroscopy UV-VisibleKarthikeyan G100% (1)
- INSTRUMENTATION Lab MBIO PDFDocument4 pagesINSTRUMENTATION Lab MBIO PDFjelo cruzNo ratings yet
- Spectrochemical AnalysisDocument6 pagesSpectrochemical Analysisroku shinNo ratings yet
- Hotometry: Presenter: Dr. Anurag Yadav Moderator: Mr. Arun KumarDocument45 pagesHotometry: Presenter: Dr. Anurag Yadav Moderator: Mr. Arun KumarOsmmn KaleNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Laboratory - SpectrophotometryDocument2 pagesClinical Chemistry Laboratory - SpectrophotometrynikkiNo ratings yet
- Important Concepts in UV-Vis and IR SpectrosDocument53 pagesImportant Concepts in UV-Vis and IR SpectrosmarkkkkkNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy: Spectral Distribution of Radiant EnergyDocument28 pagesSpectroscopy: Spectral Distribution of Radiant EnergyKarim BiswasNo ratings yet
- 1 PPSC UVVis and FTIR 1Document43 pages1 PPSC UVVis and FTIR 1Naeem AnwarNo ratings yet
- 6 Dan 7. Bahan Kuliah GLP, SpektroDocument30 pages6 Dan 7. Bahan Kuliah GLP, SpektroFildzah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Technology For Spectroscopic Techniques (UV-Vis Spectrophotometry)Document6 pagesTechnology For Spectroscopic Techniques (UV-Vis Spectrophotometry)Sosuke AizenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26/27: Molecular Absorption SpectrometryDocument14 pagesChapter 26/27: Molecular Absorption SpectrometryS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Color Wavelength NM Violet Blue Cyan Green Yellow Orange RedDocument4 pagesColor Wavelength NM Violet Blue Cyan Green Yellow Orange RedJhenard John Lansangan BeltranNo ratings yet
- Dr. Tayyaba Noor School of Chemical and Materials Engineering National University of Sciences and Technology IslamabadDocument25 pagesDr. Tayyaba Noor School of Chemical and Materials Engineering National University of Sciences and Technology Islamabadabc xyzNo ratings yet
- Absorbance Rather Than Transmittance Is Most Useful In: SpectrophotometryDocument3 pagesAbsorbance Rather Than Transmittance Is Most Useful In: SpectrophotometryDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- To Print Analytical MethodsDocument5 pagesTo Print Analytical MethodsShanelle ValeñaNo ratings yet
- 0 Shimadzu Basic Spectro - UV IR AASDocument36 pages0 Shimadzu Basic Spectro - UV IR AASAmandaNo ratings yet
- A Short Introduction To Ultraviolet-Visible SpectrosDocument2 pagesA Short Introduction To Ultraviolet-Visible SpectrosJafar MohammadNo ratings yet
- Analytical Instruments: Reference Text: R S Khandpur "Handbook of Analytical Instrumentation"Document78 pagesAnalytical Instruments: Reference Text: R S Khandpur "Handbook of Analytical Instrumentation"chakrimvnNo ratings yet
- Uvvis 1Document4 pagesUvvis 1AlejandraNo ratings yet
- Radiant Power: Time Solute Spends in Stationary Phase Time Solute Spends in Mobile PhaseDocument5 pagesRadiant Power: Time Solute Spends in Stationary Phase Time Solute Spends in Mobile PhaseDaisy Shane AtayanNo ratings yet
- PH 109 - PrelimsDocument3 pagesPH 109 - PrelimsbaytadokiNo ratings yet
- CCP 4.1 - PRELIMS (Incomplete)Document3 pagesCCP 4.1 - PRELIMS (Incomplete)baytadokiNo ratings yet
- Analytical MethodsDocument15 pagesAnalytical MethodsPojangNo ratings yet
- CCP 4.1 - PRELIMS (Updated)Document4 pagesCCP 4.1 - PRELIMS (Updated)baytadokiNo ratings yet
- Uv-Visible Spectroscopy TheoryDocument8 pagesUv-Visible Spectroscopy TheoryHamdan afzalNo ratings yet
- Embryo Lec Reviewer Chapter 5Document9 pagesEmbryo Lec Reviewer Chapter 5Erika Mae Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- Karakterisasi - Material - UV-Visible Spectroscopy - 240206 - 114342Document22 pagesKarakterisasi - Material - UV-Visible Spectroscopy - 240206 - 114342friska.ziliwu2590No ratings yet
- Lec Module 1 Pharm AnalysisDocument20 pagesLec Module 1 Pharm AnalysisJonas BorjNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometry: Dr. Danish Khan Department of Biochemistry Uims, PrayagrajDocument21 pagesSpectrophotometry: Dr. Danish Khan Department of Biochemistry Uims, PrayagrajPranjul MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit - IDocument19 pagesUnit - IManikandan KNo ratings yet
- INSTRUMENTATIONDocument43 pagesINSTRUMENTATIONLawrence Genelago GamboaNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy-2 PDFDocument60 pagesAtomic and Molecular Spectroscopy-2 PDFHaseeb HaiderNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Spectroscopy & Molecular Spectroscopy: Analytical Chemistry LectureDocument39 pagesAn Introduction To Spectroscopy & Molecular Spectroscopy: Analytical Chemistry Lecture陳庠廷No ratings yet
- UV VIS Phenol LabDocument6 pagesUV VIS Phenol LabJoão Paulo FioriNo ratings yet
- UV Vis InstrumentationDocument17 pagesUV Vis InstrumentationKD LoteyNo ratings yet
- Biosensors: Wei-Chih Wang Southern Taiwan University of TechnologyDocument31 pagesBiosensors: Wei-Chih Wang Southern Taiwan University of TechnologyDann DomeNo ratings yet
- Uv Visible Spectroscopy : By:-Sarika Singh. Fy M-Pharmacy (QAT)Document32 pagesUv Visible Spectroscopy : By:-Sarika Singh. Fy M-Pharmacy (QAT)aditya mhatre100% (2)
- Uv Visible SpectrosDocument48 pagesUv Visible SpectrosDhanvanth100% (7)
- High Energy PMT TPMZ0003EDocument76 pagesHigh Energy PMT TPMZ0003Egoutu41No ratings yet
- DG-Lecture 1 - UV-VISDocument35 pagesDG-Lecture 1 - UV-VISArjun MaharajNo ratings yet
- Nov-UV-Spectro B. TechDocument28 pagesNov-UV-Spectro B. Techmsk3kiidNo ratings yet
- UV-visible Molecular Absorption SpectrosDocument33 pagesUV-visible Molecular Absorption SpectrosaargovindNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometers: Robert M. DondelingerDocument6 pagesSpectrophotometers: Robert M. DondelingerJorge SaenzNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronic Detectors: OutlineDocument54 pagesOptoelectronic Detectors: OutlineShivam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Polymer Analysis by UVDocument10 pagesPolymer Analysis by UVnethumini GunawardanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture4-Linkage in AADocument15 pagesLecture4-Linkage in AAGOCNo ratings yet
- ComponentsPrincipleandApplicationsofUVVis Spectophotometer DRSJDocument20 pagesComponentsPrincipleandApplicationsofUVVis Spectophotometer DRSJAnurak OnnnoomNo ratings yet
- CHEM F313: Instrumental Methods of Analysis: UV-Vis Spectrometry (Contd.)Document17 pagesCHEM F313: Instrumental Methods of Analysis: UV-Vis Spectrometry (Contd.)AYUSH SHARMANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Analytical MethodsDocument104 pagesChapter 4 Analytical MethodsCL SanchezNo ratings yet
- Spectro Photo Me TryDocument4 pagesSpectro Photo Me TryRajsuryan SinghNo ratings yet
- ComponentsPrincipleandApplicationsofUVVis Spectophotometer DRSJDocument20 pagesComponentsPrincipleandApplicationsofUVVis Spectophotometer DRSJgigigiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry I Analytic Techniques: Violet BlueDocument5 pagesClinical Chemistry I Analytic Techniques: Violet BlueBenedict EntrampasNo ratings yet
- UV - Vis Spectroscopy: Mjla2015 - Spectrometric Methods 1Document15 pagesUV - Vis Spectroscopy: Mjla2015 - Spectrometric Methods 1Angeli Marie PadillaNo ratings yet
- 3 CC1Document6 pages3 CC1marianNo ratings yet
- FTIR SpectrosDocument26 pagesFTIR SpectroshaiderrazauberNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Analytical Biochemistry: Chapter - 1 Spectrophotometry and ColorimetryDocument35 pagesLecture Notes Analytical Biochemistry: Chapter - 1 Spectrophotometry and ColorimetryHarpreet Singh100% (3)
- An Introduction to Ultrathin Organic Films: From Langmuir--Blodgett to Self--AssemblyFrom EverandAn Introduction to Ultrathin Organic Films: From Langmuir--Blodgett to Self--AssemblyNo ratings yet
- Gemmological Instruments: Their Use and Principles of OperationFrom EverandGemmological Instruments: Their Use and Principles of OperationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- IJETAEHorn Antennadesign The Conceptsand ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesIJETAEHorn Antennadesign The Conceptsand ConsiderationsIbraheim ZidanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Transmission Characterisrtics of Optical Fiber-Bending (OFC)Document10 pagesLecture 12 - Transmission Characterisrtics of Optical Fiber-Bending (OFC)samarthNo ratings yet
- Quantel Optimis II Service Manual 51 60Document10 pagesQuantel Optimis II Service Manual 51 60Vladimir LevchenkoNo ratings yet
- Solar Simulation: Oriel Product TrainingDocument32 pagesSolar Simulation: Oriel Product TrainingrickNo ratings yet
- Defectoscopy Lab - NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTS OF THE ALLOYSDocument4 pagesDefectoscopy Lab - NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTS OF THE ALLOYScecilchifticaNo ratings yet
- CH6 Electromagnetic InductionDocument45 pagesCH6 Electromagnetic InductionJignesh Bhavsar100% (1)
- Trafoindo Catalogue Instrument Transformers PDFDocument6 pagesTrafoindo Catalogue Instrument Transformers PDFRidwan FNo ratings yet
- Csec Lenses 22Document3 pagesCsec Lenses 22ashNo ratings yet
- Physics 571 Lecture #23: 1 Acousto-Optic Modulators (AOM)Document4 pagesPhysics 571 Lecture #23: 1 Acousto-Optic Modulators (AOM)ss626No ratings yet
- Build A Double Bazooka Antenna (K3DAV Version)Document11 pagesBuild A Double Bazooka Antenna (K3DAV Version)Steven BaynesNo ratings yet
- An001 enDocument13 pagesAn001 enQuynh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 3 QuestionsTinozivasheNo ratings yet
- Physics - IX-X-52Document52 pagesPhysics - IX-X-52BMT TCYSNo ratings yet
- Teori Dasar GeneratorDocument26 pagesTeori Dasar GeneratorFadly RidhoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Week 15) - Machines (AC Machines) - HMDocument23 pagesChapter 4 (Week 15) - Machines (AC Machines) - HMRoshan Jawad ZafirNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 GSUDocument20 pagesTutorial 4 GSUDon Rayburn PilanNo ratings yet
- Lance-Optical Analysis of TitaniaDocument24 pagesLance-Optical Analysis of Titaniaak vishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument2 pagesExampleTy Phan100% (1)
- Fiber OpticsDocument31 pagesFiber OpticsSyed Muhammad Munavvar Hussain88% (8)
- The Eye WorksheetDocument3 pagesThe Eye WorksheetCally ChewNo ratings yet
- Elevating NIR Photonic Integration With Tantalum-Niobium PentoxideDocument16 pagesElevating NIR Photonic Integration With Tantalum-Niobium PentoxideTasmiah TunazzinaNo ratings yet
- Ultrav RaysDocument10 pagesUltrav Raysharry smithNo ratings yet
- DCMT Lecture Notes FullDocument112 pagesDCMT Lecture Notes FullMidun RamkumarNo ratings yet
- Light Physics Class 10 Part 1Document12 pagesLight Physics Class 10 Part 1Kishwar SachanNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Split Up 2022-23 (27.07.22)Document6 pagesXii Physics Split Up 2022-23 (27.07.22)HADINo ratings yet
- Lumen Method CalculationsDocument6 pagesLumen Method CalculationsSajjad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Design Frequency and Array ParametersDocument5 pagesDesign Frequency and Array ParametersDanny LopezNo ratings yet
- Errors Using Joules To Time Out Test LenghtsDocument8 pagesErrors Using Joules To Time Out Test Lenghtsnikopigni2No ratings yet
- Pages From Switched Reluctance Motor PDFDocument10 pagesPages From Switched Reluctance Motor PDFHAMID SULIAMANNo ratings yet