Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SJFSN-ID25 Part4
Uploaded by
anteros facesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SJFSN-ID25 Part4
Uploaded by
anteros facesCopyright:
Available Formats
Scientific Journal of Food Science & Nutrition
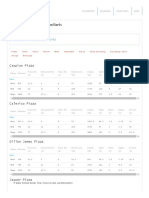
Table 3: RDA (%) values for Cu, Zn, Ca, Mg, P, Na and K for 1-12 years children.
Minerals 1-3 years 4-8 years 9-12 years
Male Female Male Female Male Female
Cu 52.65 57.06 30.68 30.45 15.29 17.01
Zn 39.13 42.43 17.72 17.64 9.63 9.83
Ca 75.71 82.14 40.0 39.90 26.76 27.34
Mg 38.95 42.23 21.70 21.64 12.41 17.73
P 74.69 80.98 51.81 51.65 18.04 18.41
Na 16.95 18.37 10.65 10.61 7.41 7.55
K 22.04 23.89 13.12 13.08 9.64 9.82
RDA: Recommended Daily Allowance.
0.107mg/ day which is about 15.29% of RDA for 9-12 years children. that daily intake of essential mineral through milk consumption in
The DI values of Cu were below their respective range of [23] in all all age groups was lower than their recommended reference ranges.
age group of children. In RDA contribution results revealed that buffalo’s milk had good
contribution for Ca followed by P, Cu, Mg, Zn, K and Na for all age
Zinc is required for the integration of many physiological systems
group children.
[24], it has also catalytic role in each class of enzymes [25]. The highest
DI value of Zn via milk intake was 1.273 mg/ day which represents REFERENCES
about 42.43% of RDA for 1-3 years children and lowest daily intake of
1. Bundy DAP, de Silva N, Horton S, Jamison DT, Patton GC. 2017. Disease
zinc was 0.770 mg/ day, which is about 9.625% of RDA for 9-12 years
Control Priorities, Third Edition: Volume 8. Child and adolescent health and
children. The provisional maximum tolerable daily intake of zinc set development. Washington, DC: World Bank.
by [26] is 0.3 mg/ kg/ bw/ day which is higher than the current DI
values of zinc. Various studies like [2,27] had associated zinc intake 2. Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP, Bhutta ZA, Christian P, de Onis M, et al.
Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-
with reduced incidence, severity and mortality due to diarrhoea.
income countries. Lancet. 2013; 382: 427-451. https://bit.ly/2YR5QHt
The highest daily intake of calcium was 575.58 mg/ day which 3. Hoppe C, Mølgaard C, Michaelsen KF. Cow’s milk and linear growth in
accounts for 82.23% of RDA in 1-3 years children and the lowest intake industrialized and developing countries. Annual Rev Nutr. 2006; 26: 131-171.
of calcium was 348.41 mg/ day which represents about 26.80% RDA https://bit.ly/2ZI7zPo
of calcium in 9-12 years children. The current DI values of calcium in
4. Kunz C, Rudloff S, Baier W, Klein N, Strobel S. Oligosaccharides in human
1-12 years age group children were lower than recommended daily
milk. Structural, functional and metabolic aspects. Ann Rev Nutr. 2000; 20:
allowance of calcium recommended by [23]. Upper tolerable intake 699-722. https://bit.ly/3111wpy
limit of calcium set by [28] is 2500 mg/ day for 1-8 years and 3000
5. Verrocchio ML, Di Francia A, Masucci F, Romano R, Proto V. Fatty acid
mg/ day for 9-18 years, these values are much higher than the present
composition of mediterranean buffalo milk fat. Italian J Animal Sci. 2007; 6:
findings. About 70% of calcium intake in developed countries is
509-511. https://bit.ly/31rz6Fn
obtained from milk and milk products [29].
6. AOAC, Official Methods of Analysis, Association of official analytical chemists,
The highest daily intake of magnesium and phosphorous was Arlington, Va, USA, 15th edition, 1990.
71.79 and 372.55 mg/ day, these values represent 38.94% and 80.98%
7. IDF (International Dairy Federation Bulletin). Chemical Residues in milk and
of RDA for magnesium and phosphorous in 1-3 years children. The
milk products I.D.F Documents, 1979; 133.
lowest daily intake of magnesium and phosphorous was 43.45 mg/ day
and 225.51 mg/ day, which corresponds to 12.41% and 18.04% RDA 8. National Research Council. Nutrient requirements of dairy cattle. 7th edition.
of magnesium and phosphorous in 9-12 years children. In Western National Academy Sciences. Washington. 2001; 236-267.
countries milk and dairy products account 16-21% for magnesium 9. Guha A, Gera S, Sharma A. Evaluation of milk trace elements, lactate 412
and 30-45% for phosphorous intake [30,31]. dehydrogenase, alkaline phosphatase and aspartate aminotransferase
activity of subclinical 413 mastitis as and indicator of subclinical mastitis in
Sodium and potassium are interrelated, essential nutrients that riverine buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2012; 25: 353-
play vital functional roles in the body, including being important 360. https://bit.ly/2KCuUvT
for nerve signal transmission, muscle contraction, and fluid balance.
10. Mondal M, Pyne SK, Samanta G, Roy R. Studies on trace minerals in cow
Highest daily intake values of sodium and potassium were 183.74 and
443 and buffalo milk in red lateritic zone of West Bengal. International Journal
716.99 mg/ day, these accounts for 18.37% and 23.89% of RDA for of Bio-research 444 on Environmental and Agricultural Science. 2015; 1: 36-
1-3 years children. Lowest daily intake of Na and K was 111.2 and 38. https://bit.ly/2Tl1vdt
434.01 mg/ day, which are about 7.41% and 9.64% of RDA for 9-13
11. EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies.
years children.
Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for calcium. EFSA Journal.
2015; 13: 82.
CONCLUSION
12. Canabadly-Rochellea LS, Mellemab M. Physical-chemical comparison of
The present study may be concluded that the daily intake
cow milk proteins versus soy proteins in their calcium-binding capacities.
of essential minerals was higher in 1-3 years age group children Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng Aspects. 2010; 366: 110-112.
followed by 4-8 and 9-12 years children. Furthermore it was noticed https://bit.ly/2MR2cds
SCIRES Literature - Volume 5 Issue 1 - www.scireslit.com Page - 018
You might also like
- Sunita BhoiteDocument8 pagesSunita Bhoiteprajakta kuralkarNo ratings yet
- Scientifi C Journal of Food Science & Nutrition: Keywords: Milk Essential Minerals Daily Intake Urban Area JamshoroDocument1 pageScientifi C Journal of Food Science & Nutrition: Keywords: Milk Essential Minerals Daily Intake Urban Area Jamshoroanteros facesNo ratings yet
- Relationships Between Body Condition Score in Dry-Off, Calving or Different Lactation Days and Selected Reproductive Parameters in Dairy CowsDocument7 pagesRelationships Between Body Condition Score in Dry-Off, Calving or Different Lactation Days and Selected Reproductive Parameters in Dairy CowsMaksar Muhuruna LaodeNo ratings yet
- Articulo de Leche Exposion Tercer Corte-Convertido1Document15 pagesArticulo de Leche Exposion Tercer Corte-Convertido1Jeferson Lopez RomeroNo ratings yet
- Proposal KuDocument25 pagesProposal Kuajes coolNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument4 pagesArticlebentoeNo ratings yet
- SJFSN-ID25 Part3Document1 pageSJFSN-ID25 Part3anteros facesNo ratings yet
- Dairy CattleDocument2 pagesDairy CattleLonely WolfNo ratings yet
- Prepartum Level of Dietary Cation-Anion Difference Fed To Nulliparous Cows: Acid-Base Balance, Mineral Metabolism, and Health ResponsesDocument20 pagesPrepartum Level of Dietary Cation-Anion Difference Fed To Nulliparous Cows: Acid-Base Balance, Mineral Metabolism, and Health ResponsesRoney ZimpelNo ratings yet
- Dietary Cation-Anion Difference Effects On PerformDocument10 pagesDietary Cation-Anion Difference Effects On PerformMaria MorenoNo ratings yet
- 084didier34 37Document5 pages084didier34 37leo06031314No ratings yet
- 2013 South West Nutrition ProceedingDocument174 pages2013 South West Nutrition ProceedingEuler RabeloNo ratings yet
- Adelanwaand Medugu 20151Document8 pagesAdelanwaand Medugu 20151Lokoro MarinoNo ratings yet
- 1. QUAIL EGGS CONSUMPTION AND THE LEVELS OF SELECTED MINERAL IN HEALTHY STUDENTS OF NNAMDI AZIKIWE UNIVERSITY, NNEWI. Nwankwo Emilia, Meludu Samuel Chukwuemeka, Dioka Emmanuel C , Nnodim Johnkennedy, Ezeugwunne pricilla International Journal of Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2016, 6(4):pp. 1-5. Abstract PDFDocument5 pages1. QUAIL EGGS CONSUMPTION AND THE LEVELS OF SELECTED MINERAL IN HEALTHY STUDENTS OF NNAMDI AZIKIWE UNIVERSITY, NNEWI. Nwankwo Emilia, Meludu Samuel Chukwuemeka, Dioka Emmanuel C , Nnodim Johnkennedy, Ezeugwunne pricilla International Journal of Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2016, 6(4):pp. 1-5. Abstract PDFEarthjournal PublisherNo ratings yet
- Zinc in Human MilkDocument43 pagesZinc in Human MilkFajar YuniftiadiNo ratings yet
- Afriani2018-Fe Dan ZincDocument6 pagesAfriani2018-Fe Dan ZincTitin FirawiwiraraNo ratings yet
- An MSC Project Proposal Presentation: Essien Aniebiet Uduak (19Pcp02022) Supervisor: Prof. I. S. AFOLABIDocument20 pagesAn MSC Project Proposal Presentation: Essien Aniebiet Uduak (19Pcp02022) Supervisor: Prof. I. S. AFOLABIaniebiet essienpgsNo ratings yet
- Influence of Supplementation of Fallen Apple On The Performance of Lactating CowsDocument4 pagesInfluence of Supplementation of Fallen Apple On The Performance of Lactating CowsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Digestion of Microalgal Biomass From Freshwater Species Isolated in Alberta, Canada For Monogastric and Ruminant Animal Feed ApplicationsDocument10 pagesIn Vitro Digestion of Microalgal Biomass From Freshwater Species Isolated in Alberta, Canada For Monogastric and Ruminant Animal Feed ApplicationsDiny NadiraNo ratings yet
- Digestibility, Performance and Economic Efficiency of Diets Containing Phytase and Distillers Dried Grains With Solubles For Growing PigsDocument12 pagesDigestibility, Performance and Economic Efficiency of Diets Containing Phytase and Distillers Dried Grains With Solubles For Growing PigsItzel Alexandra TorresNo ratings yet
- Loughrill PDFDocument10 pagesLoughrill PDFShalinee PrasadNo ratings yet
- Effect of Consumption of The Nutrient-Dense, Freshwater Small FishDocument17 pagesEffect of Consumption of The Nutrient-Dense, Freshwater Small FishFaisalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For AnemiaDocument186 pagesNutrition For AnemiaDimple SinghNo ratings yet
- Summary IdDocument19 pagesSummary IdMaya CindiatiNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Impact of Sprouted Pennisetum Glaucum, Functional Ingredients On Covid-19Document5 pagesNutritional Impact of Sprouted Pennisetum Glaucum, Functional Ingredients On Covid-19International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Protein Sparing Effects of Carbohydrates in The Diet of The Crayfish Procambarus Clarkii Chuang Wen Full ChapterDocument33 pagesEvaluation of The Protein Sparing Effects of Carbohydrates in The Diet of The Crayfish Procambarus Clarkii Chuang Wen Full Chapterramona.perez809100% (2)
- Efects of Daily ZincDocument12 pagesEfects of Daily ZincSumanjit DasNo ratings yet
- Nutri5 PDFDocument3 pagesNutri5 PDFfkkfoxNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Feeding Rate On Growth Performance and Body Composition of Russian Sturgeon (Acipenser Gueldenstaedtii) JuvenilesDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Feeding Rate On Growth Performance and Body Composition of Russian Sturgeon (Acipenser Gueldenstaedtii) Juvenilesdaniel cretuNo ratings yet
- 17 Gibson 2017Document9 pages17 Gibson 2017Dinda Asa AyukhalizaNo ratings yet
- Processing and ProductsDocument6 pagesProcessing and ProductsyoselinNo ratings yet
- Trace MineralDocument13 pagesTrace MineralAbdul Alim YaminNo ratings yet
- Darkwa MG Dan CaDocument6 pagesDarkwa MG Dan CaBella DirkNo ratings yet
- Advances in Marine Antifouling Coatings and TechnologiesDocument5 pagesAdvances in Marine Antifouling Coatings and Technologiesasaad lahmarNo ratings yet
- 6730-Article Text-12059-1-10-20210531Document5 pages6730-Article Text-12059-1-10-20210531Lorenzo Nieto PizarroNo ratings yet
- Actual Nutrition of Breastfeeding Women in Kashkadarya RegionDocument3 pagesActual Nutrition of Breastfeeding Women in Kashkadarya RegionCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Still Forklift Xe22 Xe30 Spare Parts List 40248047800Document22 pagesStill Forklift Xe22 Xe30 Spare Parts List 40248047800garrettmartinez090198pxz100% (116)
- 56 Exploring The Effect of Mutigrain Flour On Glycemic Index of Diabetic RatsDocument4 pages56 Exploring The Effect of Mutigrain Flour On Glycemic Index of Diabetic RatsOdilia Rondang Mauli SimarmataNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Concerns and Health Effects of Vegetarian Diets: Winston John Craig, PHD, RDDocument8 pagesNutrition Concerns and Health Effects of Vegetarian Diets: Winston John Craig, PHD, RDSarbu AndraNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Composition For Fortified Complementary FoodsDocument9 pagesNutrient Composition For Fortified Complementary FoodsFegiNo ratings yet
- Messina 2014Document6 pagesMessina 2014nta.gloffkaNo ratings yet
- Treatment Anaemea Moringa Oleifera Powder PDFDocument3 pagesTreatment Anaemea Moringa Oleifera Powder PDFCisco SilvaNo ratings yet
- Requerimientos 2019Document15 pagesRequerimientos 2019Stephanie Nicole Vásquez GuerraNo ratings yet
- Wa0001.Document10 pagesWa0001.MUTIARA KHANSA FADILLANo ratings yet
- Vitamin C Sources, Functions and AnalysisDocument18 pagesVitamin C Sources, Functions and AnalysisTi MaNo ratings yet
- Total Energy Intake and Frequency of Food Consumption in Relation To Body Mass Index of Adult Population in NigeriaDocument5 pagesTotal Energy Intake and Frequency of Food Consumption in Relation To Body Mass Index of Adult Population in NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Articulo 3vDocument16 pagesArticulo 3vKevin Jose Gonzalez MoreloNo ratings yet
- PDF 1 (Makanan Bayi)Document5 pagesPDF 1 (Makanan Bayi)RianFadlyaAmhaNo ratings yet
- Daily Consumption of Growing-Up Milk Is Associated With Less Stunting Among Indonesian ToddlersDocument7 pagesDaily Consumption of Growing-Up Milk Is Associated With Less Stunting Among Indonesian ToddlersAnugerah DestiaNo ratings yet
- FulltextDocument10 pagesFulltextZulema EmirNo ratings yet
- Fpls 12 682842Document20 pagesFpls 12 682842Nama RajasekharNo ratings yet
- Asra Thesis 1Document32 pagesAsra Thesis 1Asra Zafar khanNo ratings yet
- ASSESMENT OF HEAVY METALS Assessment of PDFDocument10 pagesASSESMENT OF HEAVY METALS Assessment of PDFAnwar UL HassanNo ratings yet
- Foods 09 00175 v2Document16 pagesFoods 09 00175 v2Arunkumar ANo ratings yet
- Palupi - 2021 - Food Security During Pandemic - PDF 40 ShowDocument66 pagesPalupi - 2021 - Food Security During Pandemic - PDF 40 ShowPutri RimtyaNo ratings yet
- Trisodium Citrate Use in Dairy Cows and Effects On Daily Milk Yield and QualityDocument4 pagesTrisodium Citrate Use in Dairy Cows and Effects On Daily Milk Yield and QualityDr-Sadaqat Ali RaoNo ratings yet
- I J R P S: Proximate, Minerals, and Vitamins in Chayote FlourDocument4 pagesI J R P S: Proximate, Minerals, and Vitamins in Chayote FlourHazel BalonglongNo ratings yet
- Veterinary and Animal Science: Original ArticleDocument8 pagesVeterinary and Animal Science: Original ArticleDias HanifNo ratings yet
- Brmedj01450 0022Document3 pagesBrmedj01450 0022Kamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- MOD Pizza Nutritional FactsDocument3 pagesMOD Pizza Nutritional FactsyogurtgreekNo ratings yet
- PRE-TEST in COOKERY GRADE 9Document1 pagePRE-TEST in COOKERY GRADE 9mary grace manalangNo ratings yet
- Ryzon Baking BookDocument88 pagesRyzon Baking Bookbsaracco1100% (4)
- Hittite CuisineDocument3 pagesHittite Cuisineapi-273732504No ratings yet
- II. Learning Skills From The MELCS: Page-Prepared By: Cristine Q. GorubatDocument3 pagesII. Learning Skills From The MELCS: Page-Prepared By: Cristine Q. GorubatLerwin GaringaNo ratings yet
- Creme Brulee Recipe - Alton Brown - Food NetworkDocument1 pageCreme Brulee Recipe - Alton Brown - Food NetworkmtlpcguysNo ratings yet
- Sweet Blue Lupin Growing GuideDocument4 pagesSweet Blue Lupin Growing Guidecontadino_impazzitoNo ratings yet
- Export Strategies For The Halal MarketDocument14 pagesExport Strategies For The Halal MarketNur IskandarNo ratings yet
- NSF International / Nonfood Compounds Registration ProgramDocument2 pagesNSF International / Nonfood Compounds Registration ProgramLuciano Oliveira TurraNo ratings yet
- Sabudana DosaDocument9 pagesSabudana DosaSavithri MurthyNo ratings yet
- Reference Codex StandDocument16 pagesReference Codex Standgameel thabitNo ratings yet
- Food MenuDocument4 pagesFood Menualok kundaliaNo ratings yet
- Organic Feeds Using Indigenous Microbial Fermented Imf Feeds For Organic Free Range Native Pigs and ChickensDocument67 pagesOrganic Feeds Using Indigenous Microbial Fermented Imf Feeds For Organic Free Range Native Pigs and ChickenskarikambingNo ratings yet
- THINK L1 Unit 3 GrammarDocument2 pagesTHINK L1 Unit 3 Grammarsol_zota13100% (1)
- Level: B1 Pearson Business English Lessons: February 2019Document5 pagesLevel: B1 Pearson Business English Lessons: February 2019Piotr LorekNo ratings yet
- Free Food DiaryDocument31 pagesFree Food DiaryBianca Cristina Prandi100% (1)
- Food Waste: Commitments & AchievementsDocument37 pagesFood Waste: Commitments & Achievementsana salehNo ratings yet
- SWOT White RadishDocument1 pageSWOT White Radishalyaa adriana100% (1)
- Fast Food ShopDocument2 pagesFast Food ShopMuhammad MunsifNo ratings yet
- MRBR Ageing Overview: QuantityDocument129 pagesMRBR Ageing Overview: QuantityIngrida1113No ratings yet
- Franzo 2017Document2 pagesFranzo 2017Aña FelicienNo ratings yet
- Kerbside Recycling Calendar - Week 1: February 2018 March 2018 April 2018 May 2018Document2 pagesKerbside Recycling Calendar - Week 1: February 2018 March 2018 April 2018 May 2018Graeme HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Croatian Eno Gastronomy 2014 2015 EN PDFDocument98 pagesCroatian Eno Gastronomy 2014 2015 EN PDFZoran H. VukchichNo ratings yet
- Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesTeaching PlanGeralyn KaeNo ratings yet
- Best Ever Vegan Brownies Recipe - Nora CooksDocument2 pagesBest Ever Vegan Brownies Recipe - Nora Cooksash hillsNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: Catalino D. Salazar National High School - Senior High School Subay, Cardona, RizalDocument7 pagesBusiness Plan: Catalino D. Salazar National High School - Senior High School Subay, Cardona, RizalAivanfred SarangueroNo ratings yet
- Review On The High Pressure Technology HPT For Food Preservation 2157 7110.1000135Document5 pagesReview On The High Pressure Technology HPT For Food Preservation 2157 7110.1000135MohsinNo ratings yet
- Beer PlantDocument62 pagesBeer PlantAjay Kr DuttaNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian Nutrition For TeenagersDocument2 pagesVegetarian Nutrition For TeenagersVegan FutureNo ratings yet
- Impact Assessment Survey Questionnaire: S.No Questions (A) (B) (C) (D)Document6 pagesImpact Assessment Survey Questionnaire: S.No Questions (A) (B) (C) (D)Nishant GauravNo ratings yet