Professional Documents
Culture Documents
All Questions Are Compulsory
Uploaded by
Arijit PramanikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
All Questions Are Compulsory
Uploaded by
Arijit PramanikCopyright:
Available Formats
UTTAR BANGA KRISHI VISWAVIDYALAYA
FACULTY OF TECHNOLOGY
MID-TERM EXAMINATION
APPLIED ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION (EE 351)
FULL MARKS: 30 TIME ALLOWED: 45 MIN
All questions are compulsory
Choose the correct alternative: - 20X0.75
1)
i) If the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the anode of the diode, then it is known as
a) Forward biased
b) Reverse biased
c) Equilibrium
d) Schottky barrier
ii) If the voltage of the potential barrier is V0. A voltage V is applied to the input, at what moment will the barrier disappear?
a) V< V0
b) V= V0
c) V> V0
d) V<< V0
iii) During the reverse biased of the diode, the back resistance decrease with the increase of the temperature. Is it true or false?
a) True
b) False
iv) What will be the output of the following circuit? (Assume 0.7V drop across the diode)
a) 12V
b) 12.7V
c) 11.3V
d) 0V
v) In a P-N junction the potential barrier is due to the charges on either side of the junction, these charges are
a) Majority carriers
b) Minority carriers
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Fixed donor and acceptor ions
vi) For a P-N junction diode, the current in reverse bias may be
a) Few mili-amperes
b) Between 0.2 A and 15 A
c) Few amperes
d) Few micro or nano amperes
vii) A P-N junction
a) Has low resistance in forward as well as reverse directions
b) Has high resistance in forward as well as reverse directions
c) Conducts in forward direction only
d) Conducts in reverse direction only
viii) In a reverse biased PN junction, the current through the junction increases abruptly at
a) 0.5 V
b) 1.1 V
c) 0.72 V
d) Breakdown voltage
ix) Mobile electrons of P-side of the P-N junction diode constitute
a) Minority current carriers
b) Majority current carriers
c) Depending upon voltage they may be either majority or minority current carriers
d) None of the above
x) A simple diode rectifier has ‘ripples’ in the output wave which makes it unsuitable as a DC source. To overcome this one can
use
a) A capacitor in series with a the load resistance
b) A capacitor in parallel to the load resistance
c) Both of the mentioned situations will work
d) None of the mentioned situations will work
xi) For full-wave rectified sine wave, rms value is
(a) 0.707 im
(b) 0.6036 im
(c) 0.5 im
(d) 0.318 im
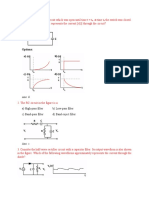
xii) What is the circuit in the given diagram called?
a) Clipper
b) Clamper
c) Rectifier
d) None of the mentioned
xiii) Which of the following condition is true for cut-off mode?
a) The collector current is zero
b) The collector current is proportional to the base current
c) The base current is non zero
d) All of the mentioned
xiv) Which of the following is true for a pnp transistor in active region?
a) CB junction is reversed bias and the EB junction is forward bias
b) CB junction is forward bias and the EB junction is forward bias
c) CB junction is forward bias and the EB junction is reverse bias
d) CB junction is reversed bias and the EB junction is reverse bias
xv) Collector region of BJT is always
a) Lightly doped
b) Moderately doped
c) Heavily doped
d) Not doped
xvi) Process of linearly increasing amplitude of an electrical signal is called
a) Switching
b) Amplification
c) Multiplexing
d) Fabrication
xvii) In a transistor, the base current is about ………….. of emitter current
a) 25%
b) 20%
c) 35 %
d) 5%
xviii) At the base-emitter junctions of a CE transistor, one finds ……………
a) A reverse bias
b) A wide depletion layer
c) Low resistance
d) None of the above
xix) Most of the majority carriers from the emitter ………………..
a) Recombine in the base
b) Recombine in the emitter
c) Pass through the base region to the collector
d) None of the above
xx) In a transistor if β = 100 and collector current is 10 mA, then IE is …………
a) 100 mA
b) 10.1 mA
c) 110 mA
d) None of the above
2. Draw neatly and explain the V-I charactereristics of a pn junction. 2+2
3. A full-wave rectifier uses two diodes, the internal resistance of each diode may be assumed constant at 20 Ω. The transformer
secondary r.m.s. secondary voltage from centre-tap to each end of the secondary is 50 V and load resistance is 980 Ω. Find: i) The
mean load current, ii) The r.m.s. value of load current. 2+2
4. Why is PIV important in rectifier service? 2
5. A transistor is connected in common emitter (CE) configuration in which collector supply is 8 V and the voltage drop across
resistance resistance RC connected in the collector circuit is 0.5 V. The value of Rc= 800 Ω. If α=0.96, determine: i) collector-
emitter voltage ii) base current. 2+2
6. Draw the neat sketch with label of common base (CB) PNP transistor configuration with externally input signal, bias batteries
and collector resistance. 1
---------------------
You might also like
- Electronics UploadDocument4 pagesElectronics UploadChetna SinghalNo ratings yet
- EC21101 Basic Electronics ES 2018Document4 pagesEC21101 Basic Electronics ES 2018Santanu KunduNo ratings yet
- Lab QuizDocument4 pagesLab Quizvenktesh22No ratings yet
- Edoc - Pub - Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th EditionDocument11 pagesEdoc - Pub - Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th EditionHabtamu TekleNo ratings yet
- Analog, Digital and Power Electronics 100 Important MCQsDocument13 pagesAnalog, Digital and Power Electronics 100 Important MCQsHamdam NazarovNo ratings yet
- Tle Exam - Basic ElectronicsDocument12 pagesTle Exam - Basic Electronicsbabylyn akilNo ratings yet
- IA FormatDocument2 pagesIA Formatpatilvk2003No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky ISBN Test BankDocument10 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky ISBN Test Banklee100% (24)
- Test Bank For Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11Th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky Isbn 0132622262 9780132622264 Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11Th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky Isbn 0132622262 9780132622264 Full Chapter PDFlouise.pushard527100% (19)
- Electronics Devices and Circuits SET 1,2,3Document24 pagesElectronics Devices and Circuits SET 1,2,3Avinash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Est Apr 15 PDFDocument15 pagesEst Apr 15 PDFSrikanth AllamsettyNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics MCQ Test 7 28th April 2020 PDFDocument10 pagesAnalog Electronics MCQ Test 7 28th April 2020 PDFPalani CNo ratings yet
- Ee441 Digital Electronics Circuits: Sec C 1 Quiz Total Marks 20 Name I.D#Document2 pagesEe441 Digital Electronics Circuits: Sec C 1 Quiz Total Marks 20 Name I.D#M Usman RiazNo ratings yet
- Easa Part 66 Module 4 Electronics Multi Choice QUESTIONS (Feedback From Students) (Answers Should Be Verified)Document46 pagesEasa Part 66 Module 4 Electronics Multi Choice QUESTIONS (Feedback From Students) (Answers Should Be Verified)ajay r100% (1)
- Last Area Day 8 - Basic Electronics KTC-1Document7 pagesLast Area Day 8 - Basic Electronics KTC-1ellajanepoNo ratings yet
- Last Area Day 8 - Basic Electronics-1Document7 pagesLast Area Day 8 - Basic Electronics-1ellajanepoNo ratings yet
- Test Diode 2Document7 pagesTest Diode 2Ahmad AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Exam MCQsDocument12 pagesLab Exam MCQsShivansh LaadNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication Engineering (Ece) 220 Objective Questions and AnswerDocument37 pagesElectronics and Communication Engineering (Ece) 220 Objective Questions and AnswerVenkatesh TatikondaNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits: GATE EC Topic Wise QuestionsDocument50 pagesAnalog Circuits: GATE EC Topic Wise Questionsdeepthi1993100% (1)
- Ques Lect4 5 KT BJT RelaysDocument3 pagesQues Lect4 5 KT BJT RelaysTejas G. ShendeNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics (0500625) SET 1Document8 pagesAnalog Electronics (0500625) SET 1Avinash PandeyNo ratings yet
- PH4B01U Electronics 2Document4 pagesPH4B01U Electronics 2AsjathNo ratings yet
- DL 290Document3 pagesDL 290Gagan SLNo ratings yet
- Dsaaasdg FgdsDocument6 pagesDsaaasdg Fgdstetimo mekutoNo ratings yet
- Session Question From 2017 T0 2018 Module 04 B1Document39 pagesSession Question From 2017 T0 2018 Module 04 B1Satyam KumarNo ratings yet
- ECA Mid-1 ECE 2-2Document5 pagesECA Mid-1 ECE 2-2Mohan DasNo ratings yet
- Easter End of Term 2023 ELE Exam G10Document3 pagesEaster End of Term 2023 ELE Exam G10Shivshankar ChaitramNo ratings yet
- MCQs in Diode ApplicationsDocument16 pagesMCQs in Diode ApplicationsRJ BedañoNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Diode Circuits: PES's Modern College of Engineering, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication EngineeringDocument23 pagesUnit-I: Diode Circuits: PES's Modern College of Engineering, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering1514VARAD DUDHALMALNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Re: BHEL Engineer Trainee Model Question Paper of Electronics MajorDocument13 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Re: BHEL Engineer Trainee Model Question Paper of Electronics MajorAnbarasan RamamoorthyNo ratings yet
- BSNL GE-JTO Recruitment Examination: Magnetic FieldDocument10 pagesBSNL GE-JTO Recruitment Examination: Magnetic Fieldbrth_brthNo ratings yet
- Jto QuestionsDocument246 pagesJto Questionsanirudha0012No ratings yet
- In Electrical Electronic MeasurementDocument29 pagesIn Electrical Electronic Measurementsiddhartha bharadwajNo ratings yet
- TLE3Document10 pagesTLE3Jhen AndesNo ratings yet
- Case Study 6 AcDocument6 pagesCase Study 6 Acramayodi223No ratings yet
- Question Bank BEEE FinalDocument183 pagesQuestion Bank BEEE Finalgadepranjali04No ratings yet
- Network Analysis Mcqs Unit 01 & 02 Basics of Network & Network TheoremsDocument6 pagesNetwork Analysis Mcqs Unit 01 & 02 Basics of Network & Network TheoremsPankaj KaleNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis Mcqs Unit 01 & 02 Basics of Network & Network TheoremsDocument6 pagesNetwork Analysis Mcqs Unit 01 & 02 Basics of Network & Network TheoremsPankaj KaleNo ratings yet
- AISSCE ASGNMT CHapter 7 Class 12Document4 pagesAISSCE ASGNMT CHapter 7 Class 12Sajid KhanNo ratings yet
- VinayDocument35 pagesVinayAkash sakhujaNo ratings yet
- Quiz FinalDocument15 pagesQuiz FinalbethuelNo ratings yet
- Dgca-Qb-No 4 - Q 57Document6 pagesDgca-Qb-No 4 - Q 57BharathiNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper: Basic ElectronicsDocument3 pagesModel Question Paper: Basic Electronicsravishpy100% (2)
- BSNL JTO (Junior Telecom Officers) Previous Year PAPER - Part 1Document21 pagesBSNL JTO (Junior Telecom Officers) Previous Year PAPER - Part 1Saraswathi AsirvathamNo ratings yet
- Aptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Document22 pagesAptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Navyadeepika. KokkiralaNo ratings yet
- RRB Junior Engineer Electrical Model Paper 3 PDFDocument6 pagesRRB Junior Engineer Electrical Model Paper 3 PDFMallikarjunBhiradeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7-ElectronicsDocument5 pagesTutorial 7-ElectronicsBriana PalmerNo ratings yet
- Recent-Recruitment Test Question (Preliminary) of Rural Electrification Board (REB)Document4 pagesRecent-Recruitment Test Question (Preliminary) of Rural Electrification Board (REB)sakib_buet_eee_13No ratings yet
- Question Bank - Unit - 1 Part - A (Each Question Carries 1 Mark)Document8 pagesQuestion Bank - Unit - 1 Part - A (Each Question Carries 1 Mark)Nithya SNo ratings yet
- ELEX Evaluation 6Document4 pagesELEX Evaluation 6Achilles AldaveNo ratings yet
- MCQ's Chap 16aDocument5 pagesMCQ's Chap 16aArham MunirNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - CH-7 Alternating Current (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks WiseDocument41 pagesClass Xii - CH-7 Alternating Current (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks Wisesamaran270sNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document30 pagesCH 7terasaini77No ratings yet
- BSNL Paper On 20Th June, 2008 Visit Site For More InformationDocument11 pagesBSNL Paper On 20Th June, 2008 Visit Site For More InformationReganNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Machineries UsedDocument8 pagesMachineries UsedArijit PramanikNo ratings yet
- Loops 1Document20 pagesLoops 1Arijit PramanikNo ratings yet
- Hisar BCKVDocument61 pagesHisar BCKVArijit PramanikNo ratings yet
- Tractor Transmission SystemDocument9 pagesTractor Transmission SystemArijit PramanikNo ratings yet
- Uttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya: Faculty of Technology Mid Term Examination-2022Document1 pageUttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya: Faculty of Technology Mid Term Examination-2022Arijit PramanikNo ratings yet
- All Questions Are CompulsoryDocument3 pagesAll Questions Are CompulsoryArijit PramanikNo ratings yet
- Ujt GoodDocument31 pagesUjt GoodRaja ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Design A Decade Counter.: What Is VHDL?Document2 pagesDesign A Decade Counter.: What Is VHDL?shockwaveNo ratings yet
- Tunnel DiodeDocument13 pagesTunnel DiodeNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- PDZ B Q - SerDocument11 pagesPDZ B Q - SerntchtdNo ratings yet
- Shockley & Pin DiodeDocument27 pagesShockley & Pin Diodekaneesha0% (1)
- Physics and Modeling of Microelectronic Devices: BITS PilaniDocument44 pagesPhysics and Modeling of Microelectronic Devices: BITS PilaniKrunalKapadiya1No ratings yet
- Analogue ElectronicsDocument92 pagesAnalogue ElectronicsjoeNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab ManualDocument112 pagesEDC Lab ManualPradeep Kumar SNo ratings yet
- SiliconDocument56 pagesSiliconLuan MinhNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document126 pagesClass 1madhu eceNo ratings yet
- Week1 - Diode Semiconductor2Document20 pagesWeek1 - Diode Semiconductor2ALEN chiaNo ratings yet
- (Macmillan Engineering Series) William F. Waller AMITPP AssIRefEng (Eds.) - Rectifier Circuits-Macmillan Education UK (1972)Document135 pages(Macmillan Engineering Series) William F. Waller AMITPP AssIRefEng (Eds.) - Rectifier Circuits-Macmillan Education UK (1972)Gấu XùNo ratings yet
- Edc PPT1Document109 pagesEdc PPT1ALEX SAGARNo ratings yet
- Analog Integrated CircuitDocument349 pagesAnalog Integrated CircuitRamon PrankeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On Semiconductor TheoryDocument36 pagesMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On Semiconductor TheoryHENRY SINGCOL75% (4)
- Dokumen - Tips - Electronic Devices 9th Edition by Floyd Pp1aDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Electronic Devices 9th Edition by Floyd Pp1aAmr AbdelnaserNo ratings yet
- EASA PART 66 Module 4 Electronic FundamentalsDocument88 pagesEASA PART 66 Module 4 Electronic Fundamentalsghuran khatweNo ratings yet
- @cbse - Xyz Arihant Term 2 PhysicsDocument176 pages@cbse - Xyz Arihant Term 2 PhysicsArush SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Experiment Experiment Experiment Experiment: Aboratory AnualDocument5 pagesExperiment Experiment Experiment Experiment Experiment: Aboratory AnualHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Basic Electronics: StructureDocument23 pagesUnit 4 Basic Electronics: StructureParminder singh parmarNo ratings yet
- Junction LeakageDocument9 pagesJunction LeakageMayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Thyristors and Controlled Rectifiers: EE328 Power Electronics Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mutlu BOZTEPE Ege University, Dept. of E&EDocument79 pagesThyristors and Controlled Rectifiers: EE328 Power Electronics Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mutlu BOZTEPE Ege University, Dept. of E&ESilvana JimenezNo ratings yet
- M04Document66 pagesM04Tormod BergNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics 1Document64 pagesAnalog Electronics 1AbhishekNo ratings yet
- 30CPQ035-45 N0612 Rev.aDocument4 pages30CPQ035-45 N0612 Rev.atakahashikeisuke505No ratings yet
- EN3ES1 Basic Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Diode and Zener Diode Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesEN3ES1 Basic Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Diode and Zener Diode Page 1 of 5Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture14 P-N Junctions 4 - QuantitativeDocument14 pagesLecture14 P-N Junctions 4 - QuantitativeAbd TashNo ratings yet
- L-2 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 4Document6 pagesL-2 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 4GagneNo ratings yet
- Sem 2Document78 pagesSem 2Tech TeamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Lab MANUALDocument24 pagesElectronic Devices Lab MANUALna_hariprsadNo ratings yet