Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Contoil Flow Rate
Contoil Flow Rate
Uploaded by
Nachste IdCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Contoil Flow Rate
Contoil Flow Rate
Uploaded by
Nachste IdCopyright:
Available Formats
Fuel oils
Characteristics of different fuels
Fuel extra light light medium heavy Bunker C
Density at 15° C min. kg/dm3 0.82 0.82 0.82 0.82 0.90
max. kg/dm3 0.86 0.95 0.96 0.99 1.01
Specific volume at average density l/kg 1.19 1.12 1.12 1.11 1.08
Viscosity at 20° C mPa.s 8 14 50 420 4200
Viscosity at 40° C mPa.s 3 5 16 60 380
Viscosity at 100° C mPa.s – – 3 10 35
Energy value kWh/kg 11.8 10.6 11.4 11.2 11.0
Indicative values on power for burners and engines
Burners
Burner Fuel oil meter
Power Flow rate heating fuel EL Flow rate Size
up to kW kg/h l/h Qmin...Qn l/h DN
500 42 50 1... 50 4
1 300 113 135 4 ...135 8
4 000 336 400 10 ... 400 15
10 000 840 1 000 30 ... 1 000 20
20 000 1 680 2 000 75 ... 2 000 25
60 000 5 040 6 000 225 ... 6 000 40
200 000 16 800 20 000 750 ... 20 000 50
Formula for consumption in litres/hour: Example:
Burner power in kW 600 kW
= 62 l/h
Energy value of fuel in kWh/kg x density in kg/dm3 11.8 kWh/kg x 0.82 kg/dm3
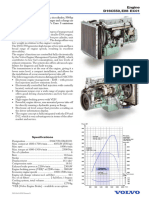
Engines
Engine Fuel oil meter 1)
Power up to Diesel fuel consumption Flow rate Size
approx. PS ca. kW l/h Qmin...Qn l/h DN
250 184 50 1... 50 4
680 500 135 4 ... 135 8
2 000 1 470 400 10 ... 400 15
5 000 3 680 1 000 30 ... 1 000 20
10 000 7 360 2 000 75 ... 2 000 25
30 000 22 000 6 000 225 ... 6 000 40
100 000 73 600 20 000 750 ... 20 000 50
1) For differential measurement the flow meter has to be selected according to the pump flow rate and the flow in the return pipe.
Formula: 1 HP = 0.736 kW 1 kg Diesel at 0.84 kg/dm3 = 1.19 l
1 kW = 1.36 HP
Rule of thumb: approx. 190 g/kWh correspond to 0.226 l/kWh
approx. 140 g/HP correspond to 0.167 l/HP/h
32
You might also like
- Objective Physics For NEET Vol I by Abhay KumarDocument582 pagesObjective Physics For NEET Vol I by Abhay KumarSharjeel Khan100% (5)
- Tk01 Revised Assignment3Document131 pagesTk01 Revised Assignment3FauzulNo ratings yet
- 4 Vibration Analysis Basics PDFDocument37 pages4 Vibration Analysis Basics PDFjuanNo ratings yet
- Ygnis Ingl+ S Multiflam 170.1-200.1Document24 pagesYgnis Ingl+ S Multiflam 170.1-200.1DihorulNo ratings yet
- Physics 5054 OL P1 MCQs 2015-2019 All VsDocument309 pagesPhysics 5054 OL P1 MCQs 2015-2019 All VsHanaa Ibrahim Ali50% (2)
- MRIDocument274 pagesMRIGuillermo Sasso Pacheco100% (2)
- Insulation Coordination Study Rev 01Document5 pagesInsulation Coordination Study Rev 01Ahmed SaberNo ratings yet
- Pump Curve: Colour CodeDocument24 pagesPump Curve: Colour CodeP N100% (1)
- Air-To-Water Heat Pump: Shanghai Hezhong Carrier Air-Conditioning Equipment Co., LTDDocument7 pagesAir-To-Water Heat Pump: Shanghai Hezhong Carrier Air-Conditioning Equipment Co., LTDguy namNo ratings yet
- CE Physics 1985 Paper 2 Page 1 of 13Document13 pagesCE Physics 1985 Paper 2 Page 1 of 13jshfjksNo ratings yet
- Multi V Water IV Outside Unit Service Manual Exploded View Model Arwb Las4Document33 pagesMulti V Water IV Outside Unit Service Manual Exploded View Model Arwb Las4Jose CuevasNo ratings yet
- Combustion & Fuels: Cement Process Engineering Vade-MecumDocument15 pagesCombustion & Fuels: Cement Process Engineering Vade-MecumJesus RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 10 Basic Fact About ClinkerDocument52 pages10 Basic Fact About ClinkermngyooNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Diameter For Methanol-IPA System (Continuous) - Top Boil Up PropertiesDocument3 pagesCalculation of Diameter For Methanol-IPA System (Continuous) - Top Boil Up PropertiesBagadi AvinashNo ratings yet
- Daily On Load / Off Load TestDocument8 pagesDaily On Load / Off Load TestFlexiNo ratings yet
- Intercambiadores - Ejercicios MaterialDocument62 pagesIntercambiadores - Ejercicios MaterialLuiz Gustavo YamamotoNo ratings yet
- Dalmia Cement, DalmiapuramDocument32 pagesDalmia Cement, DalmiapuramBülent BulutNo ratings yet
- 01 10basicfactsCKenglDocument52 pages01 10basicfactsCKenglmahmoud13No ratings yet
- Intercambiadores - Tablas y GráficosDocument62 pagesIntercambiadores - Tablas y GráficosLuiz Gustavo YamamotoNo ratings yet
- Kirloskar DG 5-30 KVADocument4 pagesKirloskar DG 5-30 KVABujjibabu KattaNo ratings yet
- DG SetDocument4 pagesDG SetabhishitewariNo ratings yet
- EediDocument5 pagesEedielifkuda94No ratings yet
- DataSheet LOMBARDINI (CHD SERIES)Document4 pagesDataSheet LOMBARDINI (CHD SERIES)CristianTeodorescuNo ratings yet
- PS 438903221 T4900-T41200 enDocument2 pagesPS 438903221 T4900-T41200 enjamirvillarroelNo ratings yet
- Fuel SystemDocument6 pagesFuel SystemAbdon Delfin Jr.No ratings yet
- Fuel Oils: Characteristics of Different FuelsDocument1 pageFuel Oils: Characteristics of Different FuelsBiodunNo ratings yet
- Diesel Pile Hammers: Metric Units - US UnitsDocument8 pagesDiesel Pile Hammers: Metric Units - US UnitsCHRISTOPHER MANRIQUE GRANADOSNo ratings yet
- Diesel Pile Hammers: Metric Units - US UnitsDocument8 pagesDiesel Pile Hammers: Metric Units - US UnitspandyatusharNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Marine Diesel Engine D2862LE496 (V12-2000)Document3 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: Marine Diesel Engine D2862LE496 (V12-2000)mlaouhi MajedNo ratings yet
- Form - Trial Mix Report: Technical Marketing Department CustomerDocument6 pagesForm - Trial Mix Report: Technical Marketing Department CustomerRedi PascaNo ratings yet
- Catalago Quemadores Riello-A Aceite 01Document24 pagesCatalago Quemadores Riello-A Aceite 01Arnold Figueroa cassianiNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document3 pagesLab 2adityapillai01No ratings yet
- 20-50-FICHAS - 1-Signed - CompressedDocument60 pages20-50-FICHAS - 1-Signed - CompressedMariuxi BayasNo ratings yet
- Kyma Ship Performance: Trial Report: Vessel: Voyage: Report Period ToDocument3 pagesKyma Ship Performance: Trial Report: Vessel: Voyage: Report Period TosaeshwaranNo ratings yet
- HMAP BR 201410-01 ZX870LCH-5G IndonesiaDocument2 pagesHMAP BR 201410-01 ZX870LCH-5G IndonesiaAwanNo ratings yet
- Focs Plus Ldw1003 - GBDocument4 pagesFocs Plus Ldw1003 - GBRafael LopezNo ratings yet
- Kyma Ship Performance: Trial Report: Vessel: Voyage: Report Period ToDocument3 pagesKyma Ship Performance: Trial Report: Vessel: Voyage: Report Period ToGilbert San JoseNo ratings yet
- Conversion Reactor PDFDocument3 pagesConversion Reactor PDFDeep SinojiyaNo ratings yet
- Light Oil Burner Quemadores de Gasóleo Queimadores A GasóleoDocument17 pagesLight Oil Burner Quemadores de Gasóleo Queimadores A GasóleoTinotenda RunesuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Shapiro Solutions 7th EdDocument207 pagesChapter 8 Shapiro Solutions 7th EdKalopsia SwevenNo ratings yet
- PLAXIS ReportDocument13 pagesPLAXIS ReportUnknown_unknown_unknownNo ratings yet
- KD440 PDFDocument4 pagesKD440 PDFHarpreet Singh100% (1)
- 1011 LbenDocument6 pages1011 LbenCALVINNo ratings yet
- Design 3ADocument10 pagesDesign 3ANkosinathi MthiyaneNo ratings yet
- WEG 3kW 2P B3 IE3 WIMES Data SheetDocument7 pagesWEG 3kW 2P B3 IE3 WIMES Data SheetA aaa AaaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledKuber SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Kruger Ventilation Industries Pte LTD: A B C D N°xØDocument1 pageKruger Ventilation Industries Pte LTD: A B C D N°xØAzher ANo ratings yet
- fouling factor 중량 비체적: ft^2/Btu m^2/Kcal lb/ft kg/m lb/ft^3 kg/m^3 0.3689556791 1.4881889764 16.018732594Document27 pagesfouling factor 중량 비체적: ft^2/Btu m^2/Kcal lb/ft kg/m lb/ft^3 kg/m^3 0.3689556791 1.4881889764 16.018732594김종민No ratings yet
- Nikrothal LX: (Resistance Heating Wire and Resistance Wire)Document2 pagesNikrothal LX: (Resistance Heating Wire and Resistance Wire)yasir127No ratings yet
- Diesel CalculationsDocument5 pagesDiesel CalculationspavanraneNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Scheme - Leachate TreatmentDocument1 pageProcess Flow Scheme - Leachate TreatmentNandhagopal SNo ratings yet
- Fiche Technique 25.2 À 40kwDocument1 pageFiche Technique 25.2 À 40kwsaloume2006No ratings yet
- Journal Pone 0074403 s001Document3 pagesJournal Pone 0074403 s001Sunday PaulNo ratings yet
- PT Kruger Ventilation Indonesia: A B C D N°xØDocument5 pagesPT Kruger Ventilation Indonesia: A B C D N°xØSalamet TeguhNo ratings yet
- EMISIONES Eedi MethodologyDocument11 pagesEMISIONES Eedi MethodologyrbrlunaNo ratings yet
- GHJTYGJDocument13 pagesGHJTYGJUnknown_unknown_unknownNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi FH 16 Ruel RatioDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi FH 16 Ruel Ratiokukuh sugiyatnoNo ratings yet
- Ts0031uk01 Riello 40 FDocument16 pagesTs0031uk01 Riello 40 Fcorsini999No ratings yet
- Ape Diesel D125 D180 Manual 20100402Document30 pagesApe Diesel D125 D180 Manual 20100402Binh le ThanhNo ratings yet
- Water OutDocument1 pageWater OutAlberto SandNo ratings yet
- WEG 15kW 2P B3 IE3 WIMES Data SheetDocument7 pagesWEG 15kW 2P B3 IE3 WIMES Data Sheetabel manuel chico oleceNo ratings yet
- Fleet 650-1Document2 pagesFleet 650-1Laurent CHENUNo ratings yet
- Methanol Recovery Calculation 31-12-2023Document1 pageMethanol Recovery Calculation 31-12-2023Preetpal SinghNo ratings yet
- 7500 CFM - 0.7 Inwg - TdaDocument1 page7500 CFM - 0.7 Inwg - Tdasu hermanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ExercisesDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Exercisesasiri201912No ratings yet
- VAV CAV Documentation ADocument20 pagesVAV CAV Documentation AHarish Menon100% (1)
- A Review On Green Hydrogen Future of Green Hydrogen in IndiaDocument7 pagesA Review On Green Hydrogen Future of Green Hydrogen in IndiaSPE Baghdad sectionNo ratings yet
- TDP - 2019 - Public - Forum - Presentation - 30 - Oct2019 - Final1Document223 pagesTDP - 2019 - Public - Forum - Presentation - 30 - Oct2019 - Final1anon_b186No ratings yet
- Clas Note 5Document142 pagesClas Note 5yusNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: LECTURE 9-BDA 20103Document40 pagesDynamics: LECTURE 9-BDA 20103Musfirah MustaffaNo ratings yet
- As of 31 March 2021: Summary of Indicative Power ProjectsDocument2 pagesAs of 31 March 2021: Summary of Indicative Power ProjectsBearingmanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DiodesDocument9 pagesSemiconductor Diodessitaram rajNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - ECE 3144 - Sept 2020 - FinalDocument5 pagesAssignment 1 - ECE 3144 - Sept 2020 - FinalClinton NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- 2023-Li-A Study On The Joule-Thomson Effect of During Filling Hydrogen in High Pressure TankDocument10 pages2023-Li-A Study On The Joule-Thomson Effect of During Filling Hydrogen in High Pressure TankJesús MateoNo ratings yet
- Tuned Mass Damper With Fractional Derivative Damping: F. RudingerDocument6 pagesTuned Mass Damper With Fractional Derivative Damping: F. RudingerAnibal Bendezu BarretoNo ratings yet
- CTV SLB033 en - 07172020Document2 pagesCTV SLB033 en - 07172020Nguyen ThuongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 PDFDocument32 pagesLecture 2 PDFWazif ZakwanNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Study of Thermodynamics Properties of Landau Levels in Inas Two-Dimensional Electron GasDocument8 pagesTheoretical Study of Thermodynamics Properties of Landau Levels in Inas Two-Dimensional Electron GasIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Solar Thermal Energy CollectorsDocument30 pagesChapter Four Solar Thermal Energy CollectorsJoel LogboNo ratings yet
- Telemecanique LC1F265 DatasheetDocument28 pagesTelemecanique LC1F265 DatasheetRAUL ORTIZNo ratings yet
- Challenge-2003-1 - Out in The Field - in Hot Water - The World On A SpringDocument2 pagesChallenge-2003-1 - Out in The Field - in Hot Water - The World On A Springsanits591No ratings yet
- Cognito - Physics QuizDocument1 pageCognito - Physics QuizYay YayayNo ratings yet
- 第2章Document1 page第2章rogerNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1555219825210Document12 pagesOrca Share Media1555219825210Milx Jyms AvilaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Fluid Machanics-05-Subjective Unsolved C.B.S.EDocument2 pagesElasticity and Fluid Machanics-05-Subjective Unsolved C.B.S.ERaju SinghNo ratings yet
- NTPCDocument4 pagesNTPCSriram VenkatachariNo ratings yet
- Design Calculations: Optimization 3: Material Balance CalculationDocument15 pagesDesign Calculations: Optimization 3: Material Balance CalculationMvelo PhungulaNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics PT-2Document2 pages11th Physics PT-2raghavendra jNo ratings yet