Professional Documents
Culture Documents
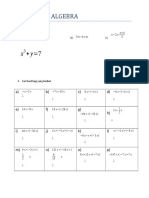
Worksheet 4. Algebraic Language.: A 8 y 4 y y y
Uploaded by
DianaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
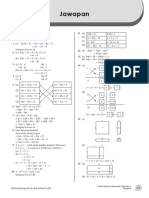
Worksheet 4. Algebraic Language.: A 8 y 4 y y y
Uploaded by
DianaCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 4. Algebraic Language.
1. Calculate:
a ¿−7 x 3+ 6 x 3 b) 3 y 2 +9 y 2−2 y 2 c) −5 x 4 ∙8 y
d) 3 x 2 ∙ 4 y 3 e) 15 xyz : 3 xyz f) 16 x 3 y 4 : 2 x 2 y
2. Work out these operations:
a) 6 x 3−2 x+ 3 x 2−8 x + x 2
b) 4 x y 2 +7 x 3 y 2−(6 x y 2 +3 x 3 y 2 )
3. Given the polynomials P ( x ) =2 x 5−3 x 4 +3 x 2−5 and
Q ( x ) =x5 +6 x 4 −4 x3 −x+7 work out: P ( x ) +2 Q ( x ) ∧P ( x )−Q ( x ) .
4. Work out this product: (3 x 2+5 x−6)(8 x2−3 x + 4)
5. Take out the common factor in these polynomials:
a ¿ x ¿2+ 5 x e) 3 x 3−6 x +9 i) 6 x 2 y 2−3 y 2 +30 x 2 y
3
b ¿ 2 x −x f ¿ x ¿ −x + x
3 9 4
j ¿ 3 x+ 6 y−9 z
3 2
c ¿ 3 x −6 x +9 g) 4 3
6 x −24 x +12 x
2
k) ( x +1 )( x−3 )+ ( x −3 ) ( x +2 )
3 2
d ¿ 3 x −6 x +9 x
5 2
h ¿−4 x +3 x −x l) 3 ( x+ 1 )+ ( 6+6 x )
6. Considering the polynomials written bellow p(x), q(x) and r(x) ,work out:
a) p(x) + q(x);
b) p(x) - q(x);
c) p(x) + q(x) - r(x);
d) p(x) - q(x) -r(x).
p( x )=3x 2 +5x−6 ; q( x )=5x 2 +8x−9 ; r ( x )=3x +4 .
7. Considering the polynomials p(x) and q(x) written bellow, work out:
a) p(x) + q(x);
b) q(x) - p(x);
c) p(x)·q(x).
3 2 3 2
p( x )=x −5x +7 ; q (x )=2x +6x −3x+1 .
8. Considering the polynomials p(x), q(x) & r(x) written bellow, calculate:
a) p(x) + q(x);
b) p(x) - q(x);
c) p(x) + q(x) - r(x);
d) p(x) - q(x) -r(x).
3 2 3 2 3
p( x )=4x +3x −5x +6 ; q (x )=x −6x +2x−7 ; r ( x )=x −7 .
9. Considering the polynomials p(x), q(x) and r(x) written bellow, calculate:
a) p(x)·q(x);
b) p(x)·r(x);
c) q(x)·r(x).
2 2
p( x )=4x −13x+20 ; q( x )=10x −7x+8 ; r ( x )=5x−1 .
10. Considering the polynomials p(x), q(x) and r(x) written bellow, calculate:
a) p(x)·q(x);
b) p(x)·r(x);
c) q(x)·r(x).
p( x )=2x 4 + x 2−2 ; q ( x )=2x 4 −x 2 +4 ; r (x )=3x 4 +15.
11. Considering the polynomials p(x) and q(x) written bellow, calculate:
a) p(x) + q(x);
b) p(x) - q(x);
c) p(x)·q(x).
p( x )=5x 4 +4x 3 +3x 2 +2x +1 ; q( x )=x 4 −x 2−2.
12. Divide these polynomials using Ruffini’s rule. Which one is an exact division?
a ) ( 4x 2−13x +10 ) : ( x−2 ) ; b ) ( 5x2 + 8x−9 ) : ( x+ 1 ) ; c ) ( x 4 −x 2−2 ) : ( x−1 ) .
c ) ( x 3 +6x 2 +5x−12 ) : ( x +4 ) ; d ) ( 4x 3 −9x +8 ) : ( x+ 2 ) ; e ) ( 7x 4 −5x2 +1 ) : ( x−1 ) .
f ) ( 1−x 6 ) : ( 1+ x ) ; g ) ( 4x3 + 3x2 −5x+ 6 ) : ( x−2 ) ; h) ( 2x 4 +3x 2−5 ) : ( x +3 ) .
Calculate using the remarkable identities:
( x+4 )2 ( √ 3x+ y )2 ; (7x+2y )(7x−2y );
( x−5)
2 (−a+5b )( a+5b);
( 10a−3b )2 ;
( x3 −3 )2
(−2h−3z )2 . (2 7 2 7
)(
a+ b a− b .
5 3 5 3 )
2 3 2
(3 x + x ) ( 5 x−1 )2
(2x−3 )2
( 2 x 2−1/ 2 )
2 (12 x+ 34 y )(12 x−34 y );
( √7−3z )( √7+3z ) ;
(−5h+3m ) (−5h−3m ) .
14. Factorize these polynomials indicating their roots.
a ) x 3 +6x2 −31x−36;
b ) x 3 −9x 2 −5x+33;
c ) x 3 −2x2 −45x+126 .
15. Find a polynomial with only these roots:
a) -5, 3, 8
b) 0, 3, 6
16. Find the roots of these polynomials and factorize them:
a ) x 3 +6x2 −31x−36; d ) 2x 3 +6x 2 −50x+42;
b ) x 3 −9x 2 −5x+33; e ) 3x3 −15x 2 −3x+15;
c ) x 3 −2x2 −45x+126 . f ) x3 −9x .
g) x 3 −13x2 +42x; j ) x 3 −4x 2 −37x+40;
h ) 4x3 −32x 2+4x+168; k ) x 3 +13x2 +42x;
i) x3 −3x 2 −88x−240 . l) x 3−7x 2 +7x +15 .
m) x 3−4x 2−103x−182; o ) x3 +8x 2−80x−384;
n ) x 3−7x 2−16x +112; p) 11x 3 +21x 2 −35x+3;
ñ ) x3−4x2 +9x−10 . q ) x3 −23x 2 +135x−225 .
r) x 3 −9x 2−84x+196;
s) x 3 −3x2 −97x +99;
t ) x3 +6x 2−61x−210 .
You might also like
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Factor TheromDocument1 pageFactor TherommanavomguptaNo ratings yet
- Chuyên Đề Về Giải Phương Trình Baøi 1.Giaûi caùc phöông trình sauDocument5 pagesChuyên Đề Về Giải Phương Trình Baøi 1.Giaûi caùc phöông trình sauNanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- M × 2 QR Abc ×6 Ac : Basic Skills: Topic 0: Expressions and Algebraic Equations DateDocument4 pagesM × 2 QR Abc ×6 Ac : Basic Skills: Topic 0: Expressions and Algebraic Equations DateEvan ChenNo ratings yet
- Revisao Matematica1Document2 pagesRevisao Matematica1Eliu AraujoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Algebraic Expressions: Pre-Calculus and Calculus - Indb 67 13/7/2017 5:56:57 PMDocument2 pagesChapter 2 - Algebraic Expressions: Pre-Calculus and Calculus - Indb 67 13/7/2017 5:56:57 PMDiego TrianaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Week1 KeyDocument5 pagesLaboratory Week1 KeyhasanmunnabcicNo ratings yet
- 2018 MCR 3UI Exam Review PackageDocument12 pages2018 MCR 3UI Exam Review PackageNHNo ratings yet
- Class X Quadratic EquationsDocument3 pagesClass X Quadratic EquationsTanishNo ratings yet
- 3-3 Multiplying Polynomials by Monomials CYUDocument5 pages3-3 Multiplying Polynomials by Monomials CYUvNo ratings yet
- Factorising Using The Difference of Two Squares: (X - A) (X + A) X - ADocument4 pagesFactorising Using The Difference of Two Squares: (X - A) (X + A) X - Aerika putriNo ratings yet
- Calcul NR - RealeDocument1 pageCalcul NR - RealeIzabelle ButurugaNo ratings yet
- Multiplying PolynomialsDocument4 pagesMultiplying PolynomialsFarrah QuiyanNo ratings yet
- Uitkomsten Analyse 1 LW 4 Definitief 2Document14 pagesUitkomsten Analyse 1 LW 4 Definitief 2Caroline SpildoorenNo ratings yet
- Keefe 20 September 2023Document3 pagesKeefe 20 September 2023wisnuNo ratings yet
- MATH 30.13 Long Test 1 Practice Problems-3Document2 pagesMATH 30.13 Long Test 1 Practice Problems-3enzo.goNo ratings yet
- LimitDocument11 pagesLimitKristan Glen PulidoNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 6linear EquationsDocument5 pagesTOPIC 6linear Equationsasu069422No ratings yet
- Algebra Guía de Estudio Examen EmpresaDocument8 pagesAlgebra Guía de Estudio Examen EmpresaLucrecia Lucia BorgiaNo ratings yet
- A1 U9 TestDocument3 pagesA1 U9 Testapi-274495401No ratings yet
- Learning ACTIVITY SHEETS For Grade 9Document5 pagesLearning ACTIVITY SHEETS For Grade 9999saitama 999No ratings yet
- Solutions To Sec 2 Express Mid-Year Revision 2: X X X XDocument7 pagesSolutions To Sec 2 Express Mid-Year Revision 2: X X X Xlow_jacksonNo ratings yet
- Clasificación de NúmerosDocument5 pagesClasificación de NúmerosJulio César DoloresNo ratings yet
- Ecuatii Fise XDocument1 pageEcuatii Fise XDiana OprescuNo ratings yet
- Soluciones Polinomios: Descomposición Factorial: Matemáticas 3º Eso - ÁlgebraDocument2 pagesSoluciones Polinomios: Descomposición Factorial: Matemáticas 3º Eso - ÁlgebraInes Maria Lanza DominguezNo ratings yet
- 31 Linear InequalitiesDocument3 pages31 Linear InequalitiesCally ChewNo ratings yet
- Algebra - Factorising (2. Exe)Document5 pagesAlgebra - Factorising (2. Exe)Zach ChngNo ratings yet
- BasicWS 1Document4 pagesBasicWS 1Jason YipNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Algebraic ExpressionsDocument8 pagesUnit 4 - Algebraic Expressionsbemdas0% (1)
- Math 1022 - Beginning of Semester ReviewDocument2 pagesMath 1022 - Beginning of Semester ReviewRashid DavisNo ratings yet
- C4 RevisionDocument52 pagesC4 RevisionMoustafa SohdyNo ratings yet
- Modul AlgebraDocument10 pagesModul AlgebraPusatTuisyen FaizaJaya Sg BesiNo ratings yet
- Msm111-Tutorial Sheet One - 210913 - 180017Document2 pagesMsm111-Tutorial Sheet One - 210913 - 180017Oscar MwanzaNo ratings yet
- MTH1101 Worksheet 2Document2 pagesMTH1101 Worksheet 2Ghansham SamarooNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-09-02 at 9.10.40 PMDocument24 pagesScreenshot 2022-09-02 at 9.10.40 PMvarunasathishkumar555No ratings yet
- Remainder TheromDocument1 pageRemainder TherommanavomguptaNo ratings yet
- Ficha 1: Repaso de Ecuaciones 1ºgrado Sin DenominadoresDocument1 pageFicha 1: Repaso de Ecuaciones 1ºgrado Sin DenominadoressabaterromerojNo ratings yet
- Quinta Lista de Exerc Icios de Revis Ao Polin Omios. Produtos Not Aveis. Fatora C Ao. Equa C Oesdo2 GrauDocument3 pagesQuinta Lista de Exerc Icios de Revis Ao Polin Omios. Produtos Not Aveis. Fatora C Ao. Equa C Oesdo2 GrauVonWinkelmannNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expression Linear Equation Practice ExerciseDocument3 pagesAlgebraic Expression Linear Equation Practice ExerciseUtkarshKumbhareNo ratings yet
- Ecuacin de 1er GradDocument1 pageEcuacin de 1er GradReik Luiz DiazNo ratings yet
- Zadaci Za VježbuDocument3 pagesZadaci Za VježbuAna PetrićNo ratings yet
- T2P2 Penyelesaian Lengkap PDFDocument4 pagesT2P2 Penyelesaian Lengkap PDFQhairina Sofea0% (1)
- Algebra Year9 AdvDocument9 pagesAlgebra Year9 AdvYung ATMNo ratings yet
- FACTORING COMPLETELYDocument12 pagesFACTORING COMPLETELYTurhan BAYRAKTARNo ratings yet
- G.T A 1Document5 pagesG.T A 1jyllianefgasconNo ratings yet
- Ibmec - Introdução ao Cálculo 1o ListaDocument2 pagesIbmec - Introdução ao Cálculo 1o ListadanieldebianNo ratings yet
- Algebra Worksheet2Document1 pageAlgebra Worksheet2Samjit WellyNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Intensified Review for Final ExamDocument9 pagesAlgebra 2 Intensified Review for Final ExamAceNo ratings yet
- Math - G9 - Worksheet#3 - Algebraic - Expressions - Extra PracticeDocument6 pagesMath - G9 - Worksheet#3 - Algebraic - Expressions - Extra PracticeAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- MATH 101 Tutorial 2Document2 pagesMATH 101 Tutorial 2Belem CarterNo ratings yet
- Tarea de MatematicasDocument4 pagesTarea de MatematicasGiovanny Silva AyastaNo ratings yet
- Hukum IndeksDocument33 pagesHukum Indekssyaaban69No ratings yet
- Factorizar polinomiosDocument3 pagesFactorizar polinomiosJuanaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths - EquationsDocument50 pagesGCSE Maths - EquationsPrinceShalomNo ratings yet
- 6th 7th SPARK OTDocument8 pages6th 7th SPARK OTabhysanaacoNo ratings yet
- m26 Rev3t PDFDocument2 pagesm26 Rev3t PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Summer Math Assignment 2022Document5 pagesAlgebra 2 Summer Math Assignment 2022Start2panicNo ratings yet
- Act AlgebraDocument3 pagesAct AlgebraFlorencia Rial OviedoNo ratings yet
- Guia Ecuac Q Fracc OctDocument1 pageGuia Ecuac Q Fracc OctppozoaNo ratings yet
- Algebra CHSL 2020Document26 pagesAlgebra CHSL 2020Easy learningNo ratings yet
- Toxicity Study of Salacia Reticulata Extract PowderDocument9 pagesToxicity Study of Salacia Reticulata Extract PowderAnh LevanNo ratings yet
- Self-Operated Pressure Regulators ANSI Version: T 2513 EN Type 41-23 Universal Pressure Reducing ValveDocument6 pagesSelf-Operated Pressure Regulators ANSI Version: T 2513 EN Type 41-23 Universal Pressure Reducing ValveagrovadoNo ratings yet
- How to Write a Resume for a Job ApplicationDocument4 pagesHow to Write a Resume for a Job ApplicationPhuong Dang AnhNo ratings yet
- Thematic Teaching in Basic EducationDocument13 pagesThematic Teaching in Basic EducationCyryhl Gutlay100% (1)
- Modelling and simulating patient pathways at a Moroccan mother-child hospitalDocument7 pagesModelling and simulating patient pathways at a Moroccan mother-child hospitalashlyduartNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization Using Bottom Ash and Areca Fiber: Experimental Investigations and Reliability AnalysisDocument11 pagesSoil Stabilization Using Bottom Ash and Areca Fiber: Experimental Investigations and Reliability AnalysisHugo Dario Machaca CondoriNo ratings yet
- Thermal Expansion of Iridium at High TemperaturesDocument5 pagesThermal Expansion of Iridium at High TemperaturesAntonio CamaranoNo ratings yet
- ASTM E1845 - Standard Practice For Calculating Pavement Macrotexture Mean Profile Depth PDFDocument4 pagesASTM E1845 - Standard Practice For Calculating Pavement Macrotexture Mean Profile Depth PDFrendy100% (1)
- Logical FallaciesDocument15 pagesLogical FallaciesLouis Marvil AbalaNo ratings yet
- Asturo Sandblasting Guns enDocument3 pagesAsturo Sandblasting Guns enHonoluluNo ratings yet
- Impact of Performance Management at InfosysDocument8 pagesImpact of Performance Management at InfosysN Pritam DasNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution Method ExplainedDocument37 pagesMoment Distribution Method ExplainedSuleiman Yusuf JibrilNo ratings yet
- FAW-Guidance Note-2 PDFDocument2 pagesFAW-Guidance Note-2 PDFaiktiplarNo ratings yet
- Through Hole Connector Solder Joint Hole FillDocument4 pagesThrough Hole Connector Solder Joint Hole FillRandom AccessNo ratings yet
- Working Paper No: 384: Amit GuptaDocument26 pagesWorking Paper No: 384: Amit Guptanpr_mishraNo ratings yet
- 15.production and Productivity Improvement Measures at MOIL-MOILDocument8 pages15.production and Productivity Improvement Measures at MOIL-MOILkatta_sridharNo ratings yet
- Science News - June 19, 2021 USADocument36 pagesScience News - June 19, 2021 USAblabla11No ratings yet
- AStudyof Planning Designand Constructionof Buildingsin Hilly Regionsof IndiaDocument11 pagesAStudyof Planning Designand Constructionof Buildingsin Hilly Regionsof IndiaRiddhi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis Alan Wijaya 2018Document2 pagesMSC Thesis Alan Wijaya 2018Alan WijayaNo ratings yet
- Research 3Document76 pagesResearch 3Jackson IbascoNo ratings yet
- Empirical Correlation Between CaliforniaDocument94 pagesEmpirical Correlation Between CaliforniaRefilwe MoorosiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Halal Awareness, Halal Logo and Attitude On Foreign Consumers' Purchase IntentionDocument19 pagesEffect of Halal Awareness, Halal Logo and Attitude On Foreign Consumers' Purchase IntentionandiahmadabrarNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - English For TOEFL PreparationDocument26 pagesGroup 7 - English For TOEFL PreparationNindySJaNo ratings yet
- Pseudo-Chomsky ThreeDocument4 pagesPseudo-Chomsky ThreeTyler ShortNo ratings yet
- Competitive Club Soccer: Parents' Assessments of Children's Early and Later Sport Specialization - PDocument12 pagesCompetitive Club Soccer: Parents' Assessments of Children's Early and Later Sport Specialization - PAodhan Jane MooneyNo ratings yet
- Water Budget Equation Exercise Problems SolvedDocument10 pagesWater Budget Equation Exercise Problems SolvedSheeraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Thermo ScientificDocument29 pagesThermo ScientificTaeng SoshiNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Alexis T. Lopez, BSHM 3 ASS #1: Quality Service in HM and TMDocument6 pagesSubmitted By: Alexis T. Lopez, BSHM 3 ASS #1: Quality Service in HM and TMWyn TerNo ratings yet
- Implementasi Perda Sampah KendariDocument15 pagesImplementasi Perda Sampah KendariretnoayuNo ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithms: Department of Computer Science, University of New Mexico, AlbuquerqueDocument4 pagesGenetic Algorithms: Department of Computer Science, University of New Mexico, AlbuquerqueESMAILNo ratings yet