Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHY 102 Summer 2020 DC and AC Circuits
Uploaded by
Ambrin AishaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PHY 102 Summer 2020 DC and AC Circuits
Uploaded by
Ambrin AishaCopyright:
Available Formats
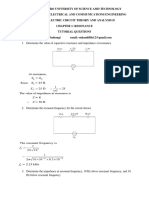
PHY 102/ Summer 2020
DC Circuits
36. A 25 F capacitor is connected through a 4 M resistor to a constant potential difference of 200 V.
Compute (a) the charge at time 5s (b) the current in the same instant (c) the time require for the charge to
increase from 5×10-04 C to 7×10-04 C (d) the final charge in the circuit (e) the relaxation time and half-life of
the circuit.
37. An inductor of inductance 3 H and a resistance 18 is connected to a battery of 30 V. Find (a) the initial
rate of increase of current in the circuit (b) the rate of increase current at the instant when the current is 1.5
A (c) the current 0.5 s after the circuit is closed (d) the final steady state current (e) the time required to
increase the current to 63 % of its final value?
38. (a) Show that the two expressions for the self inductance, namely NΦ/i and ε/(di/dt) have the same unit (b)
Show that L/R and RC both have the unit of time.
AC Circuits
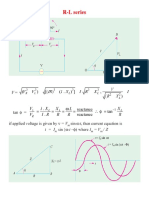
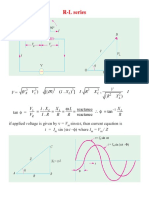
39. In an R-L-C series circuit, the source has constant voltage amplitude of 100 V and a frequency 1000 rad/s.
R=500, L=0.9 H , C=3.0F. Suppose a series circuit contains only resistor and inductor in series. (a) What
is the impedance of the circuit? (b) what is the current amplitude? (c) What are the voltage amplitudes
across the resistor and inductor? (d) What is the phase angle ? Does the current lag or lead?
40. In an R-L-C series circuit, the source has constant voltage amplitude of 100 V and a frequency 1000 rad/s.
R=500Ω, L=0.9 H , C=3.0μF. Suppose a series circuit contains only resistor and capacitor in series. (a)
What is the impedance of the circuit? (b) what is the current amplitude ? (c) What are the voltage
amplitudes across the resistor and capacitor? (d) What is the phase angle φ? Does the current lag or lead?
41. In an R-L-C series circuit, the source has constant voltage amplitude of 100 V and a frequency 1000 rad/s.
R=500Ω, L=0.9 H , C=3.0μF. Suppose a series circuit contains only capacitor and inductor in series. (a)
What is the impedance of the circuit? (b) what is the current amplitude? (c) What are the voltage amplitudes
across the capacitor and inductor? (d) What is the phase angle φ? Does the current lag or lead?
42. In an R-L-C series circuit, the source has constant voltage amplitude of 100 V and a frequency 1000 rad/s.
R=500Ω, L=0.9 H , C=3.0μF. (a) What is the impedance of the circuit? (b) what is the current amplitude? (c)
What are the voltage amplitudes across the resistor, capacitor and inductor? (d) What is the phase angle φ?
Does the current lag or lead?
43. A resistor of 500 and a capacitor 2 F are connected in parallel to a voltage supply 282 V and having an
angular frequency 377 rad/sec. Find (a) The current amplitude in the resistor (b) The current amplitude in
the capacitor (c) the phase angle and (d) the line current amplitude.
44. A 120 resistor, a 0.1F capacitor, and a 0.1 H inductor are connected in parallel to a voltage source of
100 V. (a) What is the resonant frequency? (b) What is the maximum current through the parallel
combination at the resonant frequency? (c) What is the maximum current through the resistor at resonance?
(d) What is the maximum current through the inductor at the resonance? (e) What is the maximum energy
stored in the inductor at resonance? In the capacitor?
45. A 120 resistor, a 0.1F capacitor, and a 0.1 H inductor are connected in series to a voltage source of 100
V. (a) what is the resonant frequency? (b) What is the maximum current through the combination at the
resonant frequency? (c) What is the maximum current through the resistor at resonance? (d) What is the
maximum voltage across the capacitor at the resonance? (e) What is the maximum energy stored in the
capacitor at resonance?
Reference: University Physics by Sears, Zemansky and Young : Ch. 29, 34 & 36
You might also like
- Sound Healing e BookDocument44 pagesSound Healing e Bookgusperreas7280100% (10)
- Universal LawsDocument18 pagesUniversal Lawscns100% (1)
- How Magick & ESP Work - QuantumDocument5 pagesHow Magick & ESP Work - Quantumx15f194858No ratings yet
- BBC Engineering Training Manual - Microphones (Robertson)Document380 pagesBBC Engineering Training Manual - Microphones (Robertson)Nino Rios100% (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Acoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCDocument14 pagesAcoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCKomal ChopadaNo ratings yet
- Circuits 2Document3 pagesCircuits 2lesterPECE100% (5)
- Bedini's Free Energy Generator PDFDocument7 pagesBedini's Free Energy Generator PDFturangga ranayaNo ratings yet
- Spooky2 Schumann Resonance For Beginners 7-Nov-2015 PDFDocument9 pagesSpooky2 Schumann Resonance For Beginners 7-Nov-2015 PDFtestnationNo ratings yet
- Is Iso 20283 2 2008Document22 pagesIs Iso 20283 2 2008ferdincaninNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 4: Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesTutorial - 4: Practice ProblemsParthaMoulikNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits ResonanceDocument19 pagesAC Circuits ResonanceIan GuiebNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesFrom EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- ITALVIBRAS - Selecting The Vibrator - A GuideDocument59 pagesITALVIBRAS - Selecting The Vibrator - A Guidenasser100% (1)
- 2007 Book IntegratedRingResonators PDFDocument270 pages2007 Book IntegratedRingResonators PDFDurgesh Joshi100% (1)
- A Design Guide For Footfall Induced Vibration of StructuresDocument84 pagesA Design Guide For Footfall Induced Vibration of StructuresVictor José Mendoza ManjarrésNo ratings yet
- LCL Filter DesignDocument8 pagesLCL Filter DesignAlex RochaNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch28 Test BankDocument13 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch28 Test Bankifghelpdesk0% (1)
- Physics in The QuranDocument5 pagesPhysics in The QuranSaqib Ahmed100% (1)
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - 05-Subjective Unsolved (C.B.S.E.) LevelDocument2 pagesAlternating Current - 05-Subjective Unsolved (C.B.S.E.) LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 12 Alternating Current CircuitDocument3 pagesTutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuithuijing966No ratings yet
- Tutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuit 1 - New SDocument4 pagesTutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuit 1 - New STan Nian HanNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- QstnsDocument1 pageQstnssymphonyNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Problems 33Document12 pagesProblems 33Daniyar MuratovNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Ac XiiDocument4 pagesWorksheet Ac XiiYug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesPractice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits: Multiple Choiceapi-127299018No ratings yet
- Bio Assign 1Document17 pagesBio Assign 1Gaurav ShekharNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: AnswerDocument22 pagesAlternating Current: AnswersmsubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Series Resonance Circuit Problems & SolutionsDocument2 pagesSeries Resonance Circuit Problems & SolutionsHubert SemenianoNo ratings yet
- Forum Diskusi 7-1 (Alternating Current)Document5 pagesForum Diskusi 7-1 (Alternating Current)Reyhan Julianto PribadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Key - ExerciseDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - Key - Exercisevenkatalakshmi civilNo ratings yet
- Review Questions Review QuestionsDocument31 pagesReview Questions Review QuestionssrinivasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDocument3 pagesTutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- RLC SERIES& Parallel QUIZDocument3 pagesRLC SERIES& Parallel QUIZMoshotle InnocentNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document1 pageAssignment 8Pavan KhetrapalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document2 pagesChapter 7Monisha RNo ratings yet
- Ac and Emi MCQSDocument5 pagesAc and Emi MCQSGuru ki physicsNo ratings yet
- LCR circuit problems and solutionsDocument2 pagesLCR circuit problems and solutionsNeha AttriNo ratings yet
- Serway 6 e Problems 33Document12 pagesSerway 6 e Problems 33Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- Lect 3 CH 3 PDFDocument9 pagesLect 3 CH 3 PDFكرار عبدالحسين قاسمNo ratings yet
- Lect 3 CH 3 PDFDocument9 pagesLect 3 CH 3 PDFكرار عبدالحسين قاسمNo ratings yet
- Calculate impedance, current, power factor and phasor diagrams for R-L-C series circuitsDocument9 pagesCalculate impedance, current, power factor and phasor diagrams for R-L-C series circuitsكرار عبدالحسين قاسم مسائي 23 BNo ratings yet
- ECE 226 Chapter 1 Tutorial QuestionsDocument20 pagesECE 226 Chapter 1 Tutorial QuestionsFilbert OmbongiNo ratings yet
- Electronics RefresherDocument2 pagesElectronics RefresherPaolo Steven PolintanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 30 Qa CircuitsDocument9 pagesAssignment 30 Qa Circuitskamisatoayaka010No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions / Practice Test Electrical Circuits - Set 1Document8 pagesMultiple Choice Questions / Practice Test Electrical Circuits - Set 1BrixxxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document24 pagesChapter 15Beverly PamanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 PDFSYAFIQAH ISMAIL100% (1)
- BEE Tutorial 7Document3 pagesBEE Tutorial 7Atharva NairNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Fundamentals QuizDocument4 pagesAC Circuits Fundamentals QuizCris Diane G. DatingginooNo ratings yet
- Electrical Network Analisis Ppt1Document38 pagesElectrical Network Analisis Ppt1Isaac P PlanNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - CH-7 Alternating Current (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks WiseDocument41 pagesClass Xii - CH-7 Alternating Current (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks Wisesamaran270sNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document30 pagesCH 7terasaini77No ratings yet
- 일반물리학및실험2 과제풀이 (2011-2학기Document7 pages일반물리학및실험2 과제풀이 (2011-2학기choiyunjungNo ratings yet
- AISSCE ASGNMT CHapter 7 Class 12Document4 pagesAISSCE ASGNMT CHapter 7 Class 12Sajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 INAC X1X2Document2 pagesAssignment 1 INAC X1X2Joyce GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document2 pagesAssignment 7Pavan KhetrapalNo ratings yet
- Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesAc CircuitsJeremy HensleyNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument7 pagesAC Circuits Practice Problems and SolutionscontrasterNo ratings yet
- MSC Electrical 2015 AllDocument16 pagesMSC Electrical 2015 AllYipeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 AC Revision QuestionsDocument46 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 AC Revision Questionssudhanshu narvekarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - PF and Parallel AC CircuitsDocument12 pagesLesson 4 - PF and Parallel AC CircuitsMichael SalvahanNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Ac Worksheet 2022Document5 pagesCH 7 Ac Worksheet 2022Hamad FarooqueNo ratings yet
- Ac ProblemsDocument1 pageAc ProblemsPramit PaulNo ratings yet
- ECT&T 7th Ed Chap 17 SolsDocument21 pagesECT&T 7th Ed Chap 17 SolsGelou Robert RazonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 1Document1 pageTutorial - 1Shreyansh KashaudhanNo ratings yet
- Assign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Document4 pagesAssign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Sunil JainNo ratings yet
- Resonance Damping in Array Cable Systems by Wind Turbine Active Filtering in Large Offshore Wind Power Plants - Kocewiak2017Document9 pagesResonance Damping in Array Cable Systems by Wind Turbine Active Filtering in Large Offshore Wind Power Plants - Kocewiak2017Christian JimenezNo ratings yet
- Rec No 132 pdf2241 PDFDocument43 pagesRec No 132 pdf2241 PDFsanil petereNo ratings yet
- What is Calculus and its ApplicationsDocument5 pagesWhat is Calculus and its ApplicationshahahahahaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics IV: OscillationsDocument17 pagesMechanics IV: Oscillations66 SB jay gotiNo ratings yet
- Beam vibrations on springsDocument10 pagesBeam vibrations on springsBelaliaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 10 Studyguide360Document44 pagesClass 11 Physics Notes Chapter 10 Studyguide360krithicksenthilvelanNo ratings yet
- Seta D 23 02149Document34 pagesSeta D 23 02149Paúl ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Vibration Serviceability of Footbridges: A Comparative Study of 3 Design MethodologiesDocument16 pagesVibration Serviceability of Footbridges: A Comparative Study of 3 Design Methodologiesjeff_56No ratings yet
- Wave QuestionsDocument11 pagesWave Questionsabh_omegaNo ratings yet
- Control of Flow-Induced Cavity ResonanceDocument4 pagesControl of Flow-Induced Cavity ResonanceJabez RichardsNo ratings yet
- Waves, Sound, LightDocument27 pagesWaves, Sound, LightEmmanuella okoNo ratings yet
- (Junoon e JEE) (3.0) Alternating CurrentDocument227 pages(Junoon e JEE) (3.0) Alternating CurrentvermaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Electrical Circuits ECE Board Exam PracticeDocument180 pagesMCQ Electrical Circuits ECE Board Exam Practiceian rafael japsayNo ratings yet
- The Resonance of Jericho: Kate RosenblattDocument3 pagesThe Resonance of Jericho: Kate Rosenblattoutdash2No ratings yet
- AN005-Design and DSP Implementation of 3.3-kW Resonant LLC On-Board ChargerDocument23 pagesAN005-Design and DSP Implementation of 3.3-kW Resonant LLC On-Board ChargerRudhi KurniawanNo ratings yet