Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 7 - Extra Practice Unit 2
Uploaded by
chunxiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 7 - Extra Practice Unit 2
Uploaded by
chunxiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Home Quit
Name Date
Master 2.18 Extra Practice 1
Lesson 2.1: Representing Integers
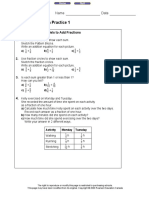
1. Write the integer modelled by each set of tiles.
a) b)
c) d)
e) f)
2. Use coloured tiles. Draw two different models for each integer.
a) –7
b) +8
c) –2
d) +6
3. Which integer is modelled by each set of tiles?
a) 5 yellow tiles and 13 red tiles b) 28 yellow tiles and 24 red tiles
c) 15 yellow tiles and 8 red tiles d) 37 yellow tiles and 41 red tiles
4. a) You have 3 yellow tiles and want to model –4.
How many red tiles do you need?
b) You have 6 red tiles and want to model +7.
How many yellow tiles do you need?
c) You have 5 yellow tiles and want to model +2.
How many red tiles do you need?
d) You have 8 red tiles and want to model –5.
How many yellow tiles do you need?
The right to reproduce or modify this page is restricted to purchasing schools.
This page may have been modified from its original. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Canada
Home Quit
Name Date
Master 2.19
Extra Practice 2
Lesson 2.2: Adding Integers with Tiles
Use coloured tiles.
1. Find each sum.
a) (+6) + (–12) b) (–10) + (–4) c) (–8) + (–9)
d) (+11) + (+7) e) (–13) + (+5) f) (+12) + (–6)
2. Represent each sentence with integers, then find each sum.
What does the sum represent?
a) The elevation of the base of the building is 345 m above sea level.
The building is 50 m high.
b) The elevation of the base of the building is 75 m below sea level.
The building is 15 m high.
c) The elevation of the top of the trench is 237 m below sea level.
The trench is 10 m deep.
d) The elevation of the entrance to the mine is 1500 m above sea level.
The mine is 450 m deep.
3. These are the scores on each hole of mini-golf. Find the total score.
Score –2 +1 0 +3 –1 +2 –1 0 –2
4. Complete each magic square.
a) b)
+3 –7 +8
+2 +6 –5 –3
+1 –1 –1 +2
+3 +1
The right to reproduce or modify this page is restricted to purchasing schools.
This page may have been modified from its original. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Canada
Home Quit
Name Date
Master 2.20
Extra Practice 3
Lesson 2.3: Adding Integers on a Number Line
1. Use a number line to add. Check with coloured tiles.
a) (+4) + (–6) b) (–5) + (–4)
c) (–7) + (+8) d) (–10) + (+3)
2. Use a pattern to find each sum.
a) (+3) + (–4) b) (+5) + (–6)
c) (–8) + (+3) d) (–6) + (+8)
3. Write an addition statement for each situation. Find the sum.
What does the sum represent?
a) The temperature in Victoria was +15ºC in the afternoon.
By midnight, the temperature had dropped 8ºC.
b) The temperature in Calgary was –10ºC.
A Chinook caused the temperature to rise 12ºC.
c) The temperature in Ottawa was –3ºC.
A cold front passed and the temperature dropped 8ºC.
d) The temperature in St. John's was –4ºC at 4 a.m.
By noon, the temperature had risen 10ºC.
4. Add.
a) (+5) + (–12) + (–4) b) (–7) + (+15) + (–12)
c) (–18) + (–3) + (+10) d) (+9) + (–6) + (–7)
The right to reproduce or modify this page is restricted to purchasing schools.
This page may have been modified from its original. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Canada
Home Quit
Name Date
Master 2.21 Extra Practice 4
Lesson 2.4: Subtracting Integers with Tiles
1. Use tiles to subtract.
a) (+7) – (+4) b) (–9) – (–5) c) (+8) – (+12)
d) (–3) – (–8) e) (+7) – (–3) f) (–5) – (+4)
2. What do you subtract from each integer to get the answer +4?
Use coloured tiles if they help.
a) +6 b) –3 c) +1 d) 0
3. What do you subtract from each integer in question 2 to get the answer –4?
4. Subtract.
a) (–5) – (–8) b) (–12) – (–4) c) (+8) – (+11)
d) 0 – (+3) e) (–8) – (–5) f) (+11) – (+8)
5. Complete the magic square for a magic sum of 0.
Subtract –2 from each entry. Is it still a magic square?
–1 –3
+2
+3 –4
The right to reproduce or modify this page is restricted to purchasing schools.
This page may have been modified from its original. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Canada
Home Quit
Name Date
Master 2.22 Extra Practice 5
Lesson 2.5: Subtracting Integers on a Number Line
1. Use a number line to subtract.
a) (–5) – (–4) b) (–6) – (+3) c) (+8) – (+12)
d) (+7) – (+2) e) (–3) – (+5) e) (–7) – (–8)
2. Use patterns to subtract.
a) (+4) – (–3)
Start with (+4) – (+1).
b) (–2) – (+5)
Start with (+6) – (+5).
c) (+5) – (+8)
Start with (+9) – (+8).
3. Find the difference between:
a) Mount Everest, Nepal, at 8850 m above sea level and Java Trench, Indian
Ocean, 7125 m below sea level
b) Puerto Rico Trench, Atlantic Ocean at 8648 m below sea level and Java
Trench, Indian Ocean, 7125 m below sea level
c) An airplane cruising at an altitude of 3500 m and a submarine at
a depth 975 m
d) A kite at an altitude of 112 m and a bird at an altitude of 145 m
4. The difference between (+56) and (+45) is –11.
a) Write the subtraction statement.
b) Write another subtraction statement using two negative integers with this
difference.
c) Write another subtraction statement using a positive integer and a negative
integer with this difference.
The right to reproduce or modify this page is restricted to purchasing schools.
This page may have been modified from its original. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Canada
Home Quit
Name Date
Master 2.23 Extra Practice Sample Answers
Extra Practice 1 – Master 2.18 Extra Practice 3 – Master 2.20
Lesson 2.1 Lesson 2.3
1. a) –4 b) +6 c) +1 1. a) –2 b) –9 c) +1 d) –7
d) –5 e) 0 f) +3 2. a) –1 b) –1 c) –5 d) +2
2. Answers may vary. 3. Each sum represents the final temperature in degrees
a) Celsius.
a) (+15) + (–8) = +7 b) (–10) + (+12) = +2
b) c) (–3) + (–8) = –11 d) (–4) + (+10) = +6
4. a) –11 b) –4 c) –11 d) –4
Extra Practice 4 – Master 2.21
Lesson 2.4
c) 1. a) +3 b) –4 c) –4
d) +5 e) +10 f) –9
d) 2. a) (+6) – (+2) = +4 b) (–3) – (–7) = +4
c) (+1) – (–3) = +4 d) 0 – (–4) = +4
3. a) (+6) – (+10) = –4 b) (–3) – (+1) = –4
c) (+1) – (+5) = –4 d) 0 – (+4) = –4
4. a) +3 b) –8 c) –3
3. a) –8 b) +4 c) +7 d) –4 d) –3 e) –3 f) +3
4. a) 7 b) 13 c) 3 d) 3 5. Yes
–1 +4 –3
Extra Practice 2 – Master 2.19
–2 0 +2
Lesson 2.2
1. a) –6 b) –14 c) –17 +3 –4 +1
d) +18 e) –8 f) +6
2. a) (+345) + (+50) = +395; the elevation of the top of the Extra Practice 5 – Master 2.22
building is 395 m above sea level. Lesson 2.5
1. a) –1 b) –9 c) –4
b) (–75) + (+15) = –60; the elevation of the top of the d) +5 e) –8 f) +1
building is 60 m below sea level. 2. a) (+4) – (+1) = +3
(+4) – 0 = +4
c) (–237) + (–10) = –247; the elevation of the bottom of the (+4) – (–1) = +5
trench is 247 m below sea level. (+4) – (–2) = +6
(+4) – (–3) = +7
+7
d) (+1500) + (–450) = +1050; the elevation of the bottom
b) (+6) – (+5) = +1
of the mine is 1050 m above sea level.
(+5) – (+5) = 0
3. (–2) + (+1) + 0 + (+3) + (–1) + (+2) + (–1) + 0 + (–2) = 0 (+4) – (+5) = –1
4. a) (+3) – (+5) = –2
+5 –2 +3 (+2) – (+5) = –3
(+1) – (+5) = –4
0 +2 +4 0 – (+5) = –5
(–1) – (+5) = –6
+1 +6 –1 (–2) – (+5) = –7
–7
b) c) (+9) – (+8) = +1
–7 –6 +7 +8 (+8) – (+8) = 0
(+7) – (+8) = –1
+4 +6 –5 –3 (+6) – (+8) = –2
(+5) – (+8) = –3
+5 –1 +2 –4
–3
0 +3 –2 +1 3. a) +15 975 m or –15 975 m b) –1523 m or +1523 m
c) +4475 m or –4475 m d) –33 m or +33 m
4. a) (+45) – (+56) = –11 b) (–17) – (–6)
c) (–6) – (+5)
The right to reproduce or modify this page is restricted to purchasing schools.
This page may have been modified from its original. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Canada
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Calculus 4th Edition Jon Rogawski Colin Adams Robert FranzosaDocument14 pagesSolution Manual For Calculus 4th Edition Jon Rogawski Colin Adams Robert FranzosaKeith Estrada100% (42)
- Complex Numbers WorksheetDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers WorksheetArsalan RaisaniNo ratings yet
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 8 June Exam 2019 PDFDocument14 pagesMathematics Grade 8 June Exam 2019 PDFzinhle shozi0% (1)
- Dwnload Full Calculus Early Transcendentals 4th Edition Rogawski Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Calculus Early Transcendentals 4th Edition Rogawski Solutions Manual PDFthiesfeldrolandaus100% (11)
- Complex Numbers WorksheetDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers WorksheetckuxinvileNo ratings yet
- Wetlands of India (Assignment Task)Document28 pagesWetlands of India (Assignment Task)Cryogen101 TheAssassinNo ratings yet
- 2 4 and 2 5 g7 Extra Practice With Answer KeyDocument3 pages2 4 and 2 5 g7 Extra Practice With Answer Keyapi-2391420910% (1)
- Lesson 2Document2 pagesLesson 2api-2889220720% (1)
- Practice Unit Test - Integers: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument6 pagesPractice Unit Test - Integers: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDennis AlbisoNo ratings yet
- BOOK 02 Answers FinalDocument61 pagesBOOK 02 Answers FinalJamiya 2016No ratings yet
- Written Ex 2000Document12 pagesWritten Ex 2000au auNo ratings yet
- Presence of God Mock MathsDocument15 pagesPresence of God Mock MathsKafui AugustineNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Algebra Test With AnswersDocument4 pagesYear 7 Algebra Test With AnswersTatianaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesAlgebra Practice ProblemsAi DeonaNo ratings yet
- Quadratics - QuizizzDocument4 pagesQuadratics - QuizizzazournaNo ratings yet
- End of Chapter Examinations 2020 Chapter 1: Introducing Symbols Mathematics Time: 1 HourDocument2 pagesEnd of Chapter Examinations 2020 Chapter 1: Introducing Symbols Mathematics Time: 1 HourAdrian V KistamaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment in Mathematics 8: Basic Education DepartmentDocument4 pagesPre-Assessment in Mathematics 8: Basic Education DepartmentJea TaladroNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice: Write The Letter of The Correct Answer Before Each Number. Ax + BX + C 0Document5 pagesMultiple Choice: Write The Letter of The Correct Answer Before Each Number. Ax + BX + C 0regor velascoNo ratings yet
- Grade7 1289520 1 2564.qDocument2 pagesGrade7 1289520 1 2564.qCloe BantayanNo ratings yet
- mathWorksheetEnglishVII PDFDocument41 pagesmathWorksheetEnglishVII PDFKokkilaa Parameswaran100% (1)
- FDM QP Spring 2020 FINAL PDFDocument5 pagesFDM QP Spring 2020 FINAL PDFAdrianNo ratings yet
- Igcse Maths Ce 0580 0980 WB AnswersDocument29 pagesIgcse Maths Ce 0580 0980 WB Answersmunirul islamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Mini Lecture ReviewDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Mini Lecture ReviewPrince K. TaileyNo ratings yet
- Calculus Early Transcendentals 4th Edition Rogawski Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesCalculus Early Transcendentals 4th Edition Rogawski Solutions Manualcrenate.bakshish.7ca96100% (29)
- Maths-D FormDocument6 pagesMaths-D FormagamNo ratings yet
- Elementary Geometry Book (561-616)Document56 pagesElementary Geometry Book (561-616)Juliana SaraivaNo ratings yet
- Fort ST 2012 2U Prelim HY & SolutionsDocument14 pagesFort ST 2012 2U Prelim HY & SolutionsJacob NathNo ratings yet
- 7 4 Numeracy PDFDocument9 pages7 4 Numeracy PDFalcilene almeidaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Early Transcendentals 4th Edition Rogawski Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesCalculus Early Transcendentals 4th Edition Rogawski Solutions ManualJacquelineLopezsnto100% (14)
- Grade 9 Paper MathsDocument14 pagesGrade 9 Paper Mathsමේනුක සූවින්දNo ratings yet
- Answers To ExercisesDocument14 pagesAnswers To ExercisesAiman MazlanNo ratings yet
- First Periodic Test in MTH 8Document3 pagesFirst Periodic Test in MTH 8Susan Lorsano100% (2)
- Instructions: Answer All The Questions: (B) (I) Calculate The Value ofDocument12 pagesInstructions: Answer All The Questions: (B) (I) Calculate The Value ofesyahzulNo ratings yet
- Expansions and FactorisationsDocument2 pagesExpansions and FactorisationsGrace ThunNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Exam - MAth 8Document3 pages1st Periodic Exam - MAth 8Mike Jeron MartinezNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers NewDocument2 pagesComplex Numbers Newcharviicharvii2007No ratings yet
- Where N Is An Integer, and R Is A RationalDocument8 pagesWhere N Is An Integer, and R Is A RationalYonathan RenggaNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers WorksheetDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers WorksheetKienNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Practice Test: Unit 2 Integers: Name DateDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Practice Test: Unit 2 Integers: Name Dateapi-288922072No ratings yet
- Complex Numbers WorksheetDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers WorksheetArsalan RaisaniNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers WorksheetDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers WorksheetAlbert Jn BaptisteNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice 5Document2 pagesExtra Practice 5api-288922072No ratings yet
- Number System Class Study SheetDocument13 pagesNumber System Class Study Sheetmamta01234deviNo ratings yet
- (EXE) Chapter 2 Quadratic FunctionsDocument26 pages(EXE) Chapter 2 Quadratic FunctionsSamuel Sim Shien ShuangNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Integers Test RegehrDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Integers Test Regehrapi-637312278No ratings yet
- Math 7 - Extra Practice Unit 1Document13 pagesMath 7 - Extra Practice Unit 1chunxiaNo ratings yet
- E-Book 'Worksheets Volume #1 - Algebra' Revision From GCSE Maths TutorDocument32 pagesE-Book 'Worksheets Volume #1 - Algebra' Revision From GCSE Maths Tutorgcsemathstutor100% (1)
- Get Ready: Name: - DateDocument20 pagesGet Ready: Name: - DatehdhdhdNo ratings yet
- Sydney Tech 2019 2U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument19 pagesSydney Tech 2019 2U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsFrenchieAlphaNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document4 pagesTest 2Yan KyawNo ratings yet
- Y4 Maths Revision SheetsDocument10 pagesY4 Maths Revision SheetsMohammed RamadanNo ratings yet
- BoxStories PDFDocument2 pagesBoxStories PDFdanNo ratings yet
- BoxStories PDFDocument2 pagesBoxStories PDFdanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - Number Stories and Algebra: Find Out What Happens To The Given Numbers in The Following StoriesDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1 - Number Stories and Algebra: Find Out What Happens To The Given Numbers in The Following StoriesdanNo ratings yet
- Test PracticeDocument17 pagesTest PracticeAntonette Frilles GibagaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Maths Exam November 2016 L KlempDocument7 pagesGrade 7 Maths Exam November 2016 L KlempOthelia SmitNo ratings yet
- MAT1100 Tutorial Sheet 2 - 2022 PDFDocument3 pagesMAT1100 Tutorial Sheet 2 - 2022 PDFSezy ZambiaNo ratings yet
- Atlib CDocument1 pageAtlib CRash GSNo ratings yet
- Algebra ReviewDocument3 pagesAlgebra ReviewMicah SharpNo ratings yet
- Jumpstarters for Algebra, Grades 7 - 8: Short Daily Warm-ups for the ClassroomFrom EverandJumpstarters for Algebra, Grades 7 - 8: Short Daily Warm-ups for the ClassroomNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - Extra Practice Unit 5Document11 pagesMath 7 - Extra Practice Unit 5chunxiaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - Extra Practice Unit 4Document11 pagesMath 7 - Extra Practice Unit 4chunxiaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - Extra Practice Unit 3Document11 pagesMath 7 - Extra Practice Unit 3chunxiaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - Extra Practice Unit 1Document13 pagesMath 7 - Extra Practice Unit 1chunxiaNo ratings yet
- Kuswata 2006 Enam Dekade Penelitian EkologiDocument46 pagesKuswata 2006 Enam Dekade Penelitian EkologiahasanlukmanNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Bridges ICE IStructE Part1Document21 pagesSeismic Design of Bridges ICE IStructE Part1fethi42No ratings yet
- Geomorphology: Clément Roux, Adrien Alber, Mélanie Bertrand, Lise Vaudor, Hervé PiégayDocument9 pagesGeomorphology: Clément Roux, Adrien Alber, Mélanie Bertrand, Lise Vaudor, Hervé PiégayElaine Gisell Caro MendezNo ratings yet
- Draft Geology PDFDocument53 pagesDraft Geology PDFVAIBHAV TIWARINo ratings yet
- II.A. Geology of Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) Former ArmmDocument3 pagesII.A. Geology of Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) Former ArmmMatthew Julius TatelNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: Calasiao Comprehensive National High SchoolDocument2 pagesI. Objectives:: Calasiao Comprehensive National High SchoolFreddie AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Huggett - 1975 - Soil Landscape Systems A Model of Soil GenesisDocument22 pagesHuggett - 1975 - Soil Landscape Systems A Model of Soil GenesisAndrés David VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Geography Note Booklet Grade 9 PDFDocument72 pagesGeography Note Booklet Grade 9 PDFiitope.n.op100% (1)
- Geography Workbook Answer Key - 3.7Document6 pagesGeography Workbook Answer Key - 3.7deepha vrNo ratings yet
- 03.07mkoquake Gemini SeismicDocument27 pages03.07mkoquake Gemini SeismicKurinjivelan PalaniyandiNo ratings yet
- Biomineralization of Plants As Long Term Carbon SinkDocument4 pagesBiomineralization of Plants As Long Term Carbon SinkRyanNo ratings yet
- Sts Study Guide Hatag Nyag Answer UgmaDocument18 pagesSts Study Guide Hatag Nyag Answer UgmaTribunalo, Aliana R.No ratings yet
- English 1st BguDocument192 pagesEnglish 1st BguRaziel ReaverNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Michael Menker GIRMADocument119 pagesDissertation Michael Menker GIRMAEfremWakjiraHodeNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument11 pagesEnvironmental ScienceKimberly kate AlambraNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Population Growth On Land Degradation, Case of Rwamagana District (2000-2020)Document23 pagesThe Impact of Population Growth On Land Degradation, Case of Rwamagana District (2000-2020)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 21-Đề Ôn Tập Số 21 - Dap AnDocument4 pages21-Đề Ôn Tập Số 21 - Dap AnAnh MaiNo ratings yet
- StreamflowDocument72 pagesStreamflowdzikrydsNo ratings yet
- Sand Cone DataDocument15 pagesSand Cone DataAde Septiani PutriNo ratings yet
- ST - MArtinsIsland ParticleSizeAnalysisDocument33 pagesST - MArtinsIsland ParticleSizeAnalysisJihad AlboureeniNo ratings yet
- Holcim Coal Spill Reveals Other Environmental IssuesDocument3 pagesHolcim Coal Spill Reveals Other Environmental IssuesJane Tadina FloresNo ratings yet
- Poster 22216 PDFDocument1 pagePoster 22216 PDFHaneen AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Pranter CV Detailed WebDocument19 pagesPranter CV Detailed WebZamzuri ZaidinNo ratings yet
- Khewra GorgeDocument24 pagesKhewra Gorgejawad100% (4)
- Land Resource and Energy ResourcesDocument11 pagesLand Resource and Energy ResourcesGautam GopalNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument57 pagesWater ResourcesA S M Hefzul Kabir100% (3)
- Criticalloadsofheavymetals Heavy Metalsin SoilsDocument28 pagesCriticalloadsofheavymetals Heavy Metalsin Soilsandy mizwarNo ratings yet
- Materi Kuliah ReferensiDocument10 pagesMateri Kuliah ReferensiLeo PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Science 7Document10 pagesDaily Lesson Log Science 7Erma JalemNo ratings yet