Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geiger Muller Counter (G-M Counter (What Is Geiger Muller Counter
Uploaded by
Ben AhmedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geiger Muller Counter (G-M Counter (What Is Geiger Muller Counter
Uploaded by
Ben AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
المملكة العربية السعودية
Ministry of Education وزارة التعليم
Al-Baha University جامعة الباحة
Faculty of Science كلية العلوم
Physics Program برنامج الفيزياء
Geiger muller counter (G-M counter (
What is Geiger muller counter:
This is a gas based detector which uses ionization of gas by radiation as the primary
tool to detect radiation. The tube is in the form of:
The cylinder and is filled up with noble gas at certain low pressure.
Anode: metallic string which runs through the central axis of the cylindrical
shape
Cathode: outer shell serves . One end of the tube has radiation permeable
window
Any radiation incident on the tube window will ionize the noble gas. The electrons
thus ejected will get attracted towards the anode whereas the heavy ions will move
slowly towards cathode. These charges will further ionize more number of atoms
thereby setting up an avalanche of ions and electrons which sets up a discharge
current. The current causes the voltage between the anode and cathode to drop which
the counter detects as a signal.
The figure1 shows the complete experimental set up for the experiment. The tube is
mounted on a structure which have different slots to place the source. The tube is
connected to the GM Counter Console which hosts the electronics for amplification
and counting. It also provides the necessary power
We will study 3 Experiments about Geiger muller counter:
1. Plotting of Plateau curve
2. Dead time of G-M counter (Two source method)
3. Efficiency of G-M counter
Experiment (1): Plotting of Plateau curve
Objectives:
Plotting of Plateau curve and Determination of threshold voltage and operating
voltage of G-M counter
Tools:
Geiger muller counter
Radioactive source.
High-voltage power supply
Theory:
To observe the effect of incident radiation on GM tube, we need to increase the
voltage between anode and cathode, to a value where the gas amplification sets in.
This voltage is called (Threshold Voltage) or (starting voltage) Thereafter, the
counting rate keeps on increasing till the voltage reaches a knee value beyond which
the count rate becomes saturated or constant. In this constant region of operation all
the primary events are recorded irrespective of the energy. This flat region is called
(Plateau of the counter). If we keep still keep on increasing the voltage, the tube will
run in to continuous (discharge region) which is not desirable. The mid point of the
plateau region is taken to be the (Operating Voltage) of the GM tube and once
determined, the tube must be operated at this value for subsequent experiments.
Experiment procedure:
1. After setting up the GM tube and electronics we can start our experiment.
2. Place the source at a distance of around 6 mm.
3. One can set up a starting voltage around 240V with increase voltage 40V each
time.
4. Set the time of 1 min.
5. Stop the experiment at around 740V or before.
6. To count background counts in the laboratory. repeat the steps without a source
7. Subtract the corresponding background count from each reading and record the
correct counts vs voltage in table.
8. plot of Corrected Count Rate vs Voltage.
Experimental Nuclear Physics (1) Dr. Salwa Sayed
Mohamed
Experiment (1): Name:
Plotting of Plateau curve Student number:
Complete the table below:
Time = 60 Second
Background B.G N=
No. Voltage (V) Count (N-B. G)
Experimental Nuclear Physics (1) Dr. Salwa Sayed
Mohamed
Calculating:
1. Plot of corrected Count vs Voltage
2. Calculate:
threshold voltage =
Knee Voltage =
Operating Voltage = mean plateau region =
Experimental Nuclear Physics (1) Dr. Salwa Sayed
Mohamed
With best regards
Experimental Nuclear Physics (1) Dr. Salwa Sayed
Mohamed
You might also like
- Geiger Muller Counter (G-M Counter (Document8 pagesGeiger Muller Counter (G-M Counter (Ben AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab RPRT GM CountrDocument13 pagesLab RPRT GM CountrMuhammad ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law Lab ReportDocument5 pagesOhms Law Lab ReportI Anonymous100% (6)
- B.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualDocument87 pagesB.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualSwastika sainNo ratings yet
- Franck-Hertz Experiment: Experiments For B. Tech. 1 Year Physics LaboratoryDocument6 pagesFranck-Hertz Experiment: Experiments For B. Tech. 1 Year Physics LaboratoryHypo KadambariNo ratings yet
- Meter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge PrincipleDocument12 pagesMeter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge PrincipletahsNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Geophysics Lab Report: Rohit Kumar 16EX20021Document12 pagesNuclear Geophysics Lab Report: Rohit Kumar 16EX20021Rohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Ee303 Lab5Document6 pagesEe303 Lab5Tariq AlharbiNo ratings yet
- E1 03 PDFDocument8 pagesE1 03 PDFreza515heiNo ratings yet
- GM CounterDocument4 pagesGM CounterPRATHAMESH MOHILENo ratings yet
- Garcia&Gelle AdLab GeigerMullerCounterDocument3 pagesGarcia&Gelle AdLab GeigerMullerCounterkashawna fujiwaraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 PDFDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 PDFHITESHBHAI TADVINo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document8 pagesLab Report 1Eagle DesignsNo ratings yet
- Franck Hertz Experiment With Argon: 1. PurposeDocument5 pagesFranck Hertz Experiment With Argon: 1. PurposeKomal DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Instruction For The Journal Write-UpDocument22 pagesInstruction For The Journal Write-Upsubhajana646No ratings yet
- Lebanese International University School of Engineering: Department of Engineering Electric Circuits Lab EENG301LDocument14 pagesLebanese International University School of Engineering: Department of Engineering Electric Circuits Lab EENG301LOmar SroujiNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Lab ManualDocument53 pagesApplied Physics Lab Manualarehanliaqat8125100% (3)
- Geiger M Uller Counter (GM Counter)Document26 pagesGeiger M Uller Counter (GM Counter)AviteshNo ratings yet
- Lab1 - Manuel AbadieDocument6 pagesLab1 - Manuel AbadieManuel AbadieNo ratings yet
- Applied - Physics - Ii - Lab - ManualDocument36 pagesApplied - Physics - Ii - Lab - Manualssukhmeet551No ratings yet
- APLR2Document12 pagesAPLR2Adeel YounusNo ratings yet
- Instituto Politécnico Nacional: Practica 3 2da Ley de KirchhoffDocument9 pagesInstituto Politécnico Nacional: Practica 3 2da Ley de KirchhoffYovanny RiveraNo ratings yet
- Elab3 Jan 09Document13 pagesElab3 Jan 09Marlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- 6 Frank-HertzDocument6 pages6 Frank-HertzWasimNo ratings yet
- Gamma Spectroscopy: Pre-Lab: Physics 160 Principles of Modern Physics Laboratory Session #9Document5 pagesGamma Spectroscopy: Pre-Lab: Physics 160 Principles of Modern Physics Laboratory Session #9Mohammad AlmistarehiNo ratings yet
- Expt. No.7-Series Circuit (Manual and Tabulation)Document3 pagesExpt. No.7-Series Circuit (Manual and Tabulation)Ryan S. BudionganNo ratings yet
- Phys 212l Lab Report 10 Table 2Document10 pagesPhys 212l Lab Report 10 Table 2api-609727211No ratings yet
- RC CircuitsDocument4 pagesRC Circuitsjack daniels0% (1)
- Lebanese International University School of EngineeringDocument12 pagesLebanese International University School of EngineeringHassan RashedNo ratings yet
- Subject: Physics Laboratory Subject Code: Phs 383 Reg No:19U10781Document34 pagesSubject: Physics Laboratory Subject Code: Phs 383 Reg No:19U10781ShanmukhNo ratings yet
- Lebanese International University School of Engineering: (5 Points)Document13 pagesLebanese International University School of Engineering: (5 Points)Omar SroujiNo ratings yet
- Resistance and Ohms LawDocument8 pagesResistance and Ohms LawShannon NormanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Construction Kit Lab: Part 1: Ohm's LawDocument13 pagesCircuit Construction Kit Lab: Part 1: Ohm's LawRAFIQANo ratings yet
- PHYWE (2013) Alpha-Energies of Different Sources With Multi Channel Analyzer, ManualDocument4 pagesPHYWE (2013) Alpha-Energies of Different Sources With Multi Channel Analyzer, ManualLuis Percy VargasNo ratings yet
- EE 311 (Electronics I) Lab Time: Tuesday 1-3: Ahmad Alshatri 0908942 Mohammad Alharbi 0910685Document5 pagesEE 311 (Electronics I) Lab Time: Tuesday 1-3: Ahmad Alshatri 0908942 Mohammad Alharbi 0910685Mohammad AlharbiNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Name of The Experiment: Verification of KVL & Voltage Devider RuleDocument7 pagesBangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Name of The Experiment: Verification of KVL & Voltage Devider RuleSayeed Mohammed100% (1)
- Oscilloscope Voltage Measurements: Department of Electrical Engineering - CEAT, UP Los BañosDocument4 pagesOscilloscope Voltage Measurements: Department of Electrical Engineering - CEAT, UP Los BañosSagnale UnnoNo ratings yet
- FaradayDocument5 pagesFaradaysapna24No ratings yet
- G01 Physics Lab 6Document11 pagesG01 Physics Lab 6Irtisam AlaviNo ratings yet
- Geiger Lab ReportDocument8 pagesGeiger Lab Reportmusu.yanguba9329100% (1)
- 203 Lab04 Circuits Sum08 PDFDocument6 pages203 Lab04 Circuits Sum08 PDFJun MendozaNo ratings yet
- Exp-3 Fe15 - 52 KeshavDocument7 pagesExp-3 Fe15 - 52 Keshavomkar patilNo ratings yet
- QSP Lab Manual 2024Document20 pagesQSP Lab Manual 2024Vaibhav BkNo ratings yet
- Eee Lab ReportDocument9 pagesEee Lab ReportNasimNo ratings yet
- Operating Characteristics of GM CounterDocument7 pagesOperating Characteristics of GM Counterrishi4charmNo ratings yet
- Experiment b3Document7 pagesExperiment b3Cek AjaNo ratings yet
- Lab - 1 Diode Char & RectifiersDocument5 pagesLab - 1 Diode Char & Rectifiersdgebeyehu90No ratings yet
- Ee310 Experiment 6 PDFDocument26 pagesEe310 Experiment 6 PDFJoseph KitongaNo ratings yet
- GM CounterDocument29 pagesGM CounterDhanapal PalNo ratings yet
- Rosemary Ainslie. Quantum October 2002Document5 pagesRosemary Ainslie. Quantum October 2002MANNAJANELAGUNANo ratings yet
- ESN 104 Circuit Construction Kit LabDocument12 pagesESN 104 Circuit Construction Kit LabRhona CantagoNo ratings yet
- Phy108 Lab Manual PDFDocument30 pagesPhy108 Lab Manual PDFSumaya Akter Ruhi 2022610642No ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument13 pagesElectricity and MagnetismMohd KhairulNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Polarisation Measurements With The Sawyer-Tower MethodDocument4 pagesTime Domain Polarisation Measurements With The Sawyer-Tower MethodRakesh SandarativjuNo ratings yet
- Bauerly - CW NMRDocument9 pagesBauerly - CW NMRBrandon BauerlyNo ratings yet
- Umkc Circuits Lab 1Document9 pagesUmkc Circuits Lab 1AlexEckhoffNo ratings yet
- Expt. No.6 (Ohm's Law)Document2 pagesExpt. No.6 (Ohm's Law)Ryan S. BudionganNo ratings yet
- ورقة عمل Microsoft Excel جديدDocument2 pagesورقة عمل Microsoft Excel جديدBen AhmedNo ratings yet
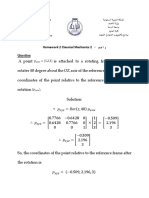
- HomeWork 2 Mechanics 2Document1 pageHomeWork 2 Mechanics 2Ben AhmedNo ratings yet
- ابع واجب المحاضرة الأولى معادلات تفاضليةDocument1 pageابع واجب المحاضرة الأولى معادلات تفاضليةBen AhmedNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics 2: Homework 2 SolutionDocument2 pagesClassical Mechanics 2: Homework 2 SolutionBen AhmedNo ratings yet
- Homework Electronics 1Document3 pagesHomework Electronics 1Ben AhmedNo ratings yet
- Advanced Vocabulary Second AssignmentDocument2 pagesAdvanced Vocabulary Second AssignmentBen AhmedNo ratings yet
- 348 - 38835 - BA124 - 2018 - 4 - 2 - 1 - Area and VolumeDocument13 pages348 - 38835 - BA124 - 2018 - 4 - 2 - 1 - Area and Volumephysics a2No ratings yet
- Free-Samples - Amie - Chapters - Single Stage and Multi Stage Amplifiers-Sec-B-EcDocument38 pagesFree-Samples - Amie - Chapters - Single Stage and Multi Stage Amplifiers-Sec-B-EcSivakumar PothirajNo ratings yet
- Chavez Vs JBCDocument4 pagesChavez Vs JBCjanmerNo ratings yet
- Ethics PaperDocument126 pagesEthics PaperDarshanSinghS100% (1)
- Combinatorial Chemistry Amp High Throughput Screening PDFDocument2 pagesCombinatorial Chemistry Amp High Throughput Screening PDFLamarcusNo ratings yet
- Jordan ResumeDocument3 pagesJordan Resumeapi-462816920No ratings yet
- Masters CompScience SOPDocument3 pagesMasters CompScience SOPSantosh ShetNo ratings yet
- Outpatient Appointment Systems in Healthcare - A Review of Optimization StudiesDocument32 pagesOutpatient Appointment Systems in Healthcare - A Review of Optimization Studiesgabrieelcrazy100% (1)
- Backward Design Unit PlanDocument7 pagesBackward Design Unit Planapi-333108999No ratings yet
- St. Paul City Council Legislation TextDocument3 pagesSt. Paul City Council Legislation TextPGurusNo ratings yet
- 01 Qlik Sense Product PresentationDocument103 pages01 Qlik Sense Product PresentationDinesh KarthikNo ratings yet
- BS EN 12596 - Dynamic Viscosity by Vacuum CapillaryDocument22 pagesBS EN 12596 - Dynamic Viscosity by Vacuum CapillaryCraig LongNo ratings yet
- Principles of Accounting - Course SyllabusDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Accounting - Course SyllabusChristian Emil ReyesNo ratings yet
- Criteria of Reviewing Instructional Strategy PlanDocument2 pagesCriteria of Reviewing Instructional Strategy PlanIvy Mie SagangNo ratings yet
- Indefinite and Definite ArticlesDocument11 pagesIndefinite and Definite ArticlesRahela FoltNo ratings yet
- "WONDER" FilmDocument4 pages"WONDER" FilmDaniela GimenezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam-Eng 105Document2 pagesMidterm Exam-Eng 105Maria Elizabeth Hinggoy LamamigoNo ratings yet
- Demonio - A QuedaDocument4 pagesDemonio - A QuedaAnderson AugustoNo ratings yet
- Scott Berman - Platonism and The Objects of Science (2020, Bloomsbury Academic) PDFDocument193 pagesScott Berman - Platonism and The Objects of Science (2020, Bloomsbury Academic) PDFMohammed SultanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Master RepsolDocument96 pagesSyllabus Master RepsolsdfjkasNo ratings yet
- Transaction ManagerDocument62 pagesTransaction ManagerAnonymous 5cMeyYyxhNo ratings yet
- Evening PrayerDocument3 pagesEvening PrayerVinz B. SalmazanNo ratings yet
- (PD ISO GUIDE 30) - Reference Materials. Selected Terms and DefinitionsDocument16 pages(PD ISO GUIDE 30) - Reference Materials. Selected Terms and DefinitionsCarolinaNo ratings yet
- Big 1988Document145 pagesBig 1988Tony EmmerNo ratings yet
- AD420Document16 pagesAD420Muhammad Qasim RaufNo ratings yet
- Part One. Read The Passage and Fill in The GapsDocument3 pagesPart One. Read The Passage and Fill in The GapsThanhtùng BùiNo ratings yet
- General Surgery Sample TestDocument16 pagesGeneral Surgery Sample TestNix14No ratings yet
- TOS For EIM Grade 9 & 10Document2 pagesTOS For EIM Grade 9 & 10Sanja Shishin100% (4)
- The Two IvansDocument38 pagesThe Two IvansBobNo ratings yet
- SWOT ANALYSIS Dumaguin Ralph Justine B.Document3 pagesSWOT ANALYSIS Dumaguin Ralph Justine B.Edmarkmoises ValdezNo ratings yet
- Mercury QuestionsDocument6 pagesMercury Questionsapi-239586293No ratings yet
- Fixed Income Portfolio Benchmarks 2012 01Document10 pagesFixed Income Portfolio Benchmarks 2012 01Grimoire HeartsNo ratings yet