Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti-Cancer Drugs: (Cytotoxic Chemotherapy Salvage)
Uploaded by
Yuku BabyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anti-Cancer Drugs: (Cytotoxic Chemotherapy Salvage)
Uploaded by
Yuku BabyCopyright:
Available Formats
ANTI-CANCER DRUGS
(CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY &SALVAGE)
Classification and alkylating agents
Common toxicities of alkylating agents:
1. Myelosuppression (dose-limiting)
• Anemia
• Neutropenia
• Thrombocytopenia
• Pancytopenia
2. Nausea and Vomiting
3. Alopecia
4. Sterility – Gonadal damage
5. Mucositis – oral ulcers
6. Intestinal denudation – Diarrhea
7. Neurotoxicity
• Altered mental status
• Coma
• Seizures
• Ataxia
8. Pulmonary fibrosis
9. Veno-occlusive disease of liver (VOD)
10. Secondary malignancies (mostly AML)
Antimetabolites
Interaction between 6-MP / Azathioprine and XO inhibitors:
6-MP and Azathioprine
↓ Xanthine oxidase
Inactive metabolites
• Hence, XO inhibitors inhibit the metabolism of 6-MP and Azathioprine, increasing their
plasma levels and risk of toxicities.
• Therefore, the doses of 6-MP and azathioprine need to be reduced.
©Aakash EduTech Private Limited | Visit us at pgplus.aakashdigital.com | Contact us: 011-40705055
Drugs for hairy cell leukemia:
• Cladribine (DOC)
• Interferon – α
• Pentostatin
• Vemurafenib (due to presence of V600E BRAF mutations)
Other cytotoxic agents
Metabolism of irinotecan:
Irinotecan
↓ Carboxylesterases in liver
Active metabolite (SN-38)
↓ UGT1A1
Inactivate SN-38 glucuronide
• Polymorphisms in UGT1A1 such as in Gilbert’s syndrome can lead to accumulation of
the drug and drug toxicity.
• Hence, irinotecan should be avoided in patients with UGT1A1 polymorphisms.
Flagellate dermatitis:
• Adverse effect of – Bleomycin
• Bands of pruritic erythema
• Involving arms, back, scalp and hands
• Treatment: Topical steroids
Salvage therapy
Treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting:
Early (< 24 h): Ondansetron
Late (> 24 h): Aprepitant
Treatment of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression:
CHEMOTHERAPY-INDUCED PREFERRED TREATMENT
Anemia Erythropoietin
Neutropenia Filgrastim
Thrombocytopenia Oprelvekin (rIL11)
©Aakash EduTech Private Limited | Visit us at pgplus.aakashdigital.com | Contact us: 011-40705055
ANTI-CANCER AGENTS - (TARGETED THERAPY)
Hormonal agents
Tamoxifen:
SERM – Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator
Agonist:
• Bone
• Uterus
• (+ CVS)
Antagonist:
• Breast
Fulvestrant:
• SERD (Selective Estrogen Receptor Down-regulator)
• Antagonist at all estrogen receptors
• Also known as ‘Pure anti-estrogen’
• Approved for – metastatic ER +ve breast cancer
• Dose: 250 mg IM once monthly in the buttocks
• Long T½: ~ 40 days
Aromatase inhibitors:
Examples:
• Letrozole
• Anastrozole
• Exemestane (irreversible)
Tyrosine kinase and protein synthesis inhibitors
Erlotinib:
• Competitive inhibitor of ATP binding to EGFR1 (ErbB1)
• Oral bioavailability significantly increased by food – NOT given with food to avoid
toxicity
• Approved for locally advanced / metastatic non-small cell lung CA
Gefitinib different from erlotinib:
• Oral bioavailability not affected by food – can be given irrespective of meals
• Approved for – Refractory non-small cell lung CA
©Aakash EduTech Private Limited | Visit us at pgplus.aakashdigital.com | Contact us: 011-40705055
Hand-foot syndrome (HFS) v/s Hand-foot-skin reaction (HFSR):
HAND-FOOT
HAND-FOOT SKIN REACTION (HSFR)
SYNDROME (HFS)
Lesions Diffuse Sharply demarcated
Areas involved Palms and soles Heels, metatarsal heads, other areas
of friction
Characteristics Erythema and edema Erythmatous, edematous, tender
blisters that may evolve into painful
calluses
Pain Painful Painful
Associated Capecitabine Drugs inhibiting multiple tyrosine
with 5-FU kinases
Monoclonal antibodies – 1 (Production, anti-TNF-alpha agents and Bevacizumab)
Anti-TNF-α antibodies:
Indications:
• RA
• AS
• Plaque psoriasis (including psoriatic arthritis)
• Crohn’s disease
Contraindications:
1. Active infection / High risk of infection (including TB)
2. Malignancy / Pre-malignancy
3. Immune suppressed state (including HIV)
4. Hepatitis B
5. SLE
6. Multiple sclerosis
7. CHF
8. Pregnancy
9. Lactation
Adverse effects of Bevacizumab:
• Potential for vessel injury and bleeding → Pulmonary haemorrhages
• Arterial thromboembolic events – stroke or MI
• Hypertension. If poorly controlled → reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy or CHF
• GI perforation
©Aakash EduTech Private Limited | Visit us at pgplus.aakashdigital.com | Contact us: 011-40705055
• Asymptomatic proteinuria (more common in CA ovary and primary colon CA)
Monoclonal antibodies – 2 (Remaining antibodies)
Reactivation of JC and BK viruses associated mainly with – Rituximab
Dose of basiliximab: 2 doses of 20 mg each
1st dose: within 2 hours prior to transplant
2nd dose: 4 days after transplant
Examples of some of the monoclonal antibodies:
Drug (M.ab) Target Indication
Catumaxomab CD3 and EpCAM Malignant ascites
Ramucirumab VEGFR 2 Gastric CA
Lung CA
Panitumumab EGFR Colorectal CA
Trastuzumab HER2/neu (EGFR2) Breast CA
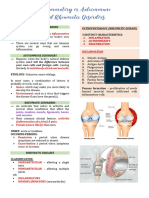
Immunosuppressants
Adverse effects of calcineurin inhibitors:
Cyclo > Tacro Tacro > Cyclo
• Hypertension • Nephrotoxicity
• Hirsutism • Neurotoxicity
• Hyperplasia of gums • Hepatotoxicity
• Diabetes mellitus
• Diarrhea
• Alopecia
Drugs for rheumatoid arthritis:
(A): CONVENTIONAL DMARDs
• Methotrexate
• Sulfasalazine
• Hydroxychloroquine
• Leflunomide
©Aakash EduTech Private Limited | Visit us at pgplus.aakashdigital.com | Contact us: 011-40705055
(B): BIOLOGIC DMARDs:
TARGET DRUGS
TNF-α • Infliximab
• Adalimumab
• Etanercept
• Golimumab
• Certolizumab
CD80/86 Abatacept
IL-6 Tocilizumab
JAK Tofacitinib
(C): NON-DMARDs (only for symptomatic relief)
• NSAIDs
• Steroids
Immunostimulants
Adverse effects of thalidomide:
1. Sedation
2. Constipation
3. Peripheral neuropathy (most serious)
4. Fatigue
5. Deep vein thrombosis
6. Hypothyroidism
7. Teratogenicity
• Phocomelia
• Mobius syndrome
Anti-cancer drugs causing peripheral neuropathy:
1. Vinca alkaloids
2. Taxanes
3. Platinum analogues
4. Thalidomide
5. Bortezomib
Indications of Interferon-α:
• Hairy cell leukaemia
• Follicular lymphomas
• Malignant melanoma
©Aakash EduTech Private Limited | Visit us at pgplus.aakashdigital.com | Contact us: 011-40705055
• AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma
• Mycosis fungoides
• Condyloma acuminata
• Chronic hepatitis B
• Chronic hepatitis C (+ Ribavirin)
❑ ❑ ❑
©Aakash EduTech Private Limited | Visit us at pgplus.aakashdigital.com | Contact us: 011-40705055
You might also like
- Sotai: Natural ExerciseDocument120 pagesSotai: Natural ExerciseZudan Ady Wijaya Apt100% (3)
- Anticancer DrugsDocument117 pagesAnticancer DrugsKishore Chandra Korada100% (2)
- Davinci Medical Academy Pharmacology NotesDocument12 pagesDavinci Medical Academy Pharmacology NotesYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Cancer Drug StudyDocument14 pagesCancer Drug StudyIamanamay Trinidad100% (1)
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument49 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM100% (4)
- Immuno Modulator SDocument62 pagesImmuno Modulator SAntony Prakash RajNo ratings yet
- DR Colbert Keto Diet PDFDocument11 pagesDR Colbert Keto Diet PDFHamilton Durant100% (1)
- Pharmacology - Mnemonics PDFDocument140 pagesPharmacology - Mnemonics PDFItharshan Indreswaran76% (17)
- Chemo Drugs-FinalDocument45 pagesChemo Drugs-FinalApril Mae Magos Labrador100% (1)
- Anti Cancer ChemotherapyDocument103 pagesAnti Cancer ChemotherapyMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulators: Ma. Stephanie Fay S. Cagayan, MDDocument67 pagesImmunomodulators: Ma. Stephanie Fay S. Cagayan, MDFaye Cagayan100% (1)
- Pathology Mci One Liners MCQDocument21 pagesPathology Mci One Liners MCQadiNo ratings yet
- Duterte: I'm Not Interested in Going Beyond My TermDocument3 pagesDuterte: I'm Not Interested in Going Beyond My TermMarjorie Delrosario PilonNo ratings yet
- ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS AND THE CELL CYCLEDocument5 pagesANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS AND THE CELL CYCLEKath DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Pharma Cvs Endocrine RespDocument15 pagesPharma Cvs Endocrine RespYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Antifungal - Anticancer 21Document83 pagesAntifungal - Anticancer 21DR AbidNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology Diseases Group CDocument73 pagesRheumatology Diseases Group CDiana NurulNo ratings yet
- Antineoplastic Agents: Samuel A. Camorongan, RNDocument45 pagesAntineoplastic Agents: Samuel A. Camorongan, RNSamuel CamoronganNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulator 2014Document56 pagesImmunomodulator 2014LeilybadryaNo ratings yet
- 61.drugs For Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument7 pages61.drugs For Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseireneNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapeutic Agents and AntiinfectivesDocument64 pagesChemotherapeutic Agents and AntiinfectivesAnthony RiggsNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal and AntihelminticDocument36 pagesAntiprotozoal and AntihelminticDiriba feyisaNo ratings yet
- Paskaita 55 SND Cancer ENDocument10 pagesPaskaita 55 SND Cancer ENjernsssNo ratings yet
- A. Antineoplastic DrugsDocument48 pagesA. Antineoplastic DrugsKim Shyen BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Anti Neoplastic AgentsDocument16 pagesAnti Neoplastic AgentsNathaniel VelascoNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Drugs: Mechanisms and Side EffectsDocument13 pagesAnticancer Drugs: Mechanisms and Side EffectsPham PhamIoNo ratings yet
- 38.ANTIRETROVIRALS PDFDocument5 pages38.ANTIRETROVIRALS PDFireneNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cancer TherapyDocument102 pagesDrugs For Cancer TherapyPUTRI CHRISTIANTI TELAUMBANUA 1No ratings yet
- The Immunosuppression 2021Document10 pagesThe Immunosuppression 2021Muhammad AliNo ratings yet
- ANTINEOPLASTIC REPORTDocument71 pagesANTINEOPLASTIC REPORTmrsr64zpcdNo ratings yet
- Anti-Cancer Drugs: Mechanisms and Side EffectsDocument30 pagesAnti-Cancer Drugs: Mechanisms and Side EffectsMr VoralpenNo ratings yet
- LMR Pharmacology - CnsDocument6 pagesLMR Pharmacology - CnsYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Terapi Sistemik Pada Kanker Dengan Obat Anti Kanker (OAK) Pada Saat Pandemi COVID-19Document31 pagesTerapi Sistemik Pada Kanker Dengan Obat Anti Kanker (OAK) Pada Saat Pandemi COVID-19dayarni buuloloNo ratings yet
- Basic of Cancer TherapyDocument100 pagesBasic of Cancer TherapyPrapassorn PayantakomNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants Drdhriti 131109120033 Phpapp01Document18 pagesAnticoagulants Drdhriti 131109120033 Phpapp01Munazza QuraishiNo ratings yet
- Hema 2 WBCDocument30 pagesHema 2 WBCAngge Aquino OfficialNo ratings yet
- Drug Allergy Diagnosis, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument21 pagesDrug Allergy Diagnosis, Symptoms and TreatmentIndahYuliiarniPutriNongtjiNo ratings yet
- Prof. - Sanjay - Khattri - Anti - Rheumatoid - DrugsDocument29 pagesProf. - Sanjay - Khattri - Anti - Rheumatoid - DrugsBe GameNo ratings yet
- Anticancer drugsDocument44 pagesAnticancer drugsTommy ZeusNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Drug AllergyDocument21 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Drug AllergyIndahYuliiarniPutriNongtjiNo ratings yet
- Immune System Drugs - FinalDocument56 pagesImmune System Drugs - FinalSarte Rachelle AnneNo ratings yet
- Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument48 pagesManagement of Rheumatoid ArthritisAlexNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Liver DisordersDocument19 pagesDrug Induced Liver Disorders22 Prem PatelNo ratings yet
- RheumatoidArthritis 1Document26 pagesRheumatoidArthritis 1Lava calolaNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Liver Disease (DILD) : Yousif.A Qari Consultant Gastroenterologist KauhDocument30 pagesDrug-Induced Liver Disease (DILD) : Yousif.A Qari Consultant Gastroenterologist KauhEllen BalawelingNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Liver Disease (DILD) : PredictableDocument23 pagesDrug-Induced Liver Disease (DILD) : PredictableSisno SujanaNo ratings yet
- Anti ProtozoaDocument29 pagesAnti ProtozoaIsheanesu MugwisiNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Drugs Final PDFDocument8 pagesAnticancer Drugs Final PDFAisha Jamil100% (1)
- Non Steroid Antiinflammatory Drugs & Drugs Use in The Treatment of GoutDocument28 pagesNon Steroid Antiinflammatory Drugs & Drugs Use in The Treatment of GoutVevi VarcetyNo ratings yet
- Board II Review PDFDocument131 pagesBoard II Review PDFJohnNo ratings yet
- Board II Review PDFDocument131 pagesBoard II Review PDFJohnNo ratings yet
- DILIDocument40 pagesDILIYunik YuliapsariNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco Logy Imm Une Syste M Drugs: Julia Leonor Huaringa Lagomarsino, RN February 13, 2009Document12 pagesPharmaco Logy Imm Une Syste M Drugs: Julia Leonor Huaringa Lagomarsino, RN February 13, 2009julialeoNo ratings yet
- 17.04.2020 Psoriasis DD & TreatmentDocument43 pages17.04.2020 Psoriasis DD & TreatmentsujataNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Therapy Tasneem 1Document54 pagesDermatology Therapy Tasneem 1halaNo ratings yet
- Obat Antijamur Dan Antihistamin: Dr. Elly Usman, M.Si, AptDocument17 pagesObat Antijamur Dan Antihistamin: Dr. Elly Usman, M.Si, AptChindyNo ratings yet
- Course Code: Course Name: Colorectal Cancer PharmacologyDocument36 pagesCourse Code: Course Name: Colorectal Cancer PharmacologyInternational Cancer InstituteNo ratings yet
- INFLAMMATORY or AUTOIMMUNE RHEUMATIC DISORDERSDocument16 pagesINFLAMMATORY or AUTOIMMUNE RHEUMATIC DISORDERSShaun Gabriel AmpoNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Liver InjuryDocument26 pagesDrug-Induced Liver InjuryUsamaNo ratings yet
- AtorvastatinDocument15 pagesAtorvastatinACanNo ratings yet
- AntiNeo SEDocument93 pagesAntiNeo SEJerome BentleyNo ratings yet
- Cancer chemotherapy 2Document8 pagesCancer chemotherapy 2vrst7fhbq5No ratings yet
- Inhibitors of Immune Response (site of actionDocument39 pagesInhibitors of Immune Response (site of actionGd SuarantaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Postpartum Care ActivityDocument13 pagesDrug Study: Postpartum Care ActivityJohn Paul DimaunahanNo ratings yet
- Drkamalkv 1 Ans June-14Document13 pagesDrkamalkv 1 Ans June-14Akshay MedkarNo ratings yet
- ENT signs, symptoms and proceduresDocument14 pagesENT signs, symptoms and proceduresYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- LMR Ent - Nose and Paransal SinusesDocument7 pagesLMR Ent - Nose and Paransal SinusesYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Integrated Learning LMR OpthamologyDocument11 pagesIntegrated Learning LMR OpthamologyYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- LMR Ent Ear: Embroyology and Anatomy of EarDocument10 pagesLMR Ent Ear: Embroyology and Anatomy of EarYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Pharma GeneralDocument7 pagesPharma GeneralYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Pharma GeneralDocument7 pagesPharma GeneralYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Pharma LMRDocument21 pagesPharma LMRAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- LMR Ent - Throat: Diseases of Oral Cavity and Salivary GlandsDocument8 pagesLMR Ent - Throat: Diseases of Oral Cavity and Salivary GlandsYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- All of The Following Are Actions of Muscarinic Antogonists, ExceptDocument173 pagesAll of The Following Are Actions of Muscarinic Antogonists, ExceptYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Pharma DiureticsDocument12 pagesPharma DiureticsYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument18 pagesPHARMACOLOGYYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System:: CatecholaminesDocument4 pagesAutonomic Nervous System:: CatecholaminesYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Pharma AntimicrobialsDocument19 pagesPharma AntimicrobialsYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Chapter 27880 1Document4 pagesRevision Notes Chapter 27880 1Yuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Aiims Pharma QueDocument23 pagesAiims Pharma QueYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Chapter 27876 1Document5 pagesRevision Notes Chapter 27876 1Yuku BabyNo ratings yet
- All of The Following Are Actions of Muscarinic Antogonists, ExceptDocument173 pagesAll of The Following Are Actions of Muscarinic Antogonists, ExceptYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- LMR Git and Liver: Non Neoplastic Polyps Neoplastic Polyp Familial Polyposis SyndromeDocument4 pagesLMR Git and Liver: Non Neoplastic Polyps Neoplastic Polyp Familial Polyposis SyndromeYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Chapter 27878 1Document4 pagesRevision Notes Chapter 27878 1Yuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Lmr-Hematology: Bad Prognostic Factors For ALLDocument3 pagesLmr-Hematology: Bad Prognostic Factors For ALLYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- JIPMER MCQsDocument7 pagesJIPMER MCQsjskingNo ratings yet
- Patho General GeneticsDocument9 pagesPatho General GeneticsYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- LMR Git and Liver: Non Neoplastic Polyps Neoplastic Polyp Familial Polyposis SyndromeDocument4 pagesLMR Git and Liver: Non Neoplastic Polyps Neoplastic Polyp Familial Polyposis SyndromeYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Patho Cns Lung ThyroidDocument5 pagesPatho Cns Lung ThyroidYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Jwara Roga With Ayurvedic HerbsDocument2 pagesTreatment of Jwara Roga With Ayurvedic HerbsSN WijesinheNo ratings yet
- Post COVID-19 Intelligent Public Healthcare Management - The Next Frontier To Handle Epidemic OutbreaksDocument6 pagesPost COVID-19 Intelligent Public Healthcare Management - The Next Frontier To Handle Epidemic OutbreaksturnaNo ratings yet
- Kidney StonesDocument2 pagesKidney StonesNick BantoloNo ratings yet
- Serpentina ResearchDocument16 pagesSerpentina ResearchAlfie BurbosNo ratings yet
- Review of Vestibular Migraine: Current Understanding and Future DirectionsDocument15 pagesReview of Vestibular Migraine: Current Understanding and Future DirectionsSerdar MeteNo ratings yet
- Anemia Gravis MH HF Worm InfectionDocument5 pagesAnemia Gravis MH HF Worm InfectionPutri KartikaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Root Syndrome Sc4Document50 pagesCervical Root Syndrome Sc4Anang FajarNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Term Paper TopicsDocument8 pagesAbnormal Psychology Term Paper Topicsc5jbmre7100% (1)
- Cor Triatriatum: From of Surgery and University ofDocument9 pagesCor Triatriatum: From of Surgery and University ofAyuRizkyAndhinyNo ratings yet
- Resonium CDocument5 pagesResonium Cfion90002003No ratings yet
- Arroz Con Mango PDFDocument197 pagesArroz Con Mango PDFVanshika JainNo ratings yet
- Gingivitis & PeriodontitisDocument24 pagesGingivitis & PeriodontitisHafid Nur ArzanudinNo ratings yet
- Doh Updated Prog M-RDocument49 pagesDoh Updated Prog M-Rdeeday echavezNo ratings yet
- Best ENT Surgeon in Hyderabad - ENT HospitalDocument14 pagesBest ENT Surgeon in Hyderabad - ENT HospitalMagnasVNo ratings yet
- EPOS Guide to RhinosinusitisDocument20 pagesEPOS Guide to RhinosinusitisMargaretha Syane LientunganNo ratings yet
- Aynadis Thesis CorrectedDocument78 pagesAynadis Thesis CorrectedBantider GetachewNo ratings yet
- GangreneDocument18 pagesGangreneFelita Surya RiniNo ratings yet
- Louis Pasteur Vs Antoine Béchamp and The Germ Theory of Disease Causation - 1Document15 pagesLouis Pasteur Vs Antoine Béchamp and The Germ Theory of Disease Causation - 1Eduardo FilhoNo ratings yet
- Healthy Habits Summative TestDocument1 pageHealthy Habits Summative Testliz100% (1)
- PEG Vs Nasogastric Tube FeedingDocument64 pagesPEG Vs Nasogastric Tube FeedingTarek ElsefiNo ratings yet
- Project NewDocument33 pagesProject Newceeyem83% (12)
- Chapter 28 Child With A Gastrointestinal ConditionDocument85 pagesChapter 28 Child With A Gastrointestinal Conditionsey_scottNo ratings yet
- ChlorphromazineDocument2 pagesChlorphromazineanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Fluids and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument69 pagesSeminar On Fluids and Electrolyte ImbalanceShib Shankar Roy100% (4)
- "Terry": Patrizia Mae R. Mantes Introduction To Philosophy of Human Person 11 - Blessed OsannaDocument2 pages"Terry": Patrizia Mae R. Mantes Introduction To Philosophy of Human Person 11 - Blessed OsannaPatrizia Mae Rellores MantesNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6021 Assessment 3 Quality Improvement Presentation PosterDocument4 pagesNURS FPX 6021 Assessment 3 Quality Improvement Presentation Posterjoohnsmith070No ratings yet
- Infliximab: Drug Treatment InformationDocument7 pagesInfliximab: Drug Treatment InformationAlin-Ionuț SălcianuNo ratings yet